Several common Excel libraries openpyxl, xlrd/xlwt, xlwings and xlsxwriter are explained in detail.
In order to further understand the similarities and differences of each library, so that it can be used flexibly in different scenarios, this paper will horizontally compare 7 common modules that can operate Excel files, and consolidate learning while comparing the common operations of each module!
First, let's grasp the characteristics of different libraries as a whole
"-
Xlrd, xlwt and xlutils have their own limitations, but they complement each other and cover Excel files, especially xls file operation. Xlwt# can be generated xls , file, xlrd , can read existing files xls , file, xlutils , connects two modules , xlrd , and , xlwt , so that users can read and write one at the same time xls file. In short, xlrd is responsible for reading, xlwt is responsible for writing, and xlutils is responsible for providing assistance and connection
-
xlwings , can easily read and write the data in Excel files, and can modify the cell format
-
XlsxWriter , is a tool for writing xlsx} file format module. It can be used to write text, numbers and formulas, and supports cell formatting, pictures, charts, document configuration, automatic filtering and other features. But it cannot be used to read and modify Excel files
-
openpyxl} through the workbook "workbook - sheet - cell" mode xlsx# files can be read, written and changed, and the style can be adjusted
-
pandas is no stranger to us. It is a powerful module for data processing and analysis. Sometimes it can also be used to automate Excel processing
If you are too lazy to look at the detailed comparison process, you can directly look at the final summary chart, and then pull it to the end of the article to collect some praise, even if you learn it
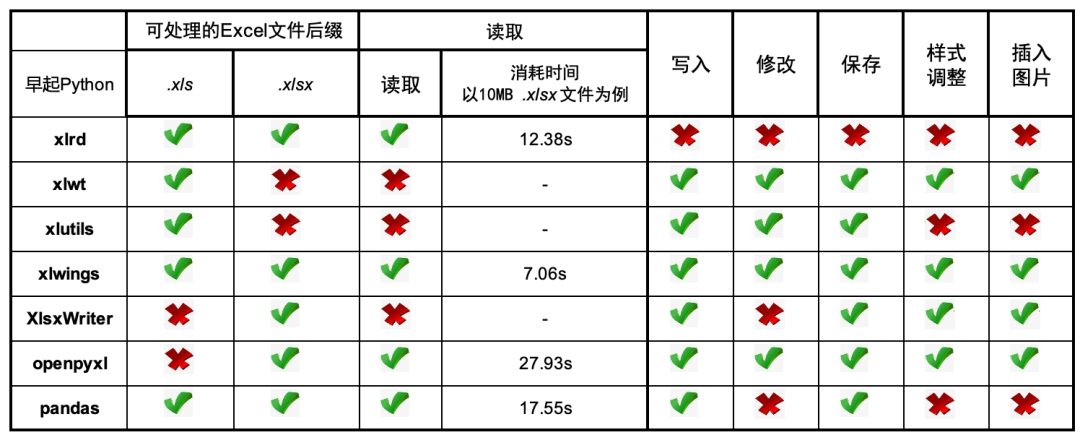
1, Installation
All 7 modules are non-standard libraries, so they need to be installed in {pip} on the command line:
pip install xlrd pip install xlwt pip install xlutils pip install xlwings pip install XlsxWriter pip install openpyxl pip install pandas
Two. Module import
Most modules can be imported directly by name, and some modules use abbreviations:
import xlrd import xlwt import xlwings as xw import xlsxwriter import openpyxl import pandas as pd
The xlutils module is the bridge between xlrd and xlwt and its core function is to copy a copy read into memory through xlrd Xls , object, and then copy the object through , xlwt , modification The contents of the xls# table. Xlutils , can copy and convert the Book object of , xlrd , into the Workbook object of , xlwt , and usually import the , copy , sub module in the module:
import xlutils.copy
3, Read Excel file
3.1 obtaining documents
Not all 7 modules can read Excel files, and even if they can read Excel files, they should be discussed by different suffixes, as follows:
"-
xlwt, xlutils, XlsxWriter cannot read the file
-
xlrd# can be read xls # and xlsx file
-
xlwings # can be read xls # and xlsx file
-
openpyxl} can read xlsx file
-
pandas} can be read xls # and xlsx file
The following uses two 10MB xls # and xlsx} file to test:
xls_path = r'C:\xxx\Desktop\test.xls' xlsx_path = r'C:\xxx\Desktop\test.xlsx'
3.1.1}xlrd# reading files
xlrd# can be read xls # and xlsx file
xls = xlrd.open_workbook(xls_path) xlsx = xlrd.open_workbook(xlsx_path)
3.1.2 # xlwings # reading files
xlwings , directly connects to apps, that is, excel applications, and then work books and worksheet sheets. xlwings , requires an environment with Excel applications installed. xlwings , can read xls # and xlsx file
app = xw.App(visible=True, add_book=False) #The program is visible. Only open without creating a new workbook app.display_alerts = False #Warning off app.screen_updating = False #Screen update off # wb = app.books.open(xls_path) wb = app.books.open(xlsx_path) wb.save() #Save file wb.close() #Close file app.quit() #Close program
3.1.3 openpyxl read file
openpyxl} can read xlsx file
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(xlsx_path)
If read xls# file will report an error:
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(xls_path)
openpyxl.utils.exceptions.InvalidFileException: openpyxl does not support the old .xls file format, please use xlrd to read this file, or convert it to the more recent .xlsx file format.
3.1.4 # pandas # read files
pandas} can be read xls # and xlsx file
xls = pd.read_excel(xls_path, sheet_name='Sheet1') xlsx = pd.read_excel(xlsx_path, sheet_name='Sheet1')
Next, compare the four modules and read 10MB under the same configuration computer The time of xlsx# file (running for 3 times to get the average value), and the code used is:
import time
import xxx
time_start = time.time()
xxx
time_end = time.time()
print('time cost: ', time_end-time_start, 's')
The final test result is that xlwings , is the fastest to read 10MB files, xlrd , is the second, and openpyxl , is the slowest (depending on the computer, the results are for reference only)
The table read into the Excel file is summarized as follows: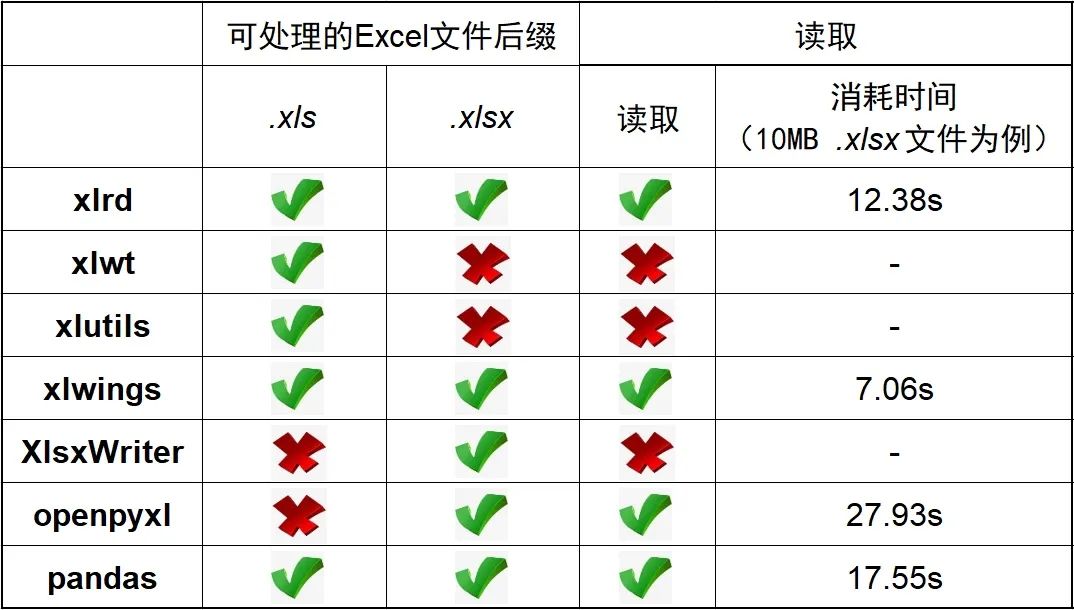
3.2 obtaining worksheets
For the above four modules that can read Excel files, the way to obtain worksheet sheet is further discussed
3.2.1}xlrd) get worksheet
You can find by sheet name:
sheet = xlsx.sheet_by_name("Sheet1")
You can also find by index:
sheet = xlsx.sheet_by_index(0)
3.2.2 # xlwings # get worksheet
xlwings # worksheets are divided into active worksheets and specific worksheets under the specified Workbook:
sheet = xw.sheets.active #In the active workbook sheet = wb.sheets.active #In a specific Workbook
3.2.3 openpyxl get worksheet
The. active method gets the first worksheet of the workbook by default
sheet = wb.active
In addition, you can also obtain the worksheet by specifying the worksheet name:
sheet = wb['Sheet1']
3.2.4 # pandas # get worksheet
There is no {pandas} thing about getting the worksheet alone, because the worksheet has been and must be specified to read when reading the file:
xlsx = pd.read_excel(xlsx_path, sheet_name='Sheet1')
4, Create Excel file
Briefly summarize the creation of Excel files:
"-
xlrd, xlutils , cannot create Excel file
-
xlwt} can only be created xls file, cannot be created xlsx file
-
xlwings can be created xls # and xlsx file
-
XlsxWriter , can create xlsx file
-
openpyxl} can create xls # and xlsx file
-
pandas} does not have the concept of creating Excel, but can be generated when stored xls or xlsx file
4.1}xlwt} creating files
xlwt} can only be created xls file, cannot be created xlsx file
xls = xlwt.Workbook(encoding= 'ascii')
#Create a new sheet table
worksheet = xls.add_sheet("Sheet1")
4.2 # xlwings # create files
xlwings can be created xls # and xlsx# file, you only need to write the suffix clearly when saving it last. Use the following command:
wb = app.books.add()
Whether you create or open a new workbook, you need to save the workbook, close the workbook, and close the program, that is:
wb.save(path + r'\new_practice.xlsx') wb.close() app.quit()
