preface
I only sent this article because I came to write a simple operation about git at the invitation of my friends yesterday. Friends used svn as version control before. Now the company uses git as version tool. Due to time problems, I will simply sort out the GIT commands commonly used in work to facilitate friends to attribute git commands as soon as possible. A picture is attached as a souvenir.
Hahaha, it's funny to meet familiar talents!
Topic
Entering the topic, we will introduce git from the following ten aspects.
1. How to create a git project
Create a new project on gitlab or GitHub - "" create a blank project - "" enter the project name
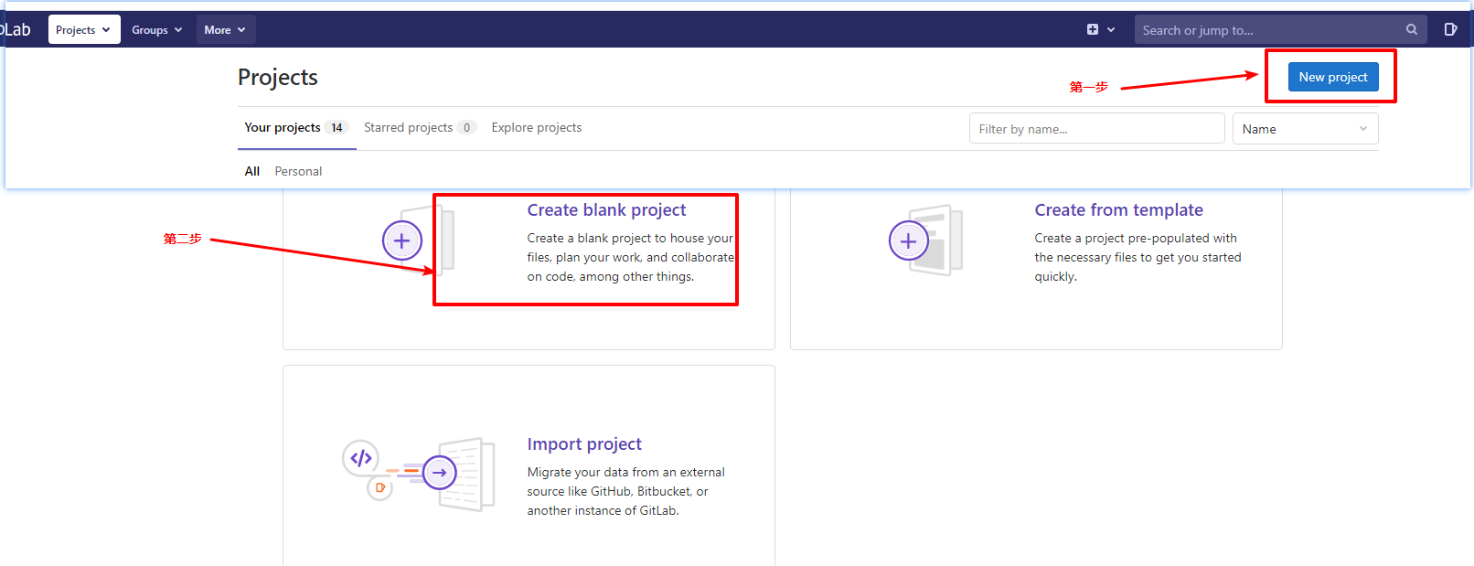
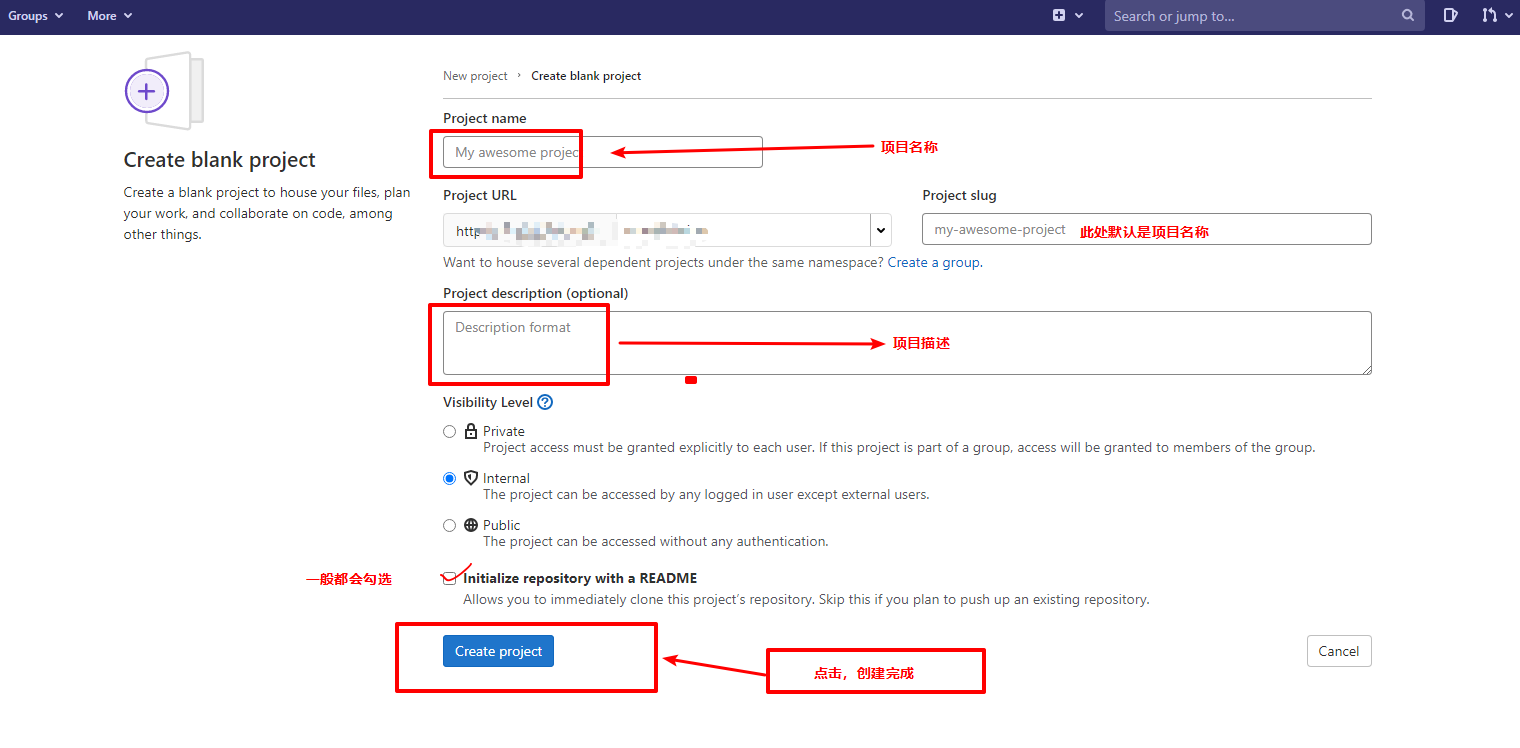
Local operation: after obtaining the code, it is automatically bound to the remote branch
git clone address cd Directory just downloaded touch README.md git add README.md git commit -m "add README" git push -u origin master
Note: generally, after the project is created, you will be given the corresponding code example of creating a local code warehouse.
