Summary of Myqsl knowledge points
1, Database related concepts
- DB: a database that holds a set of organized data containers
- DBMS: database management system, also known as database software (product), is used to manage data in DB
- sql structured query language is a language used to communicate with DBS
2, mysql common commands
1. View all current databases
show databases;
2. Open the specified library
use Library name
3. View all tables in the current library
show tables;
4. View all tables of other libraries
show tables from Library name;
5. Create table
create table Table name(
Column name, column type,
Column name column type
...
);
6. View table structure
desc Table name;
7. View server version
Method 1: log in to the mysql server
select version();
Method 2: no login to mysql server
mysql –version mysql -V
Syntax specification of mysql
1. It is not case sensitive, but it is recommended that keywords be capitalized, table names and column names be lowercase
2. Each command ends with a semicolon (sometimes \ g)
3. Each command can be indented or wrapped as needed
4. Notes
Single line notes: # note text
Single line comment: - comment (– must be followed by a space)
Multiline notes: / note text/
Advanced 1: basic query
Syntax:
select Query list from Table name;
characteristic:
- The query list can be fields, constant values, expressions and functions in the table
- The query result is a virtual table
1. Single field in query table
SELECT last_name FROM employees;
2. Query multiple fields in the table
SELECT last_name,salary,email FROM employees;
3. Query all fields in the table
SELECT * FROM surface; (Order is the order in the table)
be careful:
1. use the library before operation
2. The emphasis sign ` ` can easily identify the field
4. Query constant value
SELECT 100; SELECT 'john'
5. Query expression
SELECT 100*98;
Note: character type and date type must use single quotation marks
6. Query function
SELECT VERSION();
7. Alias
#Mode 1 (use as)
SELECT 100%98 AS result; SELECT last_name AS surname,first_name AS name FROM employees;
#Mode 2 (use space)
SELECT first_name surname,last_name name FROM employees;Benefits:
1. Easy to understand
2. If the fields queried have duplicate names, alias can be used to distinguish them
Case: query salary, and the display result is out put
SELECT salary AS "out put" FROM employees;
Note: at this time, there is a space between out and put. It is recommended to add double quotation marks
8. De duplication (add DISTINCT before the field)
All department numbers involved in the case query employee table
SELECT DISTINCT department_id FROM employees;
9. + function
/*operator
For example, select 100+90 (the two operands are numeric and add)
select '123'+90 (One of them is character type, trying to convert character type to numeric type
If the conversion is successful, continue to add
select 'john'+90 If the conversion fails, the character type is converted to 0
select null+0 As long as one party is null, the result must be null
*/
concat splicing
Case: query the employee's first name and last name, connect them into a field, and display them as names
SELECT CONCAT('a','b','c') AS result;
SELECT
CONCAT(last_name,first_name) AS full name
FROM
employees ;
supplement
ifnull: determines whether the field or expression is null. If it is null, the specified value is returned
select ifnull (commission_pct,0 ) from employees;
isnull: determines whether a field or expression is null, returns 1 if yes, and returns 0 if No
case
Display the structure of departments and query all the data in it
DESC departments; SELECT * FROM departments;
Show all jobs in employees_ ID (cannot be repeated)
SELECT DISTINCT job_id FROM employees;
All columns of the employee table are displayed. The columns are comma linked, and the column header is displayed as out_put
SELECT IFNULL(commission_pct, 0) AS Bonus rate, commission_pct FROM employees ; SELECT CONCAT(`first_name`,',',`last_name`,',',`job_id`,',',IFNULL(commission_pct, 0)) AS out_put FROM employees;
Advanced 2: condition query
Syntax:
select
Query list
from
Table name
where
Screening conditions
classification
- Filter condition operators by condition expression: < > = < > =<=
- Filter logical operators by logical expression: & & |! and or not
- like between and in is null
1, Filter by conditional expression
Case 1: query employee information with salary greater than 12000
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary>12000;
Case 2: query the employee name and department number whose department number is not equal to 90
SELECT last_name,department_id FROM employees WHERE department_id<>90;
2, Filter by logical expression
Case 1: query employee name, salary and bonus with salary between 10000 and 20000
SELECT last_name,salary,commission_pct FROM employees WHERE salary>=10000 AND salary<=20000;
