1, Algorithm principle
1. Overview
due to the different fitting models according to the number of sampling points, the random consistent sampling algorithm can extract point cloud subsets with different shapes and states. Generally, the common model parameters are well fitted, the required sampling points are less, and the amount of calculation is less. Therefore, it is usually used to fit regular geometric models with simple mathematical models such as lines, planes and spheres. It can be separated in many other point clouds and has good robustness. When fitting the plane point cloud with the random consistent sampling algorithm, the local point data in line with the parameters of the mathematical model is found by searching all the points around the plane, so as to build a subset of all the points in line with the plane model within the error threshold. After iteratively selecting multiple subsets, the optimal data point set is finally selected. The basic idea is as follows: first, consider the minimum subset of the model, and the number of point clouds in the subset is n n n. Species in sample set S S The least constituent subset is randomly selected from S. aggregate S S Number of point clouds in S S n S_n Sn, from S S Random pick in S set n n n points, fitting the model with the least constituent subset; From collection S S S, the error with the fitting model is less than the threshold t t Point cloud of t S 1 S_1 S1, if S 1 S_1 S1) the number of point clouds in the collection is greater than a certain threshold K K K defines that the target point cloud is found, otherwise resampling is performed; After a certain number of sampling, select and compare each time S 1 S_1 S1 ¢ set, select the optimal solution and define it as the target point cloud.
2. Algorithm steps
the initial segmentation of LIDAR point cloud is used to detect and eliminate useless ground point cloud. Since LIDAR point cloud belongs to three-dimensional data, the random consistent sampling algorithm of three points can be selected to eliminate ground point cloud when extracting plane. It is applicable to lidar data containing a large number of useless plane point clouds. The flow of this algorithm is shown in Figure 1.
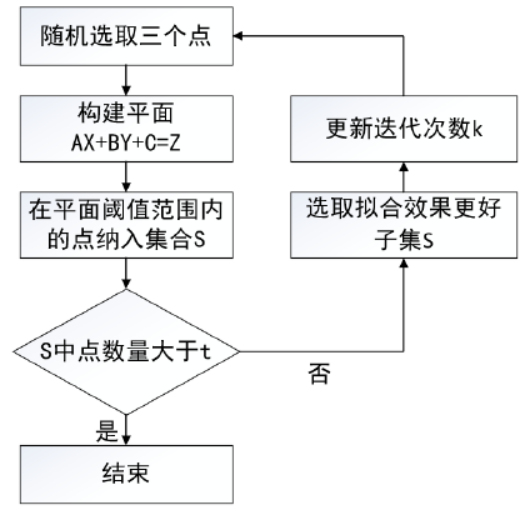
- Randomly select three points in the laser point cloud as plane subset points
- Construction plane A X + B Y + C = Z AX+BY+C=Z AX+BY+C=Z, three parameters of the plane are determined according to three preselected points A , B , C A,B,C A,B,C
- Use the created plane to determine the consensus set S 1 S_1 S1, looking for S 1 S_1 The remaining points in S1 , make S 1 S_1 S1 contains points consistent with the plane. The algorithm analysis of the distance and angle of the two parameters is carried out to determine whether a point is consistent with the created plane. The distance parameter refers to the distance between the created plane and the point, and the angle parameter refers to the angle between the normal of the created plane and the slope defined at the point. The closer a given point is to the created plane, the smaller both parameters will be.
- After threshold filtering S 1 S_1 S1} set, set threshold t t t. As S 1 S_1 The number of sets in S1 ¢ is greater than t t t is defined as the required ground point cloud plane, otherwise repeat step 1.
- Compare the selected collection
S
1
∗
S_1^*
S1 * and previous sets
S
1
S_1
S1 ¢ in the next comparison, it has better fitting effect. It is mainly judged that if there are more fitting points, the plane fitting effect is better, so use
S
1
∗
S_1^*
S1 * instead
S
1
S_1
S1 ^ set as the selected plane and set the number of iterations
k
k
k. Repeat the above process until the end of the iteration to select the best fitting place
Face plane point cloud collection for culling.
3. References
[1] Yang Xu. Filtering and segmentation of LIDAR point cloud data [D]. Harbin University of technology, 2020.p 25-28
2, Code example
1. Implementation mode I
from pclpy import pcl
import numpy as np
def point_cloud_viewer(cloud, cloud_filtered):
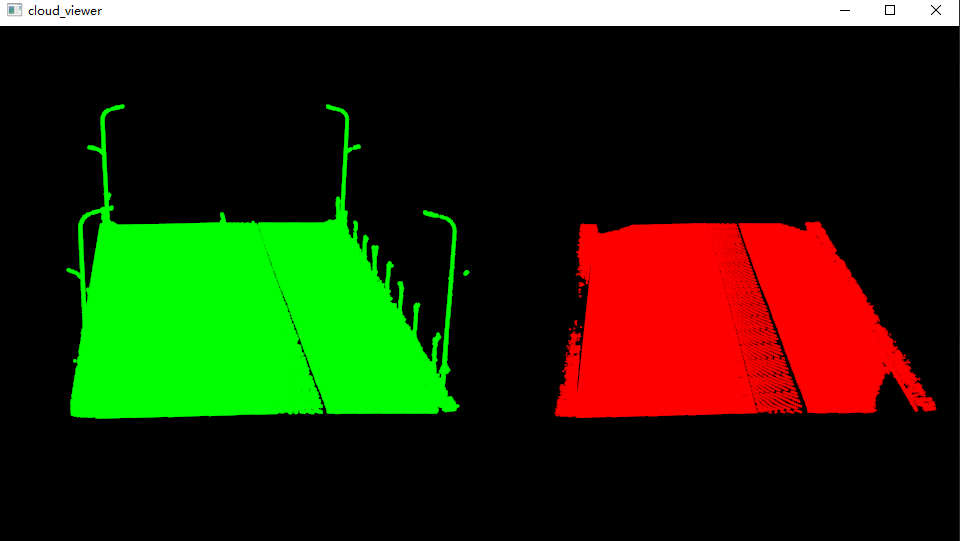
# Visual point cloud
viewer = pcl.visualization.PCLVisualizer("cloud_viewer")
v1 = 1
viewer.createViewPort(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, v1)
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, v1)
single_color = pcl.visualization.PointCloudColorHandlerCustom.PointXYZ(cloud, 0.0, 255.0, 0.0)
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud, single_color, "sample cloud1", v1)
v2 = 2
viewer.createViewPort(0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, v2)
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, v2)
single_color = pcl.visualization.PointCloudColorHandlerCustom.PointXYZ(cloud_filtered, 255.0, 0.0, 0.0)
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_filtered, single_color, "sample cloud2", v2)
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(0, 3, "sample cloud1", v1)
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(0, 3, "sample cloud2", v2)
while not viewer.wasStopped():
viewer.spinOnce(10)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# -------------------------------Read point cloud----------------------------------
cloud = pcl.PointCloud.PointXYZ()
pcl.io.loadPCDFile('40m1.pcd', cloud)
# -----------------------------RANSAC split plane------------------------------
inliers = pcl.vectors.Int() # Interior point index
# Create a random sampling consistency plane segmentation model
model_p = pcl.sample_consensus.SampleConsensusModelPlane.PointXYZ(cloud)
ransac = pcl.sample_consensus.RandomSampleConsensus.PointXYZ(model_p)
ransac.setDistanceThreshold(0.1) # Distance threshold
ransac.computeModel() # Fit
ransac.getInliers(inliers) # Get interior point index
coeffs = pcl.vectors.VectorXf() # Vector for storing plane coefficients (PCL. Vectors. Vectorxf() is the python representation corresponding to the Eigen type)
ransac.getModelCoefficients(coeffs) # Acquisition coefficient
coeff = np.array(coeffs) # Convert to a format supported by numpy
# ---------------------------Output the coefficients of the plane model----------------------------
print('The model coefficient of the fitting plane is:')
print('a=:', coeff[0])
print('b=:', coeff[1])
print('c=:', coeff[2])
print('d=:', coeff[3])
# -----------------------------Extract point cloud based on index----------------------------
inliers_cloud = pcl.PointCloud.PointXYZ()
outliers_cloud = pcl.PointCloud.PointXYZ()
extract = pcl.filters.ExtractIndices.PointXYZ()
extract.setInputCloud(cloud)
extract.setIndices(inliers)
extract.setNegative(False)
extract.filter(inliers_cloud)
extract.setNegative(True)
extract.filter(outliers_cloud)
# ---------------------------Save split results to local folder-----------------------
pcl.io.savePCDFile("inliers_cloud.pcd", inliers_cloud)
