catalogue
Positioning, layout, input elements, and transformations
Positioning, layout, input elements, and transformations
Components
An element that can be reused. QML can customize element components. This article focuses on creating components in separate files. Define a clickableimage QML for use below.
ClickableImage.qml implementation:
import QtQuick 2.0
Image {
id: root
signal clicked
MouseArea {
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: root.clicked()
}
}
Element transformations
QML elements can change the geometric state of objects through translation, rotation and scaling.
Translation: completed by X and Y coordinates
Rotation: completed by rotation attribute (0 ~ 360)
Scaling: done by scale (smaller than 1, larger than 1)
Here is a code case:
import QtQuick 2.9
import QtGraphicalEffects 1.0
Item {
width: bg.width
height: bg.height
Image {
id: bg
source: "./background.png"
}
MouseArea {
id: backgroundClicker
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: {
rocket1.x = 20
rocket2.rotation = 0
rocket3.rotation = 0
rocket3.scale = 1.0
}
}
Image {
id: rocket1
x: 20; y: 100
source: "./pole.png"
MouseArea {
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: {
rocket1.x += 5
}
}
}
ClickableImage {
id: rocket2
x: 140; y: 100
source: "./pole.png"
smooth: true
onClicked: {
rotation += 5
}
}
ClickableImage {
id: rocket3
x: 240; y: 100
source: "./pole.png"
smooth: true
onClicked: {
rotation += 5
scale -= 0.05
}
}
}Effect achieved:
Original drawing:
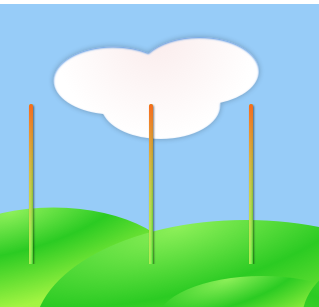
Effect after clicking:

Positioning Element
In QML, locators are used to place element objects. QtQuick module provides Row, Column, Grid and Flow as locators. Let's take a look at the effects of each locator:
Row locator
//Row
import QtQuick 2.5
Item {
id: root
width: 400; height: 120
Row {
id: row
anchors.centerIn: parent
spacing: 20
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#ea7025"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#67c111"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#00bde3"
}
}
}design sketch:

Column locator
//Column
import QtQuick 2.5
Item {
id: root
width: 120
height: 240
Column {
id: row
anchors.centerIn: parent
spacing: 20
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#ea7025"
}
Rectangle {
width: 96
height: 48
color: "#67c111"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#00bde3"
}
}
}design sketch:

Grid locator
//Grid
import QtQuick 2.5
Item {
id: root
width: 160
height: 160
Grid {
id: grid
rows: 2
columns: 2
anchors.centerIn: parent
spacing: 8
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#ea7025"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#67c111"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#00bde3"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#3c3c3c"
}
}
}design sketch:

Flow locator
//Flow
import QtQuick 2.5
Item {
id: root
width: 160
height: 160
Flow {
anchors.fill: parent
anchors.margins: 20
spacing: 20
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#ea7025"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#67c111"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#00bde3"
}
Rectangle {
width: 48
height: 48
color: "#3c3c3c"
}
}
}design sketch:
Default:

After stretching:

Repeater (repeating element)
Here is an example of the use of a Repeater with a locator. Repeaters are similar to for loops and iterators.
Look at a piece of code:
import QtQuick 2.5
Item {
id: root
width: 252
height: 252
//Use an array to define a set of color properties
property variant colorArray: ["#00bde3", "#67c111", "#ea7025"]
Grid{
anchors.fill: parent
anchors.margins: 8
spacing: 4
Repeater {
//Create 16 rectangles from repeating elements
model: 16
Rectangle {
width: 56; height: 56
//Random color selection using mathematical functions
property int colorIndex: Math.floor(Math.random()*3)
color: root.colorArray[colorIndex]
border.color: Qt.lighter(color)
Text {
anchors.centerIn: parent
color: "#f0f0f0"
//Display index
text: "Cell " + index
}
}
}
}
}
design sketch:

Layout Element
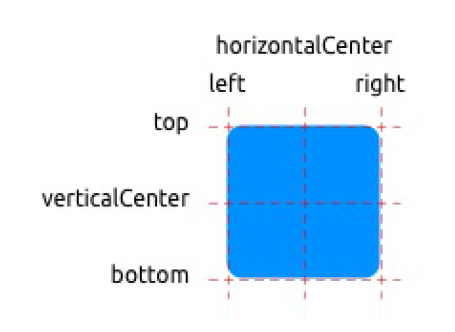
Use anchors to lay out elements in QML. Anchors are the basic attributes of the base element object and can be used by all visual QML elements.
anchors diagram:
Understand the basic usage of anchors through a piece of code:
import QtQuick 2.5
Item {
id: root
width: 400; height: 240
// M1>>
Rectangle{
id:rect1
width: 96
height: width
anchors.margins: 8
color: "#67c111"
Text {
anchors.centerIn: parent
text: '(1)'
color: "#f0f0f0"
}
}
// M2>>
Rectangle{
id:rect2
width: 96
height: width
anchors.margins: 8
color: "#00bde3"
anchors.left: rect1.right
Text {
anchors.centerIn: parent
text: '(2)'
color: "#f0f0f0"
}
}
// <<M3
Rectangle{
id:rect3
width: 32
height: width
anchors.margins: 8
color: "#67c111"
anchors.horizontalCenter: rect2.horizontalCenter
Text {
anchors.centerIn: parent
text: '(3)'
color: "#f0f0f0"
}
}
// M4>>
Rectangle{
id:rect4
width: 96
height: width
anchors.margins: 8
color: "#00bde3"
anchors.top: rect2.bottom
anchors.right: parent.right
anchors.topMargin: 10
Text {
anchors.centerIn: parent
text: '(4)'
color: "#f0f0f0"
}
}
}
design sketch:

Input Element
This section mainly introduces two text elements: TextInput and TextEdit
Text input
Text input: allows the user to enter a line of text. This element supports the use of regular expressions to restrict input.
Look at a code example:
import QtQuick 2.5
Rectangle {
width: 300
height: 80
color: "#f0f0f0"
TextInput {
id: textInput1
x: 8; y: 8
width: 250; height: 20
focus: true //Receive cursor
text: "please input text to textInput1" //Default text
KeyNavigation.tab: textInput2 //tab key to switch the cursor to textInput2
}
TextInput {
id: textInput2
x: 8; y: 36
width: 250; height: 20
text: "please input text to textInput2"
KeyNavigation.tab: textInput1
}
}design sketch:

Focus scope
focus scope defines that if the area receives focus, it is the last child element to receive focus using focus:true.
Example code:
Rectangle {
width: 300
height: 80
FocusScope {
TextInput {
id: textInput1
x: 8; y: 8
width: 250; height: 20
focus: true //Receive cursor
text: "please input text to FocusScope" //Default text
KeyNavigation.tab: textInput2 //tab key to switch the cursor to textInput2
}
}
FocusScope {
TextInput {
id: textInput2
x: 8; y: 36
width: 250; height: 20
text: "please input text to FocusScope"
KeyNavigation.tab: textInput1
}
}
}
Effect achieved:

TextEdit
The TextEdit element is similar to the TextInput element. It supports multi line text editing, but does not support text input restrictions. It provides the query function of the entered text size.
Example code:
import QtQuick 2.5
Rectangle {
width: 300
height: 80
FocusScope {
TextEdit {
id: textEdit1
x: 8; y: 8
color: "red"
width: 250; height: 100
focus: true //Receive cursor
text: "textEdit" //Default text
KeyNavigation.tab: textEdit2 //tab key to switch the cursor to textInput2
}
}
}design sketch:

Key Element
When the program is running, you can use the Key Element to perform certain operations, such as up and down to move, tab to switch focus, etc.
Example code:
import QtQuick 2.5
Rectangle {
width: 400; height: width
Rectangle{
id: square
width: 96
height: width
x: 8; y: 8
color: "#67c111"
}
focus:true
Keys.onLeftPressed: square.x -= 8 //Left move left
Keys.onRightPressed: square.x += 8 //Right move right
Keys.onUpPressed: square.y -= 8 //Up move up
Keys.onDownPressed: square.y += 8 //Down move down
Keys.onPressed: {
switch(event.key) {
case Qt.Key_Plus: //+Magnify
square.scale += 0.2
break;
case Qt.Key_Minus: //narrow
square.scale -= 0.2
break;
}
}
}
design sketch:
Default:

Move right ---- > move down ---- > zoom in: