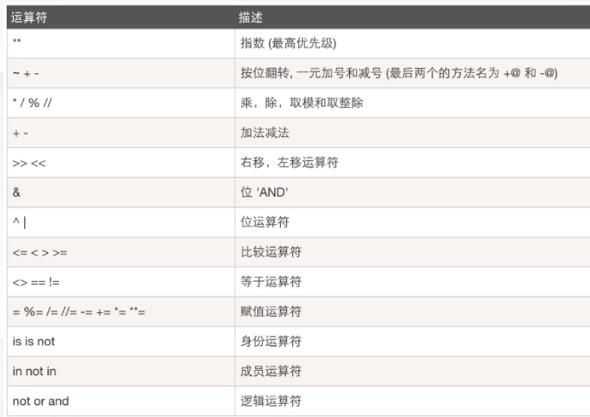
1. Arithmetic operator
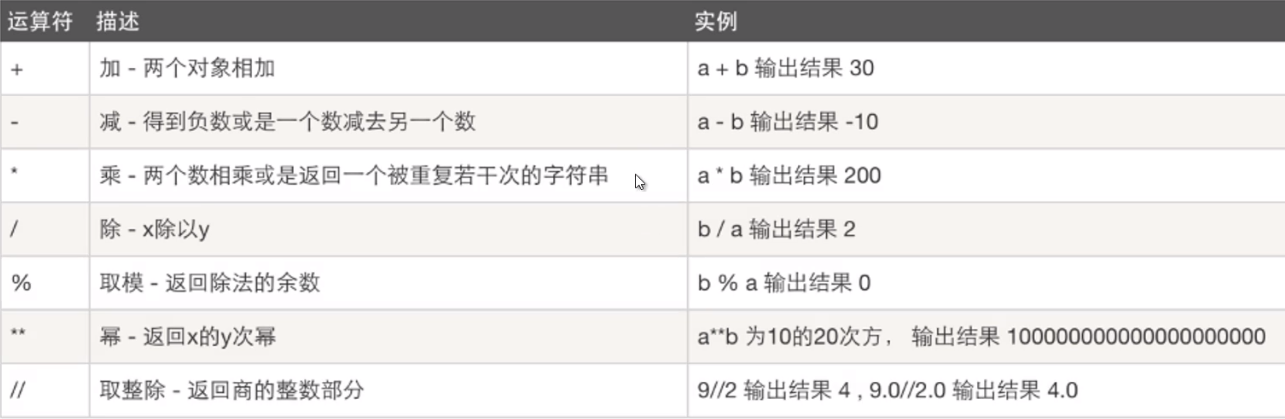
Example 1: given a three digit number, give the corresponding parameters of each position:
#Method 01: find it as a number
print("Please enter a three digit number:")
number = input()
number = int(number)
Bai_number = number //100
#Shi_number = (number - Bai_number*100)//10
Shi_number = number % 100 //10
Ge_number = number % 10
print("Hundred digit number is:",Bai_number,"The tens are:",Shi_number,"Single digit is",Ge_number)
##Method 02: find as character
print("Please enter a three digit number:")
number = input()
print("Hundred digit number is:",number[0],"The tens are:",number[1],"Single digit is",number[2])
Example 2: number of Narcissus: 1. Three digit number 2. Hundred third power + ten third power + one third power = this number
#Narcissistic number
#1.Three digit 2.One hundred third power + Three power squares + Third power = This number
print("The number of Narcissus is:")
for i in range(100,1000):
Bai_number = i //100
Shi_number = i % 100 //10
Ge_number = i % 10
if i == Bai_number ** 3 + Shi_number ** 3 + Ge_number ** 3:
print(i)
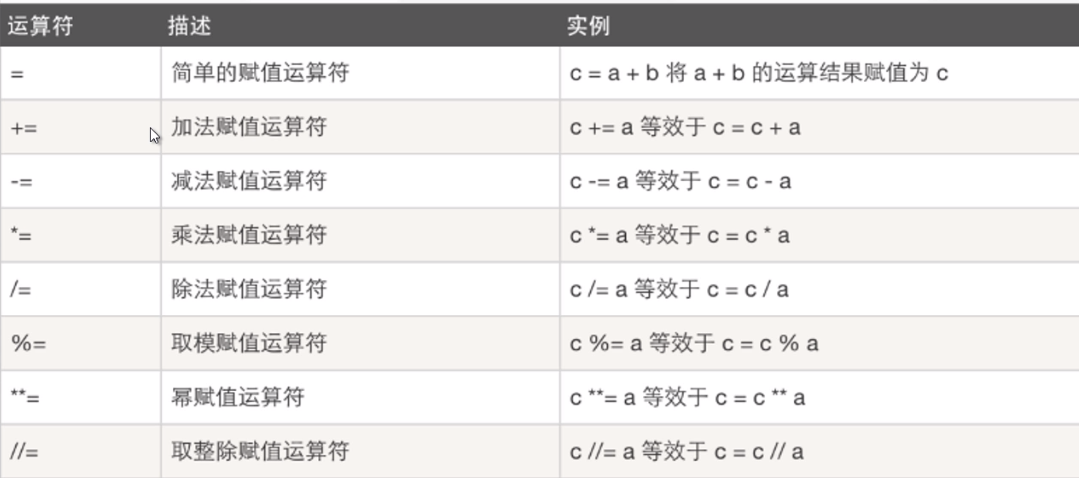
2. Assignment operator
3. Logical operators
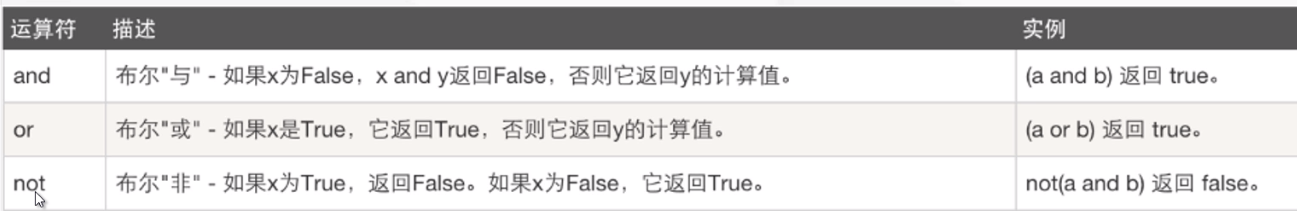
