catalogue
1) Module installation and import
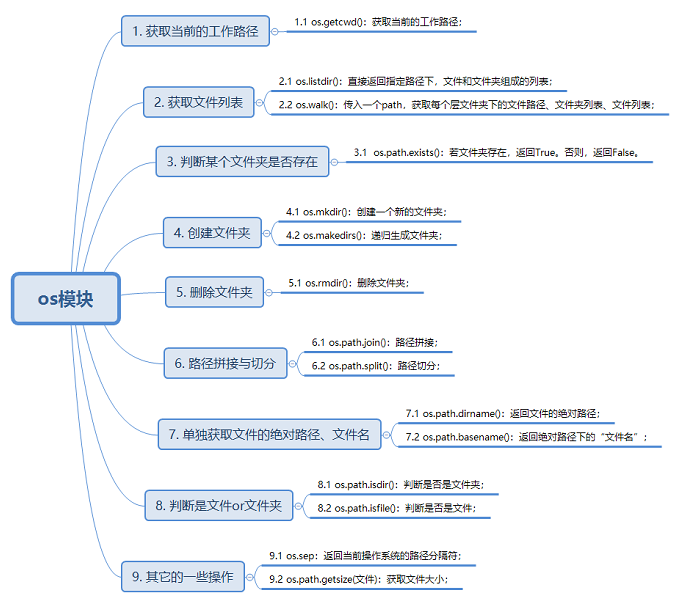
The os module is Python It is the most commonly used module to sort out files and directories in. This module provides a very rich method to deal with files and directories. Next, I will summarize some methods commonly used in my work and hope to grow with you.
1) Module installation and import
# Import import os
2)os.getcwd()
- Function: obtain the current working path;
3)os.listdir(path)
- Function: pass in any path and return a list of all files and directories under the path;
path = r"C:\Users\Desktop\publish\os modular\test_os modular" os.listdir(path)
4)os.walk(path)
- Meaning: pass in any path path, deeply traverse all subfolders under the specified path, and return a tuple composed of path, folder list and file list. The way I write in my code belongs to tuple unpacking;
- Tuple unpacking: assign each value in a tuple to different variables;
path = r"C:\Users\Desktop\publish\os modular\test_os modular"
for path,dirs,files in os.walk(path):
#Output absolute path
print(path)
#folder
print(dirs)
#Files in folders
print(files)
print("\n")
5)os.path.exists(path)
- Meaning: pass in a path path to judge whether the directory under the specified path exists. Returns True if it exists; otherwise, returns False;
path1 = 'C:\Users\Desktop\publish\os modular\huang_wei'
if os.path.exists(path1):
print("The specified folder does not exist")
else:
print("The specified folder does not exist")6)os.mkdir(path)
- Meaning: pass in a path path to create a single-layer (single) folder;
- Note: if the folder already exists, an error will be reported. Therefore, before creating a folder, you need to use OS path. The exists (path) function determines whether the folder exists;
os.getcwd() path1 = os.getcwd()+"\\huang_wei" os.mkdir(path1)
7)os.rmdir(path)
- Meaning: pass in a path and delete the folder under the specified path;
- Note: this method can only delete empty folders. Deleting non empty folders will report an error;
path1 = os.getcwd()+"\\huang_wei" os.rmdir(path1) ---------------------------------- path2 = os.getcwd()+"\\a\\b\\c" os.rmdir(path2)
8)os.path.join(path1,path2)
- Meaning: pass in two path paths and splice the paths to form a new complete path;
path = os.getcwd()
lis = ["a.jpg","b.jpg","c.jpg"]
for i in lis:
x = os.path.join(path,i)
print(x)9)os.path.split(path)
- Meaning: pass in a complete path and split it into absolute path and file name {2 parts;
path1 = r"C:\Users\Huang Wei\Desktop\publish\os modular\a.jpg" os.path.split(path1)
10)os.path.dirname(path)
- Meaning: pass in a complete file path and only get its absolute path;
path1 = r"C:\Users\Desktop\publish\os modular\a.jpg" os.path.dirname(path1) #The output result is: C:\Users\Desktop\publish\os module
11)os.path.basename(path)
- Meaning: pass in a complete file path and only get its file name;
path1 = r"C:\Users\Desktop\publish\os modular\a.jpg" os.path.basename(path1) #The output result is: a.jpg
12)os.path.isdir(path)
- Meaning: pass in a complete file path to judge whether it is a folder;
path = os.getcwd()
file_list = os.listdir()
for file in file_list:
if os.path.isdir(file):
print(file)13)os.path.isfile(path)
- Meaning: pass in a complete file path to judge whether it is a file;
path = os.getcwd()
file_list = os.listdir()
for file in file_list:
if os.path.isfile(file):
print(file)14)os.path.getsize(path)
- Meaning: pass in a complete file path and return the size of the file;
os.path.getsize("Compressed package I created.zip")