catalogue
🍈🍈Foreword
🍈🍈A brief introduction to qsort
🍈🍈Using qsort to realize a sort of integer type
🍈🍈Sorting of structures with qsort function
🍈🍈Implementation of qsort function
📢 preface
Share a library function today
This paper introduces the use and implementation of qsort
It can realize sorting that is not limited to integer, floating point, character, custom and other types
📢 A brief introduction to qsort
| qsort |
| Header file include < stdlib h> |
| Format: void * qsort(void * base, size_t num, size_t width, int (_cdecl * compare (const void*,const void *) |
| Function} realize multi type quick sorting |
| Return value = no return value |
Decompose the format
void qsort(void* base,
size_t num,
size_t width,
int(* compare)(const void* e1, const void* e2)
);
The first parameter of qsort is the first address of the array to be arranged
size_t num is the number of a type
size_t width is the width of the type, that is, the size of the type
int(* compare)(const void* e1, const void* e2) is the pointer of the comparison function. Here, the function pointer is used as the parameter to pass the parameter
The idea of callback function is used here
📌📌 A callback function is a function called through a function pointer. If the pointer (address) of a function is used as a parameter and passed to another function, when the function calls the function referred to, we say it is a callback function.
📢 Using qsort to realize a sort of integer type
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int cmp_int(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (*(int*)e1) - (*(int*)e2);
}
void test1()
{
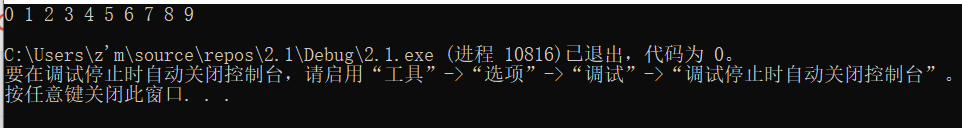
int arr[] = { 1,4,2,6,5,3,7,9,0,8 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), cmp_int);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
📢 Sorting of structures with qsort function
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Stu
{
char name[20];
int age;
float score;
};
int cmp_stu_by_socre(const void* e1, const void* e2) //Floating point in structure
{
if (((struct Stu*)e1)->score > ((struct Stu*)e2)->score)
{
return 1;
}
else if (((struct Stu*)e1)->score < ((struct Stu*)e2)->score)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
int cmp_stu_by_age(const void* e1, const void* e2) //Shaping in structure
{
return ((struct Stu*)e1)->age - ((struct Stu*)e2)->age;
}
int cmp_stu_by_name(const void* e1, const void* e2) //Character type in structure
{
return strcmp(((struct Stu*)e1)->name, ((struct Stu*)e2)->name);
}
void print_stu(struct Stu arr[], int sz) //Print function
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%s %d %f\n", arr[i].name, arr[i].age, arr[i].score);
}
printf("\n");
}
void test4()
{
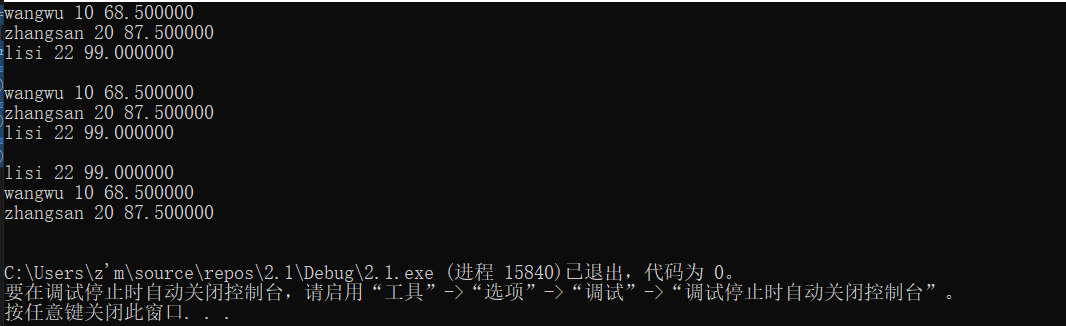
struct Stu arr[] = { {"zhangsan",20,87.5f},{"lisi",22,99.0f},{"wangwu", 10, 68.5f} };
//Sort by grades
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), cmp_stu_by_socre);
print_stu(arr, sz);
qsort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), cmp_stu_by_age);
print_stu(arr, sz);
qsort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), cmp_stu_by_name);
print_stu(arr, sz);
}
int main()
{
test4();
return 0;
}
The members of the structure include integer, floating-point and character types
They are arranged from small to large
The cmp function compares the size through the positive and negative of the return value, and the results in the figure below can be achieved
📢 Implementation of qsort function
When qsort function is implemented, it is actually related to bubble sorting
Just
Compared with bubble sorting, it can sort various types of data. Below, its function is realized through comparison
📢 Bubble sort to achieve plastic sort
void bubble(int arr[],int sz) //Bubble sort to achieve plastic sort
{
int tmp = 0; int i = 0; int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz - 1; i++)
{
for (j=0;j<sz-1;j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
{
tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
📢 Implementation of qsort function
void Swap(char* buf1, char* buf2, int width)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
char tmp = *buf1;
*buf1 = *buf2;
*buf2 = tmp;
buf1++;
buf2++;
}
}
void bubble_sort(void* base, int sz, int width, int(*cmp)(const void* e1, const void* e2))
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz - 1; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < sz - 1 - i; j++)
{
//if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
if (cmp((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width) > 0)
{
//Exchange of two elements
Swap((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width, width);
}
}
}
}📢 It can be seen that there are two differences
The first is to compare the size of two elements, which is realized through cmp comparison function
When the return value is greater than zero, the function sorts from small to large
When the return value is less than zero, the function sorts from large to small
When the return value is equal to zero, the element does not change
📢 The second difference is to realize the exchange of two elements
Bubble sorting is to achieve the purpose of exchange by introducing an intermediate variable
The qsort function exchanges bytes by calling a function and introducing the width (the size of bytes). Therefore, the char type is used to realize different types of exchange. Therefore, first of all, you need to know the size of each element in the sorting array, and then exchange four bytes of space.
Welcome to like collection and pay more attention. If you have any questions, you can raise them 😁😁😁😁