and - only when it's true
or - when one is true
not: no -- the original is true, the reverse is false
Example: determine whether the year is a leap year
print("Please enter a year:")
year = int(input())
if year % 400 == 0 or (year % 4 == 0 and year % 100 != 0):
print("%d Year of leap year" % year)
else:
print("%d Year is average year." % year)
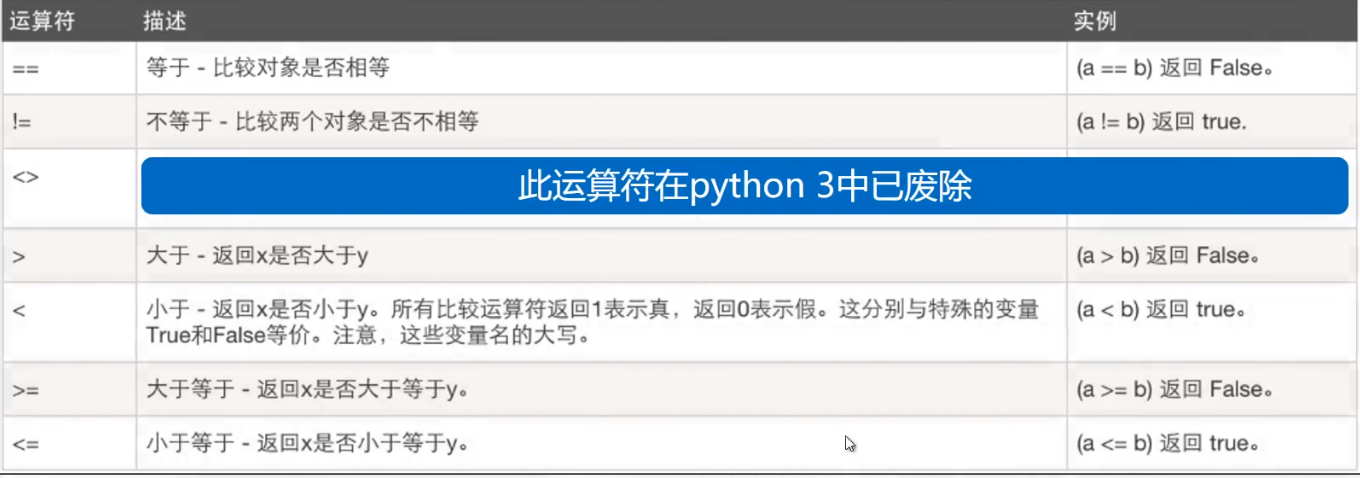
4. Comparison operator
5. Bit operator
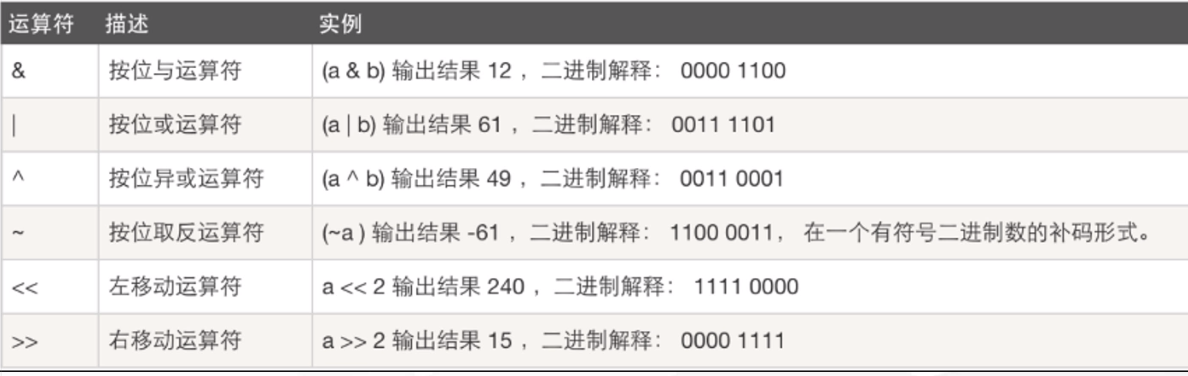
If the bit of a number is not its plus 1, it is reversed
~102 = -103
~-102 = 101
Shift right, shift left, shift left, and shift right (* 4). The number of digits increases
6. Member operator
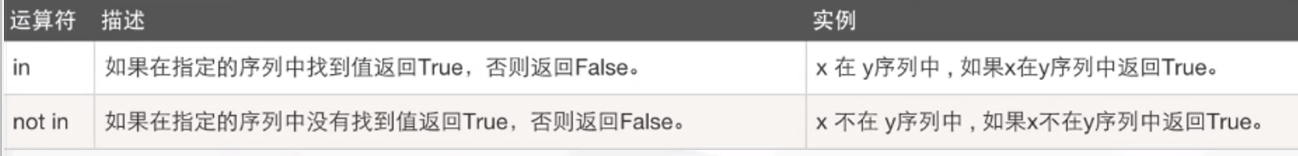
Applicable scenario 01: judge whether a string contains another string
str01 = "my name is steven"
if "steven"in str01:
print("Contain steven")
else:
print("Does not contain steven")
Applicable scenario 02: judge whether an element is included in the set
list01 = [111,222,333,444,555]
if 111 in list01:
print("Set contains 111")
else:
print("Set does not contain 111")
7. Identity operator
is/ not is: --- judge whether two objects refer to the same memory space
##False statement: judge whether two objects are equal
num01 = 100 num02 = 100 print("num01 and num02 Are they equal?",num01 == num02) print(id(num01)) print(id(num02)) print("num01 and num02 Is it the same object",num01 is num02)
Both returns are True
Character string:
str01 = "steven"
str02 = "steven"
print("str01 and str02 Are they equal?",str01==str02)
print(id(str01))
print(id(str02))
print("str01 and str02 Is it the same object",str01 is str02)
Counter example:
str03 = "steven" * 50
str04 = "steven" * 50
print("str03 and str04 Are they equal?",str03==str04)
print(id(str03))
print(id(str04))
print("str03 and str04 Is it the same object",str03 is str04)
Return True and False
is determines whether the memory addresses of two objects are the same, not whether the variables are the same
8. Ternary operator

##In C, num03 = num01 > num02? Num01: num02 (if num01 is greater than num02, output num01, otherwise take num02)
num01 = 100
num02 = 200
num03 = num01 if num01 > num02 else num02 #(If num01 greater than num02,output num01,Otherwise take num02)
print(num03)
##Landing judgement
username = input("Please enter the user name:")
password = input("Please input a password:")
result = True if username == "Admin" and password == "123.com" else False
if result:
print("Landing successfully")
else:
print("Wrong user name or password")
9. Priority of operators