Case 2: query the information of employees whose department number is not between 90 – 110 or whose salary is higher than 15000
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE NOT(department_id>=90 AND department_id<=110) OR salary>15000;
Three. Fuzzy query
like features:
1. Generally used with wildcards
wildcard
%Any number of characters
_ Any single character
1.like
Case 1: query the employee information of a contained in the employee name
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE last_name LIKE '%a%';
Case 2. Query the employee name and salary with the third character n and the fifth character l in the employee name
SELECT last_name,salary FROM employees WHERE last_name LIKE '__n_l%';
Case 3. The second character in the employee name is_ Employee name
SELECT last_name FROM employees WHERE last_name LIKE '_\_%'
#(’_KaTeX parse error: Expected group after '_' at position 1: _ ̲%' ESCAPE '' (i.e. any character can be used to express ESCAPE)
2.between and
/*
1. Using between and can improve statement conciseness
2. Including critical values
3. Do not change the order of the two critical values
*/
Case 1: query employee information with employee number between 100-120
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE employee_id BETWEEN 100 AND 120;
3.in
Meaning: judge whether the value of a field belongs to an item in the in list
characteristic
1. Use in to improve sentence conciseness
2. The value types of in list must be consistent or compatible
Case 1: query whether the employee's work type number is it_ PROG,AD_ VP,AD_ Employee name and job number of one in Pres
SELECT last_name,job_id
FROM employees
WHERE job_id IN ('IT_PROG','AD_VP','AD_PRES');
4.is null
=Or < > cannot be used to determine null values
is null or is not null determines the null value
Case 1: query employee name and bonus rate without bonus
SELECT last_name,commission_pct FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NULL; #Bonus SELECT last_name,commission_pct FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NOT NULL;
#is null PK <=>
IS NULL: only the null value can be judged, with high readability. It is recommended to use this
< = >: it can judge both null value and ordinary value, with low readability
Case:
1. Query the employee's name, department number and annual salary with employee number 176
SELECT last_name,department_id,salary*12*(IFNULL(1+commission_pct,0)) AS Annual salary FROM employees;
2. Query salary, last with no bonus and salary less than 18000_ name
SELECT salary,last_name FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NULL AND salary<18000;
3. Query the employees table, job_ Employee information whose ID is not 'IT' or salary is 12000
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE job_id<>'IT' OR salary=12000;
4. View the department table structure. The query results are as follows:
DESC departments;
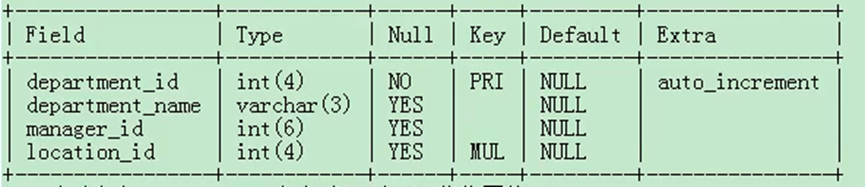
5. Query which position numbers are involved in the Department departments table
SELECT DISTINCT location_id FROM departments;

Advanced 3: sort query
Syntax:
select Query list from surface [where Screening conditions] order by Sort list [asc|desc]
characteristic:
1. asc ascending desc descending is ascending by default
2. Single field, multiple fields, expressions, functions and aliases can be supported in the order by clause
3. The order by clause is usually placed at the end of the query statement, except the limit clause (last)
Case 1: querying employee information requires that wages be sorted from high to low
SELECT * FROM employees ORDER BY salary DESC; SELECT * FROM employees ORDER BY salary ASC;
Case 2: query employee information with department No. > = 90, sort by employment time [add filter criteria]
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE department_id>=90 ORDER BY hiredate ASC;
Case 3: display employee information by annual salary level, annual salary [sort by expression]
SELECT *,salary*12*(1+IFNULL(commission_pct,0)) Annual salary FROM employees ORDER BY salary*12*(1+IFNULL(commission_pct,0)) DESC;
Case 4: display employee information by annual salary level, annual salary [sort by alias]
SELECT *,salary*12*(1+IFNULL(commission_pct,0)) Annual salary FROM employees ORDER BY Annual salary DESC;
Case 5: display employee name by name length, salary [sort by function]
SELECT LENGTH('last_name') Byte length,last_name,salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY LENGTH('last_name') DESC;
Case 6: when querying employee information, it is required to first increase the salary and then decrease the employee number
SELECT * FROM employees ORDER BY salary ASC,employee_id DESC;
Case synthesis:
1. Query employee name, department number and annual salary, in descending order of annual salary and ascending order of name
SELECT last_name,department_id,salary*12*(1+IFNULL(commission_pct,0)) Annual salary FROM employees ORDER BY Annual salary DESC,last_name ASC;
