Socket
Sockets are an abstraction layer through which applications can send or receive data, open, read, write, and close like files.Sockets allow applications to plug I/O into the network and communicate with other applications on the network.A network socket is a combination of IP addresses and ports.
Development: Sockets were originally a network communication interface developed by the University of California, Berkely, for Unix systems.Later, with the development of TCP/IP network, sockets became the most common application interface and the most common API for application development on the Internet.
Application:
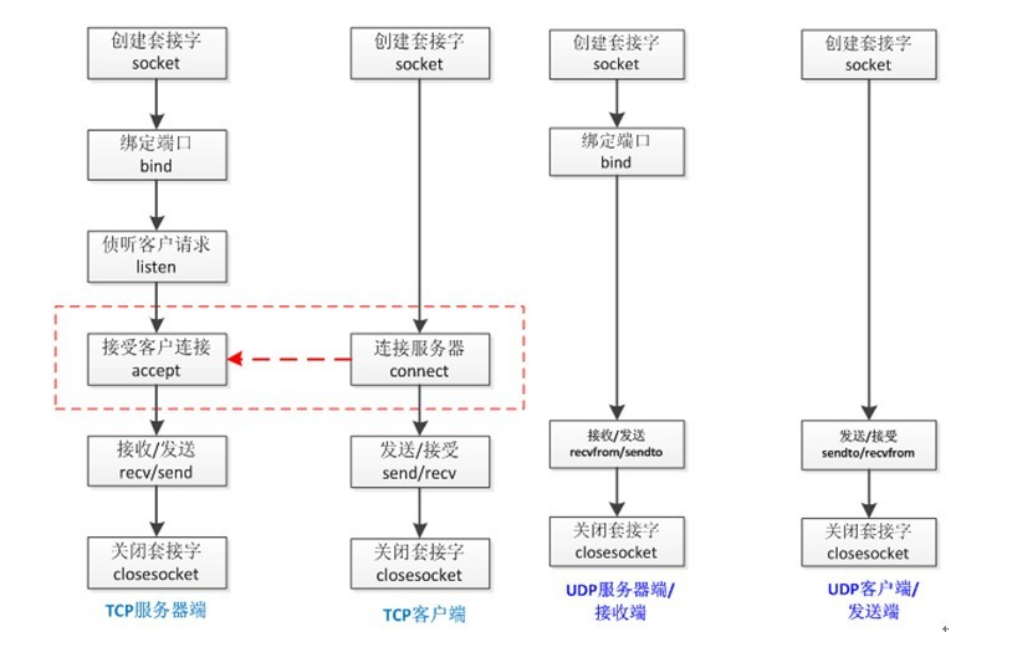
Realization:
Implement information exchange between Sever and Client based on TCP protocol
Sever side:
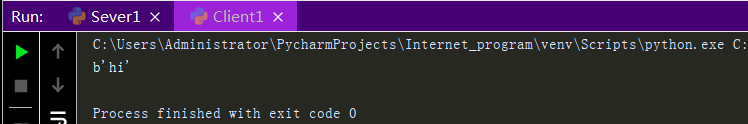
import socket sk = socket.socket() #Create a socket for the server sk.bind(('127.0.0.1',8080)) #Bind Address to Socket sk.listen() #Listen Link conn,addr = sk.accept() #Receive client connections and addresses ret = conn.recv(1024) #Receive client information print(ret) #Print client information conn.send(b'hi') #Send information to client conn.close() #Close client connections sk.close() #Close Server Socket
Client side:
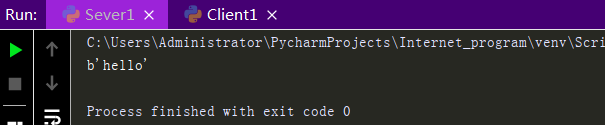
import socket sk = socket.socket() #Create Client Socket sk.connect(('127.0.0.1',8080)) #Attempt to connect to server sk.send(b'hello') #Send message to server ret = sk.recv(1024) #Receive messages from the server print(ret) #Print messages sent by the server sk.close() #Close the client's socket
Sever side and Client side should receive and send information, not just receive or receive but execute Sever side before executing Client side.