pcl.io.savePCDFile("outliers_cloud.pcd", outliers_cloud)
# visualization
point_cloud_viewer(cloud, inliers_cloud)
1.1 important functions
inliers = pcl.vectors.Int() # Interior point index coeffs = pcl.vectors.VectorXf() # Vector for storing plane coefficients (PCL. Vectors. Vectorxf() is the python representation corresponding to the Eigen type) ransac.getModelCoefficients(coeffs) # Acquisition coefficient coeff = np.array(coeffs) # Convert to a format supported by numpy
- pcl.vectors.Int(): used to represent the index of points corresponding to RANSAC algorithm in pclpy.
- pcl.vectors.VectorXf() is used to represent the parameters of RANSAC algorithm model coefficients in pclpy.
- np.array(coeffs): only when pcl.vectors.VectorXf() is converted to the data format supported by numpy can it be used for output.
2. Implementation mode 2
from pclpy import pcl
def point_cloud_viewer(cloud, cloud_filtered):
# Visual point cloud
viewer = pcl.visualization.PCLVisualizer("cloud_viewer")
v1 = 1
viewer.createViewPort(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, v1)
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, v1)
single_color = pcl.visualization.PointCloudColorHandlerCustom.PointXYZ(cloud, 0.0, 255.0, 0.0)
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud, single_color, "sample cloud1", v1)
v2 = 2
viewer.createViewPort(0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, v2)
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, v2)
single_color = pcl.visualization.PointCloudColorHandlerCustom.PointXYZ(cloud_filtered, 255.0, 0.0, 0.0)
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_filtered, single_color, "sample cloud2", v2)
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(0, 3, "sample cloud1", v1)
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(0, 3, "sample cloud2", v2)
while not viewer.wasStopped():
viewer.spinOnce(10)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Read point cloud data
cloud = pcl.PointCloud.PointXYZ()
cloud_filtered = pcl.PointCloud.PointXYZ()
cloud_p = pcl.PointCloud.PointXYZ()
cloud_f = pcl.PointCloud.PointXYZ()
reader = pcl.io.PCDReader()
reader.read('40m1.pcd', cloud)
print("PointCloud before filtering: ", cloud.width * cloud.height, " data points ")
coeffs = pcl.ModelCoefficients()
inliers = pcl.PointIndices()
seg = pcl.segmentation.SACSegmentation.PointXYZ()
# Optional
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(True)
# set up
seg.setModelType(0) # 0 is PCL:: sacmode_ PLANE
seg.setMethodType(0) # 0 is pcl::SAC_RANSAC
seg.setMaxIterations(1000) # Maximum number of iterations
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.1) # Distance threshold in m. The distance threshold determines the conditions that must be met when a point is considered to be an interior point
seg.setInputCloud(cloud) # Input point cloud
seg.segment(inliers, coeffs) # Get interior points and model coefficients
if len(inliers.indices) == 0:
print('Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset.')