4.3. XlsxWriter create file
XlsxWriter , can create xlsx} file:
xlsx = xlsxwriter.Workbook()
#Add sheet
sheet = xlsx .add_worksheet('Sheet1')
4.4 openpyxl file creation
openpyxl can create xls # and xlsx# file, you only need to write the suffix clearly when saving it last. Use the following command:
wb = Workbook() #The worksheet is created as specified in the new workbook sheet = wb.active
4.5. pandas} create file
Pandas # only need to write the suffix clearly at the last transfer. In fact, pandas} does not need to create an excel file at the beginning. It can be used after various operations around the data frame to_ Use Excel command again xls # or xlsx# as file suffix. If you must generate a blank excel file, you can use the following command:
df = pd.DataFrame([]) df.to_excel(r'C:\xxx\test1.xlsx')
5, Save file
Briefly summarize the saving of Excel files:
"-
xlrd# cannot save Excel file
-
xlwt} can be saved xls file
-
xlutils , can copy , xlrd , objects as , xlwt , objects and save them xls file
-
xlwings can be saved xls # and xlsx file
-
XlsxWriter} can save xlsx file
-
openpyxl} can be saved xlsx file
-
pandas # can be saved xls # or xlsx file
5.1}xlwt} saving documents
xlwt} can be saved xls file
# xls = xlwt.Workbook(encoding= 'ascii')
# worksheet = xls.add_sheet("Sheet1")
xls.save("new_table.xls")
5.2 xlutils save files
xlutils , can copy , xlrd , objects as , xlwt , objects and save them xls file
# xls_path = r'C:\xxxx\test.xls'
# xls = xlrd.open_workbook(xls_path)
xls_xlutils = xlutils.copy.copy(xls)
xls_xlutils.save('new_text.xls')
5.3 # xlwings# save files
xlwings can be saved xls # and xlsx file
# wb = app.books.open(xls_path) wb = app.books.open(xlsx_path) wb.save() #Save file wb.close() #Close file app.quit() #Close program
5.4 XlsxWriter save file
XlsxWriter} can save xlsx# file After the close command is executed, the file is saved while it is closed:
# xlsx = xlsxwriter.Workbook()
# sheet = xlsx .add_worksheet('Sheet1')
xlsx.close()
5.5 openoyxl saving files
openpyxl} can be saved xlsx file
# wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(xlsx_path)
# wb = Workbook()
# sheet = wb.active
wb.save('new_test.xlsx')
6. pandas} save files
pandas # can be saved xls # or xlsx file
df1 = pd.DataFrame([1, 2, 3]) df2 = pd.DataFrame([1, 2, 4]) df1.to_excel(r'C:\xxxx\test1.xls') df2.to_excel(r'C:\xxxx\test2.xlsx')
6, Gets the value of the cell
The basic premise of obtaining cell values is to be able to read files, so it is basically introduced around {xlrd, xlwings, openpyxl and pandas}. xlutils due to the ability to copy one Xls , therefore, you can use exactly the same method of reading cells as xlrd , xls , xlrd ,.
