Django Foundation
Django
Django is a tripartite Library of python and a web framework (product-level, MTV model) for building a web backend.
Create a project
django-admin startproject myweb
Create an application
python.exe .\manage.py startapp helloapp
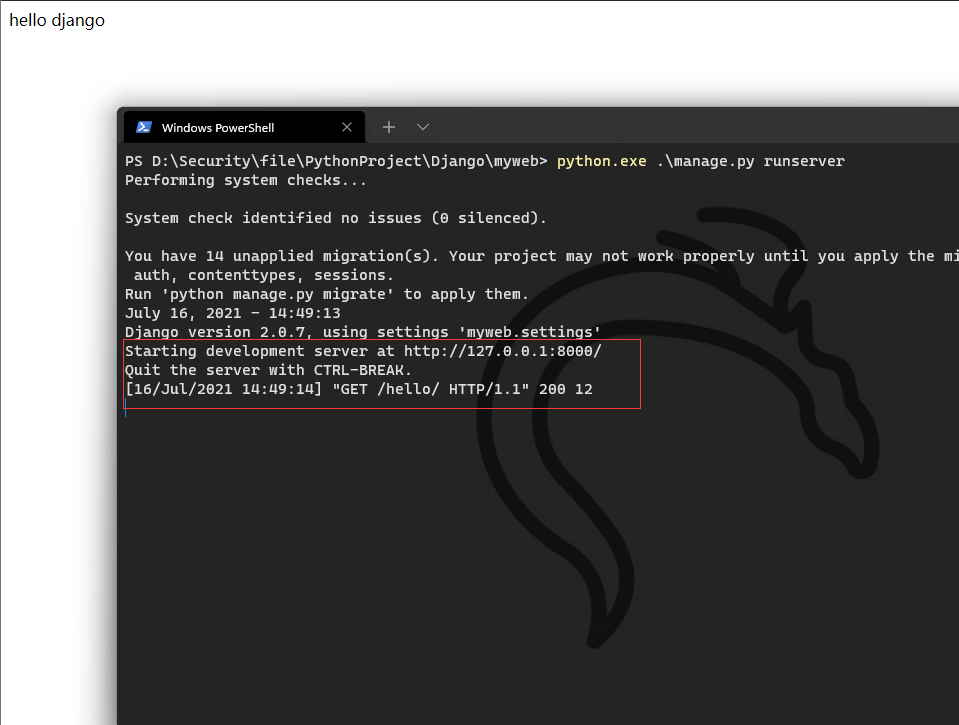
Run the project
python.exe .\manage.py runserver
Create a web framework project
django-admin startproject myweb
Frame directory structure
D:.
└─myweb --Outer Catalog
│ manage.py --django Project Interactive Command Tool
│
└─myweb --Project Directory
settings.py --Deployment and Configuration Profiles
urls.py --There is a table in it. URL Route Declaration File
wsgi.py --Be based on WSGI Of web Server Profile
__init__.py --Empty file defining package
About WSGI web Services Gateway Interface
https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-3333/
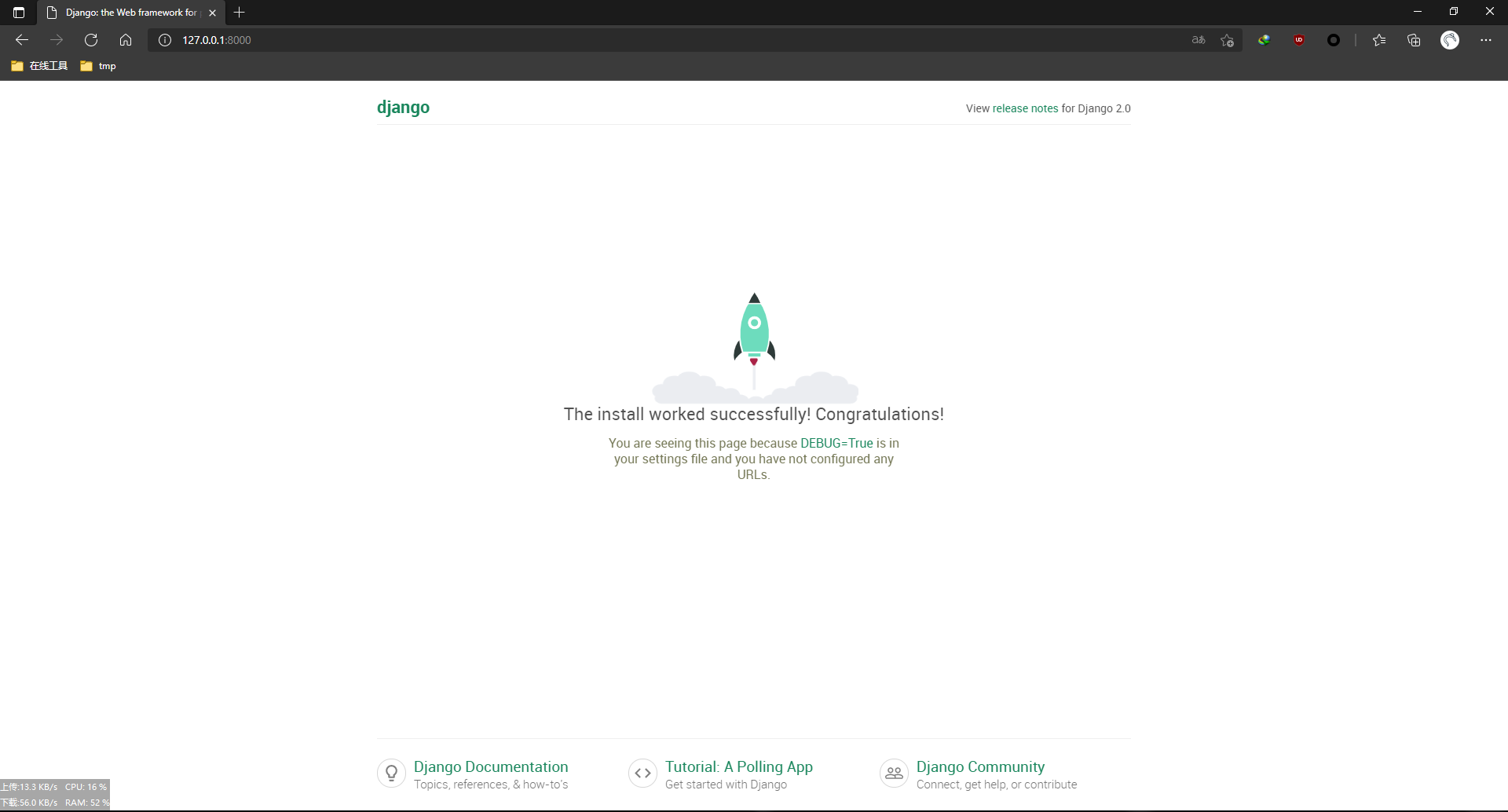
Debug Run web Framework
python.exe .\manage.py runserver
Create a specific application
python.exe .\manage.py startapp helloapp
url routing
views usually write code to handle http requests
Edit views.py file
from django.http import HttpResponse
# Create your views here.
def hello(request):
return HttpResponse("hello django")
Modify routing file to add routing information
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from helloapp.views import hello
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('hello/', hello),
]
Routing Subtable
The main route table is under the project, while the secondary route table is generally created by the developer. The main route table represents the route of the current project, and the secondary route table is generally the route of the current project.
Assume there is a connection
In addition to writing them all in the master routing table, we can separate the routing table relationship between the project and the application to make the site structure clearer.
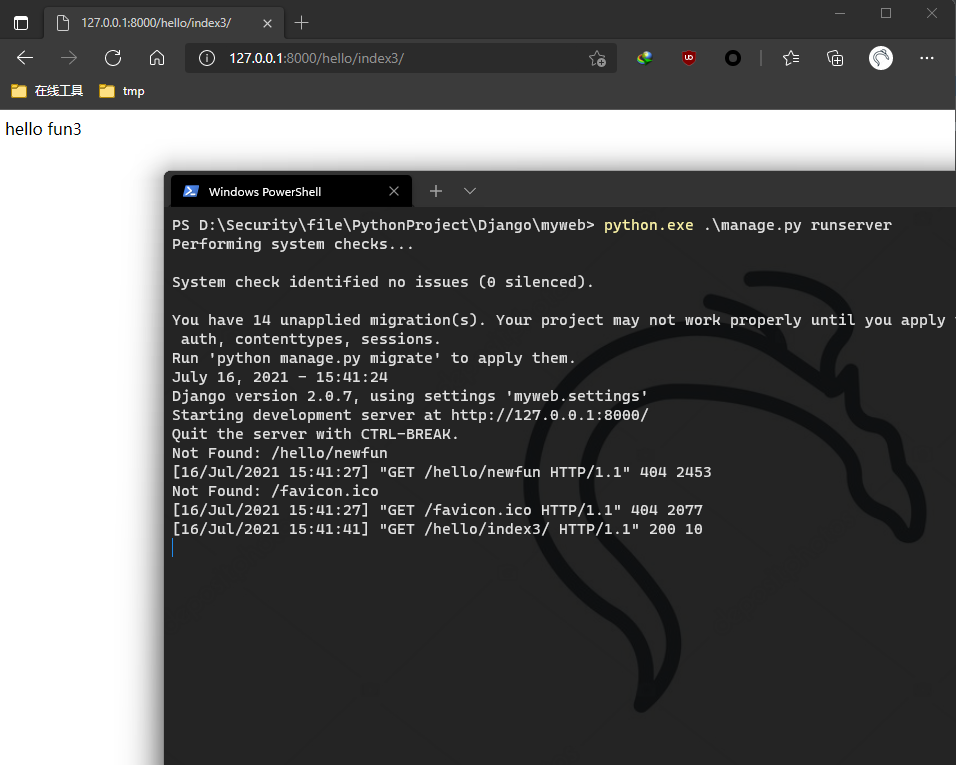
hello can be written in the primary routing table and index in the secondary routing table
http://127.0.0.1:8000/hello/index/
Primary Routing Table
Modify master routing table
Introduce include
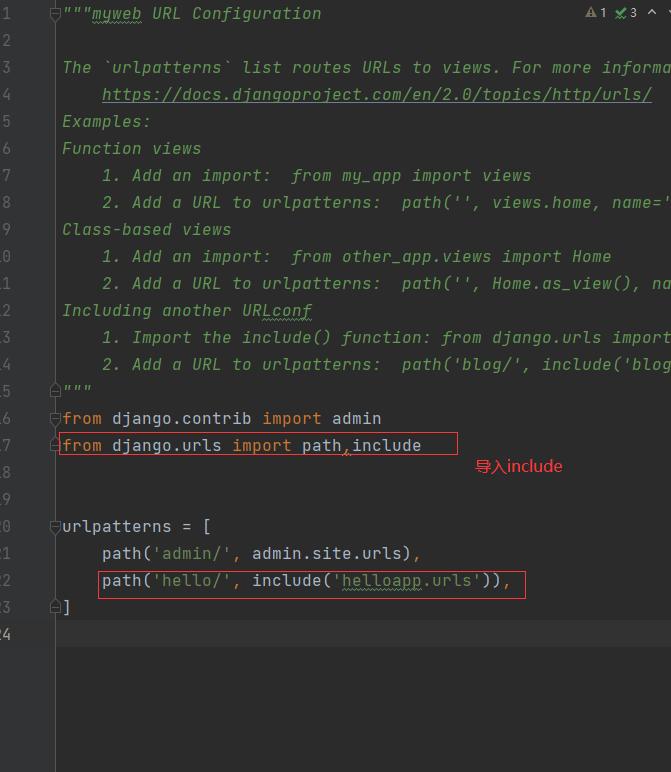
The following path('hello/', include('helloapp.urls')) indicates that whenever accessed by this path in hello, the routing information in the secondary routing table is used
Secondary Routing Table
Add a new routing file under the application file
urls.py
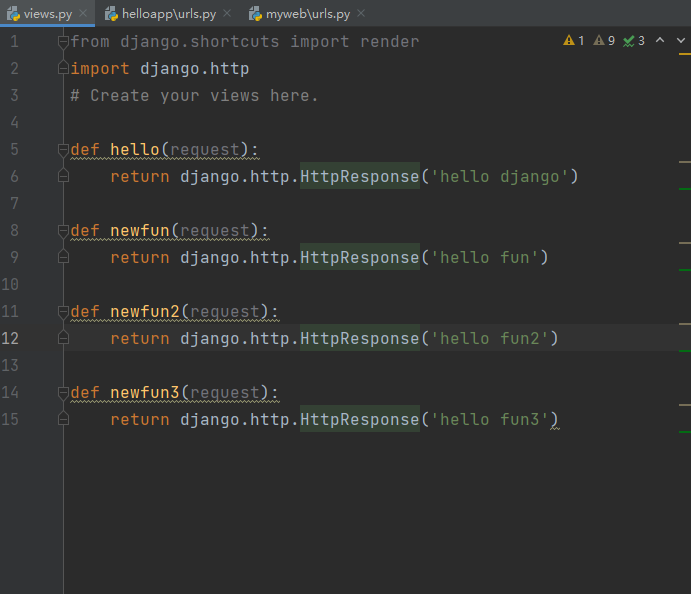
Write down the information in this routing table and access index is handled by newfun
from django.urls import path
from helloapp.views import newfun,newfun2,newfun3
