pandas: https://www.jianshu.com/p/840ba135df30
Learning direction: https://blog.csdn.net/zhiguigu/article/details/117924606
I. Basic Knowledge
Chapter 1 starting
1.1 setting up programming environment
https://www.python.org/
1.2 build Python programming environment in different operating systems
. . .
-Download geony https://www.geany.org/download/releases/
Check the installation path of computer software: https://m.kafan.cn/A/dv86l6qe3o.html
Chapter 2 variables and simple data classes
2.1 run hello_world.py
print is the name of a function, so it is displayed in blue; It knows "Hello Python world!" Is not Python code, so make it explicit
It is shown in orange. This function is called grammatical prominence
2.2 variables

2.3 string
A string is a series of characters. In Python, strings are enclosed in quotation marks, which can be single quotation marks or double quotation marks

2.3.1 use the method to modify the case of the string

Methods are operations that Python can perform on data.
In name In title(), the period after name (.) Let Python perform the operation specified by the method title() on the variable name. Each method is followed by a pair of parentheses because methods usually require additional information to complete
Its work. This information is provided in parentheses. The function title() requires no additional information, so the parentheses after it are empty.
title initial capital
upper all uppercase
lower all lowercase
2.3.2 merge (splice) strings
Note: you can only add strings to strings
full_name = first_name + " " + last_name
print("Hello, " + full_name.title() + "!")
2.3.3 use tabs or line breaks to add white space
In programming, white space generally refers to any non printing characters, such as spaces, tabs and line breaks. You can use white space to organize the output to make it easier to read.
\t causes a line of characters with spaces to be displayed between strings
\n line feed
2.3.4 delete blank
rstrip() ensures that there is no whitespace at the end of the string
lstrip() removes whitespace at the beginning of the string
strip() also removes whitespace at both ends of the string
2.3.5 avoid syntax errors when using strings
Quotation marks are not paired
Note that when writing programs, the syntax highlighting function of the editor can help you quickly find some syntax errors. When you see that Python code is displayed in the color of ordinary sentences, or ordinary sentences are displayed in the color of Python code, you can
Can mean that there is a quotation mark mismatch in the file.
2.3.6 print statement in Python 2

2.4 figures
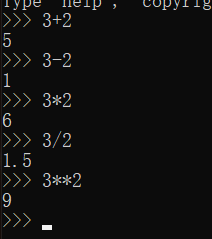
2.4.1 integer
In Python, you can add (+) subtract (-) multiply (*) divide (/) integers
Two multiplication signs indicate a power operation
Sequential execution operation
Spaces do not affect how Python evaluates expressions
2.4.2 floating point number
Python calls numbers with decimal points floating-point numbers.
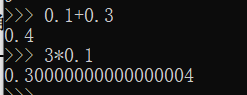
The number of decimal places contained in the result may be uncertain. For now, just ignore the extra decimal places temporarily
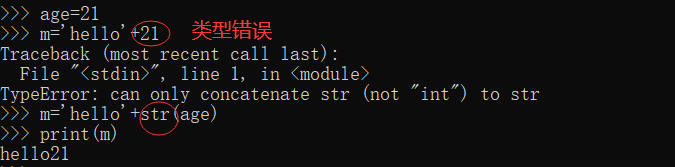
2.4.3 using the function str() to avoid type errors
2.5 notes
Use#
2.6 Zen of Python
Chapter 3 list
3.1 what is the list
A list consists of a series of elements arranged in a specific order.
The list is represented by square brackets ([]) and the elements are separated by commas
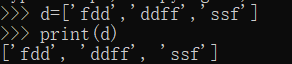
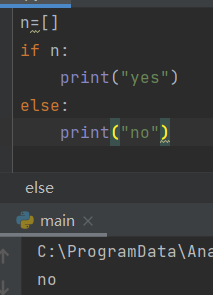
Create an empty list
n=[]
3.1.1 accessing list elements

3.1.2 index starts from 0 instead of 1
In Python, the index of the first list element is 0 instead of 1
Python provides a special syntax for accessing the last list element. By specifying an index of - 1, python returns the last list element
3.1.3 use the values in the list
3.2 modifying, adding and deleting elements
3.2.1 modifying list elements
n=['i','like','apple'] n[2]='orange' print(n)
3.2.2 adding elements to the list
- end
append
- middle
insert
3.2.3 removing elements from the list
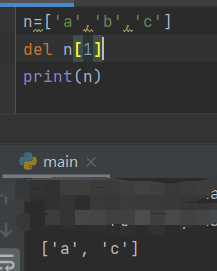
- del
The position of the element to be deleted in the list,
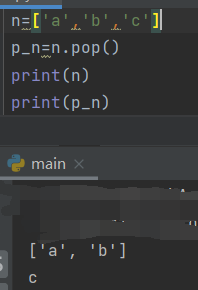
- pop

