Python Network Programming
Python provides two levels of access to network services:
1. Low level network services support basic sockets. It provides a standard BSD Sockets API, which can access all methods of the Socket interface of the underlying operating system.
2. The high-level network service module SocketServer provides a server center class, which can simplify the development of network server.
What is a Socket?
Socket is also known as "socket". Applications usually send requests or respond to network requests through "socket", so that hosts or processes on a computer can communicate.
socket() function
In Python, we use the socket() function to create sockets. The syntax format is as follows:
socket.socket([family[, type[, proto]]])
parameter
1. Family: socket family can make AF_UNIX or AF_INET.
2. Type: socket type can be divided into sock according to whether it is connection oriented or non connection oriented_ Stream or SOCK_DGRAM.
3. protocol: generally not filled in. The default value is 0.
Socket object (built-in) method


Simple example
Server
We use the socket function of the socket module to create a socket object. Socket object can set up a socket service by calling other functions.
Now we can specify the port of the service by calling the bind(hostname, port) function.
Next, we call the accept method of the socket object. This method waits for the connection of the client and returns the connection object, indicating that it has connected to the client.
The complete code is as follows:
example
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# File name: server.py
import socket # Import socket module
s = socket.socket() # Create socket object
host = socket.gethostname() # Get local host name
port = 12345 # Set port
s.bind((host, port)) # Binding port
s.listen(5) # Waiting for client connection
while True:
c,addr = s.accept() # Establish client connection
print 'Connection address:', addr
c.send('Welcome to the rookie tutorial!')
c.close() # Close connection
client
Next, let's write a simple client instance to connect to the service created above. The port number is 12345.
The socket.connect(hosname, port) method opens a TCP connection to the service provider whose host is hostname and port is port. After connecting, we can get data from the server. Remember, we need to close the connection after the operation is completed.
The complete code is as follows:
example #!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # File name: client.py import socket # Import socket module s = socket.socket() # Create socket object host = socket.gethostname() # Get local host name port = 12345 # Set port number s.connect((host, port)) print s.recv(1024) s.close()
Now let's open two terminals. The first terminal executes the server.py file:
$ python server.py
The second terminal executes the client.py file:
$ python client.py Welcome to the rookie tutorial!
When we open the first terminal again, we will see the following information output:
Connection address: ('192.168.0.118', 62461)
Python Internet module
Some important modules of Python Network programming are listed below:
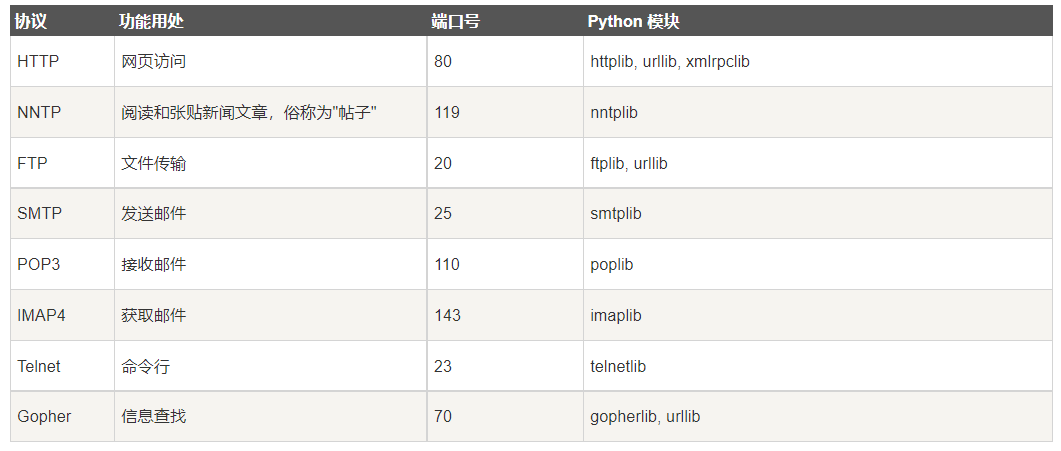
As for the simple instance, it can't run on the Mac. Several errors are reported and modified.
server.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import socket
# Establish a server
server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
server.bind(('localhost',6999)) #Bind the port to listen on
server.listen(5) #Start listening indicates that five links can be queued
while True:# conn is a link instance linked by the client and generated on the server
conn,addr = server.accept() #There will be problems when waiting for links. In fact, two values are returned
print(conn,addr)
while True:
try:
data = conn.recv(1024) #receive data
print('recive:',data.decode()) #Print received data
conn.send(data.upper()) #Then send the data
except ConnectionResetError as e:
print('Closed the busy link!')
break
conn.close()
client.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import socket# The client sends a data and receives another data
client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM) #Declare socket type and generate link object at the same time
client.connect(('localhost',6999)) #Establish a link to the local port 6969
while True:
# addr = client.accept()
# print 'connection address:', addr
msg = 'Welcome to the rookie tutorial!' #strip takes out the leading and trailing spaces of the string by default
client.send(msg.encode('utf-8')) #Send a message. Python 3 only receives btye streams
data = client.recv(1024) #Receive a message and specify that the received size is 1024 bytes
print('recv:',data.decode()) #Output the information I received
client.close() #Close this link
All simple instances are modified.
Server:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import sys
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf8')
import socket
# Establish a server
server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
server.bind(('localhost',9090)) #Bind the port to listen on
server.listen(5) #Start listening indicates that five links can be queued
while True:# conn is a link instance linked by the client and generated on the server
conn,addr = server.accept() #There will be problems when waiting for links. In fact, two values are returned
print(conn,addr)
while True:
data = conn.recv(1024) #receive data
print('recive:',data.decode()) #Print received data
conn.send(data.upper()) #Then send the data
conn.close()
client:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import sys
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf8')
import socket# The client sends a data and receives another data
client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM) #Declare socket type and generate link object at the same time
client.connect(('localhost',9090)) #Establish a link to the local port 6969
while True:
# addr = client.accept()
# print 'connection address:', addr
msg = 'Welcome to the rookie tutorial!' #strip takes out the leading and trailing spaces of the string by default
client.send(msg.encode('utf-8')) #Send a message. Python 3 only receives btye streams
data = client.recv(1024) #Receive a message and specify that the received size is 1024 bytes
print('recv:',data.decode()) #Output the information I received
client.close() #Close this link