2. Select the name and salary of employees whose salary is not 8000-17000, in descending order of salary
SELECT last_name,salary FROM employees WHERE salary NOT BETWEEN 8000 AND 17000 ORDER BY salary DESC;
3. Query the employee information contained e in the mailbox, in descending order according to the number of bytes in the mailbox, and then in ascending order according to the department number
SELECT *,LENGTH(email) FROM employees WHERE email LIKE '%e%' ORDER BY LENGTH(email) DESC,department_id ASC;
Advanced 4: common functions
Function: similar to methods in java, encapsulate a group of logical statements in the method body and expose the method name
Benefits: 1. Hiding implementation details 2. Improving code reusability
Call: select function name (argument list) [from table];
characteristic:
1. What is it called (function name)
2. What to do (function)
Classification:
1. Single line function
Such as concat, length, ifnull, etc
2. Grouping function
Function: used for statistics, also known as statistical function, aggregate function and group function
1, Character function
1.length (number of bytes to obtain parameter value)
SELECT LENGTH('john');
SELECT LENGTH('Zhang Sanfeng hahaha');
2.concat (concatenated string)
SELECT CONCAT(last_name,'_',first_name) full name FROM employees;
3.upper lower
SELECT UPPER('john');
SELECT LOWER('JoHn');
Example: change the last name to uppercase, the first name to lowercase, and then splice
SELECT CONCAT(UPPER(last_name),LOWER(first_name)) full name FROM employees;
4.substr substring (intercepted character)
#Note: the index starts at 1
#Intercepts all characters from the specified index
SELECT SUBSTR('li Mochou falls in love with Lu Zhanyuan ', 7) put_put;
#Intercepts the specified character length from the specified index
SELECT SUBSTR('li Mochou falls in love with Lu Zhanyuan ', 1,3) put_put;
#Case: the first letter of the name is uppercase, the other characters are lowercase, and then_ Splicing
SELECT CONCAT(UPPER(SUBSTR(last_name,1,1)),'_',LOWER(SUBSTR(last_name,2))) out_put
FROM employees;
5.instr returns the index of the first occurrence of the substring. If it is not found, it returns 0
SELECT INSTR('Yang Bu regretted falling in love with Yin Liuxia','Yin Liuxia') AS out_put;
6.trim remove the front and back spaces
SELECT LENGTH(TRIM(' Zhang Cuishan ')) AS out_put;
SELECT TRIM('a' FROM 'aaaaa Zhang aa Emerald aa mountain aaa') AS out_put;
7.lpad realizes left padding with specified characters
SELECT LPAD('Yin Su Su','10','*') AS out_put;
8.rpad realizes right padding with the specified characters
SELECT RPAD('Yin Su Su','10','*') AS out_put;
9.replace
SELECT REPLACE('Zhang Wuji fell in love with Zhou Zhiruo','Zhou Zhiruo','Zhao Min') AS out_put;
2, Mathematical function
Round round
SELECT ROUND(-1.45); SELECT ROUND(1.567,2);
ceil rounds up and returns > = the smallest integer of the parameter
SELECT CEIL(-1.002);
floor rounded down and returns < = the maximum integer of the parameter
SELECT FLOOR(-9.99);
truncate
SELECT TRUNCATE(1.6999,1);
Mod remainder mod(a,b) a-a/b*b
SELECT MOD(10,-3); SELECT 10%3;
3, Date function
now returns the current system date + time
SELECT NOW();
Current date returns the current system date, excluding time
SELECT CURDATE();
curtime returns the current time, excluding the date
SELECT CURTIME();
You can get the specified part, month, day, hour, minute and second
SELECT YEAR(NOW()) AS year;
SELECT YEAR('1998-1-1') AS year;
SELECT YEAR(hiredate) year FROM employees;
SELECT MONTH(NOW()) month;
SELECT MONTHNAME(NOW()) month;
str_to_date converts characters in date format to a date in the specified format
SELECT STR_TO_DATE('9-13-1999','%m-%d-%Y');
date_format converts the date to characters
SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2018/6/6','%Y year%m month%d day');
Query the employee information whose employment date is April 3, 1992
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE hiredate = '1992-4-3';
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE hiredate = STR_TO_DATE('4-3-1992','%c-%d-%Y');
Query the name and employment date of the employee with bonus (xx month / xx day, xx year)
SELECT last_name,DATE_FORMAT(hiredate,'%m month/%d day %y year') FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NOT NULL;
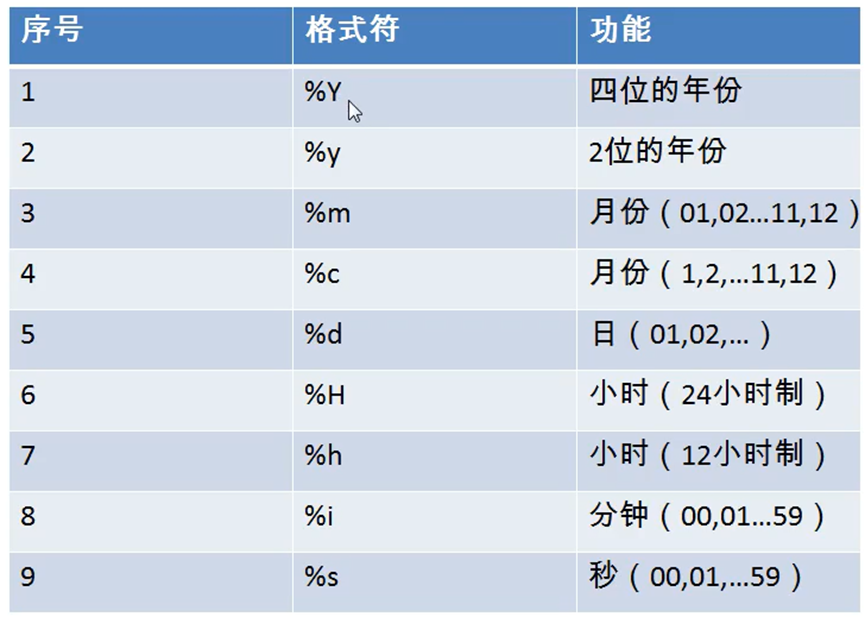
4, Other functions
SELECT VERSION(); SELECT DATABASE(); SELECT USER();
5, Process control function
1.if else function
SELECT IF(10>5,'large','Small'); SELECT last_name,commission_pct,IF(commission_pct IS NULL,'No bonus','Bonus') remarks FROM employees;
2. Use of case function I: effect of switch case
/*
case the field or expression to judge
when constant 1 then the value 1 or statement 1 to be displayed;
when constant 2 then the value 2 or statement 2 to be displayed;
...