6.1. xlrd/xlutils get cells
xlutils , because it is a direct copy of an object that , xlrd , applies to, the method used to read cells is exactly the same as , xlrd ,. xlwt# does not have the ability to read cells
# xls = xlrd.open_workbook(xls_path)
# sheet = xlsx.sheet_by_name("Sheet1")
value = sheet.cell_value(4, 6) #Cell in row 5, column 7
print(value)
rows = table.row_values(4)
cols = table.col_values(6)
for cell in rows:
print(cell)
6.2. xlwings , get cells
# app = xw.App(visible=True, add_book=False)
# app.display_alerts = False
# app.screen_updating = False
# wb = app.books.open(xls_path)
# sheet = wb.sheets.active
#Gets the value of a single cell
A1 = sheet.range('A1').value
print(A1)
#Gets the value of multiple horizontal or vertical cells and returns a list
A1_A3 = sheet.range('A1:A3').value
print(A1_A3)
#Get the values of multiple cells in a given range, return a nested list, and list by behavior
A1_C4 = sheet.range('A1:C4').value
print(A1_C4)
#Gets the value of a single cell
A1 = sheet.range('A1').value
print(A1)
#Gets the value of multiple horizontal or vertical cells and returns a list
A1_A3 = sheet.range('A1:A3').value
print(A1_A3)
#Get the values of multiple cells in a given range, return a nested list, and list by behavior
A1_C4 = sheet.range('A1:C4').value
print(A1_C4)
6.3 openpyxl get cells
# wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(xlsx_path) # wb = Workbook() # sheet = wb.active #I. value of specified coordinate range cells = sheet['A1:B5'] #II. Specify the value of the column cells = sheet['A'] cells = sheet['A:C'] #III. value of specified line cells = sheet[5] cells = sheet[5:7] #Gets the value of the cell for cell in cells: print(cell.value)
6.4 , pandas , get the value of the cell
Pandas: after reading the Excel file, convert it into a data frame object. The method of parsing the content is basically the knowledge points in the pandas system, such as iloc() . loc() . (IX) etc.:
print(df1.iloc[0:1, [1]]) print(df1.loc['b']) print(df2.ix['a', 'a']) #Some versions cancel ix and can use iat
7, Write data
Let's briefly summarize the writing of data to Excel files:
"-
xlrd# cannot write data
-
xlwt# can write data
-
xlutils , can borrow the , xlwt , method to write data
-
xlwings can write data
-
XlsxWriter # can write data
-
openpyxl} can write data
-
pandas} after reading Excel files as data frames, it abstracts the data frame level for operation, and there is no concept of writing and modifying excel cells
7.1. xlwt/xlutils write data
# xls = xlrd.open_workbook(xls_path)
# xls_xlutils = xlutils.copy.copy(xls)
# sheet = xls_xlutils.sheet_by_name("Sheet1")
# value = sheet.cell_value(4, 6)
# print(value)
sheet.write(4, 6, "New content")
7.2 # xlwings # write data
# app = xw.App(visible=True, add_book=False)
# app.display_alerts = False
# app.screen_updating = False
# wb = app.books.open(xls_path)
# sheet = wb.sheets.active
#Write 1 cell
sheet.range('A2').value = 'Daming'
#Write one row or column to multiple cells
#Horizontal write A1:C1
sheet.range('A1').value = [1,2,3]
#Longitudinal write A1:A3
sheet.range('A1').options(transpose=True).value = [1,2,3]
#Write multiple cells in range
sheet.range('A1').options(expand='table').value = [[1,2,3], [4,5,6]]
7.3 , XlsxWriter , write data
New in code_ Format , is the preset style, which will be described below
# xlsx = xlsxwriter.Workbook()
# sheet = xlsx .add_worksheet('Sheet1')
#I. write a single cell
sheet.write(row, col, data, new_format)
#A1: insert data from cell A1 and insert by row
sheet.write_row('A1', data, new_format)
#A1: insert data from cell A1 and insert by column
sheet.write_column('A1', data, new_format)
7.4. openpyxl} write data
# wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(xlsx_path) # wb = Workbook() # sheet = wb.active #I. write cell cell = sheet['A1'] cell.value = 'Business requirements' #II. Write one or more lines of data data1 = [1, 2, 3] sheet.append(data1) data2 = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] sheet.append(data2)
8, Style adjustment
Simply summarize the adjustment of Excel file style:
"-
xlrd and xlutils , can't adjust the style (it can also be said that xlutils , can, but it just borrows the method of , xlwt ,)
-
xlwt# you can adjust the style
-
xlwings can adjust the style
-
XlsxWriter} can adjust the style
-
openpyxl# can adjust the style
-
pandas} cannot adjust style
8.1}xlwt} adjust style
xlwt# supports adjusting font, border, color and other styles
#Font part #Initialize style style1 = xlwt.XFStyle() #Create fonts for styles font = xlwt.Font() font.name = 'Times New Roman' #typeface font.bold = True #Bold font.underline = True #Underline font.italic = True #Italics #Set style style1.font = font #Use style sheet.write(4, 6, "New content 1", style1) #Border part borders = xlwt.Borders() #Set Linetype borders.left = xlwt.Borders.DASHED borders.right = xlwt.Borders.DASHED borders.top = xlwt.Borders.DASHED borders.bottom = xlwt.Borders.DASHED #Set Swatch borders.left_colour = 0x40 borders.right_colour = 0x40 borders.top_colour = 0x40 borders.bottom_colour = 0x40 # style2 = xlwt.XFStyle() style2.borders = borders #Use style sheet.write(5, 8, "New content 2", style2)
8.2 # xlwings # adjust style
Briefly introduce # xlwings # the adjustment of color:
#Get color
print(sheet.range('C1').color)
#Set color
sheet.range('C1').color = (255, 0, 120)
#Clear color
sheet.range('C1').color = None
8.3 XlsxWriter adjustment style
XlsxWriter , contains a large number of functions. You can modify the style of high definition customization on the worksheet after creating the worksheet:
new_format = xlsx.add_format({
'bold': True, #Bold font
'border': 1, #Cell border width
'align': 'left', #Horizontal alignment
'valign': 'vcenter', #Vertical alignment
'fg_color': '#F4B084', #Cell background color
'text_wrap': True #Auto wrap
})
sheet.write(row, col, data, new_format)
8.4 openpyxl adjust style
openpyxl} styles mainly include font, border, paragraph alignment style, etc
#Font style from openpyxl.styles import Font cell = sheet['A1'] font = Font(name='Arial', size=12, bold=True, italic=True, color='FF0000') cell.font = font #Paragraph alignment from openpyxl.styles import Alignment cell = sheet['B2'] alignment = Alignment(horizontal='center', vertical='center', text_rotation=45, wrap_text=True) cell.alignment = alignment #Border style from openpyxl.styles import Side, Border cell = sheet['B2'] side1 = Side(style='thin', color='FF0000') side2 = Side(style='dashed') border = Border(left=side1, right=side1, top=side2, bottom=side2) cell.border = border
9, Insert picture
Briefly summarize the situation of inserting pictures into Excel files:
"-
xlrd and xlutils , can't adjust the style (it can also be said that xlutils , can, but it just borrows the method of , xlwt ,)
-
xlwt# can be inserted bmp} picture
-
xlwings can insert pictures
-
XlsxWriter , can insert pictures
-
openpyxl# can insert pictures
-
pandas # cannot insert picture
9.1 # xlwt# insert picture
xlwt# inserting a picture requires that the picture format must be bmp} format can be inserted successfully
sheet.insert_bitmap("test.bmp", 2, 3, 2, 2, 0.5, 0.5)
insert_bitmap(img, x, y, x1, y1, scale_x, scale_y)img_represents the image address to be inserted, x_represents the row, y_represents the column x1, y1_represents the pixel scale shifted downward and right from the original position_ x scale_ Y represents the ratio of width to height relative to the original image, and the image can be enlarged or reduced
9.2 # xlwings # insert picture
The following is the code for inserting pictures with xlwings , where you can specify the location
sheet.pictures.add(r'C:\\xxx.jpg')
#You can also insert at a given location
sheet.pictures.add(r'C:\\xxx.jpg', left=sheet.range('A2').left, top=sheet.range('A2').top, width=100, height=100)
9.3 XlsxWriter insert picture
The first parameter is the starting cell to insert, and the second parameter is the absolute path of the picture file
sheet.insert_image('A1', r'C:\\xxx.jpg')
9.4 openpyxl insert picture
openpyxl can also insert specified pictures into Excel and modify the size
from openpyxl.drawing.image import Image
img = Image('test.jpg')
newsize = (180, 360)
img.width, img.height = newsize #Set the width and height of the picture
sheet.add_image(img, 'A2') #Insert picture into A2 cell
Summary
The above is all about the comparison of common Excel operations according to different Python modules. The final results are summarized in the table below
