preface
With the deepening of development, the research on assembly instructions also needs to continue, mainly the analysis of assembly examples and the detailed explanation of instructions.
Then, there is a very serious problem. That is how to learn assembly code. I believe different people have different solutions, but for me, or most embedded, bottom-level or driver developers, they start with c language as their learning track. Then I also recommend a learning method, that is, from c to grey assembly, and then from assembly to c, It is also a good habit to learn new skills through the skills you have mastered.
Tip: the following is the main content of this article. The following cases can be used for reference
1, What is assembly:
In fact, it is impossible for our machine to recognize what high-level languages such as c we write. Only machine language can be recognized, and assembly language is a kind of machine language. However, assembly language can help us understand through mnemonics and other symbols. Therefore, some developers use this language for programming.
2, Example:
This is a typical example of storage and writing in official documents. I will use this example to study it in detail.
; assembly language ;Indicates the beginning of a comment ; This write routine assumes the following: ; 1. The 16 bytes of data are loaded, starting at the address in DATA_ADDR ; 2. Each word of data to be written is made up of two adjacent bytes in DATA_ADDR, ; stored in little endian format ; 3. A valid starting address (the least significant bits = 000) is loaded in ADDRH:ADDRL ; 4. ADDRH and ADDRL are located in shared data memory 0x70 - 0x7F ; BCF INTCON,GIE ; Disable ints so required sequences will execute properly BANKSEL EEADRH ; Bank 3 MOVF ADDRH,W ; Load initial address MOVWF EEADRH ; MOVF ADDRL,W ; MOVWF EEADRL ; MOVLW LOW DATA_ADDR ; Load initial data address MOVWF FSR0L ; MOVLW HIGH DATA_ADDR ; Load initial data address MOVWF FSR0H ; BSF EECON1,EEPGD ; Point to program memory BCF EECON1,CFGS ; Not configuration space BSF EECON1,WREN ; Enable writes BSF EECON1,LWLO ; Only Load Write Latches LOOP MOVIW FSR0++ ; Load first data byte into lower MOVWF EEDATL ; MOVIW FSR0++ ; Load second data byte into upper MOVWF EEDATH ; MOVF EEADRL,W ; Check if lower bits of address are '000' XORLW 0x07 ; Check if we're on the last of 8 addresses ANDLW 0x07 ; BTFSC STATUS,Z ; Exit if last of eight words, GOTO START_WRITE ; MOVLW 55h ; Start of required write sequence: MOVWF EECON2 ; Write 55h MOVLW 0AAh ; MOVWF EECON2 ; Write AAh BSF EECON1,WR ; Set WR bit to begin write NOP ; Any instructions here are ignored as processor ; halts to begin write sequence NOP ; Processor will stop here and wait for write to complete. ; After write processor continues with 3rd instruction. INCF EEADRL,F ; Still loading latches Increment address GOTO LOOP ; Write next latches START_WRITE BCF EECON1,LWLO ; No more loading latches - Actually start Flash program ; memory write MOVLW 55h ; Start of required write sequence: MOVWF EECON2 ; Write 55h MOVLW 0AAh ; MOVWF EECON2 ; Write AAh BSF EECON1,WR ; Set WR bit to begin write NOP ; Any instructions here are ignored as processor ; halts to begin write sequence NOP ; Processor will stop here and wait for write complete. ; after write processor continues with 3rd instruction BCF EECON1,WREN ; Disable writes BSF INTCON,GIE ; Enable interrupts
Example: pandas is a NumPy based tool created to solve data analysis tasks.