urlpatterns = [
path('index/', newfun),
path('index2/',newfun2),
path('index3/',newfun3),
]
Django operates on sqlite databases
sqlite does not have a stand-alone database service process, and data operations are invoked as libraries by direct providers. Django can be used directly without having to set up a data service first.
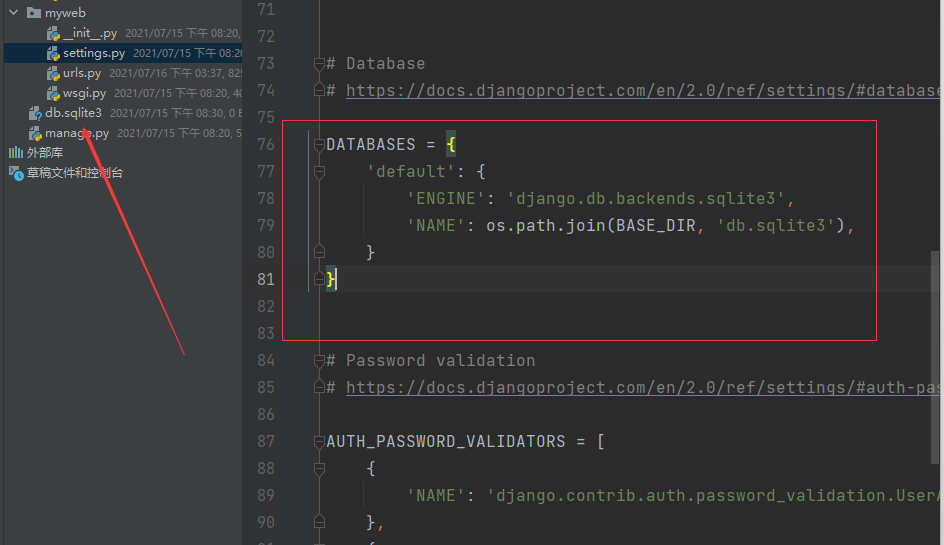
The project creates a dB when it is created. SQLite3 file, this is an empty file, we need to create the related library tables by ourselves
python manage.py migrate
Connect through database tools
ORM (object relational mapping) concept
In django, database operations are essentially done through objects of type Model, which do not use sql statements but use class methods.
