Introduction and description
Four traditional mainstream databases:
Oracle MySQL SqlServer DB2
Non relational database: Redis MongoDB
The mainstream database is relational database: there is an association relationship between tables
When we say install database, we mean install database service
When creating a database, it refers to creating a data warehouse
The data warehouse can be divided into several blocks, and each block is called a table space;
Each table space can correspond to a user
When using the database initially, first create a user, and then assign a table space to this user
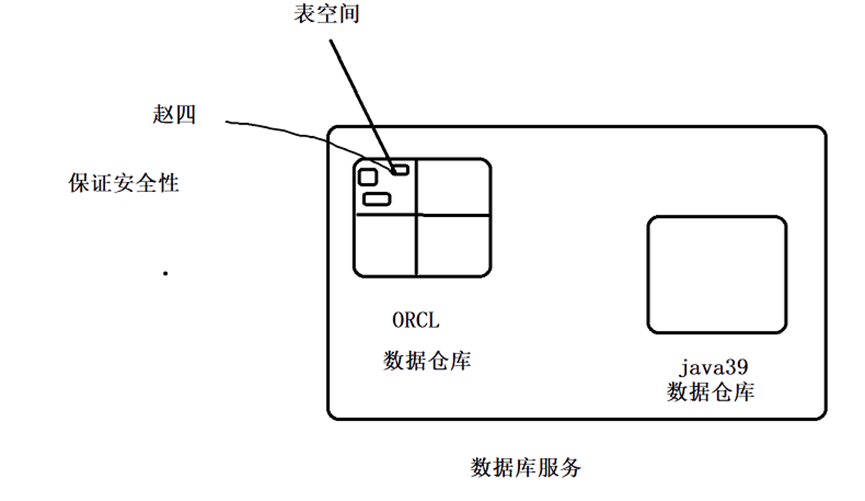
If the user is not provided with a table space to create, the default table space of Oracle will be used by default; For security purposes, a tablespace should be created for each user
. DBF means table space file, which can improve security. Users in the table space can only access the contents stored in the current table space
Standard creation process:
First create a table space, create a user, and associate the user name with this table space;
Create a new table. In this way, the new table will be created in the table space just now;
Finally, give login, add, delete and modify permissions
Create tablespace - create user (associated tablespace) - Grant login permission - Grant add, delete and modify permission
Query all tablespaces (system and its own administrator operation)
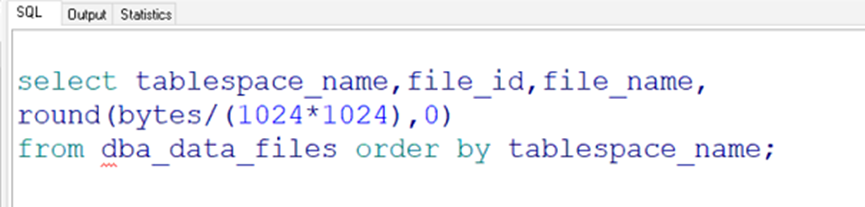
1, Create tablespace (administrator action)
create tablespace Tablespace name datafile 'Stored path' size 10M autoextend on next 10M
datafile is used to set the physical file name
Size is used to set the initial size of the tablespace
autoextend on is used to set automatic growth. If the storage capacity exceeds the initial size, it will be expanded automatically
next is used to set the size of the expanded space
How to delete a tablespace (administrator operation)
Note that you must execute the statement first, and then delete the disk space manually, otherwise Oracle will crash
drop tablespace Tablespace name
2, Create user (administrator can create user)
--Create user create user user name identified by password default table Tablespace name
identified by is used to set the user's password
Default tablespace specifies the default tablespace name
The user was created successfully, but a permission was missing, resulting in login failure
Login denied login denied; Is the lack of login permission
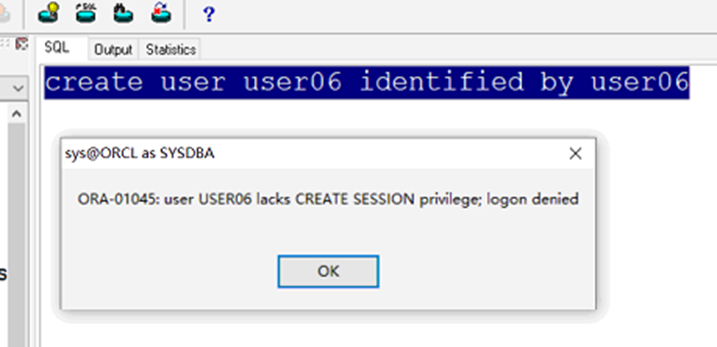
III. grant login permission
grant connect to user name;
When creating a table, it shows that there is no operation permission
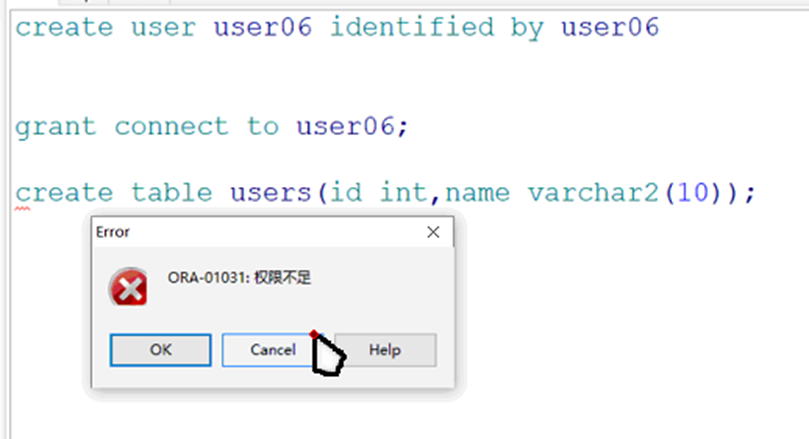
IV. grant the authority to add, delete, modify and query
grant resource to user name
Recycle permission
Note: you can't "hurt each other" at the same level, that is, delete and recycle peer users
--Reclaim login permissions revoke connect from user name; --Recycle add, delete and modify permissions revoke resource from user name;
5, Give recall administrator permission
--Give administrator permission grant dba to user name; --Withdraw administrator privileges revoke dba from user name;
Other process operation syntax
Oracle has several default users
Sys,system,scott
Sys, system is the administrator; Scott is a regular user
Reset common password (administrator)
sys as sysdba //Log in as system administrator alter user user name identified by password :
User is locked and unlocked
--Administrator execution: alter user user name account unlock;
Delete user (administrator)