else the value n or statement n to be displayed;
end
*/
/*Case: query employee salary, requirements
The department number = 30 shows that the salary is 1.1 times
The department number = 40 shows that the salary is 1.2 times
The department number = 50 shows that the salary is 1.3 times
Other departments are displayed as original wages
*/
SELECT salary Original salary,department_id, CASE department_id WHEN 30 THEN salary*1.1 WHEN 40 THEN salary*1.2 WHEN 50 THEN salary*1.3 ELSE salary END AS New salary FROM employees;
3. Use of case function 2: similar to multiple if
/*
case
when condition 1 then the value 1 or statement 1 to be displayed;
when condition 2 then the value 2 or statement 2 to be displayed;
...
else the value n or statement n to be displayed;
end
*/
#Case: query employee salary
#If the salary is greater than 20000, level A is displayed
#If the salary is greater than 15000, level B is displayed
#If the salary is greater than 10000, level C is displayed
#Otherwise, level D is displayed
SELECT salary, CASE WHEN salary>20000 THEN 'A' WHEN salary>15000 THEN 'B' WHEN salary>10000 THEN 'C' END AS Wage scale FROM employees;
Summary of common functions I
Character function
length concat substr instr trim upper lower lpad rpad
replace
Mathematical function
round ceil floor truncate mod
Date function
now curdate curtime year month monthname day hour
minute second str_to_date date_formate
Other functions
version datebase user
Control function
if case
case
1. Display system time (Note: date + time)
SELECT NOW();
2. Query the employee number, name, salary and the result after the salary is increased by 20%
SELECT employee_id,last_name,salary,salary*1.2 'new salary' FROM employees;
3. Sort the employee's names by initials and write the length of the name
SELECT LENGTH(last_name) length,SUBSTR(last_name,1,1) Initials,last_name FROM employees ORDER BY Initials;
4. Make a query to produce the following results
#<last_name> earns monthly but wants <salary*3>
#Dream Salary
#Kings earns 24000 monthly but wants 72000
SELECT CONCAT(last_name,'earns',salary,'monthly but wants',salary*3) AS 'Dream Salary' FROM employees WHERE salary=24000;
5. Use case when to realize the following conditions
| job | grade |
|---|---|
| AD_PRES | A |
| ST_MAN | B |
| IT_PROG | C |
| SA_PRE | D |
| ST_CLERK | E |
SELECT last_name,job_id AS job, CASE job_id WHEN 'AD_PRES' THEN 'A' WHEN 'ST_MAN' THEN 'B' WHEN 'IT_PROG' THEN 'C' WHEN 'SA_PRE' THEN 'D' WHEN 'ST_CLERK' THEN 'E' END AS Grade FROM employees WHERE job_id='AD_PRES';
case
1. Query the maximum value, minimum value, average value and total of employee salary
SELECT MAX(salary) mx_sal,MIN(salary) min_sal,ROUND(AVG(salary),2) ag_sal,SUM(salary) sm_sal FROM employees;
2. Query the difference days between the maximum enrollment time and the minimum enrollment time in the employee table
SELECT DATEDIFF(MAX(hiredate),MIN(hiredate)) difference FROM employees;
3. Query the number of employees whose department number is 90
SELECT COUNT(*) number FROM employees WHERE department_id=90;
Advanced 5: grouping query
Syntax:
select Grouping functions, columns(Request appears in group by behind) from surface [where [filter criteria] group by Group list [order by Clause]
be careful:
The query list must be special. It is required to be the field after the grouping function and group by
characteristic:
1. There are two types of filter criteria in group query
| data source | position | keyword | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filter before grouping | Original table | group by front | where |
| Filter after grouping | Grouped result set | After group by | having |
① The condition of grouping function must be put in the having clause
② Those who can filter before grouping shall be given priority
2. The group by clause supports single field grouping, multiple field grouping (comma separated, unordered), expression and function grouping
3. You can also add sorting and put it at the end
Import: query the average salary of each department
SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees;
Case 1: query the maximum wage of each type of work
SELECT MAX(salary),job_id FROM employees GROUP BY job_id;
Case 2: query the number of departments in each location
SELECT COUNT(*),location_id FROM departments GROUP BY location_id;
Filter criteria before adding groups
Case 1: query the average salary of each department with a character in the mailbox
SELECT AVG(salary),department_id FROM employees WHERE email LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY department_id;
Case 2: query the maximum salary of employees under each leader with bonus
SELECT MAX(salary),manager_id FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NOT NULL GROUP BY manager_id;
Filter criteria after adding grouping
Case 1: query which department has more than 2 employees
① Query the number of employees in each department
SELECT COUNT(*),department_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id;
② Filter according to the results of ① to query which department has more than 2 employees
SELECT COUNT(*),department_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id HAVING COUNT(*)>2;
Case 2: query the maximum salary of employees with bonus of each type of work > 12000
① Query the maximum salary of employees with bonus in each type of work
SELECT MAX(salary),job_id FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NOT NULL GROUP BY job_id;
② Continue to screen according to the results of ①, and the maximum salary is > 12000
SELECT MAX(salary),job_id FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NOT NULL GROUP BY job_id HAVING MAX(salary)>12000;
Case 3: query the minimum wage of each leader with leader No. > 102 and the leader No. > 5000 and their minimum wage
① Query the minimum wage of each employee under the leader
SELECT MIN(salary),manager_id FROM employees GROUP BY manager_id;
② Add filter condition: No. > 102
SELECT MIN(salary),manager_id FROM employees WHERE manager_id>102 GROUP BY manager_id;
③ Add filter criteria: minimum wage > 5000
SELECT MIN(salary),manager_id FROM employees WHERE manager_id>102 GROUP BY manager_id HAVING MIN(salary)>5000;
Filter by expression or function
Case: group by employee name length, query the number of employees in each group, and filter the information with the number > 5
① Query the number of employees of each length
SELECT COUNT(*),LENGTH(last_name) len_name FROM employees GROUP BY LENGTH(last_name);
② Add filter criteria
SELECT COUNT(*) c,LENGTH(last_name) len_name FROM employees GROUP BY len_name HAVING c>5;
Group by multiple fields
Case: query the average salary of each department and type of work
SELECT AVG(salary),department_id,job_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id,job_id;
Add sort
Case: query the average salary of each department and each type of work, and display it according to the average salary
SELECT AVG(salary),department_id,job_id FROM employees WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL GROUP BY department_id,job_id HAVING AVG(salary)>10000 ORDER BY AVG(salary) DESC;
case
1. Query each job_id maximum, minimum, average, sum of employee wages, and by job_id ascending order
SELECT MAX(salary),MIN(salary),AVG(salary),SUM(salary) FROM employees GROUP BY job_id ORDER BY job_id;
2. Check the gap between the maximum wage and the minimum wage
SELECT MAX(salary)-MIN(salary) DIFFERENCE FROM employees;
3. Query the minimum wage of employees under each manager. The minimum wage cannot be less than 6000, and it will not be counted if there is no manager
SELECT MIN(salary),manager_id FROM employees WHERE manager_id IS NOT NULL GROUP BY manager_id HAVING MIN(salary)>=6000;
4. Query all department numbers, number of employees and average salary, and in descending order of average salary
SELECT department_id,COUNT(*),AVG(salary) a FROM employees GROUP BY department_id ORDER BY a DESC;
5. Select each job_ Number of employees with ID
SELECT COUNT(*) number,job_id FROM employees GROUP BY job_id;
Advanced 6: connection query
/*
Meaning: also known as multi table query, when the query field comes from multiple tables
Cartesian product: Table 1 has m rows, table 2 has n rows, and the result is m*n rows
How does this happen: there are no valid link conditions
How to avoid: adding valid connection conditions
Classification:
Classification by age:
sql92 standard: only internal connections are supported
slq99 standard [recommended] supports internal and external (left and right) links + cross links
Classification by function
Inner connection: equivalent connection non equivalent connection self link
External connection: left external connection right external connection all external connection
Cross connect
*/
SELECT * FROM beauty; SELECT * FROM boys; SELECT NAME,boyName FROM boys,beauty WHERE beauty.boyfriend_id=boys.id;
1, sql92 standard
① The result of multi table equivalent connection is the intersection of multi tables
② N table links, at least n-1 connection conditions are required
③ The order of multiple tables is not required
④ Aliasing tables is generally required
⑤ It can be used with all the clauses described above, such as sorting, grouping and filtering
1. Equivalent link
Case 1: query the goddess name and the corresponding male god name
SELECT NAME,boyName FROM boys,beauty WHERE beauty.boyfriend_id=boys.id;
Case 2: query employee name and corresponding department name
SELECT last_name,department_name FROM employees,departments WHERE employees.department_id=departments.department_id;
2. Alias the table
① Improve sentence conciseness
② Distinguish multiple duplicate name fields
Note: if the table is aliased, the query field cannot be qualified with the original table name
Query employee name, type of work number and type of work name
SELECT last_name,e.job_id,job_title FROM employees e,jobs j WHERE e.job_id=j.job_id;
3. Can the order of two tables be changed
SELECT last_name,e.job_id,job_title FROM jobs j,employees e WHERE e.job_id=j.job_id;
4. Screening can be added
Case 1: query employee name and department name with bonus
SELECT last_name,department_name,commission_pct FROM employees e,departments d WHERE e.`department_id`=d.`department_id` AND e.`commission_pct` IS NOT NULL;
Case 2: query the Department name and city name whose second character is o in the city name
SELECT department_name,city FROM departments d,locations l WHERE d.`location_id`=l.`location_id` AND city LIKE '_o%';
5. Add group
Case 1: query the number of departments in each city
SELECT COUNT(*) number,city FROM departments d,locations l WHERE d.`location_id`=l.`location_id` GROUP BY city;
Case 2: query the Department name, department leader number and minimum wage of each department with bonus
SELECT department_name,d.manager_id,MIN(salary) FROM departments d,employees e WHERE d.`department_id`=e.`department_id` AND commission_pct IS NOT NULL GROUP BY department_name,d.manager_id;
6. Add sorting
Case: query the name of each type of work and the number of employees, in descending order by the number of employees
SELECT job_title,COUNT(*) FROM employees e,jobs j WHERE e.`job_id`=j.`job_id` GROUP BY job_title ORDER BY COUNT(*) DESC;
7. Three meter connection
Case: query employee name, department name and city
SELECT last_name,department_name,city FROM employees e,departments d,locations l WHERE e.`department_id`=d.`department_id` AND d.`location_id`=l.`location_id` AND city LIKE 's%' ORDER BY department_name DESC;
2. Non equivalent connection
Case 1: query employee's salary and salary level
SELECT * FROM job_grades; SELECT salary,grade_level FROM employees e,job_grades g WHERE salary BETWEEN g.`lowest_sal` AND g.`highest_sal` AND g.`grade_level`='A'; SELECT salary,employee_id FROM employees;