2. How do existing projects bind to remote git warehouses
cd existing_folder git init git remote add origin git Remote address git add . git commit -m "Initial commit" git push -u origin master
3. Get the existing git warehouse code
There's nothing to say about this. It's git clone
git clone git://url
4. Create / switch / delete branch
Creating and deleting branches can be done in the remote warehouse. As shown in the figure
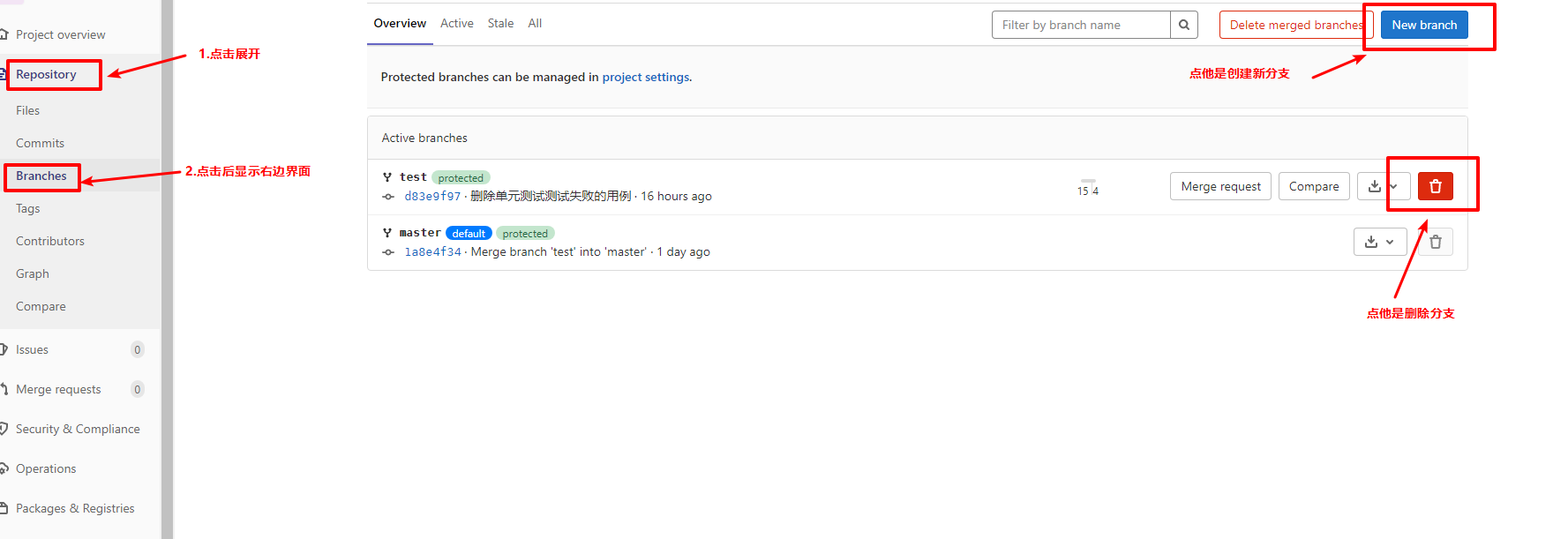
Of course, it can also be done in the local warehouse. as follows
// View the current branch and display the changed files git status
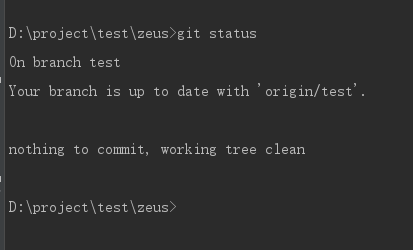
Switch branches using git checkout
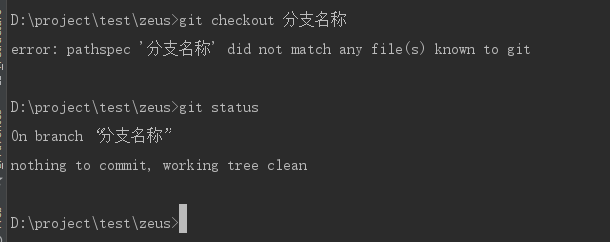
// Create a branch, creating a blank branch git checkout -b "Branch name // Switch branch git checkout Branch name
Create local branch
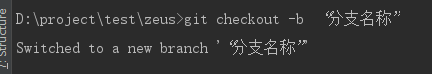
Switch to the branch you created
Push the created branch to the remote branch PS: when you have a local branch and the corresponding remote branch (if you accidentally delete the remote branch, don't panic. If you push up the local branch, the remote branch will be re created.)