When deleting a user, if there is a table, the deletion fails because of security reasons; Delete all tables before deleting users
--delete user drop user user name cascade;
Data definition language
Create alter modify drop delete
Create tablespace
--Create tablespace create tablespace Tablespace name datafile 'Stored path' size 10M autoextend on next 10M
Create user
--Create user create user user name identified by password default table Tablespace name
Create table
default Add a default value to the table --Create table create table Table name( Field name type (length), Field name type (length) default '' );
Copy a table
--Create a new table from an existing table and copy a table create table New table name as select * from Old table name;
Copy a table (do not copy the information of the table, only keep the type of the table)
--Copy only table types --Where1=2 It means that if the table is not equal, the information of the table will not be copied when copying the table, but only the type of the table Create table New table name as select * from Old table name where 1=2;
Copy a table (eliminate duplicate data)
--Create a new table using an existing table, and the data in the copied table is not duplicate create table New table name as select distinct * from Old table name;
New constraints
PK Primary key( Primary Key);UQ Only( Unique )constraint CK Check( Check )Constraints; FK Foreign key(Foreign Key)constraint --Constraint syntax (can be directly after the append table) alter table xx add constraint Constraint name constraint type specific constraint description For example: alter table product add constraint PK_PNO primary key (pno); --Add age constraint 15~40 alter table stuInfo add constraint checkAge check(stuAge>15 and stuAge<40);
Delete constraint
--Delete constraint alter table Table name drop constraint Constraint name
User locked
alter user user name account unlock
Delete table
--Delete table drop table Table name
Data manipulation language
Insert select delete delete update update
insert data
--Insert data into a table
insert into Table name values('xxx',to_date('2020-02-02','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'));
--If partial data is inserted
insert into Table name (field name, field name...) values('xxx','xxx');Query all information in the table
--Query all information in the table select * from Table name
Query the specified information
--Query the specified information select * from Table name where Primary key='xx';
Select the specified row and column display
--Specify data for row and column display select xx,xx from Table name
Filter duplicate rows
--Show filter duplicate rows select distinct xx,xx from Table name
Sort by a rule
--Sort by a rule(Descending order of age and ascending order of student number) select * from Table name order by xxage DESC,xxno ASC; --for example --ascending Ascending order select * from sc order by mark asc; --descending Descending order select * from sc order by mark desc; --The default display is asc,Can be empty
Alias display
--List alias is a custom name --'S'|| There is a in front of the student number S select 'S'||stuNO Student number, stuName"full name" FROM Table name
For example, aliases are sorted in descending order after they are displayed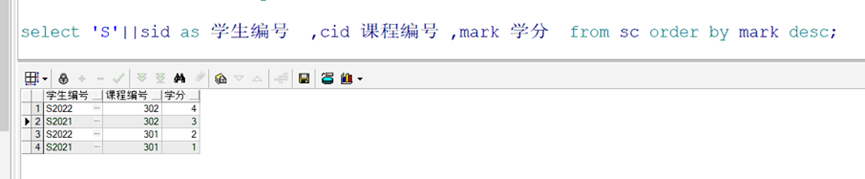
The query does not include fields for a condition
--not in Range !=Not equal to specific value
-- !=Efficiency ratio of not in High, not in It will cause full scan and abnormal index
--Department number is not equal to 10 !=
