Using API, first look at the next interface document

First, the python version 2.7 code
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
import time
import string
import random
import base64
import hashlib
import urllib
from urllib import urlencode
from requests.packages.urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarning
requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings(InsecureRequestWarning)
CommonUrl="https://api.ai.qq.com/fcgi-bin/ocr/ocr_generalocr"
app_id="Fill in your own"
AppKey="Fill in your own"
time_stamp=int(time.time())
nonce_str=''.join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters + string.digits, 15))
def MakeSign():
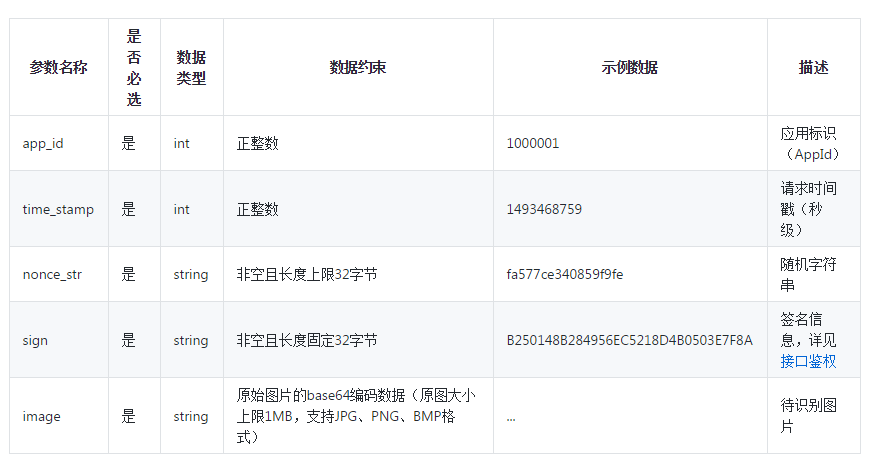
Dict ={'app_id': app_id, 'time_stamp': time_stamp, 'nonce_str': nonce_str, 'image': ImageBase64()}
T_str1 = ""
for key in sorted(Dict.keys()):
if key == 'app_key':
continue
T_str1 = T_str1 + "%s=%s&" % (key, urllib.quote(str(Dict[key]), safe=''))
T_sgin = T_str1 + 'app_key=' + AppKey
signraw=T_sgin.encode("utf-8")
hash_md5 = hashlib.md5()
hash_md5.update(signraw)
sign=hash_md5.hexdigest().upper()
return sign
def ImageBase64():
imagebase64=None
try:
with open("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\xiejiangpeng.pn1g", "rb") as f:
imagebase64 = base64.b64encode(f.read())
except Exception as ex:
print(ex)
exit()
return imagebase64
sign=MakeSign()#autograph
image=ImageBase64()#picture
#Calling OCR Picture Recognition Interface
TengXunAiCommonBody={'app_id':app_id,'time_stamp':time_stamp,'nonce_str':nonce_str,'sign':sign,'image':image}
TengXunAiCommon=requests.post(CommonUrl,TengXunAiCommonBody,verify=False)
try:
temp=TengXunAiCommon.json()["data"]["item_list"][0]["itemstring"]#Designator. Used for judging anomalies
print("The text identified is as follows:")
for i in range(0,len(TengXunAiCommon.json()["data"]["item_list"])):
print(TengXunAiCommon.json()["data"]["item_list"][i]["itemstring"])
except Exception:
print("Program exception.....")
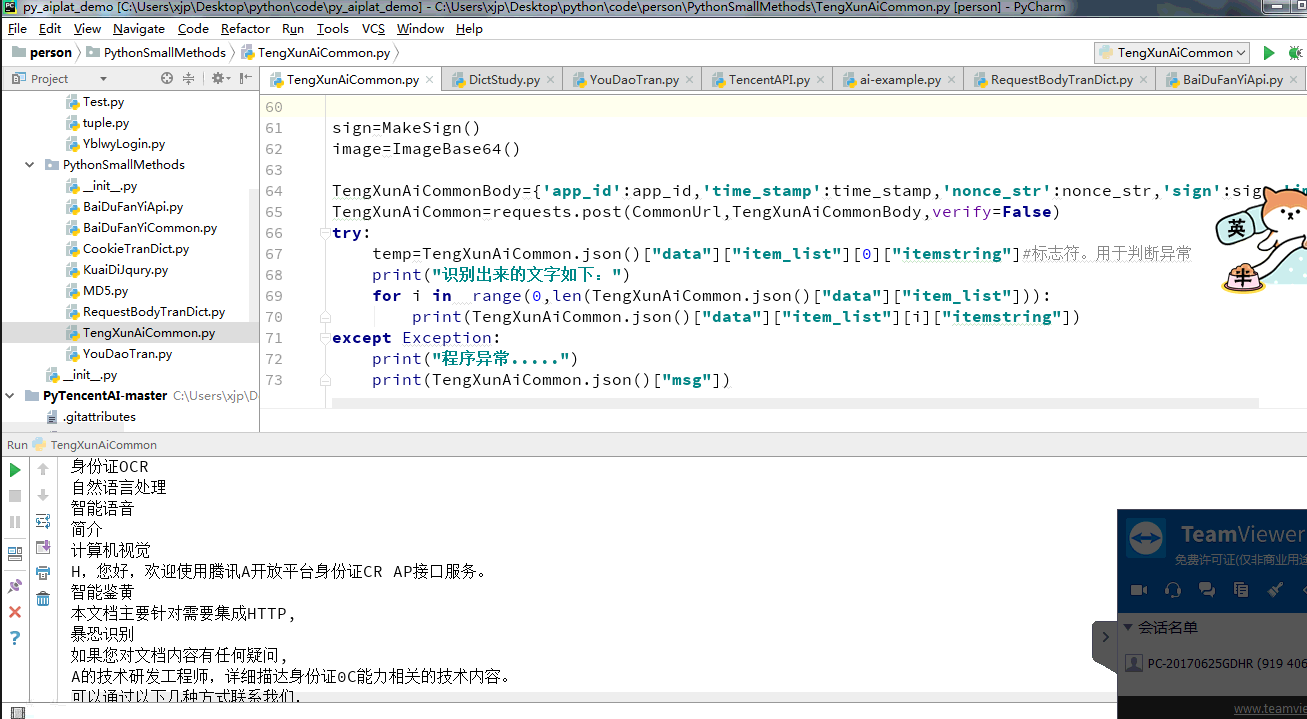
print(TengXunAiCommon.json()["msg"])Operation results:
Picture information

Interface capture record
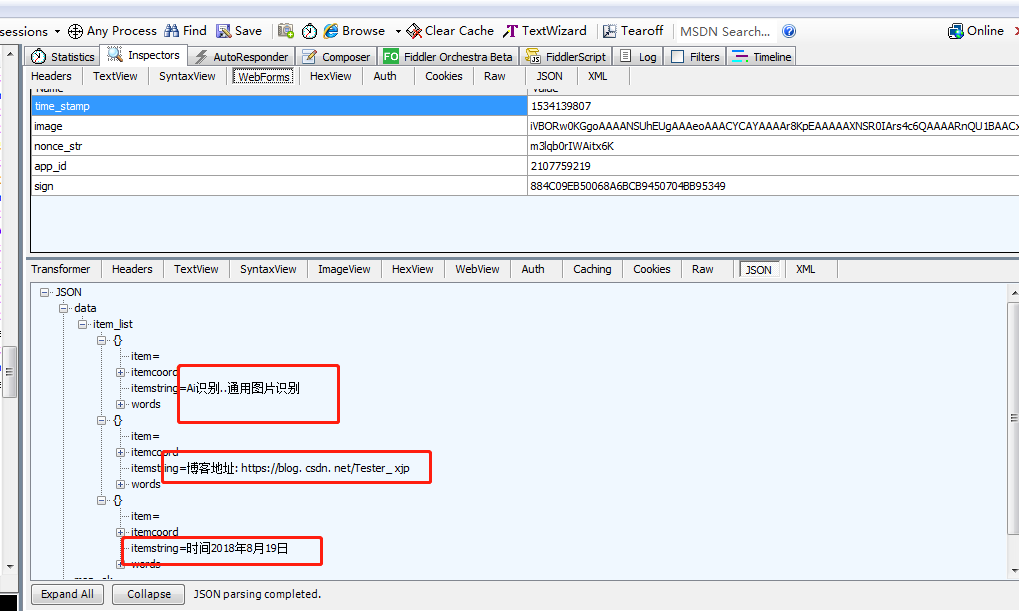
Program console output:
2. Python 3.6 code
This version differs from Python 2.7 in the following points
1. When url encoding strings
The usage in Python 2.x is:
urllib.quote(text)
In Python 3.x
urllib.parse import urlencode from urllib import parse
urllib.parse.quote(text)
2. Python 3. x encodes image with base64, and then the type of byte needs decode to be converted to str. Otherwise, joining the mosaic string will result in an additional b'leading to signature errors
3. Note that url encoding only capitalizes special symbols such as B%27. Others do not need to be capitalized strings.
4. Byte conversion to str requires decode, while str to byte requires encode. In Python 3.6, md5 encryption can only fill in byte format if input str type will make an error.
5. Urlen code (Dict). encode () can also be used directly for dict encoding (by default, value encoding corresponds to this situation).
url encode (dict). encode () first obtains a str from urlencode and then converts it into byte to encrypt md5. This is a relatively simple way. Python 2.7 uses url encoding for a single str. Here is urlencode for dict directly.
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
import time
import string
import random
import base64
import hashlib
#These are urlencode
from urllib.parse import urlencode
from urllib import parse
from requests.packages.urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarning
import urllib
requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings(InsecureRequestWarning)
CommonUrl="https://api.ai.qq.com/fcgi-bin/ocr/ocr_generalocr"
app_id="Fill in your own"
AppKey="Fill in your own"
time_stamp=int(time.time())
nonce_str=''.join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters + string.digits, 15))
T_str1=""
def MakeSign():
Dict={'app_id':app_id,'time_stamp':time_stamp,'nonce_str':nonce_str,'image':ImageBase64()}
#global T_str1
# for key in sorted(Dict.keys()):#Where sorted is looped in ascending order of key
# if key == 'app_key':
# continue
# #Accumulate keys and values other than app_key into url format)
# T_str1 = T_str1+ "%s=%s&" % (key, urllib.parse.quote(str(Dict[key]), safe=''))
# signStr=T_str1+'app_key'+"="+AppKey
# signraw=signStr.encode("utf-8")
# Md5 = hashlib.md5()
# Md5.update(signraw)
# sign = Md5.hexdigest().upper()
# print(sign)
"""Method two python3.x(imagebase64 What is generated after that is byte Instead of str) At the same time, direct to dict Conduct url in value Coding """
Dict = sorted(Dict.items(), key=lambda item: item[0], reverse=False)
Dict.append(('app_key', AppKey))
sha = hashlib.md5()
rawtext = urlencode(Dict).encode("utf-8")
sha.update(rawtext)
sign = sha.hexdigest().upper()
return sign
def ImageBase64():
imagebase64=None
try:
with open("C:\\Users\\xjp\\Desktop\\xiejiangpeng.png", "rb") as f:
imagebase64 = base64.b64encode(f.read()).decode("utf-8")#decode is required or byte is the type
except Exception as ex:
print(ex)
exit()
return imagebase64
sign=MakeSign()
image=ImageBase64()
TengXunAiCommonBody={'app_id':app_id,'time_stamp':time_stamp,'nonce_str':nonce_str,'sign':sign,'image':image}
TengXunAiCommon=requests.post(CommonUrl,TengXunAiCommonBody,verify=False)
try:
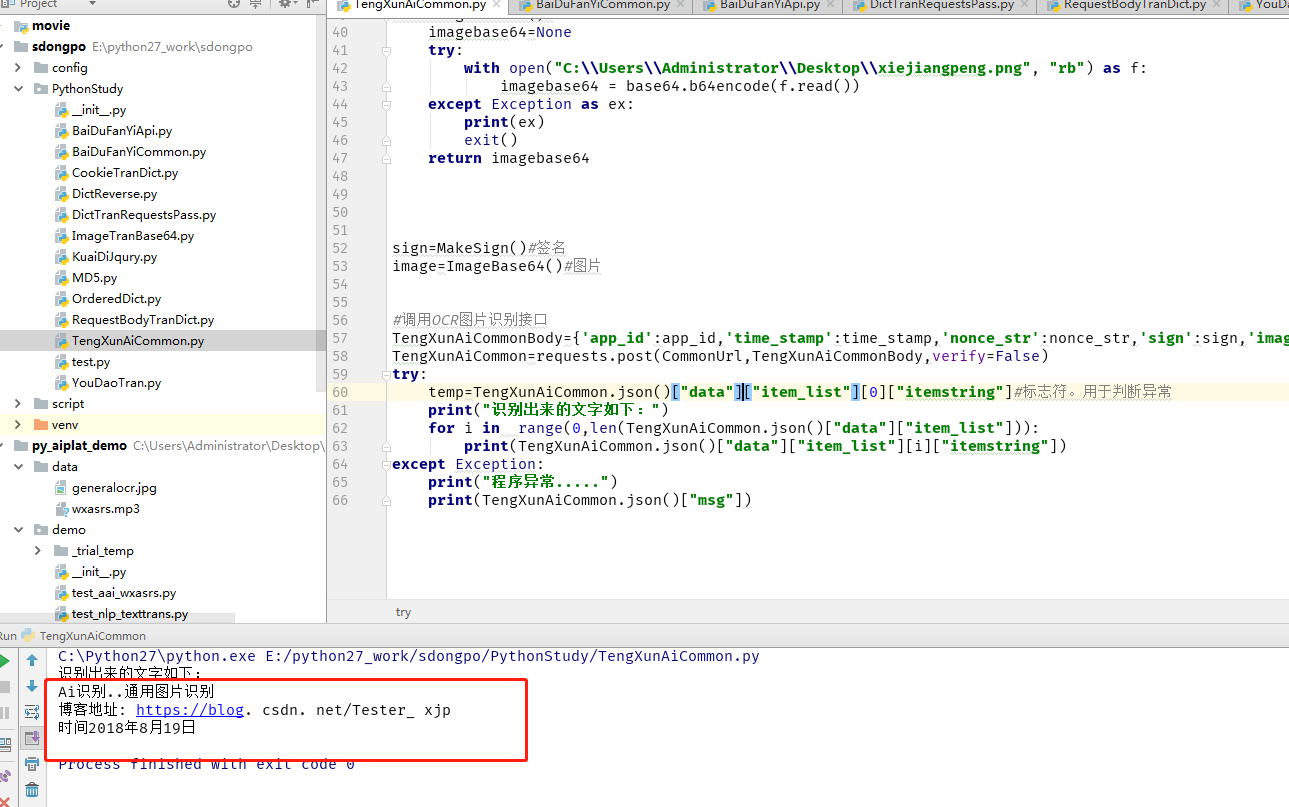
temp=TengXunAiCommon.json()["data"]["item_list"][0]["itemstring"]#Designator. Used for judging anomalies
print("The text identified is as follows:")
for i in range(0,len(TengXunAiCommon.json()["data"]["item_list"])):
print(TengXunAiCommon.json()["data"]["item_list"][i]["itemstring"])
except Exception:
print("Program exception.....")
print(TengXunAiCommon.json()["msg"])The images identified and the results of operation are as follows
Okay, there are so many introductions. The above is just how to create the interface. Next is a small example I quoted: Recognition Graphic Verification Code.
Thoughts are as follows
1. Get the Graphic Verification Code Interface, get the returned Image, and then get the src address of the picture.
2. Save it locally
3. Call Tencent Api for identification.
4. The result of recognition is copied to a parameter, which is the request parameter for sending the verification code.
The code is as follows (python 3.6)
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
import urllib
import string
import random
import base64
import hashlib
import time
#These are urlencode
from urllib.parse import urlencode
from urllib import parse
from requests.packages.urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarning
requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings(InsecureRequestWarning)
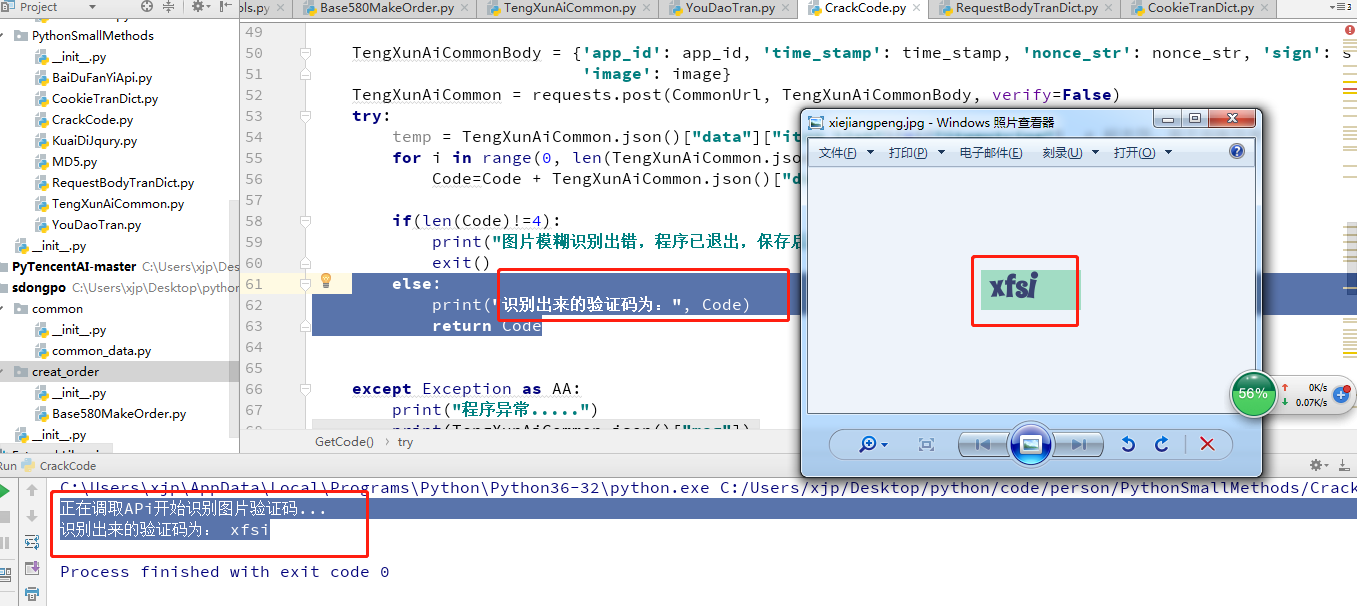
def GetCode(Address):
print("Being transferred APi Start Recognizing Picture Verification Codes...")
CommonUrl = "https://api.ai.qq.com/fcgi-bin/ocr/ocr_generalocr"
app_id = "Fill in your own"
AppKey = "Fill in your own"
time_stamp = int(time.time())
nonce_str = ''.join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters + string.digits, 15))
T_str1 = ""
Code=""
def MakeSign():
Dict = {'app_id': app_id, 'time_stamp': time_stamp, 'nonce_str': nonce_str, 'image': ImageBase64()}
"""python3.x(imagebase64 What is generated after that is byte Instead of str) At the same time, direct to dict Conduct url in value Coding """
Dict = sorted(Dict.items(), key=lambda item: item[0], reverse=False)
Dict.append(('app_key', AppKey))
sha = hashlib.md5()
rawtext = urlencode(Dict).encode("utf-8")
sha.update(rawtext)
sign = sha.hexdigest().upper()
return sign
def ImageBase64():
imagebase64 = None
try:
with open(Address, "rb") as f:
imagebase64 = base64.b64encode(f.read()).decode("utf-8") # decode is required or byte is the type
except Exception as ex:
print(ex)
exit()
return imagebase64
sign = MakeSign()
image = ImageBase64()
TengXunAiCommonBody = {'app_id': app_id, 'time_stamp': time_stamp, 'nonce_str': nonce_str, 'sign': sign,
'image': image}
TengXunAiCommon = requests.post(CommonUrl, TengXunAiCommonBody, verify=False)
try:
temp = TengXunAiCommon.json()["data"]["item_list"][0]["itemstring"] # Designator. Used for judging anomalies
for i in range(0, len(TengXunAiCommon.json()["data"]["item_list"])):
Code=Code + TengXunAiCommon.json()["data"]["item_list"][i]["itemstring"]
if(len(Code)!=4):
print("The program has exited. The address of the saved image is:",Address)
exit()
else:
print("The identified verification code is:", Code)
return Code
except Exception as AA:
print("Program exception.....")
print(TengXunAiCommon.json()["msg"])
print(AA)
exit()
#config
host="https://xxxx.xxxx.com/"
#1. Graphic Verification Code Replacement Interface
Cookie={'grwng_uid': '4b395a4c-cf01-4606-97e0-dc0ad02a7251', 'BS00002_gr_last_sent_cs1': 'BS00002-160', 'BS00002_gr_cs1': 'BS00002-160', 'gr_user_id': '354ca742-c823-4ec4-b449-25e30d6916c9', 'PHPSEGSUPER': '9r0ehinkshmto53hngm0flvp73'}
RGetUrl=requests.get(host+"wapv3/view/captcha?refresh=1",cookies=Cookie,verify=False)
ImageRoute=RGetUrl.json()["url"]
ImageSrc=host+ImageRoute#Get the picture address
#In Python 3, if Python 2 is used, urllib.urlretrieve will replace the source file by default if the same name is used.
urllib.request.urlretrieve(ImageSrc,'C:/Users/xjp/Desktop/xiejiangpeng.jpg')#Save the picture locally
ImageCode=GetCode("C:/Users/xjp/Desktop/xiejiangpeng.jpg")#Calling API Identification Verification Code
Well, finally we get the image code, which is the graphical validation code value, and then you can refer to it.
A diagram of the running result of the attached program