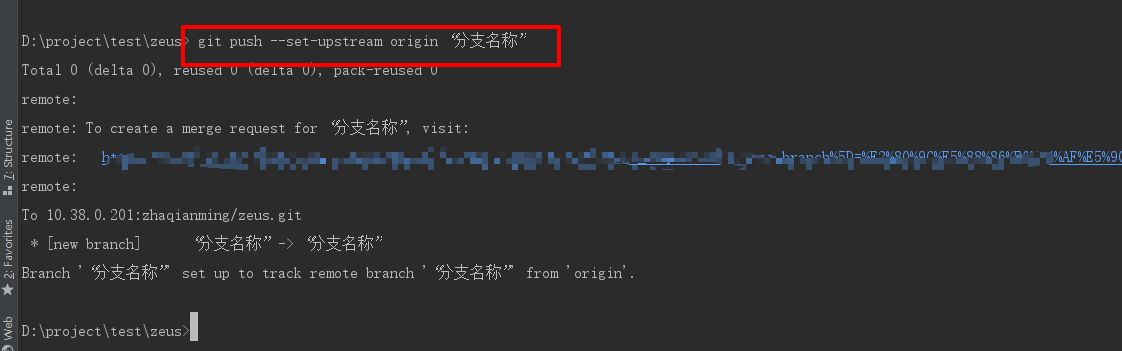
Create a branch with remote branch management
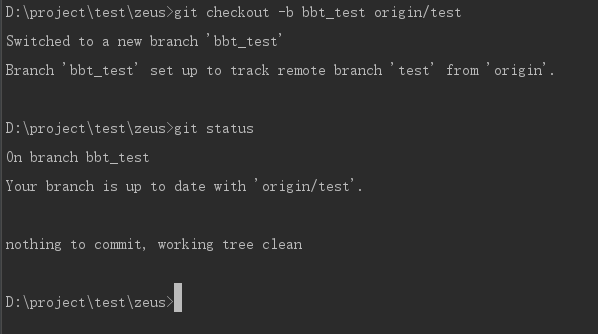
Use git branch to check whether the new branch is successful.
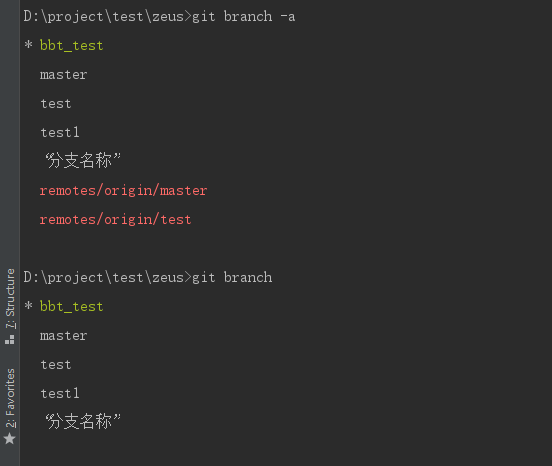
// Show local branches git branch // Show all branches (including remote branches) git branch -a
**Number identifies the currently used branch tag*
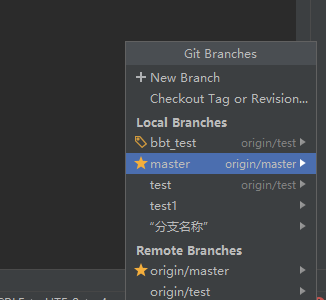
*Of course, the idea tool can also help us create branch information quickly
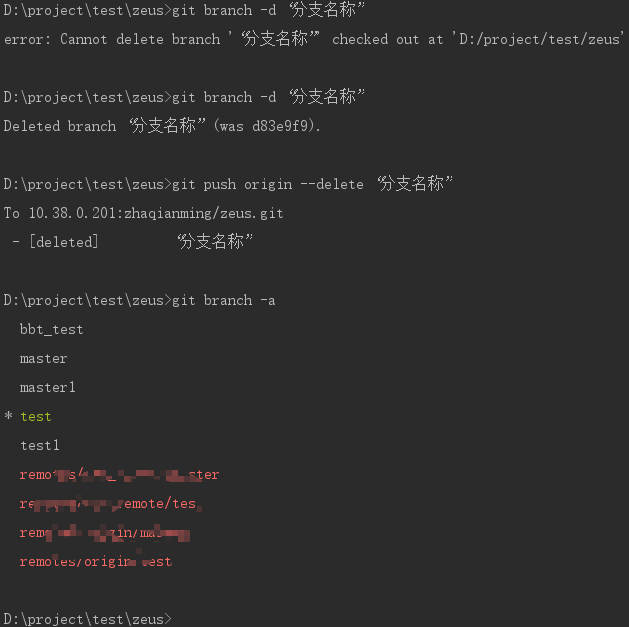
Delete branch
Delete remote branch: git push origin --delete Branch name --Remote branch git branch -d Branch name --You can delete a local branch (in the main branch)
It's impossible to kill yourself in your own branch! You know
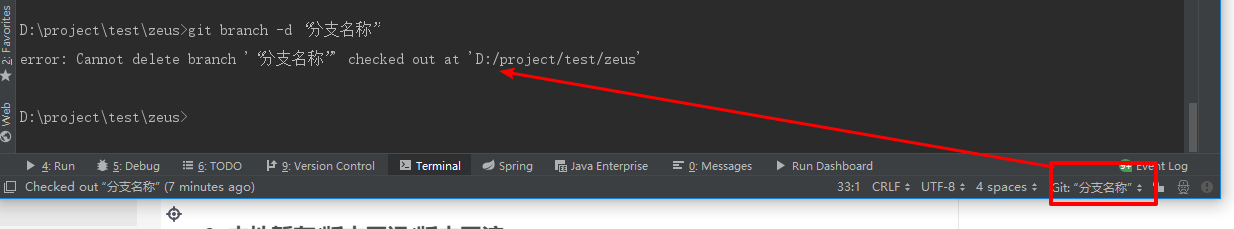
Switch to any branch to delete the local branch, execute the above command, and check the branch name and branch information through git branch -a.