select * from emp where deptno!=10;
--not in
select * from emp where deptno not in('10','20');Delete all information in the table
--Delete all field information in the table delete from Table name
Delete an information in the table
-- Delete an information in the table delete from Table name where Primary key='xx' --Delete a message,Multiple messages can and connect delete from Table name where xx=xx and xx=xx
Modify an information in a table
--Modify an information in a table --Generally, data is modified according to the primary key update Table name set xx=xx,xx=xx where Primary key='' For example: update Table name set sname='james' where sid=2023;
Transaction control language
Commit submit savepoint save pollback callback
Data control language
Grant grant revoke revocation
Give login permission
grant connet to user name
Grant permission for addition, deletion and modification
--Grant permission for addition, deletion and modification grant resource to user name
Give administrator privileges
--Give administrator privileges grant dba to user name
Recycle administrator privileges
--Recycle administrator privileges revoke dba from user name
Reclaim login permissions
--Reclaim login permissions revoke connect from user name
Recycle add, delete and modify permissions
--Recycle add, delete and modify permissions revoke resource from user name
Aggregate function
Note: the queried emp table is in scott user
AVG averaging
--avg()average value ---Average wage for all select avg(sal) from emp; --Find the average salary of department 20 select avg(sal) average wage from emp where deptno=20; --Find the average salary and department number of department No. 20 select deptno,avg(sal) average wage from emp where deptno=20 group by deptno; --Group according to the department number and find the average salary of each group select deptno,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno;
MIN minimum
--min()minimum value --Ask for the salary of the lowest paid person in our company select min(sal) from emp; --Ask for the lowest wage in department 20 select min(sal) from emp where deptno=20; --Ask for the minimum wage of each department of the company select deptno,min(sal) from emp group by deptno; --Group, add group by
MAX Max
--max()Maximum --Ask for the salary of the highest paid person in the company select max(sal)Maximum wage from emp; --Ask for the highest salary in department 30 select max(sal)Department maximum wage from emp where deptno=30; --Ask for a high salary for each department of the company select deptno,max(sal) from emp group by deptno;
SUN summation
--sun()Sum --Ask for the total monthly salary of the company select sum(sal)Total salary from emp; --Ask for the total salary paid to the 30th part of each month select sum(sal) from emp where deptno=30; --Ask for the total salary of each department of the company select deptno Department number,sum(sal)Total salary from emp group by deptno;
count accumulation
--count()accumulation --Total number of people in the company select count(*) from emp; --Ask for the number of people in department 20 select count(*) from emp where deptno=20; --You'd better not use it count(*);*Represents finding all fields select deptno,count(*) from emp group by deptno; --Find the total number of people in each department select deptno,count(empno) from emp group by deptno; --Of each department... Value, as long as more than 2000 select deptno Department number,max(sal) Maximum,AVG(sal) average value,min(sal) minimum value from emp group by deptno having avg(sal)>2000;