3 natural connection
Case: query employee name and superior name
SELECT e.employee_id,e.last_name,m.employee_id,m.last_name FROM employees e,employees m WHERE e.`manager_id`=m.`employee_id`;
case
1. Display the maximum salary and average salary in the employee table
SELECT MAX(salary),AVG(salary) FROM employees;
2. Query employee table_ id,last_ name,job_ ID by department_id descending, salary ascending
SELECT employee_id,job_id,last_name FROM employees ORDER BY department_id DESC,salary ASC;
3. Query employee table job_ The ID contains the of a and e, and a precedes e
SELECT job_id FROM employees WHERE job_id LIKE '%a%e%';
4. Display the current date, remove the space before and after, and intercept the string function
SELECT NOW(); SELECT TRIM(character FROM''); SELECT SUBSTR(str,startindex); SELECT SUBSTR(str,startindex,LENGTH);
Case:
1. Display the names, Department numbers and department names of all employees
SELECT last_name,d.department_id,department_name FROM employees e,departments d WHERE e.`department_id`=d.`department_id`;
2. Query the job of the employee in department 90_ ID and location of department 90_ id
SELECT job_id,location_id FROM employees e,departments d WHERE e.`department_id`=e.`department_id` AND e.`department_id`=90;
3. Select some fields of employees with bonus
SELECT last_name,department_name,l.location_id,city FROM employees e,departments d,locations l WHERE e.`department_id`=d.`department_id` AND d.`location_id`=l.`location_id` AND e.`commission_pct` IS NOT NULL;
4. Select the employee information of city working in Toronto
SELECT last_name,job_id,d.department_id,department_name FROM employees e,departments d,locations l WHERE e.`department_id`=d.`department_id` AND d.`location_id`=l.`location_id` AND city = 'Toronto';
5. Query each type of work, each department, type of work name and minimum wage
SELECT d.department_name,j.job_title,MIN(salary) FROM employees e,departments d,jobs j WHERE e.department_id=d.department_id AND e.job_id = j.job_id GROUP BY department_name,job_title;
6. Query the country number with more than 2 departments in each country
SELECT country_id,COUNT(*) Number of departments FROM departments d,locations l WHERE d.`location_id`=l.`location_id` GROUP BY country_id HAVING Number of departments>2;
7. Select the name and number of the designated employee, as well as the name and number of his manager
SELECT e.last_name employees,e.employee_id 'Emp#',m.last_name manager,m.employee_id 'Mgr#' FROM employees e,employees m WHERE e.manager_id=m.employee_id AND e.last_name='kochhar';
2, sql99 syntax
/*
grammar
select query list
from table 1 alias [connection type]
join table 2 alias
on connection condition
[where screening criteria]
[group by group]
[having screening criteria]
[order by sort list]
inner connection
External connection
left outer
right [outer]
full [outer]
cross connect
characteristic:
① Add sorting, grouping, filtering
② inner can be omitted
③ The filter condition is placed after where and the connection condition is placed after on
④ The effect of inner join connection is the same as that of equivalent connection of sql92 syntax, which is to query the intersection of multiple tables
*/
1) Inner connection
/*
Syntax:
select query list
from table alias
inner join table 2 alias
on connection conditions;
Classification:
equivalence
non-equivalence
Self link
*/
1. Equivalent link
Case 1: query employee name and department name
SELECT last_name,department_name FROM employees e INNER JOIN departments d ON e.`department_id`=d.`department_id`;
Case 2: query the employee name and work type name contained e in the name
SELECT last_name,job_title FROM employees e INNER JOIN jobs j ON e.`job_id`=j.`job_id` WHERE e.`last_name` LIKE '%e%';
Case 3. Query the city name and department number with department number > 3
SELECT city,COUNT(*) Number of departments FROM departments d INNER JOIN locations l ON d.`location_id`=l.`location_id` GROUP BY city HAVING Number of departments>3;
Case 4: query the Department name and number of employees in that department whose number of employees is > 3, and sort them in descending order
SELECT COUNT(*),department_name FROM employees e INNER JOIN departments d ON e.`department_id`=d.`department_id` GROUP BY department_name HAVING COUNT(*)>3 ORDER BY COUNT(*) DESC;
Case 5. Query employee name, department name and type of work, and sort by department name in descending order
SELECT last_name,department_name,job_title FROM employees e INNER JOIN departments d ON e.`department_id`=d.`department_id` INNER JOIN jobs j ON e.`job_id`=j.`job_id` ORDER BY department_name DESC;
2. Non equivalent link
Query employee salary level
SELECT salary,grade_level FROM employees e INNER JOIN job_grades g ON e.`salary` BETWEEN g.`lowest_sal` AND g.`highest_sal`;
Query the number of each salary level greater than 2, and sort by salary level in descending order
SELECT COUNT(*),grade_level FROM employees e JOIN job_grades g ON e.`salary` BETWEEN g.`lowest_sal` AND g.`highest_sal` GROUP BY grade_level HAVING COUNT(*)>20 ORDER BY grade_level DESC;
3. Self link
Employee name and superior name contained k in query name
SELECT e.last_name,m.last_name FROM employees e INNER JOIN employees m ON e.`manager_id`=m.`employee_id` WHERE e.`last_name` LIKE '%k%';
2, External connection
/*
Application scenario: used to query records that one table has but another table does not
characteristic:
1. Query results of external connection are all records in the main table
If there is a matching from the table, the matching value is displayed
If there is no matching from the table, null is displayed
External connection query result = internal connection result + there are records in the master table that are not in the slave table