5. Update / submit code
// Check whether the code is modified git status //Staging modified code git stash // The code modification is directly pulled down to the local code merge, and a commit is generated, that is, merge commit git pull = git fetch + git merege // rebase does not generate a commit, and the commit history is clean git pull --rebase == git fetch + git rebase //Add submit all codes git add . //Submit multiple file code spaces. Of course, you can add them twice git add File 1 file 2 git commit -m 'commit message' //Only the submission with any push code added will be considered as a commit. The missing file will be added for one submission git commit --amend //Push code is pushed to the current branch by default git push //Push to the specified remote branch head to point to test git push origin HEAD:test git push origin test== git push origin test:test //Forced push caution git push -f
Generally, there will be convenient operations in the IDE
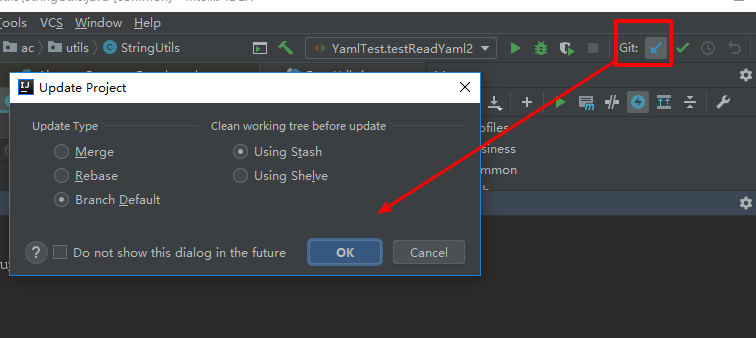
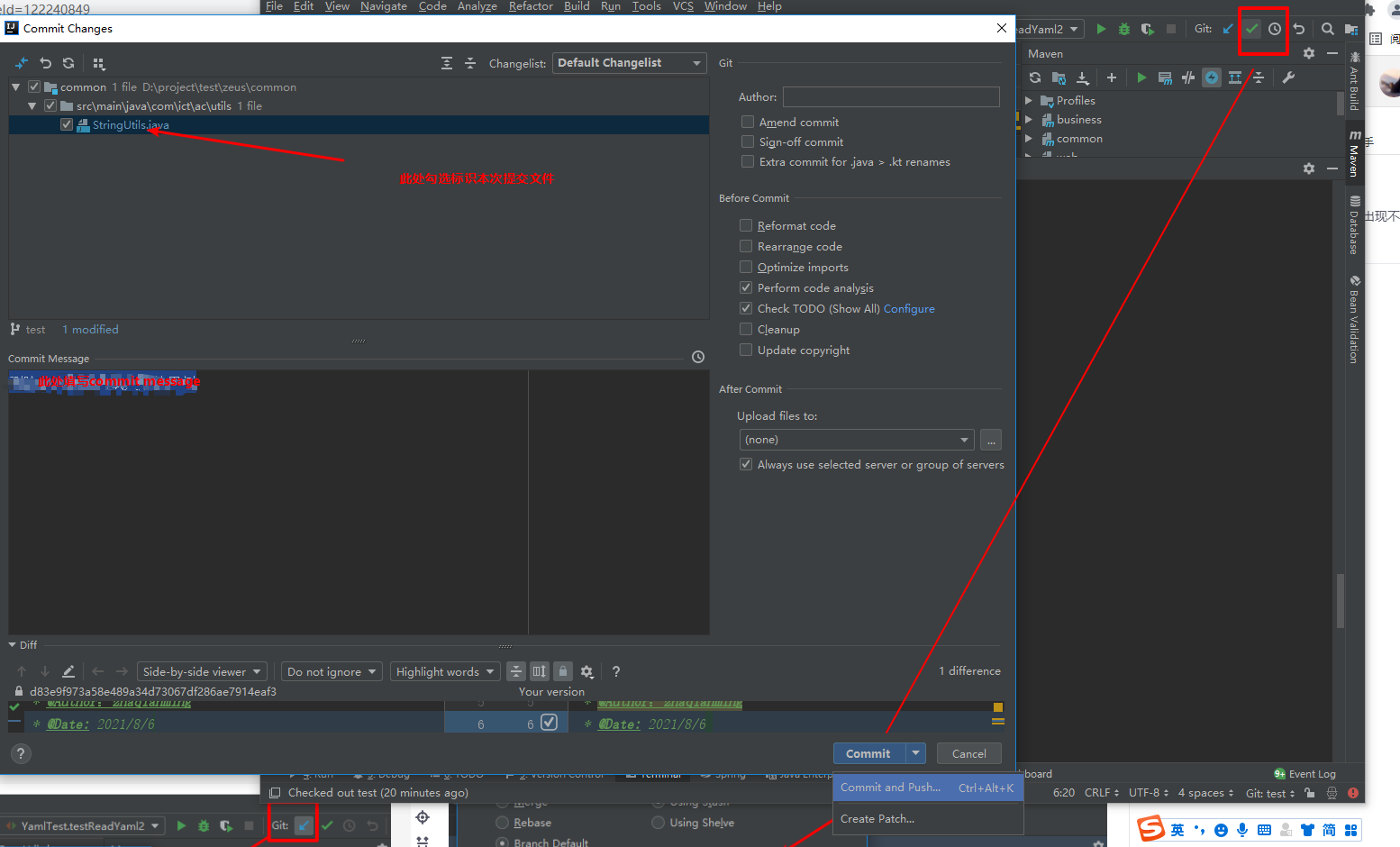
Click commit to identify the submission
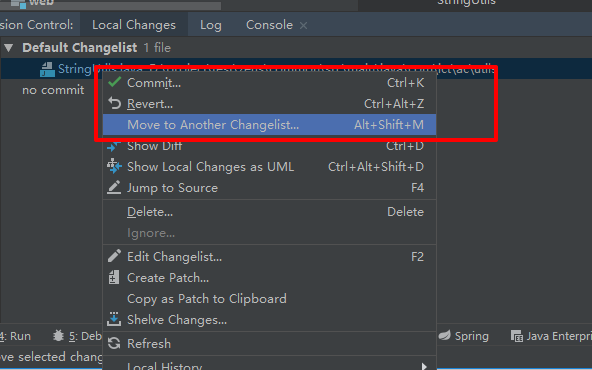
Click revert to rollback the current code and restore the code before the generation change
6. Local staging / version fallback / version rollback
Code can be temporarily stored multiple times through git stash, and git stash pop can be continuously released. Like the stack, in and out.
// Staging Code: after entering the command, all modified codes enter the staging area and need to be released manually to display the modified file git stash // Release code git stash pop //To return the code to this submission, commit only needs the first 8 bits git reset commitId(Need to go back commitid No.) //Code rollback cancels this submission git revert commitId(Need to revoke the submitted commitid No.) Version shuttle Git reflog Print your operation record every time
7. git log usage
