Prefix and brush question summary of leetcode 1
1 - subarray with the smallest length
Title Link: Title Link stamp here!!!
Idea: prefix and + binary search
Find the prefix sum of the array, find and update the smallest sub array in the prefix sum
The AC code is as follows:
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length ;
int [] sums = new int [n+1] ;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE ;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){ //Prefix and
sums[i] = sums[i-1]+nums[i-1];
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){//Binary search
int s = target + sums[i-1] ;
int bound = Arrays.binarySearch(sums,s) ;
if(bound<0){
bound = -bound - 1 ;
}
if(bound<=nums.length){
min = Math.min(min,bound-(i-1)) ;
}
}
return min==Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : min ;
}
}
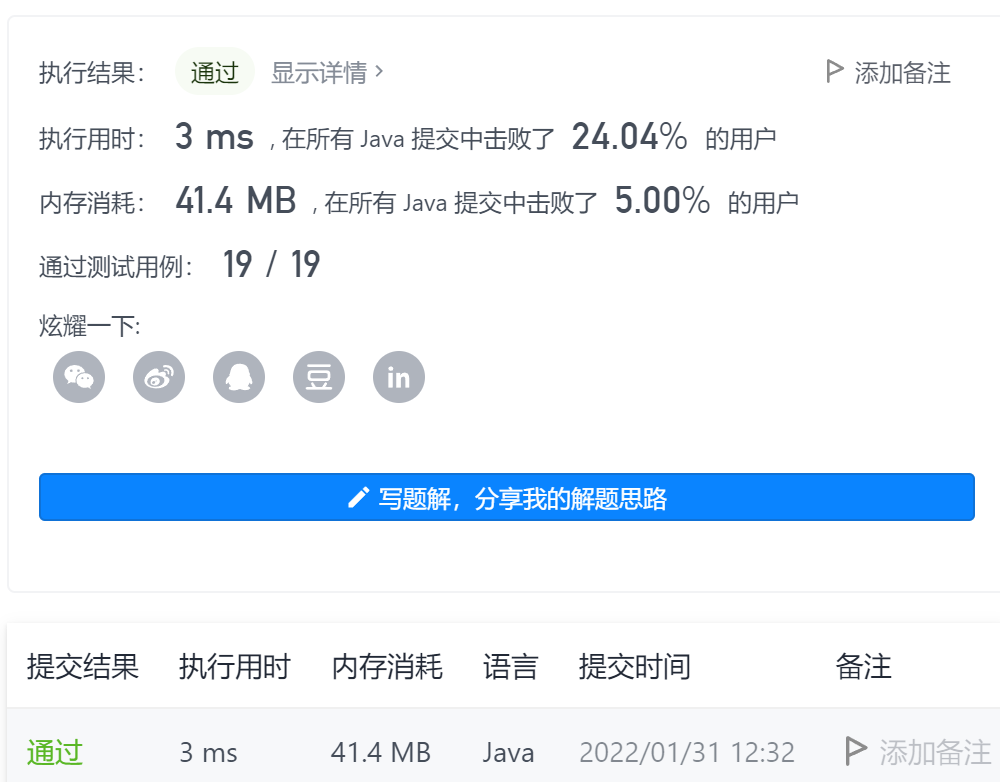
Method 2: Double finger acupuncture
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length ;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE ;
int sum = 0 ;
int left=0, right = 0 ;
while(right<n ){
sum += nums[right] ;
while(sum>=target){
min = Math.min(min, right-left+1) ;
sum -= nums[left] ;
left++ ;
}
right++ ;
}
return Integer.MAX_VALUE==min ? 0 : min ;
}
}
2 - product of arrays other than itself
Title Link: Title Link stamp here!!!
The AC code is as follows:
Idea: it is to calculate the left cumulative multiplication of each value multiplied by the right cumulative multiplication.
class Solution {
public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {
//Multiply the left cumulative value of each value by the right cumulative value
int [] res = new int [nums.length] ;
int left=1, right=1 ;
Arrays.fill(res,1) ;
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
res[i] *= left ;
left *= nums[i] ;
res[nums.length-i-1] *= right;
right *= nums[nums.length-1-i] ;
}
return res ;
}
}

It seems easier to understand and more efficient.
class Solution {
public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {
//Multiply the left cumulative value of each value by the right cumulative value
int [] res = new int [nums.length] ;
int left=1, right=1 ;
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
res[i] = left ;
left *= nums[i] ;
}
for(int i=nums.length-1; i>=0; i--){
res[i] *= right ;
right *= nums[i] ;
}
return res ;
}
}

3-continuous array
Title Link: Title Link stamp here!!!