2. The left side of the left outer connection is the main table
Right outer connection right the right is the main table
3. The same effect can be achieved by exchanging the order of the two tables outside the left and right
4. Total external connection = internal connection result + yes in Table 1 but no in Table 2 + yes in Table 2 and no in Table 1
*/
Introduction: query the goddess name whose boyfriend is not in the male god table
SELECT b.name FROM beauty b LEFT OUTER JOIN boys bo ON b.`boyfriend_id`=bo.`id` WHERE bo.`id` IS NULL;
Case 1: query which department has no employees
Left outer
SELECT d.*,e.employee_id FROM departments d LEFT OUTER JOIN employees e ON d.`department_id`=e.`department_id` WHERE e.`employee_id` IS NULL;
Right outer
SELECT d.*,e.employee_id FROM employees e RIGHT OUTER JOIN departments d ON d.`department_id`=e.`department_id` WHERE e.`employee_id` IS NULL;
All external links
SELECT b.*,bo.* FROM beauty b FULL OUTER JOIN boys bo ON b.`boyfriend_id`=bo.id;
Cross connect (Cartesian product)
SELECT b.*,bo.* FROM beauty b CROSS JOIN boys bo;
sql92 and sql99
Features: more supported by sql99
Readability: sql99 realizes the separation of link conditions and filter conditions, with high readability
case
1, Query the boyfriend information of goddess with number > 3. If it is listed in detail, it is not filled in with null
SELECT b.id,b.name,bo.* FROM beauty b LEFT OUTER JOIN boys bo ON b.`boyfriend_id`=bo.`id` WHERE b.`id`>3;
2, Query which city has no department
SELECT city,d.* FROM departments d RIGHT OUTER JOIN locations l ON d.`location_id`=l.`location_id` WHERE d.`department_id` IS NULL;
3, Query employee information with department name sal or it
SELECT e.*,d.department_name
FROM departments d
LEFT OUTER JOIN employees e
ON d.`department_id`=e.`department_id`
WHERE d.`department_name` IN('SAL','IT');
Advanced 7: subquery
/*
Meaning: select statements that appear in other statements are called subqueries or intra queries
External query statements are called primary or external queries
Classification:
Location of sub query:
After select
Only scalar subqueries are supported
After from
Support table sub query
After where or having ♥♥♥
Scalar subquery (single row)
Column subquery (multiple rows)
Row subquery
After exists (related sub query)
Table subquery
According to the number of rows and columns in the result set:
Scalar subquery (result set has only one row and one column)
Column subquery (the result set has only one column and multiple rows)
Row subquery (result set has multiple rows and columns)
Table sub query (the result set is generally multi row and multi column)
/
#1, Behind where or having
/
1. Scalar subquery (single line subquery)
2. Column subquery (multi row subquery)
3. Row sub query (multi column and multi row)
characteristic
① Subqueries are enclosed in parentheses
② Subqueries are generally placed on the right side of conditions
③ Scalar subqueries are generally used with single line operators
< >= <= = <>
Column subqueries are generally used with multi row operators
④ The execution of the sub query takes precedence over the main query. The conditions of the main query use the results of the sub query
in any/some all
*/
1. Scalar subquery
Case 1: whose salary is higher than abel
① Query salary
SELECT salary FROM employees WHERE last_name = 'Abel';
② Query employee information to meet salary > ① results
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary>(SELECT salary FROM employees WHERE last_name = 'Abel');
Case 2: return job_ The ID is the same as that of employee No. 14. Salary is more than that of employee No. 143_ ID and salary
① Query the job of employee 141_ id
SELECT job_id FROM employees WHERE employee_id=141;
② Query employee No. 143 salary
SELECT salary FROM employees WHERE employee_id=143;
③ Query employee name, job_id and salary, job required_ Id = ① and salary > ②
SELECT last_name,job_id,salary FROM employees WHERE job_id=( SELECT job_id FROM employees WHERE employee_id=141 )AND salary>( SELECT salary FROM employees WHERE employee_id=143 );
Case 3: return the last of the employee with the lowest salary_ name,job_ id,salary
① Query the company's minimum wage
SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employees;
② Query last_name,job_id,salary, and salary = ①
SELECT last_name,job_id,salary FROM employees WHERE salary = ( SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employees );
Case 4: query the Department id and the minimum wage of the Department whose minimum wage is greater than the minimum wage of No. 50 department
① Inquire about the minimum wage in department 50
SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employees WHERE department_id = 50;
② Query the minimum wage of each department
SELECT MIN(salary),department_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id;
③ Screening ②, meeting min (salary) > ①
SELECT MIN(salary),department_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id HAVING MIN(salary)>( SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employees WHERE department_id = 50 );
2. Column sub query (one column and multiple rows)
Case 1: return location_id is the name of all employees in the 1400 or 1700 department
① Query location_id is the department number of 1400 or 1700
SELECT DISTINCT department_id FROM departments WHERE location_id IN(1400,1700);
② Query the employee's name. The department number must be one of the ① list
SELECT last_name FROM employees WHERE department_id IN( SELECT DISTINCT department_id FROM departments WHERE location_id IN(1400,1700) );
Case 2: return to a job in another department_ ID is' it '_ Prog 'employee number, name and job of any employee with low salary in the Department_ ID and salary
Query job_id is' it '_ Prog 'any salary of the Department
SELECT salary FROM employees WHERE job_id='IT_PROG';