3, Instruction
In contrast, the pic instruction set is relatively small. Here is the instruction set of PIC16F1823, and then I list some simple and complex instructions
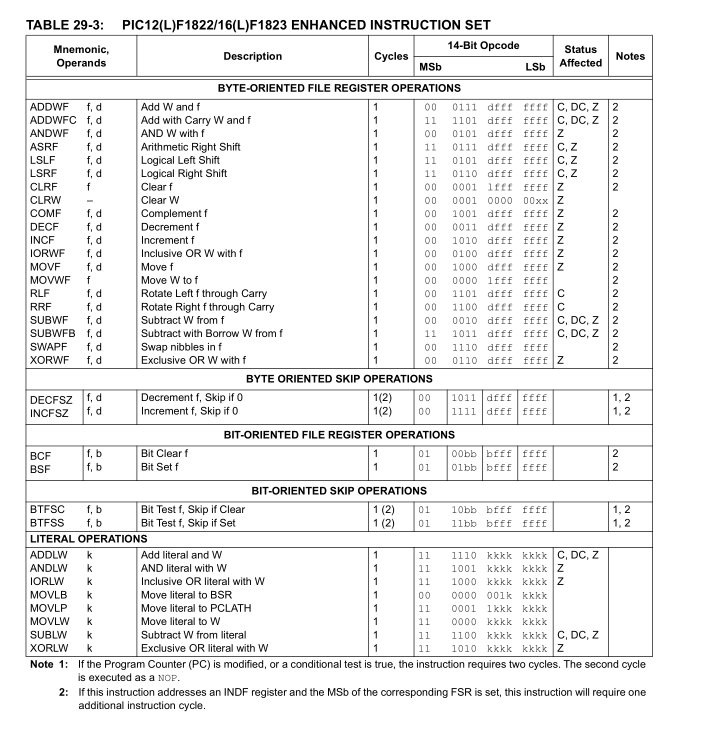
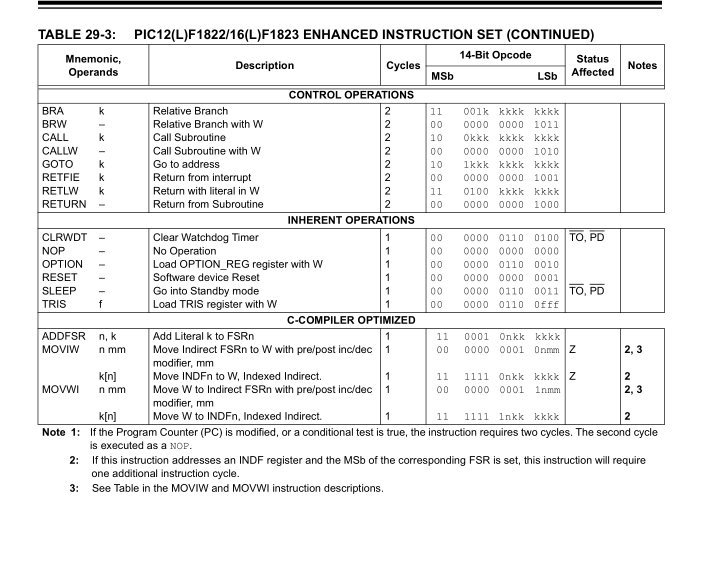
1. Simple instructions
;bcf Instruction: this instruction is actually clearing the register f The first b position BCF Bit Clear f BCF f,b Operands: 0 <f < 127 0 <b <7 Operation: 0 -> (f<b>) Status Affected: None Description: Bit 'b' in register 'f' is cleared.
;MOVF Instruction: this instruction is actually to f Move the contents of the register to d in MOVF f,d Operands: 0 <f < 127 d ->[0,1] Operation: (f) < (dest) Status Affected: Z Description: The contents of register f is moved to a destination dependent upon the status of d. If d = 0, destination is W register. If d = 1, the destination is file register f itself. d = 1 is useful to test a file register since status flag Z is affected. Words: 1 Cycles: 1 Example: MOVF FSR, 0 After Instruction W = value in FSR register Z = 1
2. Complex instructions
RRF instruction:
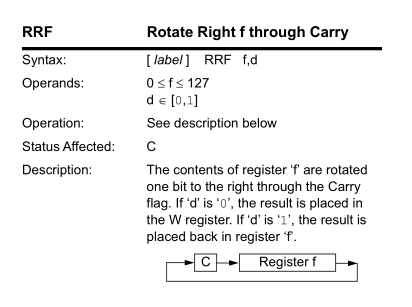
summary
In short, this article is actually to explain some compilation knowledge