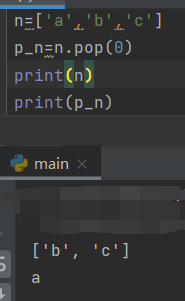
pop() to delete an element anywhere in the list, just specify the index of the element to be deleted in parentheses
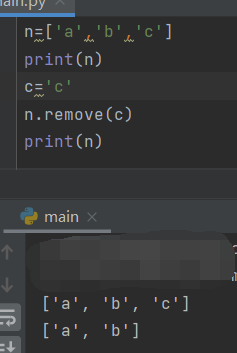
- remove
Delete the specified
The method remove() deletes only the first specified value.
If there is no in the list, it cannot be deleted, and an error will be reported
3.3 organization list
- Permanent sorting
sort in alphabetical order
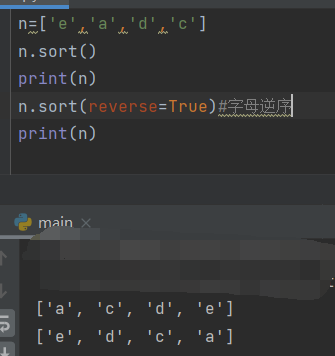
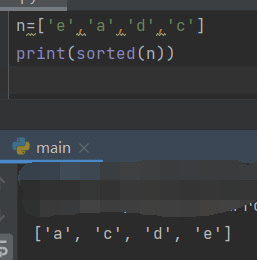
- Temporary sort
soeted
-
sleep

-
length
n=['e','a','d','c'] print(len(n))#4
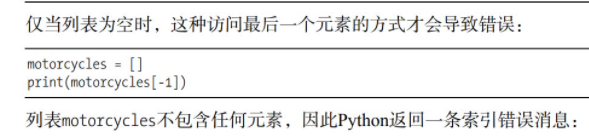
3.4 avoid index errors when using lists


Chapter 4 operation list
4.1 traverse the entire list
for loop
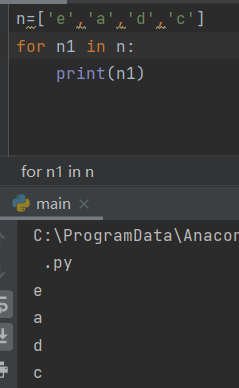
Good command conventions (singular and plural) are better
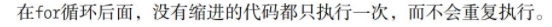
4.2 avoiding indentation errors
- No indent
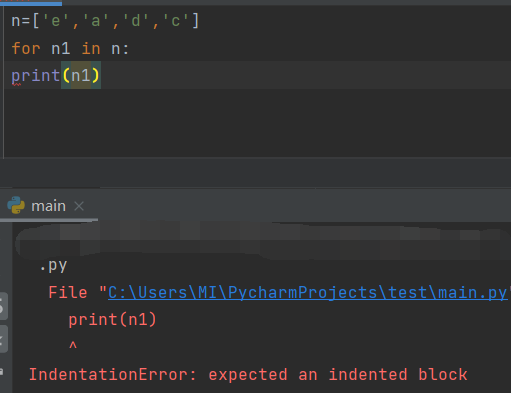
-
Missing colon
-
Unnecessary indentation
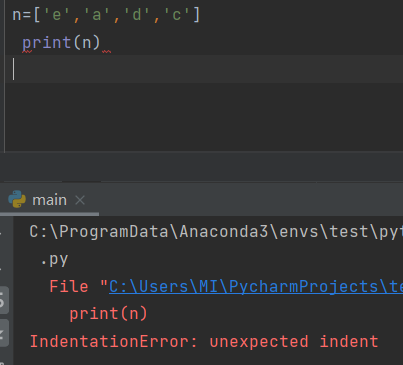
4.3 creating a list of values
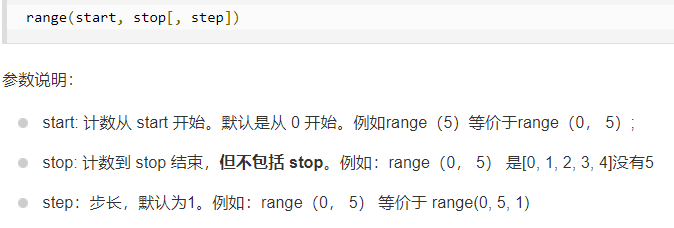
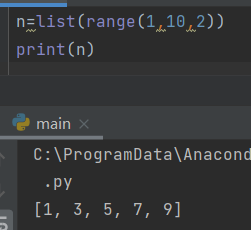
- Create a list of numbers using range()
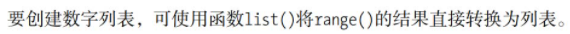
- Simple statistical calculation
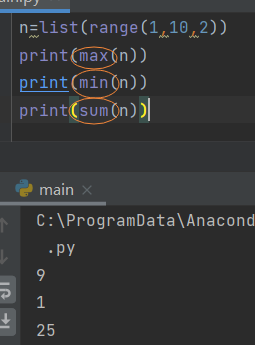
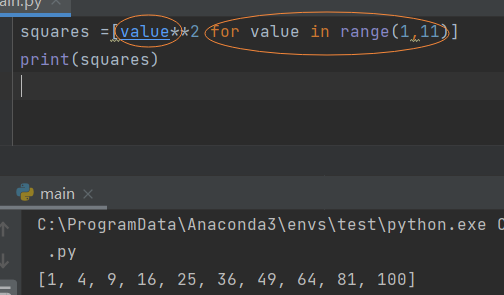
- List parsing
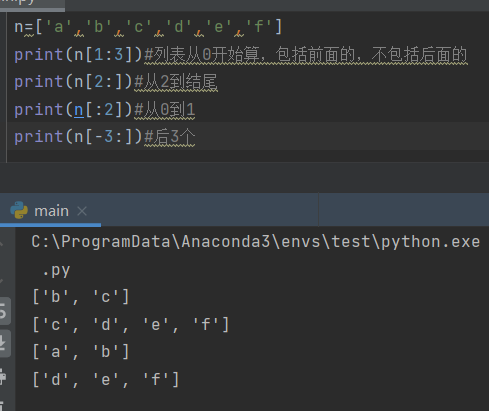
4.4 use part of the list
section
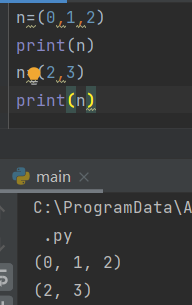
copy
n=['a','b','c','d','e','f'] n2=n[:] #n2=n means to include n2 Association in the list of n print(n) print(n2)
4.5 tuples

