I hope to take notes to record what I have learned, and I hope it can help the same beginner. I also hope that the big guys can help correct the error ~ infringement legislation and deletion.
catalogue
1, Concepts of bidirectional linked list and bidirectional circular linked list
2, Implementation of bidirectional linked list
2. Initial definition of linked list object
3. Determine whether the linked list is empty
7. Insert node at specified location
8. Deletes the node at the specified location
9. Find the node with the data
10. Traverse and output the whole linked list
11. Create linked list with input data
3, Implementation of bidirectional circular linked list
2. Initial definition of linked list object
3. Determine whether the linked list is empty
7. Insert node at specified location
8. Deletes the node at the specified location
9. Find the node with the data
10. Traverse and output the whole linked list
11. Create linked list with input data
1, Concepts of bidirectional linked list and bidirectional circular linked list
The two-way linked list has more precursors on the basis of the one-way linked list. Any node in the two-way linked list can easily access its predecessor nodes and successor nodes, which is more flexible.

The difference between bidirectional circular linked list and unidirectional circular linked list is the same as that between bidirectional linked list and unidirectional linked list.
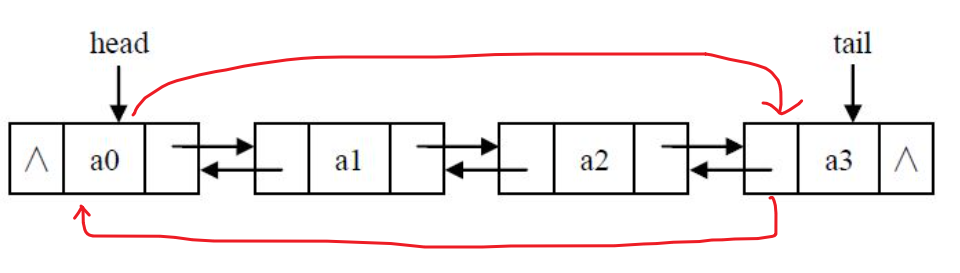
2, Implementation of bidirectional linked list
1. Create node object
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.data = data #Value range of node
self.next = None #Connect to the next node and point to null temporarily
self.pre = None #Connect to the previous node and point to null temporarily2. Initial definition of linked list object
class linkList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None #First, create a chain header and point to null temporarily3. Determine whether the linked list is empty
def isEmpty(self):
if self.head:
return False
else:
return True4. Get linked list length
def length(self):
if self.isEmpty():
return 0
else:
t = self.head
n = 1
while t.next:
t = t.next
n = n + 1
return n5. Add node to header
def addhead(self,data):
node = Node(data) #Create a new node
if self.isEmpty():
self.head = node #Reset the header of the linked list
else:
node.next = self.head #The new node is connected to the original linked list
self.head.pre = node #In front of the original head is node
self.head = node #Reset the header of the linked list6. Add node to tail
def addtail(self,data):
node = Node(data) #Create a new node
#First judge whether the linked list is empty
if self.isEmpty():
self.addhead(data)
else:
t = self.head
while t.next: #Find tail by loop
t = t.next
t.next = node #Tail connection
node.pre = t7. Insert node at specified location
def insert(self,data,index):
if index == 0 or self.isEmpty():
self.addhead(data)
elif index >= self.length():
self.addtail(data)
else:
node = Node(data)
t = self.head
n = 1
while n < index - 1:
t = t.next
n = n + 1
a = t.next
t.next = node
node.pre = t
node.next = a
a.pre = node8. Deletes the node at the specified location
def delete(self,index):
if self.isEmpty():
print("The linked list is empty")
else:
t = self.head
if index == 0:
self.head = t.next
elif index == self.length() - 1:
n = 1
while n < self.length() - 1:
t = t.next
n = n + 1
t.next = None
elif index > self.length() - 1:
print("Out of range")
elif index < 0:
print("Wrong operation")
else:
n = 1
while n < index - 1:
t = t.next
n = n + 1
a = t.next.next
t.next = a
a.pre = t9. Find the node with the data
def search(self,data):
t = self.head
n = 1
while t.next:
if t.data == data:
print(str(n) + " ")
t = t.next
n = n + 1
if (t.data == data):
print(str(n) + " ")10. Traverse and output the whole linked list
def ergodic(self):
if self.isEmpty():
print(None)
else:
t = self.head
while t.next:
print(t.data)
t = t.next
print(t.data) #Don't miss it here11. Create linked list with input data
#Create linked list with input data
def form(self,datalist):
self.addhead(datalist[0])
for i in range(1,len(datalist)):
self.addtail(datalist[i])
t = self.head
while t.next:
print(t.data)
t = t.next
print(t.data)12. Specific call
data = input("input(Bounded by spaces):")
data = data.split(" ")
datalist = []
for i in range(len(data)):
datalist.append(int(data[i]))
linkList = linkList()
linkList.form(datalist) #Create linked list
addlist = linkList.addhead(5) #Join at header node
linkList.ergodic() #Traversal output
addlist = linkList.addtail(5) #Join at tail node
linkList.ergodic() #Traversal output
linkList.search(5) #Find out if there is a node of "5"
linkList.delete(4) #Delete the 4th + 1st data
linkList.ergodic() #Traversal output
print(linkList.length()) #Output linked list length
linkList.insert(89,2) #Insert data at the specified location
linkList.ergodic() #Traversal output 3, Implementation of bidirectional circular linked list
1. Create node object
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.data = data #Value range of node
self.next = None #Connect to the next node and point to null temporarily
self.pre = None #Connect to the previous node and point to null temporarily2. Initial definition of linked list object
class linkList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None #First, create a chain header and point to null temporarily
self.tail = None3. Determine whether the linked list is empty
def isEmpty(self):
if self.head:
return False
else:
return True4. Get linked list length
def length(self):
if self.isEmpty():
return 0
else:
t = self.head
n = 1
while t.next:
if t.next == self.head:
break
t = t.next
n = n + 1
return n5. Add node to header
def addhead(self,data):
node = Node(data) #Create a new node
if self.isEmpty():
self.head = node #Reset the header of the linked list
self.tail = self.head
else:
node.next = self.head #The new node is connected to the original linked list
self.head.pre = node #Precursor connection of the original head node
self.head = node #Reset the header of the linked list
self.tail.next = self.head
self.head.pre = self.tail6. Add node to tail
def addtail(self,data):
node = Node(data) #Create a new node
#First judge whether the linked list is empty
if self.isEmpty():
self.addhead(data)
else:
t = self.head
n = 1
l = self.length()
while n < l: #Find tail by loop
n = n + 1
t = t.next
t.next = node #Tail connection
node.pre = t
node.next = self.head
self.head.pre = node
self.tail = node7. Insert node at specified location
def insert(self,data,index):
l = self.length()
if index == 0 or self.isEmpty():
self.addhead(data)
elif index >= l:
self.addtail(data)
else:
node = Node(data)
t = self.head
n = 1
while n < index - 1:
t = t.next
n = n + 1
a = t.next
t.next = node
node.pre = t
node.next = a
a.pre = node8. Deletes the node at the specified location
def delete(self,index):
if self.isEmpty():
print("The linked list is empty")
else:
t = self.head
l = self.length()
if index == 0:
self.head = t.next
self.tail.next = self.head
self.head.pre = self.tail
elif index == l - 1:
n = 1
while n < l - 1:
t = t.next
n = n + 1
t.next = self.head
self.head.pre = t
self.tail = t
elif index > l - 1:
print("Out of range")
elif index < 0:
print("Wrong operation")
else:
n = 1
while n < index - 1:
t = t.next
n = n + 1
a = t.next.next
t.next = a
a.pre = t9. Find the node with the data
def search(self,data):
t = self.head
n = 0
l = self.length()
while n < l:
if t.data == data:
print(str(n) + " ")
t = t.next
n = n + 110. Traverse and output the whole linked list
def ergodic(self):
if self.isEmpty():
print(None)
else:
t = self.head
n = 0
l = self.length()
while n < l:
print(t.data)
t = t.next
n = n + 111. Create linked list with input data
def form(self,datalist):
self.addhead(datalist[0])
for i in range(1,len(datalist)):
self.addtail(datalist[i])
t = self.head
while t.next != self.head:
print(t.data)
t = t.next
print(t.data)12. Specific call
data = input("input(Bounded by spaces):")
data = data.split(" ")
datalist = []
for i in range(len(data)):
datalist.append(int(data[i]))
linkList = linkList()
linkList.form(datalist) #Create linked list
print(linkList.length()) #Output linked list length
addlist = linkList.addhead(5) #Join at header node
linkList.ergodic() #Traversal output
addlist = linkList.addtail(5) #Join at tail node
linkList.ergodic() #Traversal output
linkList.search(5) #Find out if there is a node of "5"
linkList.delete(4) #Delete the 5th data
linkList.ergodic() #Traversal output
linkList.insert(89,2) #Insert data at the specified location
linkList.ergodic() #Traversal output Welcome to criticize and correct in the comment area, thank you~