Chain List
II. Introduction of Single Link List
One-way linked list (single linked list) is a kind of linked list. Its characteristic is that the link direction of the linked list is one-way, and the access to the linked list starts from the beginning by sequential reading. Single linked list is a kind of data structure with chain access. It uses a set of storage units with arbitrary addresses to store data elements in a linear table. The data in the linked list is represented by nodes, and each node is composed of elements (mapping of data elements) + pointers (indicating the storage location of successor elements). Elements are storage units for storing data, and pointers are address data connecting each node. Each node contains two domains, one information domain (element domain) and one link domain. This link points to the next node in the list, and the link field of the last node points to an empty value.
Linear tables with chain storage structure will use a set of arbitrary storage units to store data elements in linear tables. Because there is no need for sequential storage, linked list is faster than sequential storage in inserting and deleting data elements, but slower than sequential storage in finding a node. Using chain storage can overcome the disadvantage that sequential linear table needs to know the size of data beforehand. Linked list structure can make full use of memory space and realize flexible dynamic memory management. However, chain storage loses the characteristics of random access to arrays, and increases the pointer domain of nodes, which results in large space overhead.
III. Single List Structure
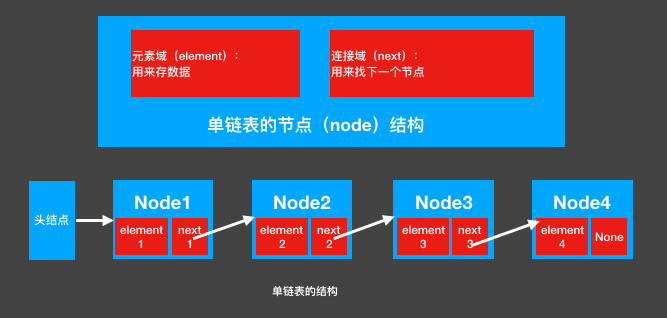
- Table element field elem is used to store specific data.
- The link field next is used to store the location of the next node (the identifier in python)
- The variable p points to the location of the head node of the linked list, from which any node in the table can be found.
4. Graphics of Common Operations of Single-linked Lists
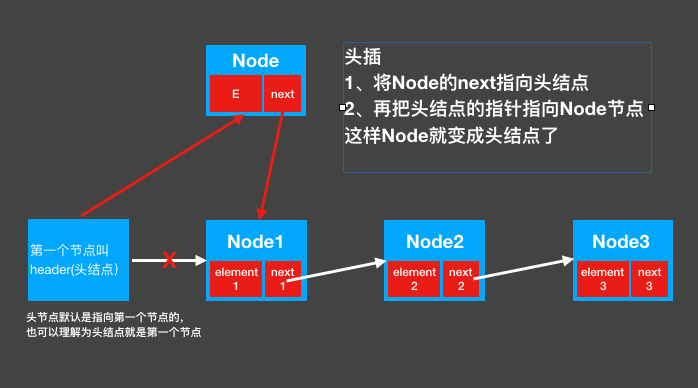
1. Head insertion
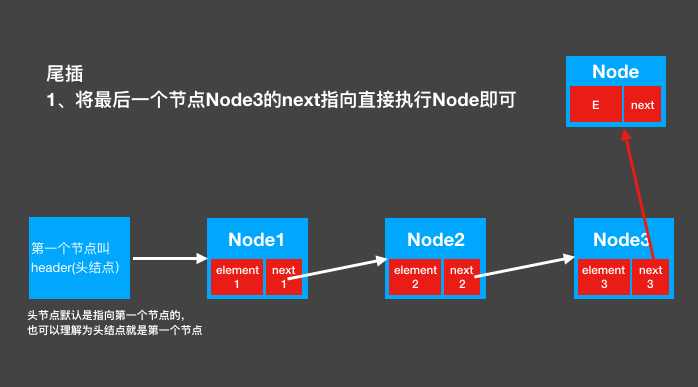
2. Tail insertion
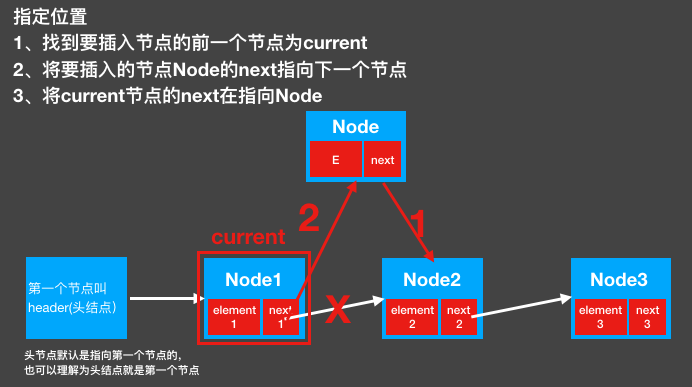
3. Designated insertion
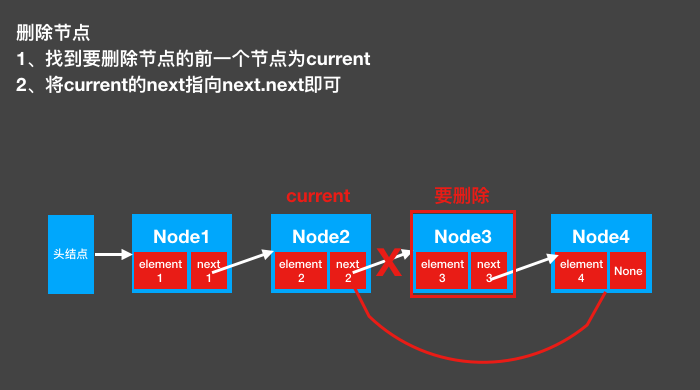
4. Delete
5. Implementation of python code for single linked list
# Create Nodes class Node(object): def __init__(self,item): self.element = item self.next = None # Create a single linked list class class SingleLinkList(object): def __init__(self): self.header = None self.length = 0 # 1,Judge whether it is empty def is_empty(self): if self.header == None: return True else: return False # 2,Head insertion def add(self,node): if self.is_empty(): self.header = node else: node.next = self.header self.header = node # currentNode = self.header self.length += 1 # 3,Tail insertion def appent(self,node): currentNode = self.header if self.is_empty(): self.add(node) else: while (currentNode.next != None): currentNode = currentNode.next currentNode.next = node self.length += 1 # 4,Specified position insertion def insert(self,node,index): currentNode = self.header if index>self.length+1 or index<=0: print("The location you want to insert is not correct. Please reproduce the selected location.") if index == 1: self.add(node) elif index == 2: node.next = self.header.next self.header.next = node self.length += 1 else: for i in range(1,index-1): currentNode = currentNode.next node.next = currentNode.next currentNode.next = node self.length += 1 # 5,ergodic def travel(self): currentNode = self.header if self.length == 0: print("The list you want to traverse has no data\n") else: print("The elements in the list you want to traverse are:",end=" ") for i in range(self.length): print("%s "%currentNode.element,end=" ") currentNode = currentNode.next print("\n") # 6,Sorting does not require swapping node locations, but only swapping data values on nodes. def list_sort(self): for i in range(0,self.length-1): currentNode = self.header for j in range(0,self.length-i-1): if currentNode.element > currentNode.next.element: temp = currentNode.element currentNode.element = currentNode.next.element currentNode.next.element = temp currentNode = currentNode.next # 7,Delete by index def remove(self,index): if index<=0 or index>self.length: print("The subscript you entered is incorrect. Please re-enter it.") return else: if index == 1: self.header = self.header.next currentNode = self.header elif index == 2: currentNode = self.header currentNode.next = currentNode.next.next else: currentNode = self.header for i in range(1,index-1): currentNode = currentNode.next currentNode.next = currentNode.next.next self.length -= 1 # 8,Find if it contains,And return the subscript def isContain(self,num): contain = 0 currentNode = self.header for i in range(self.length): if currentNode.element == num: print("%d In the linked list%d place\n"%(num,i)) contain = 1 currentNode = currentNode.next if contain == 0: print("%d Not in the list\n"%num) # 9,Finding Nodes Based on Subscripts def searchNodeByIndex(self,index): currentNode = self.header if index<=0 or index>self.length: print("The subscript you entered is incorrect. Please re-enter it.\n") return 0 else: for i in range(index-1): currentNode = currentNode.next return currentNode # 10,Modify node values based on Subscripts def modifyByIndex(self,index,num): currentNode = self.header if index<=0 or index>self.length: print("The subscript you entered is incorrect. Please re-enter it.\n") else: for i in range(index-1): currentNode = currentNode.next currentNode.element = num def main(): # Create a node object node1 = Node(1) # Create a single linked list object single_link_list = SingleLinkList() print("Verify traversal of empty linked list") single_link_list.travel() print("Verification header insertion") single_link_list.add(node1) single_link_list.travel() print("Verification tail insertion") node2 = Node(2) single_link_list.appent(node2) single_link_list.travel() print("Verify insertion by location") node3 = Node(3) single_link_list.insert(node3,1) single_link_list.travel() print("Continue validating header inserts") node4 = Node(5) single_link_list.add(node4) single_link_list.travel() print("Continue validating insertion by location") node5 = Node(4) single_link_list.insert(node5,4) single_link_list.travel() print("Verify deletion") single_link_list.remove(3) single_link_list.travel() print("Verify that a node is in the linked list") single_link_list.isContain(8) print("Verify that subscript-press lookup node") node = single_link_list.searchNodeByIndex(2) print("The value of the second node is:%s"%node.element) print("\n Validation sort") single_link_list.list_sort() single_link_list.travel() print("Verification modification") single_link_list.modifyByIndex(2,10) single_link_list.travel() if __name__ == '__main__': main()
The results are as follows:
Verify traversal of empty linked list The list you want to traverse has no data Verification header insertion The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 1 Verification tail insertion The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 1 2 Verify insertion by location The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 312 Continue validating header inserts The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 5312 Continue validating insertion by location The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 531 422 Verify deletion The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 5342 Verify that a node is in the linked list 8 is not on the list Verify that subscript-press lookup node The value of the second node is: 3 Validation sort The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 234 5 Verification modification The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 2104 5
6. C Language Code Implementation of Single Linked List
#include <stdio.h> typedef struct N { int element; struct N *next; }Node; // 1,Create Nodes Node *createNode(int num) { Node *node; node = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node)); node->element = num; node->next = NULL; return node; } // 2,Create a linked list Node *createSingleLinkList(Node *node) { Node *head = node; return head; } // 3,Get the length of the linked list int getlength(Node *head) { if (head == NULL) { return 0; } int count = 1; Node *current = head; while (current->next != NULL) { count++; current = current->next; } return count; } // 4,Head insertion Node * add(Node *head, Node *node) { if(head == NULL) { head = node; return head; } else { node->next = head; head = node; return head; } } // 5,Tail insertion Node * append(Node *head,Node *node) { Node *current = head; if (current->next == NULL) { add(head, node); } else { int len = getlength(head); for (int i = 0; i<len-1; i++) { current = current->next; } current->next = node; } return head; } // 6,Insert node by subscript Node * insert(Node *head,Node *node,int index) { int len = getlength(head); if (index<=0||index>len+1) { printf("The location you want to insert is not correct. Please reproduce the selected location."); } Node *current = head; if (index == 1) { head = add(head, node); } else if (index == 2) { node->next = head->next; head->next = node; } else { for (int i = 1; i<index-1; i++) { current = current->next; } node->next = current->next; current->next = node; } return head; } // 7,ergodic void travel(Node *head) { int len = getlength(head); printf("len = %d\n",len); Node *current = head; if (len == 0) { printf("The list you want to traverse has no data\n"); } else { printf("The elements in the list you want to traverse are: "); for (int i = 0; i<len; i++) { printf("%d ",current->element); current = current->next; } printf("\n"); } } // 8,Delete by index Node * delect(Node *head,int index) { int len = getlength(head); if (index<=0||index>len) { printf("The subscript you entered is incorrect. Please re-enter it."); return head; } else { if (index == 1) { head = head->next; } else if (index == 2) { head->next = head->next->next; } else { Node *current = head; for (int i = 1; i<index-1; i++) { current = current->next; } current->next = current->next->next; } } return head; } // 9,Find if it contains and return the subscript void isContain(Node *head,int num) { int contain = 0; Node *current = head; int len = getlength(head); for (int i = 0; i<len; i++) { if (current->element == num) { printf("%d In the linked list%d place\n",num,i+1); contain = 1; } current = current->next; } if (contain == 0) { printf("%d Not in the list\n",num); } } // 10,Finding Nodes Based on Subscripts Node *searchByIndex(Node *head , int index) { int len = getlength(head); Node *current = head; if (index<=0||index>len) { printf("The subscript you entered is incorrect. Please re-enter it."); return head; } else { for (int i = 0; i<index-1; i++) { current = current->next; } return current; } } // 11,Modify node values based on Subscripts void modifyByIndex(Node *head,int index,int num) { int len = getlength(head); Node *current = head; if (index<=0||index>len) { printf("The subscript you entered is incorrect. Please re-enter it."); } else { for (int i = 0; i<index-1; i++) { current = current->next; } current->element = num; } } int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { printf("==========1,Create Nodes==========\n"); Node * node1 = createNode(1); printf("==========2,Create a single linked list==========\n"); Node * head = createSingleLinkList(node1); travel(head); printf("==========3,Verification header insertion==========\n"); Node *node2 = createNode(0); head = add(head, node2); travel(head); Node *node3 = createNode(2); head = add(head, node3); travel(head); printf("==========4,Verification tail insertion==========\n"); Node *node4 = createNode(4); head = append(head,node4); travel(head); Node *node5 = createNode(5); head = append(head,node5); travel(head); printf("==========5,Verify subscript insertion==========\n"); Node *node6 = createNode(6); head = insert(head, node6, 1); travel(head); printf("==========6,Verify subscript deletion==========\n"); head = delect(head, 2); travel(head); printf("==========7,Verify that it contains==========\n"); isContain(head, 8); printf("==========8,Verify finding nodes based on Subscripts==========\n"); Node *n = searchByIndex(head, 1); printf("The first node is%d\n",n->element); printf("==========9,Verify modifications based on Subscripts==========\n"); modifyByIndex(head, 3, 9); travel(head); return 0; }
The results are as follows:
========== 1. Creating Nodes========== ========== 2. Creating a single linked list========== len = 1 The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 1 ========== 3. Verification Header Interpolation========== len = 2 The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 0.1 len = 3 The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 201 ========== 4. Verify tail insertion========== len = 4 The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 2014 len = 5 The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 201 445 ========== 5. Verify insertion by subscript========== len = 6 The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 620 145 ========== 6. Verify deletion by subscript========== len = 5 The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 601 445 ========== 7. Verify whether it contains========== 8 is not on the list ========== 8. Verify Finding Nodes Based on Subscripts========== The first node is 6 ========== 9. Verify modification according to subscription========== len = 5 The elements in the list you want to traverse are: 609 445
Write here to vomit blood, I believe you will see vomiting blood!!!!