P4lang compilation environment configuration
#Some words are written in the front
The author has just begun to understand the content written in the article. He has referred to a lot of network materials. He writes a blog to record the learning process. If there is any misunderstanding, he is welcome to criticize!
Installing VMVare
This step is relatively easy. Go directly to the official website of VmWare https://www.vmware.com/cn.html
If you need a registration code, just search Baidu.
Installing CentOS8 virtual machine
centos image download address
http://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos/8/isos/x86_64/
Select the DVD version (Standard Version), the largest one.
1. Open VmWare and create a new virtual machine
Just keep going to the next step (the process diagram is not saved)
2. Installation succeeded
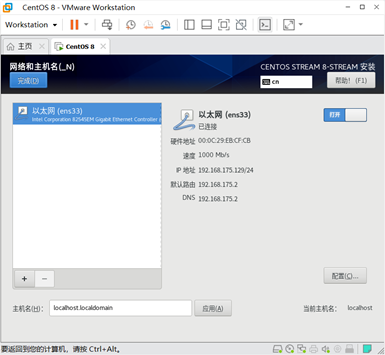
3. Configure the network connection (don't forget this step)
Install Docker
Note: the official compilation of p4 is based on ubuntu, but centos is required. It can't be configured successfully according to various tutorials, so it's a bad choice.
1. Download Docker
Installation tutorial reference https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39505065/article/details/106986475
2. Check whether Docker is successfully installed
docker version
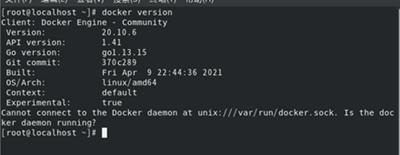
3. Open docker
service docker start
4. View the image list
docker images
Pull image
1. Pull the image
docker pull p4lang/p4c
Note: Mirror address https://registry.hub.docker.com/r/p4lang/p4c
2. Run p4c image
docker run --cap-add NET_ADMIN -it --rm p4c /bin/bash
Note:
● where – cap -addNET_ADMIN needs to be added so that there will be no errors in the following sudo part
reference resources http://hustcat.github.io/docker-config-capabilities/
● open the specified version image method and change p4c to p4c:tag
3. View the image list
docker images
Practice it
reference resources: https://www.sdnlab.com/24136.html
1. Update tools such as vim first
apt-get update apt-get install sudo apt-get install vim sudo apt-get install ping
2. Create a new file
vim test.p4
test.p4 is as follows
#include <core.p4>
#include <v1model.p4>
typedef bit<48> EthernetAddress;
typedef bit<32> IPv4Address;
header ethernet_t {
EthernetAddress dst_addr;
EthernetAddress src_addr;
bit<16> ether_type;
}
header ipv4_t {
bit<4> version;
bit<4> ihl;
bit<8> diffserv;
bit<16> total_len;
bit<16> identification;
bit<3> flags;
bit<13> frag_offset;
bit<8> ttl;
bit<8> protocol;
bit<16> hdr_checksum;
IPv4Address src_addr;
IPv4Address dst_addr;
}