Define database tables
Definition of database tables, generally models applied. Inside PY
Refer to the official documentation for field types:
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/ref/models/fields/#model-field-types
models.py
Write Fields
from django.db import models # Create your models here. from django.db import models from django.contrib import admin # Create your models here. class Customer(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=200) phone = models.CharField(max_length=200) address = models.CharField(max_length=200) admin.site.register(Customer) # Add to django admin management
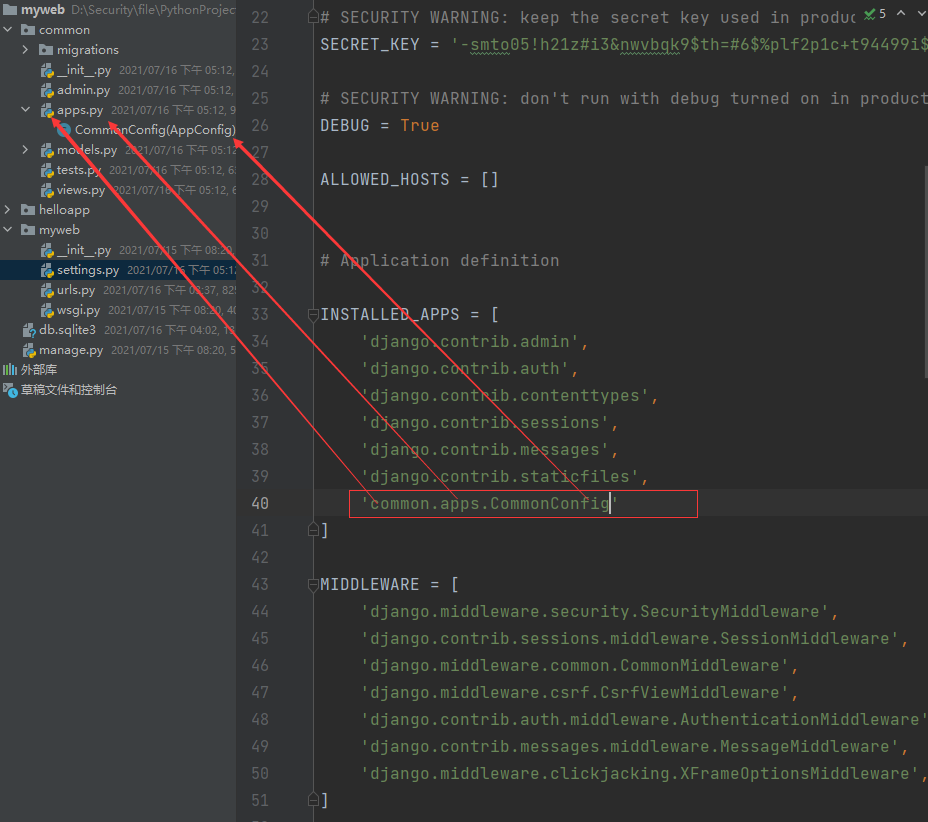
Adding configurations to the project's configuration file means we have such an application
settings.py
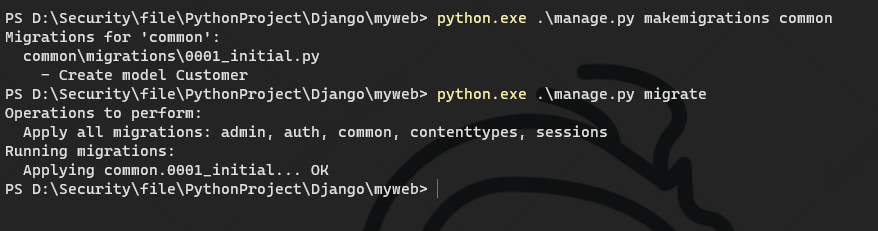
Then execute
python.exe .\manage.py makemigrations common