Use parentheses
Can redefine
4.6 setting code format
guide
indent
president
Empty line
Chapter 5 if statement
5.2 condition test
1. Characters
- equal

Case sensitive when checking equality in Python,
- Unequal
!=
2. Figures
3. Check multiple
and
or
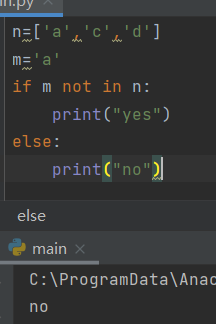
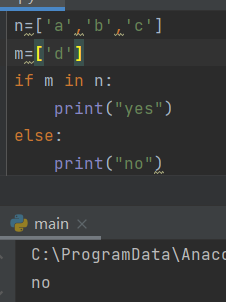
4. Is the specific value in the list
if x in y:
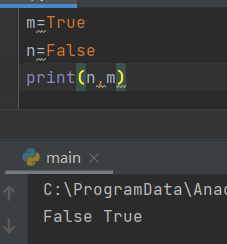
5. Boolean expression
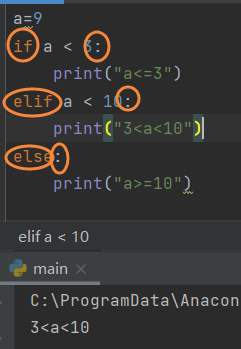
5.3 if statement
5.4 using if statements to process lists
- Check special elements
-Make sure the list is not empty
- Use multiple lists
Chapter 6 dictionary
6.2 using dictionaries
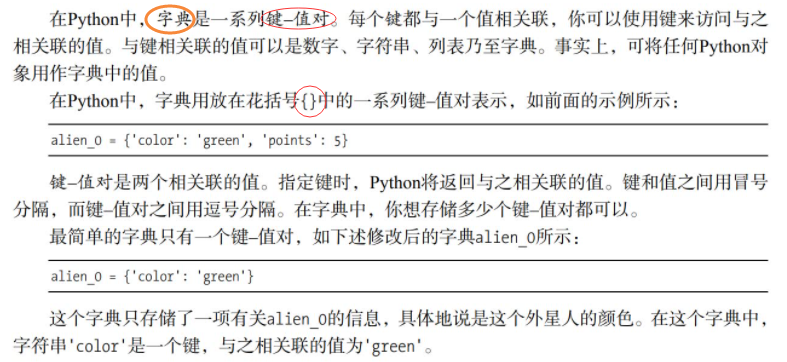
alien = {'color':'red', 'points':5}
print(alien['color']) #Accessing dictionary values
print(alien)
alien['x_position'] = 0 #Add key value pair
alien['y_position'] = 3
print(alien)
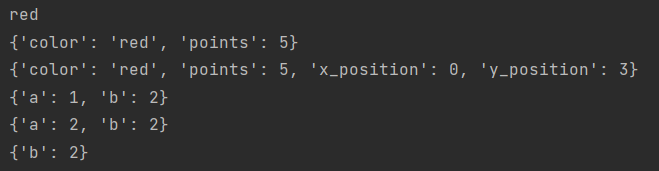
#Create an empty dictionary
m = {}
m['a'] = 1
m['b'] = 2
print(m)
m['a'] = 2 #Modify value