struct headers_t {
ethernet_t ethernet;
ipv4_t ipv4;
}
struct metadata_t {
}
error {
IPv4IncorrectVersion,
IPv4OptionsNotSupported
}
parser my_parser(packet_in packet,
out headers_t hd,
inout metadata_t meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_meta)
{
state start {
packet.extract(hd.ethernet);
transition select(hd.ethernet.ether_type) {
0x0800: parse_ipv4;
default: accept;
}
}
state parse_ipv4 {
packet.extract(hd.ipv4);
verify(hd.ipv4.version == 4w4, error.IPv4IncorrectVersion);
verify(hd.ipv4.ihl == 4w5, error.IPv4OptionsNotSupported);
transition accept;
}
}
control my_deparser(packet_out packet,
in headers_t hdr)
{
apply {
packet.emit(hdr.ethernet);
packet.emit(hdr.ipv4);
}
}
control my_verify_checksum(inout headers_t hdr,
inout metadata_t meta)
{
apply { }
}
control my_compute_checksum(inout headers_t hdr,
inout metadata_t meta)
{
apply { }
}
control my_ingress(inout headers_t hdr,
inout metadata_t meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata)
{
bool dropped = false;
action drop_action() {
mark_to_drop(standard_metadata);
dropped = true;
}
action to_port_action(bit<9> port) {
hdr.ipv4.ttl = hdr.ipv4.ttl - 1;
standard_metadata.egress_spec = port;
}
table ipv4_match {
key = {
hdr.ipv4.dst_addr: lpm;
}
actions = {
drop_action;
to_port_action;
}
size = 1024;
default_action = drop_action;
}
apply {
ipv4_match.apply();
if (dropped) return;
}
}
control my_egress(inout headers_t hdr,
inout metadata_t meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata)
{
apply { }
}
V1Switch(my_parser(),
my_verify_checksum(),
my_ingress(),
my_egress(),
my_compute_checksum(),
my_deparser()) main;
3. Compile files
p4c -b bmv2 test.p4 -o test.bmv2
Check the directory ls and test.bmv2 has been generated
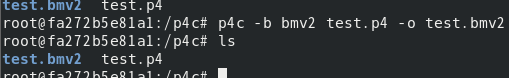
Note:
-b: Specify target
-o: Specify output path
4. Build network topology
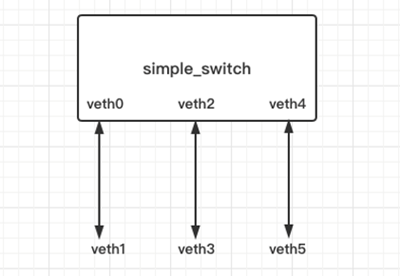
sudo ip link add name veth0 type veth peer name veth1 sudo ip link set dev veth0 up sudo ip link set dev veth1 up sudo sysctl net.ipv6.conf.veth0.disable_ipv6=1 sudo sysctl net.ipv6.conf.veth1.disable_ipv6=1 sudo ip link add name veth2 type veth peer name veth3 sudo ip link set dev veth2 up sudo ip link set dev veth3 up sudo sysctl net.ipv6.conf.veth2.disable_ipv6=1 sudo sysctl net.ipv6.conf.veth3.disable_ipv6=1 sudo ip link add name veth4 type veth peer name veth5 sudo ip link set dev veth4 up sudo ip link set dev veth5 up sudo sysctl net.ipv6.conf.veth4.disable_ipv6=1 sudo sysctl net.ipv6.conf.veth5.disable_ipv6=1
5. Start switch_simple switch
sudo simple_switch --interface 0@veth0 --interface 1@veth2 --interface 2@veth4 test.bmv2/test.json &
Next, through simple_switch_CLI program to control the P4 software switch
6. Issue routing to the routing table of the switch
Start the switch
simple_switch_CLI
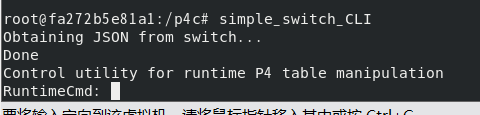
View all current tables
show_tables
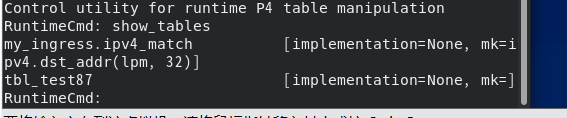 View information for the specified table
View information for the specified table
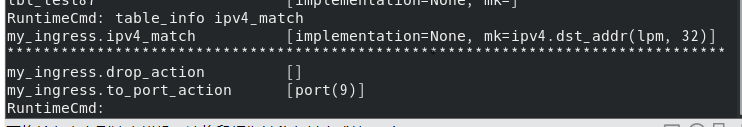
table_info ipv4_match
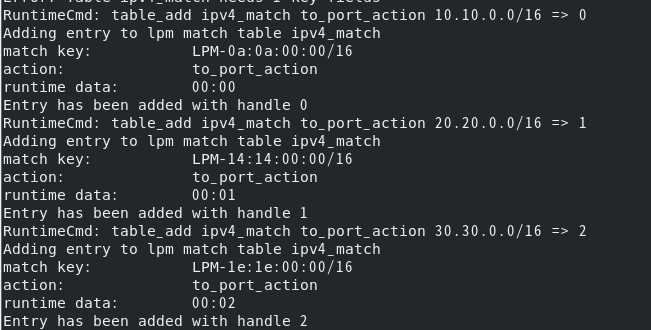
Next is the control plane, using table_ The add command adds a route to the switch. Assumptions:
port 0 (veth 0) connects 10.10.0.0/16 network segment
port 1 (veth 2) connects 20.20.0.0/16 network segment
port 2 (veth 4) connects 30.30.0.0/16 network segment
Enter the following command
table_add ipv4_match to_port_action 10.10.0.0/16 => 0 table_add ipv4_match to_port_action 20.20.0.0/16 => 1 table_add ipv4_match to_port_action 30.30.0.0/16 => 2
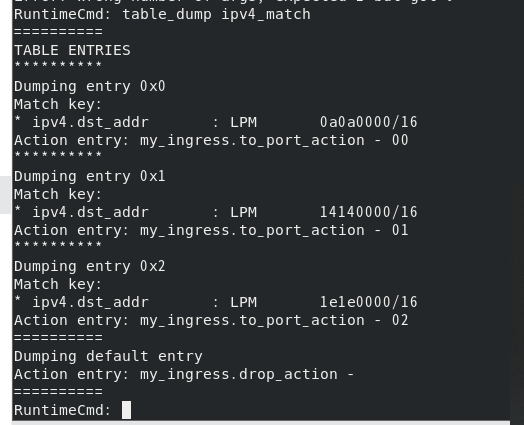
Use the command table_dump determines the table entry to be added
table_dump ipv4_match
7. Test the layer 3 forwarding of the switch
First, create a new console window, that is, multiple interfaces of the same container
docker exec -it fc9942741dca /bin/bash
Note: docker exec -it /bin/bash, where < > is the container id
When using scapy for the first time, please install the dependency first
sudo apt-get install scapy
Start scapy
sudo scapy
Packet capture of veth3 and veth5 before testing - there are no packets
sudo tcpdump -n -i veth3 sudo tcpdump -n -i veth5
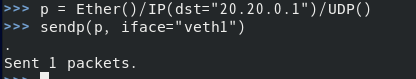
Use the scapy tool to inject the message with the destination of 20.20.0.1 from veth1
p = Ether()/IP(dst="20.20.0.1")/UDP() sendp(p,iface="veth1")
Packet capture - screenshot of three windows running at the same time: scapy sends two packets, veth3 receives them, and veth5 has no change.
sudo tcpdump -n -i veth3 sudo tcpdump -n -i veth5
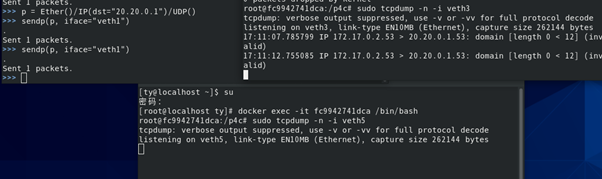
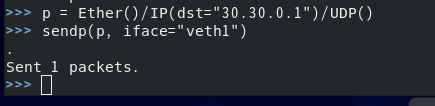
Inject the message with the destination of 30.30.0.1 from veth1 using scapy
p = Ether()/IP(dst="30.30.0.1")/UDP() sendp(p,iface="veth1")
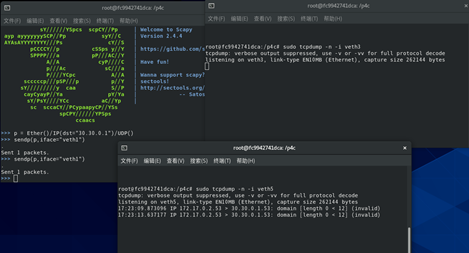
Packet capture - screenshot of the operation. scapy sends the packet from veth1, veth5 receives it, and veth3 does not change.
sudo tcpdump -n -i veth3 sudo tcpdump -n -i veth5
last! Save container
This step is really important, otherwise all tool installation and updates will be invalid!
docker commit container id demo:v1.0
demo:v1.0 is the name you want to store: version number