Migration\0001_under Generation Application Initial. Py file
python.exe .\manage.py migrate
Write to database
Each table under django needs to have a primary key. If not configured, django automatically generates a primary key as id
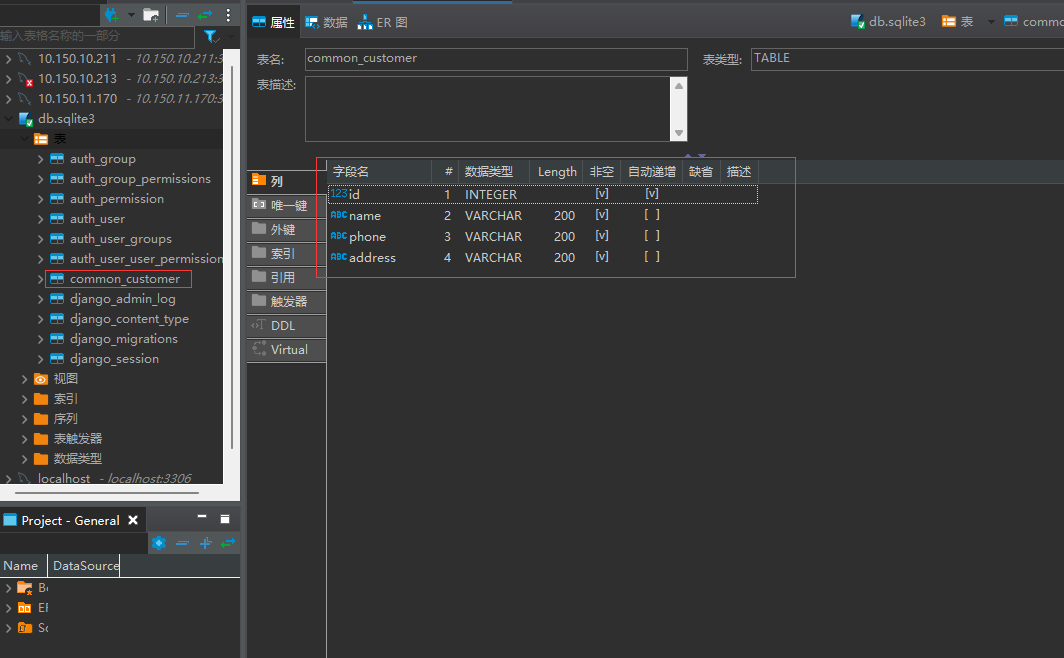
If you modify the generated table file, you need to rerun makemigrations and import the database migrate
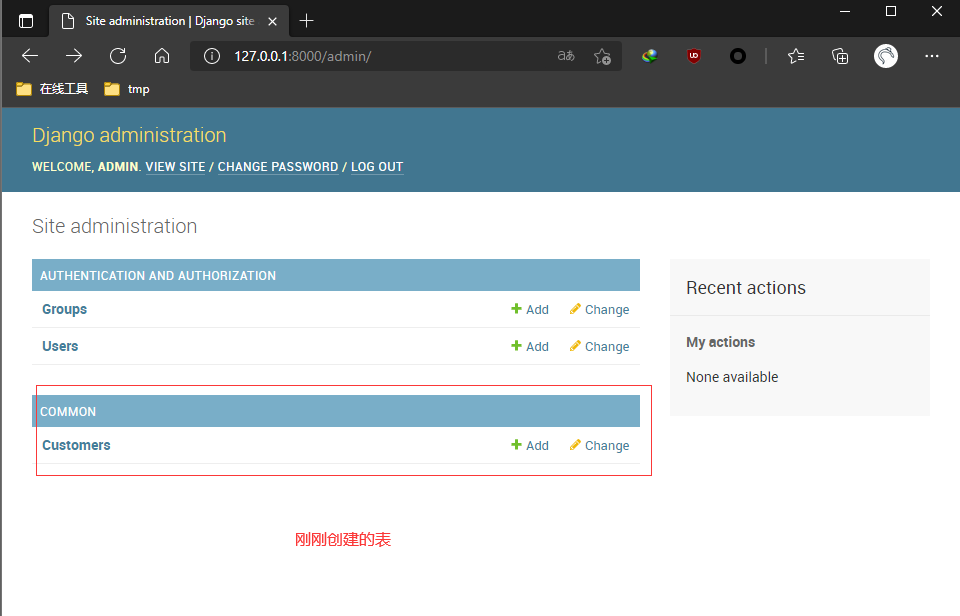
Django Admin Manages Data
Create users through createsuperuser
python.exe .\manage.py createsuperuser
Log in through django's default admin page
If admin configuration management is not introduced when creating tables
admin.site.register(Customer)
The admin in the application table is required. Py configuration management
from django.contrib import admin from .models import Customer admin.site.register(Customer)