exit(0)
# ---------------------------Output the coefficients of the plane model----------------------------
print('The model coefficient of the fitting plane is:')
print('a=:', coeffs.values[0])
print('b=:', coeffs.values[1])
print('c=:', coeffs.values[2])
print('d=:', coeffs.values[3])
# -----------------------------Extract point cloud based on index----------------------------
inliers_cloud = pcl.PointCloud.PointXYZ()
outliers_cloud = pcl.PointCloud.PointXYZ()
extract = pcl.filters.ExtractIndices.PointXYZ()
extract.setInputCloud(cloud)
extract.setIndices(inliers)
extract.setNegative(False)
extract.filter(inliers_cloud)
extract.setNegative(True)
extract.filter(outliers_cloud)
# ---------------------------Save split results to local folder-----------------------
pcl.io.savePCDFile("inliers_cloud.pcd", inliers_cloud)
pcl.io.savePCDFile("outliers_cloud.pcd", outliers_cloud)
# visualization
point_cloud_viewer(cloud, inliers_cloud)
2.1 fitting method
| Fitting method | Digital representation |
|---|---|
| SAC_RANSAC | 0 |
| SAC_LMEDS | 1 |
| SAC_MSAC | 2 |
| SAC_RRANSAC | 3 |
| SAC_RMSAC | 4 |
| SAC_MLESAC | 5 |
| SAC_PROSAC | 6 |
3. Implementation mode III
import pclpy
from pclpy import pcl
def point_cloud_viewer(cloud, cloud_filtered):
# Visual point cloud
viewer = pcl.visualization.PCLVisualizer("cloud_viewer")
v1 = 1
viewer.createViewPort(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, v1)
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, v1)
single_color = pcl.visualization.PointCloudColorHandlerCustom.PointXYZ(cloud, 0.0, 255.0, 0.0)
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud, single_color, "sample cloud1", v1)
v2 = 2
viewer.createViewPort(0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, v2)
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, v2)
single_color = pcl.visualization.PointCloudColorHandlerCustom.PointXYZ(cloud_filtered, 255.0, 0.0, 0.0)
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_filtered, single_color, "sample cloud2", v2)
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(0, 3, "sample cloud1", v1)
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(0, 3, "sample cloud2", v2)
while not viewer.wasStopped():
viewer.spinOnce(10)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# -------------------------------Read point cloud----------------------------------
cloud = pcl.PointCloud.PointXYZ()
pcl.io.loadPCDFile('40m1.pcd', cloud)
# ------------------------------RANSAC fitting plane-----------------------------
inliers, coefficients = pclpy.fit(cloud, # Input point cloud
"plane", # Fitting plane
distance=0.1) # Distance threshold
# ---------------------------Output the coefficients of the plane model----------------------------
print('The model coefficient of the fitting plane is:')
print('a=:', coefficients.values[0])
print('b=:', coefficients.values[1])
print('c=:', coefficients.values[2])
print('d=:', coefficients.values[3])
# -----------------------------Extract point cloud based on index----------------------------
inliers_cloud = pcl.PointCloud.PointXYZ()
outliers_cloud = pcl.PointCloud.PointXYZ()
extract = pcl.filters.ExtractIndices.PointXYZ()
extract.setInputCloud(cloud)
extract.setIndices(inliers)
extract.setNegative(False)
extract.filter(inliers_cloud)
extract.setNegative(True)
extract.filter(outliers_cloud)
# ---------------------------Save split results to local folder-----------------------
pcl.io.savePCDFile("inliers_cloud.pcd", inliers_cloud)
pcl.io.savePCDFile("outliers_cloud.pcd", outliers_cloud)
# visualization
point_cloud_viewer(cloud, inliers_cloud)
3.1. Attention
Mode 3 is the function encapsulation of mode 2, but the calculation result of mode 3 is not as accurate as mode 1 and mode 2.
3, Result display
The model coefficient of the fitting plane is: a=: -0.0054196 b=: 0.028334273 c=: -0.99958384 d=: 0.19884771