As a general part of software projects, log management is particularly important in both development and automated testing.
At first, I planned to use python's logging module to manage logs. Later, I saw some automation framework designs of github and others. After making a comparison, I decided to use logbook.
This blog introduces how to use the logbook module in python for reference only...
1, Download and install
1. File installation
Download the logbook installation file from the official website and install it.
Official website link: https://pypi.org/project/Logbook/
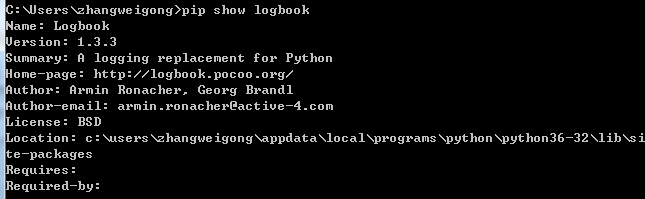
2. pip command installation
Enter CMD command line and enter pip install logbook Command to install. After the installation is successful, enter pip show logbook Command to view relevant information.
2, logbook introduction
logbook was originally designed to replace python's standard library logging module: logging. For details, please see the official document description through the link below:
Official documents: http://logbook.readthedocs.io/en/stable/index.html
3, Usage instructions
The example code is as follows: log.py
# coding=utf-8
import os
import sys
import logbook
from logbook import Logger,StreamHandler,FileHandler,TimedRotatingFileHandler
from logbook.more import ColorizedStderrHandler
def log_type(record,handler):
log = "[{date}] [{level}] [{filename}] [{func_name}] [{lineno}] {msg}".format(
date = record.time, # Log time
level = record.level_name, # Log level
filename = os.path.split(record.filename)[-1], # file name
func_name = record.func_name, # Function name
lineno = record.lineno, # Line number
msg = record.message # Log content
)
return log
# Log storage path
LOG_DIR = os.path.join("Log")
if not os.path.exists(LOG_DIR):
os.makedirs(LOG_DIR)
# Log print to screen
log_std = ColorizedStderrHandler(bubble=True)
log_std.formatter = log_type
# Log print to file
log_file = TimedRotatingFileHandler(
os.path.join(LOG_DIR, '%s.log' % 'log'),date_format='%Y-%m-%d', bubble=True, encoding='utf-8')
log_file.formatter = log_type
# Script log
run_log = Logger("script_log")
def init_logger():
logbook.set_datetime_format("local")
run_log.handlers = []
run_log.handlers.append(log_file)
run_log.handlers.append(log_std)
# Instantiation, default call
logger = init_logger()
Code parsing:
1. Define the log file type, and display it according to time, log level, test file name, function method name, number of lines and specific information;
Log level:
| level | describe |
| critical | A serious error that will cause the program to exit |
| error | Controllable error |
| warning | Warning message |
| notice | In most cases, you want to see records |
| info | In most cases, you don't want to see records |
| debug | Record of detailed output when debugging the program |
2. Define the Log storage path as the Log folder;
3. There are two log output modes of logbook: printing to the screen (it is more suitable for debugging and can be commented out during formal use) and printing to log files;
4. Define log output;
5. Instantiation to facilitate other module calls;
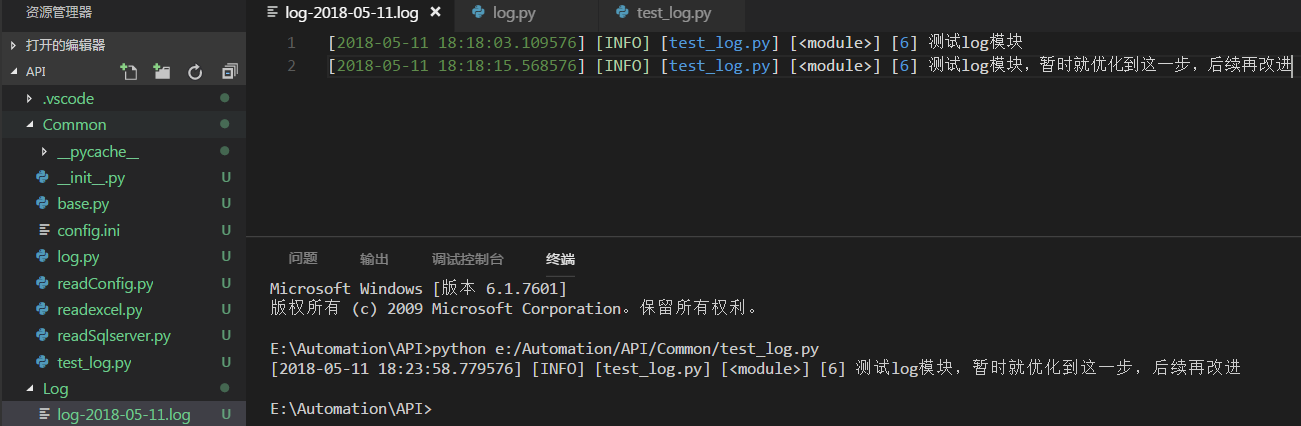
You can test whether the log is printed to the corresponding path through the test code. The test code is as follows: test_log.py
# coding=utf-8
import os
from log import run_log as logger
if __name__ == '__main__':
logger.info("test log Module, temporarily optimized to this step, and then improved later")
Test results:
####
python: using logbook module to manage logs
1. Module installation(use pip Command installation) get into cmd command,input pip install logbook install, After successful installation pip show logbook View relevant information 2. logbook brief introduction http://logbook.readthedocs.io/en/stable/index.html 3. Usage instructions import os import logbook from logbook import Logger, TimedRotatingFileHandler from logbook.more import ColorizedStderrHandler # Format log def log_type(record, handler): log = "[{date}] [{level}] [{filename}] [{func_name}] [{lineno}] {msg}".format( date=record.time, # Log time level=record.level_name, # Log level filename=os.path.split(record.filename)[-1], # file name func_name=record.func_name, # Function name lineno=record.lineno, # Line number msg=record.message # Log content ) return log # Log storage path LOG_DIR = os.path.join("Log") if not os.path.exists(LOG_DIR): os.makedirs(LOG_DIR) # Log print to screen log_std = ColorizedStderrHandler(bubble=True) # Generate log format log_std.formatter = log_type # Log print to file log_file = TimedRotatingFileHandler( os.path.join(LOG_DIR, '%s.log' % 'log'), date_format='%Y-%m-%d', bubble=True, encoding='utf-8') # Log generation format log_file.formatter = log_type # Script log run_log = Logger("global_log") def init_logger(): logbook.set_datetime_format("local") # Effective configuration run_log.handlers = [] run_log.handlers.append(log_file) run_log.handlers.append(log_std) # Instantiation, default call logger = init_logger() if __name__ == '__main__': run_log.info("test Log modular")
#####
#####