print(m)
del m['a'] #delete
print(m)
6.3 traversal dictionary
- Traverse all key value pairs
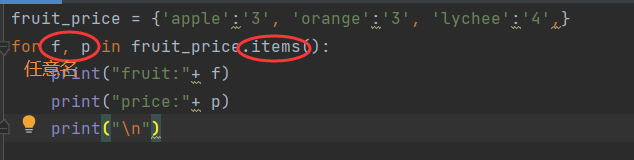
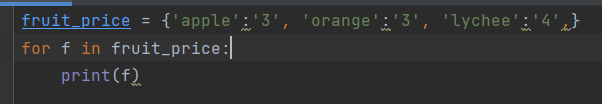
- Traverse all keys
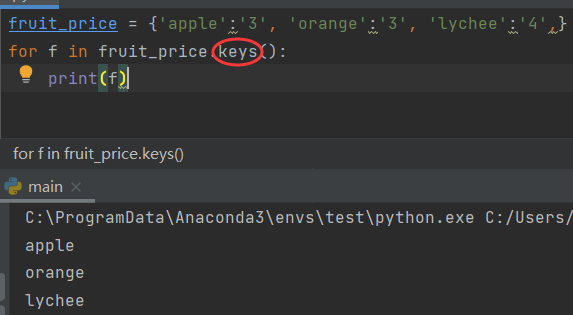 When traversing the dictionary, all keys will be traversed by default,
When traversing the dictionary, all keys will be traversed by default,
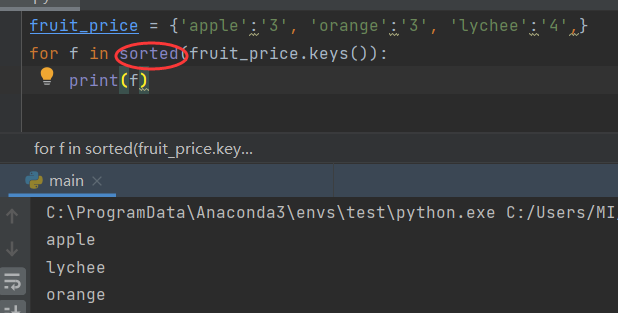
- Traverse all keys in order
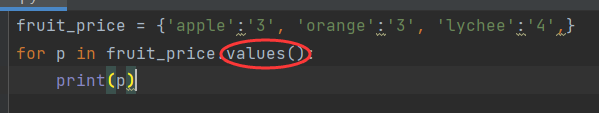
-Traverse all values
set() # eliminates the same value
6.4 nesting
Storing a series of dictionaries in a list or a list as a value in a dictionary is called nesting
Dictionary list
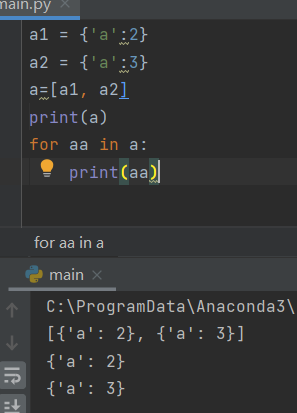
Store list in dictionary
favorite_fruits={
'Jane': ['apple','lychee'],
'May': ['banana','plum'],
'Zoe': ['persimmon'],
}
for n,fs in favorite_fruits.items():
print(n + "'s favorite fruits are:" )
for f in fs:
print("\t"+ f)
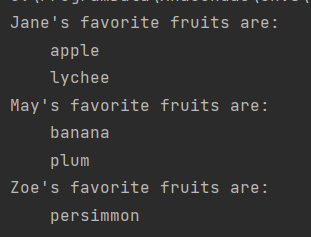
Store dictionary in dictionary

