To create an empty collection, use s=set()
d={}, default dictionary s=set() is an empty collection
The elements in a collection are out of order and cannot be obtained from a corner label
#Collection creation and traversal s={'Lin Qingxia','High Circle','Zhang Manyu'} for ele in s: print(ele) #Add to Collection s = {'Lin Qingxia','High Circle','Chinese Dream'} # s.add('zhang') # print(s) '''update# Traverse elements from a container to add to the current collection # Multiple containers''can be passed in update s.update('efgh','xczbc',(1,2,3),[4,5]) print(s) #Output {1, 2, 3,'Liang Wancong','Chinese Dream', 4, 5, 6,'Lin Qingxia','Chen Qianhui','Gaoyuan'} '''Delete Collection''' # s.remove(5) #If there is a direct deletion if there is no program error eg:s.remove(6) # s.clear() #empty # s.pop() #Randomly deletes an element in the set and has a return value. The set is empty s.discard(6) #If there is a direct deletion, if there is no program no error print(s)
Set, Subset, Superset, Union, Intersection, Difference
s1 = {1,2,3,4,5} s2 = {3,4,5,6,7} # s=s1.issubset(s2) is a subset, returns bool value False # s=s1.issuperset(s2) is a superset, returns bool value False # s=s1.union(s2) Union # s=s1.intersection(s2) intersection #s1.intersection_update(s2) #Intersection, but no return value, intersection updated to s1 # s=s1.difference(s2) difference set, the union of s1-s1 and S2 # s1.difference_update(s2) difference set, but no return value, update s1 # s=s1.symmetric_difference(s2) XOR, union-intersection of S1 and S2 s1.symmetric_difference_update(s2) # XOR, update s1 print(s1)
The role of sets
# The main purpose of a collection is to de-duplicate a list or element # l = ['Zhang San','Li Si','Wang Wu','Zhang San'] t = ('Zhang San','Li Si','King Five','Zhang San') s = set(t) print(s)
| Method | Explain |
|---|---|
| isalpha() | Returns True if string has at least one character and all characters are letters |
| isdecimal() | Returns True if string contains only numbers |
| islower() | Returns True if a string contains at least one case-sensitive character and all of these (case-sensitive) characters are lowercase |
| isupper() | Returns True if a string contains at least one case-sensitive character and all of these (case-sensitive) characters are uppercase |
| startwith(str) | Checks if the string starts with str and returns True if it does |
| endswith(str) | Checks if the string ends with str and returns True if it does |
str='00Da' a=str.isalpha() print(a) a=str.isdecimal() print(a) a=str.islower() print(a) a=str.isupper() print(a) a=str.startswith('00D') print(a) a=str.endswith('Da') print(a) '''False False False False True True'''
String Operation - Find and Replace
| Method | Explain |
|---|---|
| find(str, start=0, end=len(string)) | Detects whether str is included in a string, if start and end specify a range, checks whether it is included in the specified range, if it returns the starting index value, otherwise returns -1 |
| rfind(str, start=0, end=len(string)) | Similar to find(), but starting from the right |
| index(str, start=0, end=len(string)) | Similar to find() method, but error if str is not in string |
| rindex(str, start=0, end=len(string)) | Similar to index(), but starting on the right |
| replace(old_str, new_str, num=string.count(old)) | Returns a new string, replacing old_str in string with new_str, if num is specified, no more than num times |
str = 'hellohl' #Find left-to-right ends as soon as it is found #a=str.find('l') #You can specify where to start and end looking in this range a=str.find('l',4,len(str)) #Values to the right and left of an interval can be written very large print(a) #6 a=str.rfind('l',2,5) print(a) #3 # Error occurs when there is no difference between index and find a=str.index('e') print(a) #1 a=str.replace('l','hah',4) #4 represents the maximum number of substitutions print(a) #hehahhahohhah, change 4 to 2 and output hehahhahohl
Split and connect
| Method | Explain |
|---|---|
| partition(str) | Returns a tuple, dividing the string string into a 3-element tuple (before str, after str) |
| rpartition(str) | Like the partition() method, but look from the right |
| split(str="", num) | Returns a list, splits the string with str as the separator, and separates only num + 1 substring if num has a specified value. str contains'\r','t','n'and spaces by default |
| splitlines() | Returns a list separated by rows ('\r','\n','\r\n') |
| string1 + string2 | Stitching two strings |
| join(seq) | Returns a string, using string as a delimiter, combining all elements in seq (string representation) into a new string |
str = '''hello''' a=str.partition('e') #('h', 'e', 'llo') print(a) a=str.split('l',1) print(a) #['he', 'lo'] a=str.splitlines() print(a) # Pass Container Parameter Return String # Segmentation of string elements a=str.join('tkjght') print(a) #thellokhellojhelloghellohhellot s = str.join(['1','2','3']) print(s) #1hello2hello3
toggle case
| Method | Explain |
|---|---|
| lower() | Returns a new string, converting all uppercase characters in a string to lowercase |
| upper() | Returns a new string, converting lowercase letters in a string to uppercase |
str = '''Dell2''' a=str.lower() print(a) #qell2 a=str.upper() print(a) #QELL2
#align text str = 'hello' # Default space to current length s = str.ljust(10,'-') print(s) #hello----- s = str.rjust(10,'-') print(s) #-----hello s = str.center(10,'-') print(s) #--hello---
Remove whitespace from left and right of string
str = '---hello---' s = str.strip('-') print(s) #hello
Dictionaries

| classification | Method | Explain |
|---|---|---|
| query | Dictionary [Key] | Depending on the key value, there is no error for the key value pair |
| Dictionary.get (key) | Depending on the key value, there is no error for key value pairs | |
| Dictionary.keys() | Can be traversed to get all keys | |
| Dictionary.values() | Can be traversed to get all values | |
| Dictionary.items() | Can be traversed to get all (keys, values) | |
| ergodic | For key in dictionary | Remove the key for each element in the tuple |
d = {'china':'China','england':'Britain','france':'France'} a=d['china'] print(a) #China a=d.get('france') print(a) #France # View objects can be converted to lists # View objects cannot be manipulated print(d.keys()) #dict_keys(['china', 'england', 'france']) print(list(d.values())) #['China','Britain','France'] # Returns a nested tuple in the list of view objects for an entry print(d.items()) #dict_items([('china','China', ('england','UK'), ('france','France'))) for a in d: print(a) '''#china england france ''' print(d) #{'china':'china','england':'Britain','france':'France'}
Dictionary Add, Delete, Modify
| classification | Method | Explain |
|---|---|---|
| increase | Dictionary [Key]=Value | If a key does not exist, a key-value pair is added; if a key exists, the value of the key-value pair is modified |
| Dictionary.setDefault (key, data) | Key value pair does not exist, add key value pair; exist does not process | |
| delete | del dictionary [key] | Delete the specified key-value pair |
| Dictionary. pop (key) | Returns the deleted value by deleting the specified key-value pair | |
| Dictionary.clear() | Empty Dictionary | |
| modify | Dictionary [Key]=Data | If a key does not exist, a key-value pair is added; if a key exists, the value of the key-value pair is modified |
| Dictionary.update(key=value) | Take out the key-value pair of Dictionary 2, the key-value pair does not exist, add the key-value pair; if it exists, modify the value |
Dictionary traversal
d = {'china':'China','england':'Britain','france':'France'} # View object list nested tuples [(key,value),(key,value)] items = d.items() #items is a list, list elements are tuples, and tuples contain keys and values for key,value in items: print(key,' ',value) '''China //Britain //France''
| function | describe | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| len(item) | Calculate the number of elements in a container | |
| del item | Delete variable | |
| max(item) | Returns the maximum number of elements in a container | Dictionary compares key only |
| min(item) | Returns the minimum value of an element in a container | Dictionary compares key only |
| cmp(item1,item2) | Compare two values, -1 is less than, 0 is equal, and 1 is greater than | python3 cancels this function |
| operator | describe | Supported data types |
|---|---|---|
| + | merge | String, List, Tuple |
| * | repeat | String, List, Tuple |
| in | Existence (judgement key in dictionary) | String, List, Tuple, Collection, Dictionary |
| not in | Does not exist (key in dictionary) | String, List, Tuple, Collection, Dictionary |
| > >= == < <= | compare | String, list, tuple? |
Section
Format: String [Start Index: End Index: Step]
Slice note:
* 1. The specified interval is left closed right open and contains the start index but not the end index
* 2. Step size defaults to 1 and can be omitted
* 3. From the beginning, index numbers can be omitted and colons cannot be omitted
* 4. By the end, you can add directly after the start of the index:
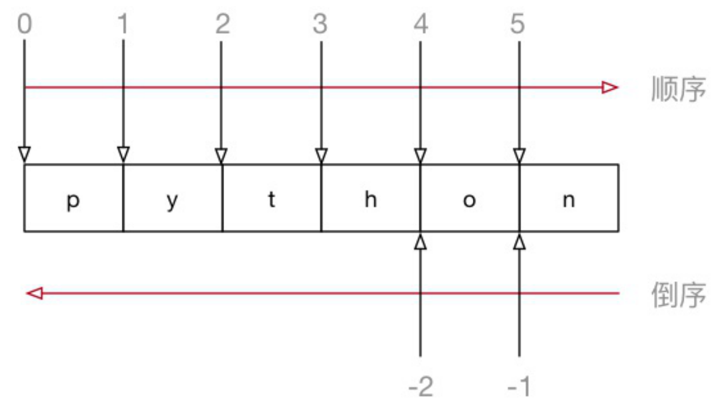
str = "Welcome to the Republic of China" # Print out the first to last two (not included) strings # newStr = str[0:-2:1] # print(newStr) # From the fifth to the first (not included) # newStr = str[-5:-1:1] #Left Close Right Open # print(newStr) # From the fourth to the last (including the last) print(str[-4:10])
Inverse index when step size is negative
str = "Welcome to the Republic of China" # Print out the corner labels 2 to 7 (inclusive) in reverse order # Name Republic of China newStr = str[2:8:-1] #Error, because the 8 is at the beginning # newStr = str[-3:1:-1] # newStr = str[7:1:-1] print(newStr)
List tuple set dictionary derivation
# 2. Create a list of all the even numbers from 1 to 100 # l = [ele for ele in range(1,101) if ele%2==0]
Comprehensive Practice
''' //Requirements: //Determine whether the date entered by the user is a valid date //Users can enter "20170229" //Determine whether it is a valid date, such as "20170229" is not a valid date and "20171345" is not a valid date //Analysis: 1.Enter Date 2.Judge Length 3.Are they all numbers 4.Is the month satisfied:>=1 <=12 5.Date of each month in normal or leap years ''' # Number of days per month for the average year p = [0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31] # Number of days per month for leap years r = [0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31] while True: # 1. Enter date date = input('Please enter a date:') # 2. Judging Length if len(date) != 8: print('Illegal date,Re-enter') continue # 3. Are they all numbers if not date.isdecimal(): print('Date must be all numbers') continue # Specific date year = int(date[:4]) month = int(date[4:6]) day = int(date[6:]) # 4.Month Satisfaction: >=1 <=12 if month<1 or month>12: print('Month not satisfied') continue # Judging whether a normal year is a leap year monthDay = 0 if (year%4==0 and year%100!=0) or year%400==0: monthDay = r[month] else: monthDay = p[month] # 5. Dates are monthly according to the average or leap year if day>monthDay: print('Date not satisfied') continue break print('Date Satisfaction')
Indexes
Dictionaries are key-value pairs to store complex data
eval becomes the original type