Encountered a problem where the address was already in use when restarting the server
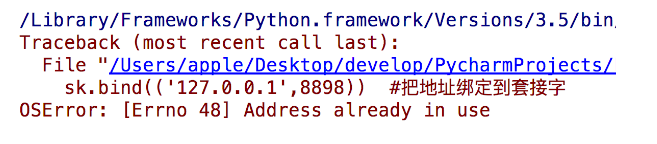
Solution:
How can clients and servers have multiple conversations?
Sever side:
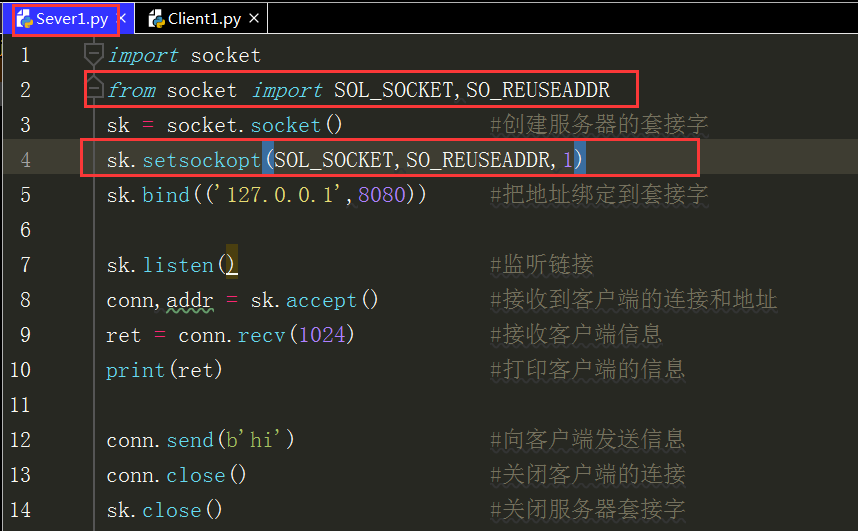
import socket from socket import SOL_SOCKET,SO_REUSEADDR sk = socket.socket() #Create a socket for the server sk.setsockopt(SOL_SOCKET,SO_REUSEADDR,1) sk.bind(('127.0.0.1',8080)) #Bind Address to Socket sk.listen() #Listen Link conn,addr = sk.accept() #Receive client connections and addresses print(addr) #Print client address ret = conn.recv(1024) #Receive client information print(ret) #Print client information conn.send(b'hi') #Send information to client print(addr) #Print client address ret = conn.recv(1024) #Receive client information print(ret) #Print client information conn.send(b'hi') #Send information to client conn.close() #Close client connections sk.close() #Close Server Socket
Client side:
import socket sk = socket.socket() #Create Client Socket sk.connect(('127.0.0.1',8080)) #Attempt to connect to server sk.send(b'hello') #Send message to server ret = sk.recv(1024) #Receive messages from the server print(ret) #Print messages sent by the server sk.send(b'hello') #Send message to server ret = sk.recv(1024) #Receive messages from the server print(ret) #Print messages sent by the server sk.close() #Close the client's socket
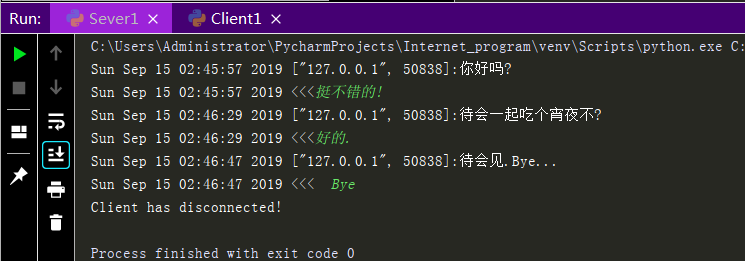
Execution results:
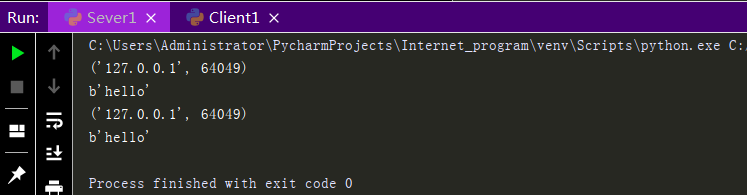
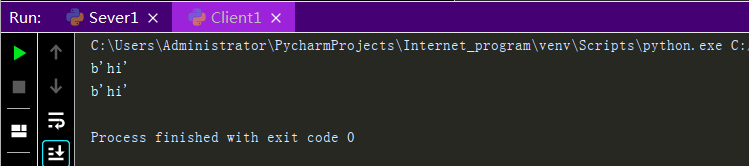
So we can complete the process of sending and receiving messages all the time just by having the Sever end receive and send messages in a loop, and the Client end send and receive messages in a loop after connecting to the Sever end, but this process is a dead loop and we need to add some conditions to make it more perfect
Sever side:
import socket import time from json import dumps from socket import SOL_SOCKET,SO_REUSEADDR sk = socket.socket() #Create a socket for the server sk.setsockopt(SOL_SOCKET,SO_REUSEADDR,1) sk.bind(('127.0.0.1',8080)) #Bind Address to Socket sk.listen() #Listen Link conn,addr = sk.accept() #Receive client connections and addresses while 1: ret = conn.recv(1024).decode('utf-8') #Receive client information if ret.strip() == 'bye' or ret.strip() == 'bye'.capitalize(): #Conditions for Jumping Out of Cycle conn.send(b'bye') #Send out bytes Type Bye print('Client has disconnected!') break print(time.asctime(time.localtime(time.time())) + ' ' + dumps(addr) + ':' + ret) #Format Print Message from Client sendInfo = input(time.asctime(time.localtime(time.time())) + ' <<<') conn.send(sendInfo.encode('utf-8')) #Send information to client conn.close() #Close client connections sk.close() #Close Server Socket
Client side:
import socket import time sk = socket.socket() #Create Client Socket sk.connect(('127.0.0.1',8080)) #Attempt to connect to server while 1: sendInfo = input(time.asctime(time.localtime(time.time())) + ' <<<') sk.send(sendInfo.encode('utf-8')) #Send message to server ret = sk.recv(1024).decode('utf-8') #Receive messages from the server if ret.strip() == 'bye' or ret.strip() == 'bye'.capitalize(): #Conditions for Jumping Out of Cycle sk.send(b'bye') #Send out bytes Type Bye print('Sever has disconnected!') break print(time.asctime(time.localtime(time.time())) + ' ["127.0.0.1", 8080]:' + ret)#Format messages from print servers sk.close() #Close the client's socket
Execution results:
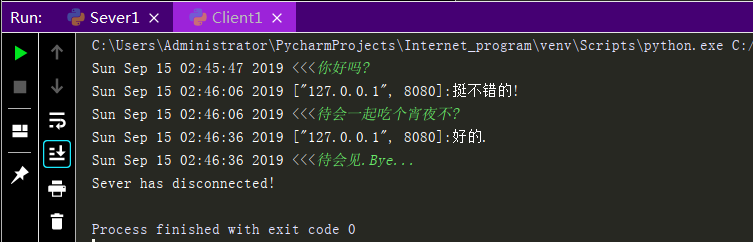
Implement information exchange between Sever and Client based on UDP protocol
Implement simple messaging
Sever side:
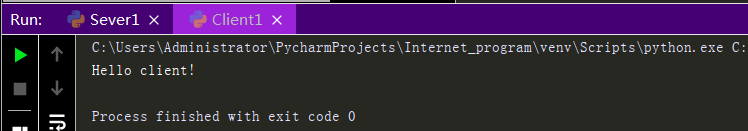
import socket sk = socket.socket(type=socket.SOCK_DGRAM) #Create Server Socket sk.bind(('127.0.0.1',8080)) #Bind Server Socket msg,addr = sk.recvfrom(1024) #Receive client information and address print(msg.decode('utf-8')) #Decode and print the information passed by the client sk.sendto(b'Hello client!',addr) #take bytes Address to which type of information is sent to the client sk.close() #Close Server Socket
Client side:
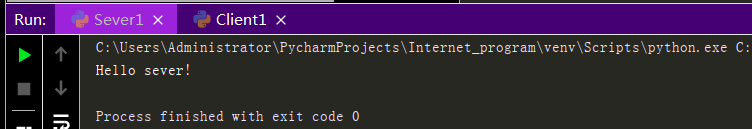
import socket sk = socket.socket(type=socket.SOCK_DGRAM) #Create Client Socket ip_port = ('127.0.0.1',8080) sk.sendto(b'Hello sever!',ip_port) #Client sends information ret,addr = sk.recvfrom(1024) #Receive the address and information of the server print(ret.decode('utf-8')) #Print received information sk.close() #Close Client Socket
Execution results:
......