② Query employee No., name, jobn_id and any one of salary, salary < ①
SELECT last_name,employee_id,job_id,salary FROM employees WHERE salary<ANY( SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees WHERE job_id='IT_PROG' )AND job_id<>'IT_PROG';
Case 3: return to a job in another department_ ID is' it '_ Prog 'employee number, name and job of all low paid employees in the Department_ ID and salary
SELECT last_name,employee_id,job_id,salary FROM employees WHERE salary<ALL( SELECT DISTINCT salary FROM employees WHERE job_id='IT_PROG' )AND job_id<>'IT_PROG';
3. Row sub query (result: one row with multiple columns)
Case: query the information of the employee with the smallest employee number and the highest salary
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE (employee_id,salary)=( SELECT MIN(employee_id),MAX(salary) FROM employees );
① Query the minimum employee number
SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employees;
② Query maximum wage
SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees;
③ Query employee information
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE employee_id=( SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employees ) AND salary=( SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees );
2, After select
/*
Only scalar subqueries are supported
*/
Case: query the number of employees in each department
SELECT d.*,( SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees e WHERE e.department_id=d.`department_id` ) number FROM departments d;
Case 2: query the Department name with employee No. = 102
SELECT ( SELECT department_name FROM departments d INNER JOIN employees e ON d.department_id=e.department_id WHERE e.employee_id=102 ) Department name;
3, After from
Case: query the salary grade of the average salary of each department
① Query the average salary of each department
SELECT AVG(salary),department_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id; SELECT * FROM job_grades;
② Linked result set and job_grade table, filter criteria, average salary between lowest_sal and highest_sal
SELECT ag_dep.*,g.`grade_level` FROM( SELECT AVG(salary) ag,department_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id ) ag_dep INNER JOIN job_grades g ON ag_dep.ag BETWEEN lowest_sal AND highest_sal
4, After exists (related sub query)
/*
Exists (complete query statement)
Result: 1 or 0
*/
Case 1: query the Department name with employees
in
SELECT department_name FROM departments d WHERE d.department_id IN( SELECT department_id FROM employees );
exists
SELECT department_name FROM departments d WHERE EXISTS( SELECT * FROM employees e WHERE d.department_id=e.`department_id` );
Case 2: query the boyfriend information without a girlfriend
in
SELECT bo.* FROM boys bo WHERE bo.`id` NOT IN( SELECT boyfriend_id FROM beauty );
exists
SELECT bo.* FROM boys bo WHERE NOT EXISTS( SELECT boyfriend_id FROM beauty WHERE bo.`id`=boyfriend_id );
Case synthesis
1. Query the name and salary of employees in the same department as Zlotkey
① Query zlotkey's Department
SELECT department_id FROM employees WHERE last_name ='Zlotkey';
② Query the name and salary of department number = ①
SELECT last_name,salary FROM employees WHERE department_id=( SELECT department_id FROM employees WHERE last_name ='Zlotkey' );
2. Query the employee number, name and salary of employees whose salary is higher than the average salary of the company
① Query average salary
SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees;
② Query the employee number, name and salary with salary > ①
SELECT last_name,employee_id,salary FROM employees WHERE salary>( SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees );
3. Query the number, name and salary of employees whose salary is higher than the average salary in each department
① Query the average salary of each department
SELECT AVG(salary),department_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id;
② Link ① result set and employees table for filtering
SELECT employee_id,last_name,salary,e.`department_id` FROM employees e INNER JOIN ( SELECT AVG(salary) ag,department_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id ) ag_dep ON e.`department_id`=ag_dep.department_id WHERE salary>ag_dep.ag;
4. Query and the employee number of the employee whose name contains the letter u who works in the same department
① Query the Department of the employee whose name contains the letter u
SELECT DISTINCT department_id FROM employees WHERE last_name LIKE '%u%';
② Query the employee number and name of any one of department number = ①
SELECT last_name,employee_id FROM employees WHERE department_id IN( SELECT DISTINCT department_id FROM employees WHERE last_name LIKE '%u%' );
5. Query Department location_ Employee number of the employee working in the Department with ID 1700
① Query location_ Part with ID 1700
SELECT DISTINCT department_id FROM departments WHERE location_id = 1700;
② Query the employee number of any department number = ①
SELECT employee_id FROM employees WHERE department_id=ANY( SELECT DISTINCT department_id FROM departments WHERE location_id = 1700 );
6. Query the name and salary of the employee whose manager is king
① Query the employee number whose name is king
SELECT employee_id FROM employees WHERE last_name = 'K_ing';
② Which employee's manager is queried_ id=①
SELECT last_name,salary FROM employees WHERE manager_id IN( SELECT employee_id FROM employees WHERE last_name = 'K_ing' );
7. Query the name of the employee with the highest salary and ask first_name and last_name is displayed as a column. The column name is last name and first name
① Query maximum wage
SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees;
② Query name of salary = ①
SELECT CONCAT(first_name,last_name) 'surname,name' FROM employees WHERE salary=( SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees );