The main contents of this chapter are as follows:
- Link model
- Python Keyword - cdef
- Typedef and function pointer
- public keyword
- Keyword cpdef
- C / C + + log to Python
- C / C + + calls Python ConfigParser
- Python to C / C + + callback
- Cython PXD
- Integration with build systems
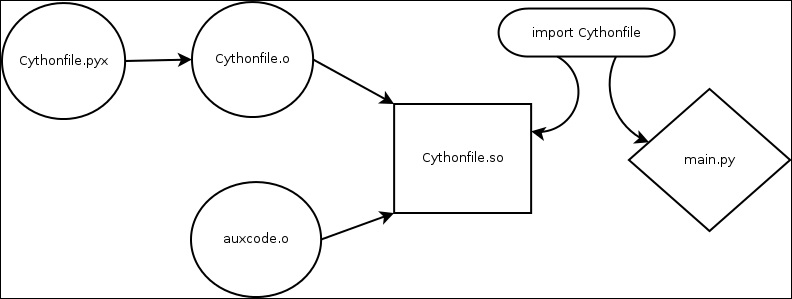
Link model
Embedding python in C/C + +
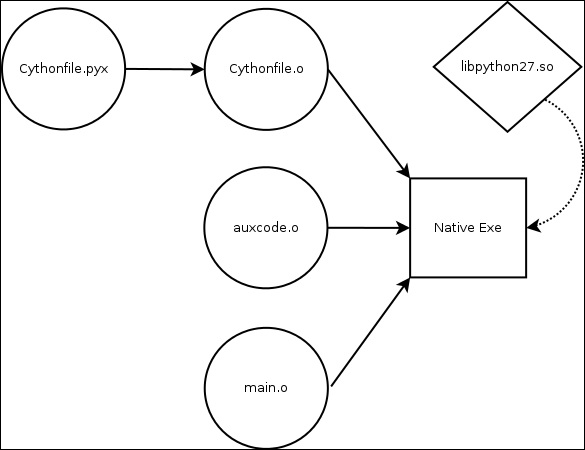
cython mode
cdef
The cdef keyword tells the compiler that the statement is a local C type or a local function. For example:
cdef int AddFunction(int, int) def square(int x): return x ** 2
Struct
C's struct can be used directly in Python. For example, mycode.h
#ifndef __MYCODE_H__ #define __MYCODE_H__ struct mystruct { char * string; int integer; char ** string_array; }; extern void printStruct (struct mystruct *); #endif //__MYCODE_H__
Implementation of printStruct function mycode.c
#include <stdio.h> #include "mycode.h" void printStruct (struct mystruct * s) { printf (".string = %s\n", s->string); printf (".integer = %i\n", s->integer); printf (".string_array = \n"); int i; for (i = 0; i < s->integer; ++i) printf ("\t[%i] = %s\n", i, s->string_array [i]); }
Python import call: mycodepy.pyx
cdef extern from "mycode.h": struct mystruct: char * string int integer char ** string_array void printStruct (mystruct *) def testStruct (): cdef mystruct s cdef char *array [2] s.string = "Hello World" s.integer = 2 array [0] = "foo" array [1] = "bar" s.string_array = array printStruct (&s)
The definition of nested structure void myfunc (struct mystruct * x) in Python: void myfunc (mystruct * x). There is no → operation symbol in cyphon. Use dot.
implement
$ make cython -3 -o mycodepy.c mycodepy.pyx gcc -g -O2 -fpic -c mycodepy.c -o mycodepy.o `python3-config --cflags` gcc -g -O2 -fpic -c mycode.c -o mycode.o gcc -g -O2 -shared -o mycodepy.so mycode.o mycodepy.o $ python Python 3.6.5 |Anaconda, Inc.| (default, Apr 29 2018, 16:14:56) [GCC 7.2.0] on linux Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> from mycodepy import testStruct >>> from mycodepy import testStruct >>> testStruct () .string = Hello World .integer = 2 .string_array = [0] = foo [1] = bar
Enum
Implementation in c:
enum cardsuit { CLUBS, DIAMONDS, HEARTS, SPADES };
Cython definition
cdef enum cardsuit: CLUBS, DIAMONDS, HEARTS, SPADES # Use cdef cardsuit card = CLUBS
Typedef and function pointer
Implementation in c:
struct foobar { int x; char * y; }; typedef struct foobar foobar_t; typedef void (*cfptr) (int)
Cython definition
cdef struct foobar: int x char * y ctypedef foobar foobar_t # Use ctypedef int * int_ptr ctypedef void (*cfptr)(int cdef cfptr myfunctionptr = &myfunc
Typedef and function pointer
This is a very powerful keyword in Python. It allows any cdef declaration with a public modifier to output the corresponding C/C + + header, where the declaration can be accessed from C/C + +. For example, we can state:
cdef public struct CythonStruct: size_t number_of_elements; char ** elements;
After compilation, the system will generate Python input. H
struct CythonStruct { size_t number_of_elements; char ** elements; };
c call requires libpython.so embedded and initialization:
#include <Python.h> int main(int argc, char **argv) { Py_Initialize (); // code in here Py_Finalize (); return 0; }
You need to initialize the
cdef public void cythonFunction (): print "inside cython function!!!"
This generates cythonfile.c and cythonfile.h.
/* Boiler plate init Python */ Py_SetProgramName (argv [0]); Py_Initialize (); /* Init our config module into Python memory */ initpublicTest (); cythonFunction (); /* cleanup python before exit... */ Py_Finalize ();
This step is similar to the import cythonfile in python
cpdef
Function declaration def can be called in Python and python, cdef can be called in c series, cpdef can be called in both, but it is not recommended to know the type and lose the type security of Python.
long returnValue = PyInt_AsLong (test (1, 0))
Example: C/C + + calls python logging
main.c
#include "NativeLogging.h" int main(int argc, char **argv) { // we want to ensure we use a command line argument for the output log file if (argc < 2) { return -1; } // use the first argument as log file SetupNativeLogging(argv[1]); // log out some stuff at different levels info("info message"); debug("debug message"); error("error message"); // close up everything including Python CloseNativeLogging(); return 0; }
NativeLogging.h
#ifndef __NATIVE_LOGGING_H__ #define __NATIVE_LOGGING_H__ #define printflike __attribute__ ((format (printf, 3, 4))) extern void printflike native_logging_info(const char *, unsigned, const char *, ...); extern void printflike native_logging_debug(const char *, unsigned, const char *, ...); extern void printflike native_logging_error(const char *, unsigned, const char *, ...); #define info(...) native_logging_info(__FILE__, __LINE__, __VA_ARGS__) #define error(...) native_logging_debug(__FILE__, __LINE__, __VA_ARGS__) #define debug(...) native_logging_error(__FILE__, __LINE__, __VA_ARGS__) extern void SetupNativeLogging(const char * logFileName); extern void CloseNativeLogging(); #endif // __NATIVE_LOGGING_H__
NativeLogging.c
#include <Python.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdarg.h> #include "PythonLoggingBackend.h" #include "NativeLogging.h" void native_logging_info(const char * file, unsigned line, const char * fmt, ...) { char buffer[256]; va_list args; va_start(args, fmt); vsprintf(buffer, fmt, args); va_end(args); char buf[512]; snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%s:%i -> %s", file, line, buffer); python_info(buf); } void native_logging_debug(const char * file, unsigned line,const char * fmt, ...) { char buffer[256]; va_list args; va_start(args, fmt); vsprintf(buffer, fmt, args); va_end(args); char buf[512]; snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%s-%i -> %s", file, line, buffer); python_debug(buf); } void native_logging_error(const char * file, unsigned line, const char * fmt, ...) { char buffer[256]; va_list args; va_start(args, fmt); vsprintf(buffer, fmt, args); va_end(args); char buf[512]; snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%s:%i -> %s", file, line, buffer); python_error(buf); } void SetupNativeLogging(const char * logFileName) { /* Boiler plate init Python */ Py_Initialize(); /* Init our config module into Python memory */ initPythonLoggingBackend(); /* call directly into our cython module parseConfig */ initLoggingWithLogFile(logFileName); } void CloseNativeLogging() { /* cleanup python before exit ... */ Py_Finalize(); }
PythonLoggingBackend.pyx
import logging cdef public void initLoggingWithLogFile(const char * logfile): logging.basicConfig(filename = logfile, level = logging.DEBUG, format = '%(levelname)s %(asctime)s: %(message)s', datefmt = '%m/%d/%Y %I:%M:%S') cdef public void python_info(char * message): logging.info(message) cdef public void python_debug(char * message): logging.debug(message) cdef public void python_error(char * message): logging.error(message)
Makefile
all: cython -2 PythonLoggingBackend.pyx gcc -g -O2 -fpic -c PythonLoggingBackend.c -o PythonLoggingBackend.o `python-config --includes` gcc -g -O2 -fpic -c NativeLogging.c -o NativeLogging.o `python-config --includes` gcc -g -O2 -fpic -c main.c -o main.o gcc -g -O2 -o example main.o PythonLoggingBackend.o NativeLogging.o `python-config --libs` clean: rm -f example PythonLoggingBackend.c *.o PythonLoggingBackend.h *.log