Idea: prefix and + hash table, change the array 0 to 1, and it becomes the maximum length of a continuous array whose prefix sum is 0.
The AC code is as follows:
class Solution {
public int findMaxLength(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>() ;
int n = nums.length ;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
if(nums[i]== 0){
nums[i] = -1 ;
}
}
int sum = 0, temp = 0 ;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
sum += nums[i] ;//Prefix and
if(sum==0){//Prefix and are 0
temp = i+1;
}
if(map.containsKey(sum)){//Prefix and are 0
temp = Math.max(i-map.get(sum),temp) ;
}else{
map.put(sum, i) ;
}
}
return temp ;
}
}

4-successive subarrays and
Title Link: Title Link stamp here!!!
Idea: prefix and + hash table
True if the prefix and the remainder of k are 0 and the array length is more than 2
True if the prefix and are equal and the data length is more than 2,
Otherwise, it is false.
The AC code is as follows:
class Solution {
public boolean checkSubarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
//Prefix and + hash table
int n = nums.length ;
if(n<2){
return false ;
}
int sum = 0 ;
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>() ;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
sum += nums[i] ;
int temp = sum % k ;
if(i>=1 && temp==0){//The prefix and the remainder of k are equal to 0
return true ;
}
if(map.containsKey(temp)){ //The prefix and the remainder of k are equal and the subscript is greater than or equal to 2
int preIndex = map.get(temp) ;
if(i-preIndex>=2){
return true ;
}
}else{
map.put(temp, i) ;
}
}
return false ;
}
}

5-subarray with sum K
Title Link: Title Link stamp here!!!
Idea 1: directly use prefix and statistics. In this way, it needs double circulation and high time complexity. However, the complexity of test case O(n^2) of this problem can also be passed
The AC code is as follows:
class Solution {
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length ;
int [] sums = new int [n] ;
sums[0] = nums[0] ;
for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++){
sums[i+1] = sums[i] + nums[i+1] ;
}
int cnt = 0 ;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
if(sums[i]==k){
cnt ++ ;
}
for(int j=i+1; j<n; j++){
if(sums[j]-sums[i]==k){
cnt ++ ;
}
}
}
return cnt ;
}
}
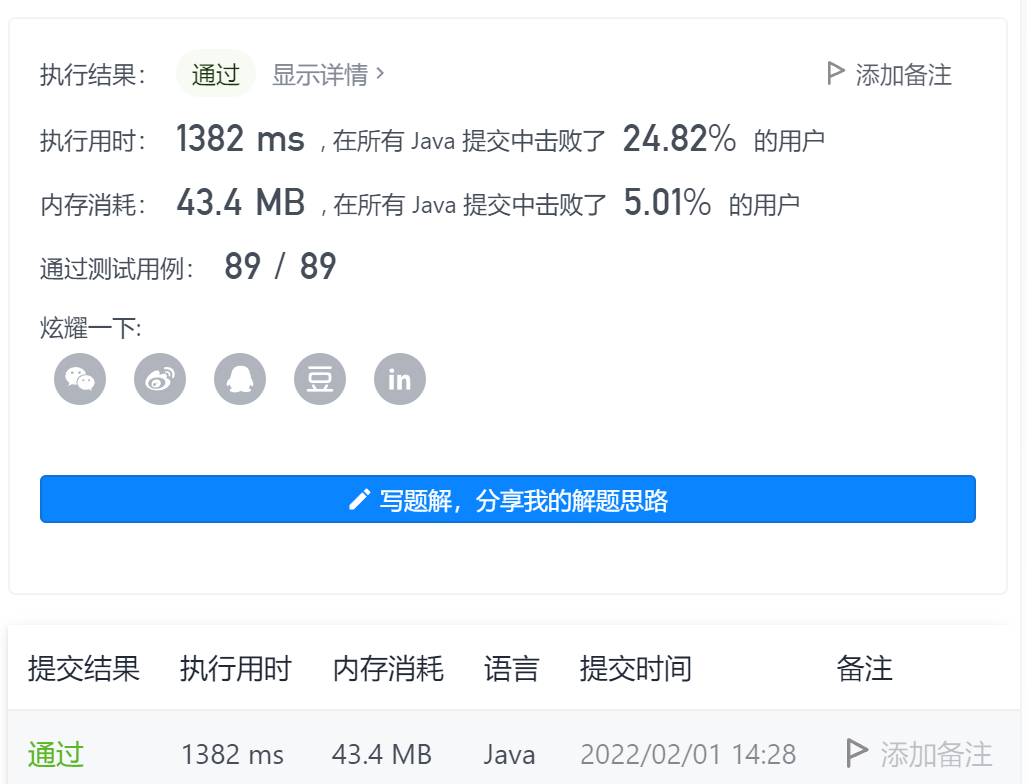
Or use prefix and + hash table to reduce the time complexity to O(n)
The AC code is as follows:
class Solution {
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length ;
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>() ;
int cnt = 0,sum = 0 ;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
sum += nums[i] ;
if(sum==k){
cnt ++ ;
}
if(map.containsKey(sum-k)){
cnt += map.get(sum-k) ;
}
map.put(sum, map.getOrDefault(sum, 0)+1) ;
}
return cnt ;
}
}
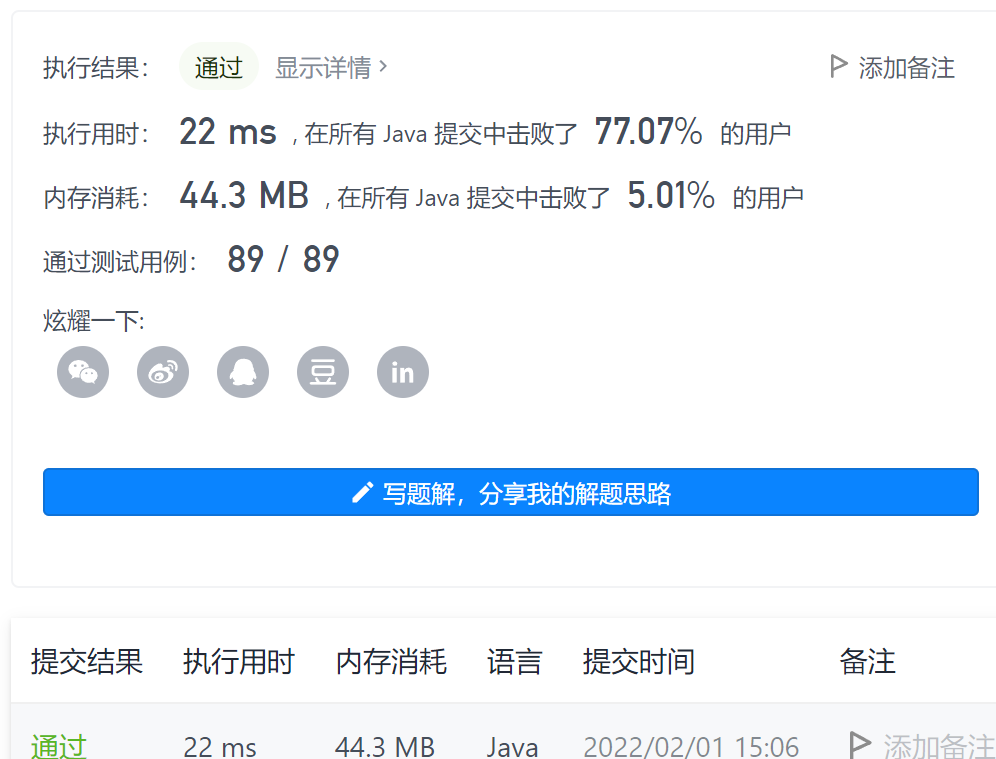
6 - number of maximum continuous 1 III
Title Link:
Idea: double pointer, also known as sliding window.
class Solution {
public int longestOnes(int[] A, int K) {
int left=0, right=0;//Left and right sides of window
int max = 0 ;//Maximum window
int zero=0 ;//Number of 0 in window
for(;right<A.length; right++){
if(A[right]==0){
zero++ ;
}
while(zero>K){
if(A[left++]==0){
zero-- ;
}
}
max = Math.max(max, right-left+1) ;
}
return max ;
}
}

Sliding window without a while loop
class Solution {
public int longestOnes(int[] A, int K) {
int left=0, right=0;//Left and right sides of window
int zero=0 ;//Number of 0 in window
for(;right<A.length; right++){
if(A[right]==0){
zero++ ;
}
if(zero>K){
zero -= (1 - A[left++]) ;
}
}
return right - left ;
}
}
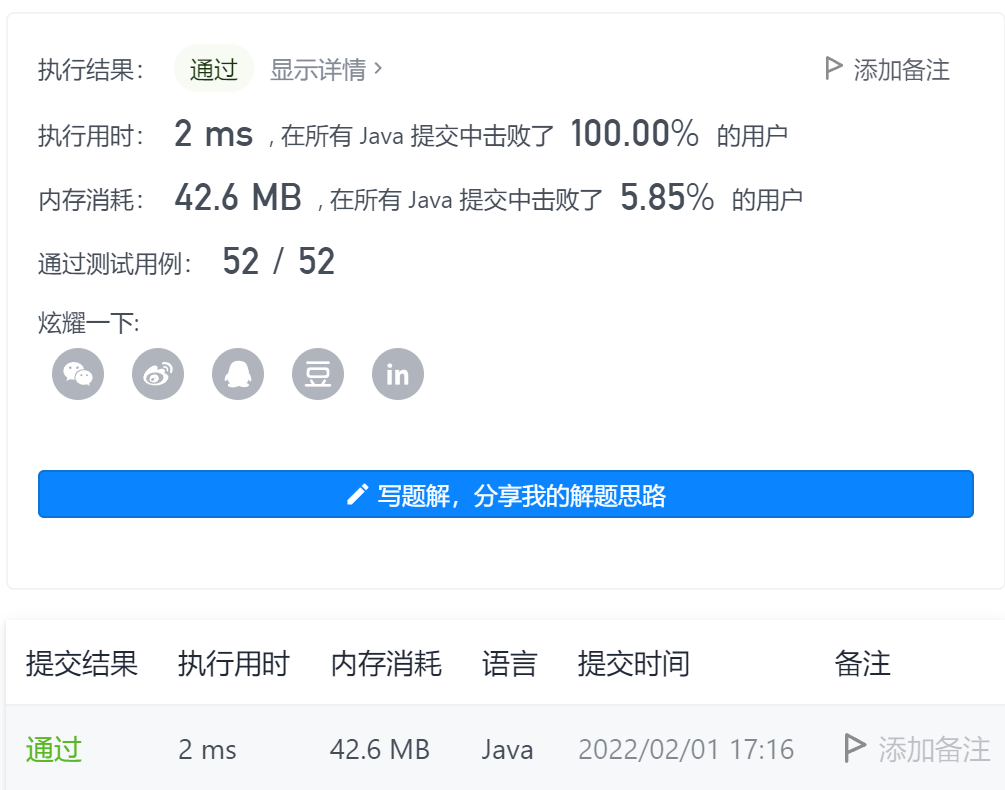
7 - find the central subscript of the array
Title Link: Title Link stamp here!!!
Idea: judge whether the prefix and at the left and right ends are equal.
The AC code is as follows:
class Solution {
public int pivotIndex(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length ;
int sum = 0 ;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++){ //If the sum from the second is equal to 0, the first is the center
sum += nums[i] ;
}
if(sum==0){
return 0 ;
}
int [] sums = new int [n] ;
sums[0] = nums[0] ;
for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++){ //Prefix Sum
sums[i+1] = sums[i] + nums[i+1] ;
}
for(int j=0; j<n; j++){ //The prefix on the right is equal to the prefix on the left
if(j+1<n && sums[j] == (sums[n-1]-sums[j+1])){
return j+1 ;
}
}
return -1 ;
}
}

8-and the same binary subarray
Title Link: Title Link stamp here!!!
Idea: prefix and + hash table
Each time you record the prefix and, find all the prefixes and values that are goal.
The AC code is as follows:
class Solution {
public int numSubarraysWithSum(int[] nums, int goal) {
//Prefix and + hash table
int sum = 0, cnt = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>() ;
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
sum += nums[i] ;
if(sum==goal){
cnt ++ ;
}
if(map.containsKey(sum-goal)){
cnt += map.get(sum-goal) ;
}
map.put(sum, map.getOrDefault(sum,0)+1) ;
}
return cnt ;
}
}
It will be reconciled and everything will be all right. Come on, boy.