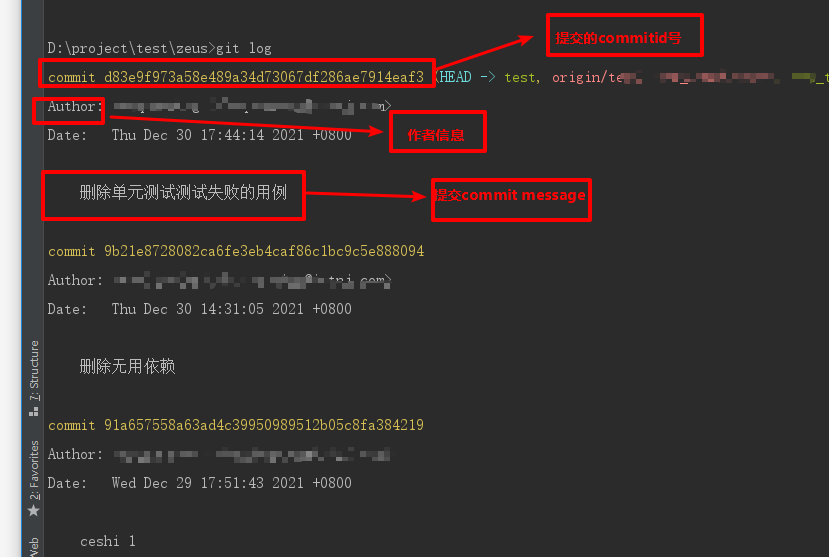
8. gitinore common configurations
//Save git password git config --global credential.helper store git config --list // View configuration information --see git config user.name git config user.email --Of the project git config user.name myName // Own user name git config user.email myEmail // Own mailbox --Global git config --global user.name globalName // Global user name git config --global user.email globalEmail // Global mailbox
9. gitinore does not take effect solution
gitignore git rm -r --cached . (git rm -r -f --cached . Force delete cache) git add . git commit -m "update .gitignore"
git token login
First time: set up connection with git
git remote add origin https://your token@github.com/url.gradelDemo.git ##`Insert code slice here ` Delete remote warehouse git remote rm origin #You can modify the alias of the connection after it has been set git remote set-url origin https://your token@github.com/url.gradelDemo.git