Chapter 7 user input and while loop
7.1 working principle of function input()
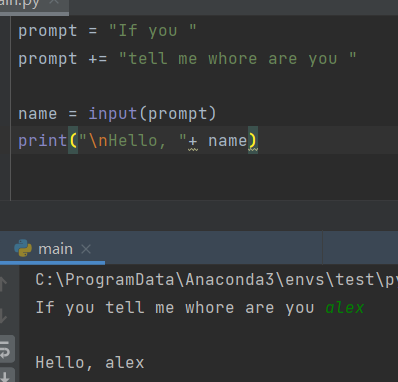
When using the function input(), Python interprets user input as a string.
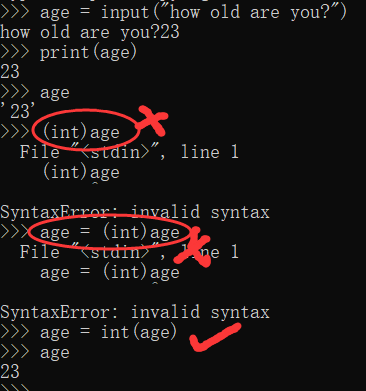
Modular operation
%Divide two numbers and return the remainder:

number = input("Enter a number, and I'll tell you if it's even or odd:")
number = int(number)
if number % 2 == 0:
print(str(number) + " is even.")
else:
print(str(number) + " is old.")
7.2 using the while loop
prompt = "\nTell me something, and I will repeat it back to you:" prompt += "\nEnter 'quit' to end the program. " message = "" while message != 'quit': message = input(prompt) print(message)
Use flag

prompt = "\nTell me something, and I will repeat it back to you:"
prompt += "\nEnter 'quit' to end the program. "
message = ""
active = True
while active:
message = input(prompt)
if message == 'quite':
active = False
else:
print(message)
Use break to exit the loop
Use continue in the loop to jump out of the current loop to the next one
7.3 using the while loop to handle lists and dictionaries
Move elements between lists
unconfirmed_users = ['alex', 'amy', 'zoe']
confirmed_users = []
#unconfirmed_users empty
while unconfirmed_users:
current_user = unconfirmed_users.pop()
print("Verifying user: " + current_user.title())
confirmed_users.append(current_user)
print("\nThe following users have been confirmed:")
for confirmed_user in confirmed_users:
print(confirmed_user.title())
Deletes all list elements that contain a specific value
pets = ['dog', 'cat', 'rabbit', 'cat']
print(pets)
while 'cat' in pets:
pets.remove('cat')
print(pets)
Chapter 8 functions
8.1 function definition

Transmission parameters
Argument and formal parameter
8.2 passing arguments
- Position argument

- Keyword argument
def describe_pet(animal_type, pet_name):
print("\nI have a " + animal_type + ".")
print("My " + animal_type + "'s name is " + pet_name.title() + ".")
describe_pet(animal_type='hamster', pet_name='harry')
describe_pet(pet_name='harry', animal_type='hamster')#That's right
- Default value

The formal parameter with default value in the formal parameter list should be placed in front of the formal parameter without default value, otherwise it will prompt:
SyntaxError: non-default argument follows default argument
def describe_pet( pet_name,animal_type='dog'):
print("\nI have a " + animal_type + ".")
print("My " + animal_type + "'s name is " + pet_name.title() + ".")
describe_pet('willie')
describe_pet('kitty','cat')
8.3 return value

def get_formatted_name(first_name, last_name):
full_name = first_name + ' ' + last_name
return full_name.title()
musician = get_formatted_name('jimi','hendrix')
print(musician)
Return dictionary
def build_person(first_name, last_name):
person = {'first':first_name, 'last':last_name}
return person
musician = build_person('jimi', 'hendrix')
print(musician)
8.4 delivery list
def greet_users(names): for name in names: msg = "Hello, " + name.title() + "!" print(msg) names = ['a','b','c'] greet_users(names)
Modify list in function

Prohibit function modification list
To solve this problem, you can pass a copy of the list to the function instead of the original; Any changes made to this function only affect the copy, not the original.
Slice notation [:] creates a copy of the list
Arbitrary number of arguments passed
def a(*numbers):
print(numbers)
for n in numbers:
print(n)
n=['a','c']
m=[1,2,3]
a(n)
a(m)
a('s','s')
a("s")
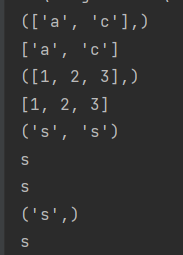
Use any number of keyword arguments p151
8.6 storing functions in modules
impor + py name
153
8.7 function preparation guide

157