Libraries and tools required and installation
The following libraries and tools will be used:
Tools:
tesseract
Testseract download address: https://digi.bib.uni-mannheim.de/tesseract/
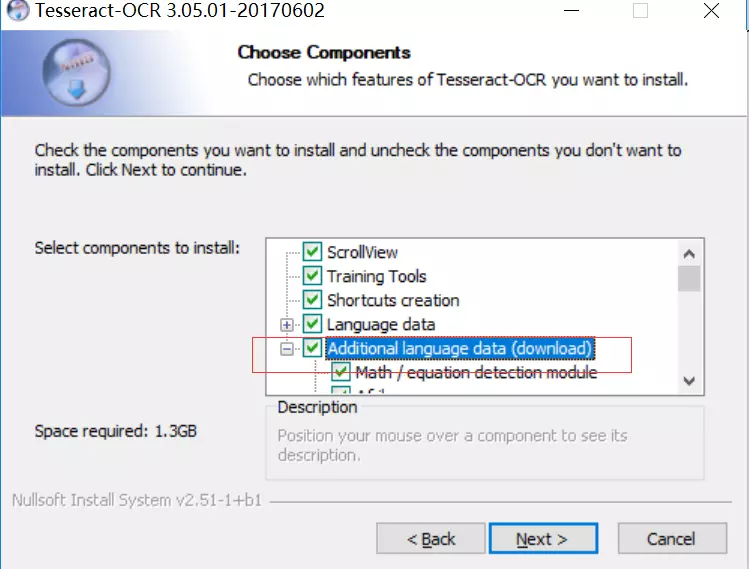
1. Download the non dev exe file suitable for your version (32 or 64 bit), and then install it all the way.
Note: if you need to support multiple languages, check it at this step, and English is supported by default:
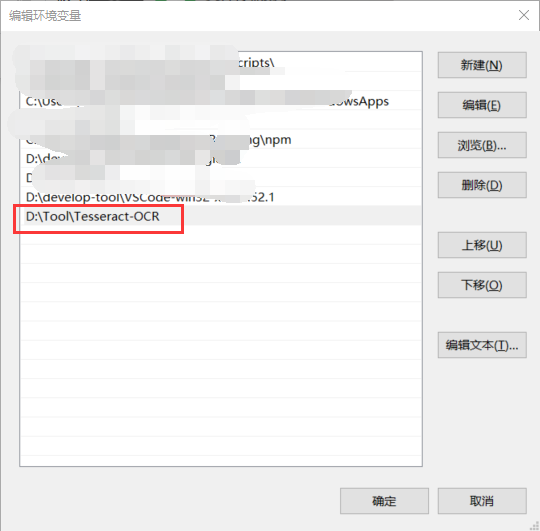
2. Configure environment variables
Configure the installation path of tesseract in path:
3. Verify that the installation was successful:
cmd, and then enter verify testseract and verify that testseract - V displays normally
Pilot and pyteseract Libraries
pip install pillow -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple --trusted-host pypi.douban.com pip install pytesseract -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
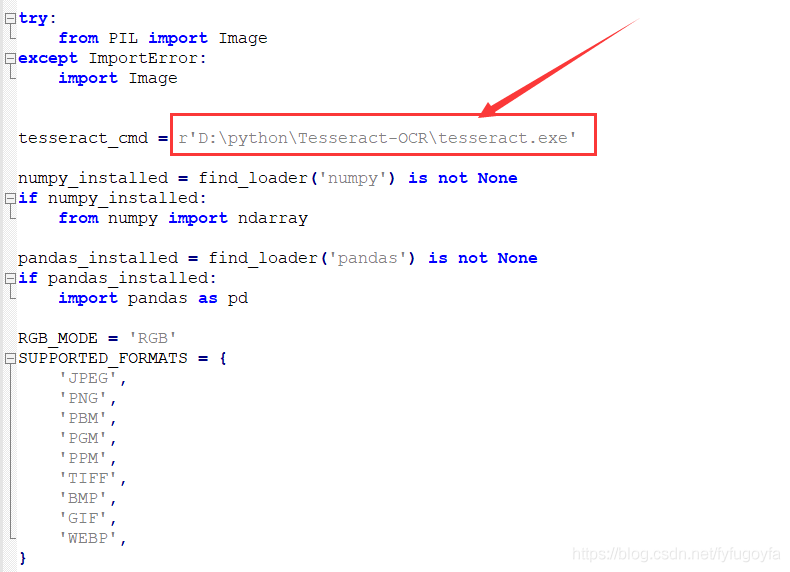
To configure the pytesseract Library:
Locate the pytesserac. Of the pytesserac library py file, open the py file, find tesseract_cmd, change its value to testseract. CMD installed just now Exe path.
Install cv2 Library:
pip3 install opencv-python
text
When the python crawler crawls the verification code of some websites, it may encounter the problem of verification code recognition. At present, most verification codes are divided into four categories:
1. Verification code for map recognition 2. Verification code to be calculated 3. Verification code for sliding slider 4. Verification code for voice
This paper aims at the simplest map recognition verification code to identify the English numbers in the verification code.
The identification verification code is usually these steps:
1. Grayscale processing: turn the color verification code image into gray image
2. Binarization: process the picture into a picture with only black and white
3. Remove the border: remove the border of the verification code image. Removing the border is to traverse the pixel points, find all the points on the four borders, and change them to white. If there is no border, you can not use it.
4. Noise reduction: remove the interference conditions in the verification code picture, such as west line and point.
5. Cutting characters or inclination correction: cutting characters individually cut the content in the verification code, which is generally used for verification code adhesion or calculation of verification code.
6. Training font library
7. Identification
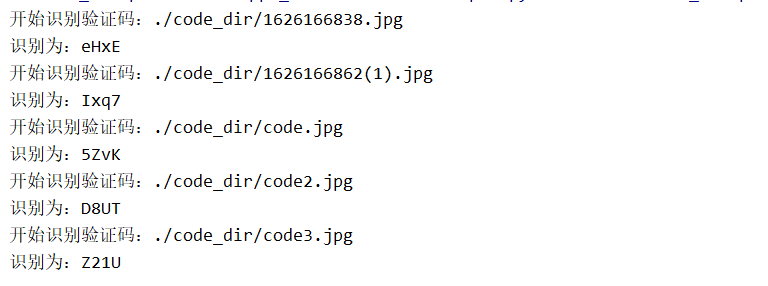
The following codes can be identified





import re
from PIL import Image
from pytesseract import *
from fnmatch import fnmatch
from queue import Queue
import cv2
import os
'''
Two folders need to be created, code_dir Folder to store verification code pictures,
out_img The folder stores the processed verification code pictures
'''
def clear_border(img,img_name):
'''Remove border
'''
filename = './out_img/' + img_name.split('.')[0] + '-clearBorder.jpg'
h, w = img.shape[:2]
for y in range(0, w):
for x in range(0, h):
# if y ==0 or y == w -1 or y == w - 2:
if y < 4 or y > w -4:
img[x, y] = 255
# if x == 0 or x == h - 1 or x == h - 2:
if x < 4 or x > h - 4:
img[x, y] = 255
cv2.imwrite(filename,img)
return img
def interference_line(img, img_name):
'''
Noise reduction of interference line
'''
filename = './out_img/' + img_name.split('.')[0] + '-interferenceline.jpg'
h, w = img.shape[:2]
# !!! opencv matrix points are inverse
# img[1,2] 1: height of picture, 2: width of picture
for y in range(1, w - 1):
for x in range(1, h - 1):
count = 0
if img[x, y - 1] > 245:
count = count + 1
if img[x, y + 1] > 245:
count = count + 1
if img[x - 1, y] > 245:
count = count + 1
if img[x + 1, y] > 245:
count = count + 1
if count > 2:
img[x, y] = 255
cv2.imwrite(filename,img)
return img
def interference_point(img,img_name, x = 0, y = 0):
"""Point noise reduction
9 Neighborhood box,Field box centered on the current point,Number of black spots
:param x:
:param y:
:return:
"""
# filename = './out_img/' + img_name.split('.')[0] + '-interferencePoint.jpg'
filename = './out_img/' + img_name.split('.')[0] + '-cutting.jpg'
# todo determines the lower limit of the length and width of the picture
cur_pixel = img[x,y]# The value of the current pixel
height,width = img.shape[:2]
for y in range(0, width - 1):
for x in range(0, height - 1):
if y == 0: # first line
if x == 0: # Top left vertex, 4 neighborhood
# 3 points next to the center point
sum = int(cur_pixel) \
+ int(img[x, y + 1]) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y]) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y + 1])
if sum <= 2 * 245:
img[x, y] = 0
elif x == height - 1: # Top right vertex
sum = int(cur_pixel) \
+ int(img[x, y + 1]) \
+ int(img[x - 1, y]) \
+ int(img[x - 1, y + 1])
if sum <= 2 * 245:
img[x, y] = 0
else: # Topmost non vertex, 6 neighborhood
sum = int(img[x - 1, y]) \
+ int(img[x - 1, y + 1]) \
+ int(cur_pixel) \
+ int(img[x, y + 1]) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y]) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y + 1])
if sum <= 3 * 245:
img[x, y] = 0
elif y == width - 1: # Bottom line
if x == 0: # Lower left vertex
# 3 points next to the center point
sum = int(cur_pixel) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y]) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y - 1]) \
+ int(img[x, y - 1])
if sum <= 2 * 245:
img[x, y] = 0
elif x == height - 1: # Lower right vertex
sum = int(cur_pixel) \
+ int(img[x, y - 1]) \
+ int(img[x - 1, y]) \
+ int(img[x - 1, y - 1])
if sum <= 2 * 245:
img[x, y] = 0
else: # Lowest non vertex, 6 neighborhood
sum = int(cur_pixel) \
+ int(img[x - 1, y]) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y]) \
+ int(img[x, y - 1]) \
+ int(img[x - 1, y - 1]) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y - 1])
if sum <= 3 * 245:
img[x, y] = 0
else: # y is not at the boundary
if x == 0: # Left non vertex
sum = int(img[x, y - 1]) \
+ int(cur_pixel) \
+ int(img[x, y + 1]) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y - 1]) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y]) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y + 1])
if sum <= 3 * 245:
img[x, y] = 0
elif x == height - 1: # Right non vertex
sum = int(img[x, y - 1]) \
+ int(cur_pixel) \
+ int(img[x, y + 1]) \
+ int(img[x - 1, y - 1]) \
+ int(img[x - 1, y]) \
+ int(img[x - 1, y + 1])
if sum <= 3 * 245:
img[x, y] = 0
else: # Qualified in 9 fields
sum = int(img[x - 1, y - 1]) \
+ int(img[x - 1, y]) \
+ int(img[x - 1, y + 1]) \
+ int(img[x, y - 1]) \
+ int(cur_pixel) \
+ int(img[x, y + 1]) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y - 1]) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y]) \
+ int(img[x + 1, y + 1])
if sum <= 4 * 245:
img[x, y] = 0
cv2.imwrite(filename,img)
return img
def _get_dynamic_binary_image(filedir, img_name):
'''
Adaptive threshold binarization
'''
filename = './out_img/' + img_name.split('.')[0] + '-binary.jpg'
img_name = filedir + '/' + img_name
print('Start identification verification code:' + img_name)
im = cv2.imread(img_name)
im = cv2.cvtColor(im,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
th1 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(im, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 21, 1)
cv2.imwrite(filename,th1)
return th1
def _get_static_binary_image(img, threshold = 140):
'''
Manual binarization
'''
img = Image.open(img)
img = img.convert('L')
pixdata = img.load()
w, h = img.size
for y in range(h):
for x in range(w):
if pixdata[x, y] < threshold:
pixdata[x, y] = 0
else:
pixdata[x, y] = 255
return img
def main():
filedir = r'./code_dir' #Folder for storing verification code
for file in os.listdir(filedir):
if fnmatch(file, '*.jpg'):
img_name = file
# Adaptive threshold binarization
im = _get_dynamic_binary_image(filedir, img_name)
# Remove border
im = clear_border(im,img_name)
# Noise reduction of interference lines for pictures
im = interference_line(im,img_name)
# Noise reduction for pictures
interference_point(im,img_name)
code_file ='./out_img/%s-cutting.jpg' % img_name.split('.')[0]
str_img = image_to_string(Image.open(code_file)) #Picture to text
cop = re.compile("[^a-z^A-Z^0-9]") # Match other characters that are not English case or numbers, and remove special characters
code_results = cop.sub('', str_img) # Replace the matching character in string1 with an empty character
print('Identified as:%s' % code_results)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()