Notes on pinyougou project (11)
SpringBoot
introduce
springboot is a back-end full stack framework (excluding page technology) produced by spring organization
Role: advocate zero configuration, do not need to integrate the framework structure, write business code directly, improve personnel utilization and development efficiency for enterprises.
Disadvantages: springboot is only suitable for small projects
Small example (1)
1, Create a normal project for maven
2, Introduce dependency and configure spring boot starter parent as parent project
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.4.0.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
3, Create the package structure and create a startup class in the upper package
4, Start class writing
package cn.itcast; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; /** * Startup class */ @SpringBootApplication public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { //Start the tomcat plug-in in the current project and run the current project SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args); } }
5, Write a controller to test
@RestController @RequestMapping("/test") public class TestController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ return "helloWorld"; } }
6, Run the main method of the startup class to start the project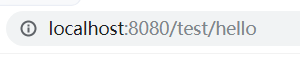

Small examples (2)
1, Modify tomcat boot port
In the resources directory, create application.properties Document and add
server.port=8081
2, Read properties file properties
Inject the property Environment and use getProperty("property name")
url=123456
@RestController @RequestMapping("/test") public class TestController { @Autowired private Environment env; @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ String url = env.getProperty("url"); return "helloWorld"+url; } }
3, Hot deployment
No need to restart tomcat after modifying the code
Note: idea does not take effect, eclipse takes effect
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> </dependency>
Integration of springboot and activemq
1, Add coordinates
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-activemq</artifactId> </dependency>
2, Configure avtivemq server
stay application.properties If not, the default message server is used
spring.activemq.broker-url=tcp://192.168.200.128:61616
3, Write message sender
@RestController @RequestMapping("/testJms") public class TestJms { @Autowired private JmsMessagingTemplate jmsMessagingTemplate; @RequestMapping("/send") public void send(String text){ //Send message to message server //Parameter 1: specify queue name //Parameter 2: what to send jmsMessagingTemplate.convertAndSend("itcast", text); } }
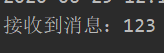
4, Receiver who wrote the message
@Component public class Consumer { /** * Define a listener to listen to messages sent from the message server * destination Is the queue from which the message is received * @param text */ @JmsListener(destination="itcast") public void readMessage(String text){ System.out.println("Message received:"+text); } }
5, Sending and receiving messages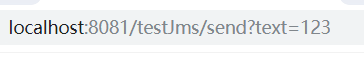
Ali greater than
1, Register alicloud account, application template and signature
2, Add a sub account and use the id and password of the sub account
3, SMS flow chart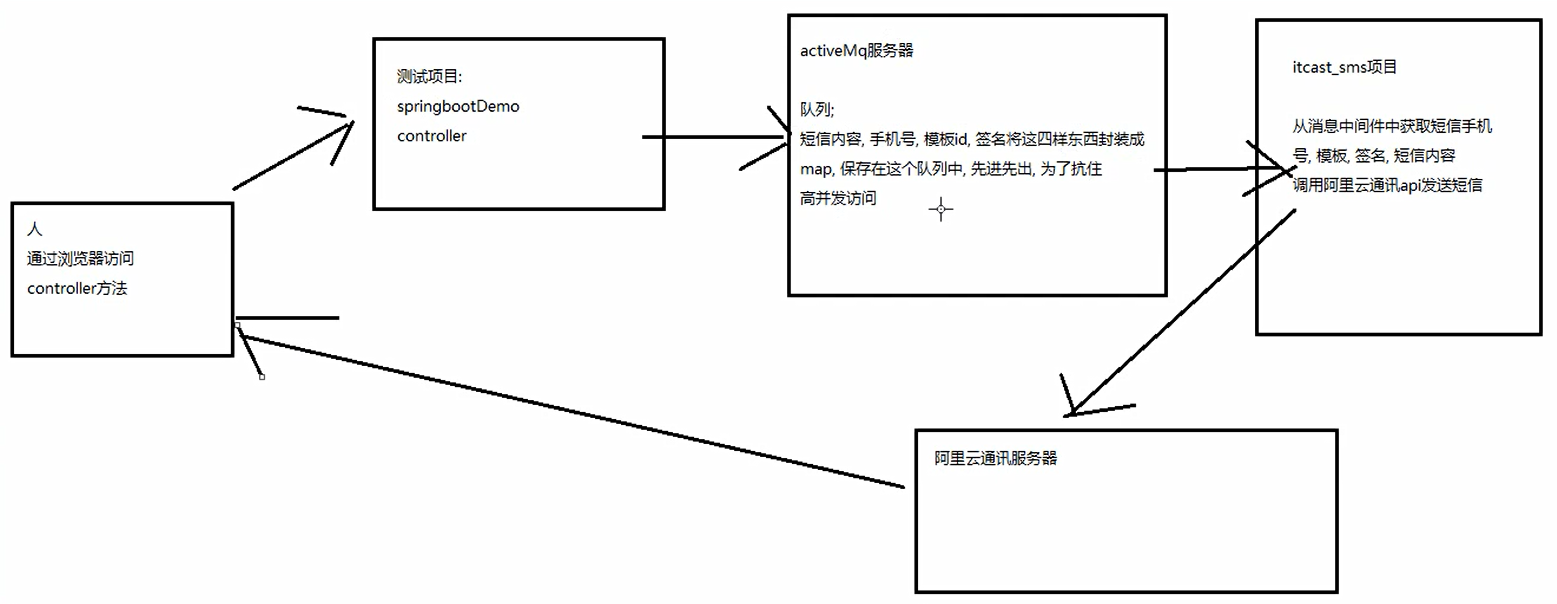
4, Add SMS tool class
@Component public class SmsUtil { //Product Name: cloud communication short message API product, developers do not need to replace it static final String product = "Dysmsapi"; //Product domain name, developers do not need to replace static final String domain = "dysmsapi.aliyuncs.com"; @Autowired private Environment env; // TODO here needs to be replaced by the developer's own AK (found on Alibaba cloud access console) /** * Send SMS * @param mobile cell-phone number * @param template_code Template No * @param sign_name autograph * @param param parameter * @return * @throws ClientException */ public SendSmsResponse sendSms(String mobile,String template_code,String sign_name,String param) throws ClientException { String accessKeyId =env.getProperty("accessKeyId"); String accessKeySecret = env.getProperty("accessKeySecret"); //Self adjusting timeout System.setProperty("sun.net.client.defaultConnectTimeout", "10000"); System.setProperty("sun.net.client.defaultReadTimeout", "10000"); //Initialization of acsClient, region ization is not supported IClientProfile profile = DefaultProfile.getProfile("cn-hangzhou", accessKeyId, accessKeySecret); DefaultProfile.addEndpoint("cn-hangzhou", "cn-hangzhou", product, domain); IAcsClient acsClient = new DefaultAcsClient(profile); //Assembly request object - please refer to console - document for details SendSmsRequest request = new SendSmsRequest(); //Required: mobile number to be sent request.setPhoneNumbers(mobile); //Required: SMS signature - can be found in SMS console request.setSignName(sign_name); //Required: SMS template - can be found in SMS console request.setTemplateCode(template_code); //Optional: the variables in the template replace the JSON string. For example, when the template content is "Dear ${name}, and your verification code is ${code}", the value here is request.setTemplateParam(param); //Optional - uplink SMS extension code (for users without special needs, please ignore this field) //request.setSmsUpExtendCode("90997"); //Optional: outId is the extended field provided to the business party, and this value is finally brought back to the caller in the SMS receipt message request.setOutId("yourOutId"); //hint an exception may be thrown here. Pay attention to catch SendSmsResponse sendSmsResponse = acsClient.getAcsResponse(request); return sendSmsResponse; } }
5, Use the message server to listen for messages
@Component public class SmsListener { @Autowired private SmsUtil smsUtil; @JmsListener(destination="sms") public void sendSms(Map<String,String> map){ try { SendSmsResponse response = smsUtil.sendSms( map.get("mobile"), map.get("template_code"), map.get("sign_name"), map.get("param") ); System.out.println("Code=" + response.getCode()); System.out.println("Message=" + response.getMessage()); System.out.println("RequestId=" + response.getRequestId()); System.out.println("BizId=" + response.getBizId()); } catch (ClientException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
6, Send message
Send mobile phone number, template code, signature name and verification code respectively
@RequestMapping("/sendSms") public void sendSms(){ Map map=new HashMap(); map.put("mobile", "cell-phone number"); map.put("template_code", "Template id"); map.put("sign_name", "Signature name"); map.put("param", "{\"code\":\"123456\"}"); jmsMessagingTemplate.convertAndSend("sms",map); }