Version: qwt-6.1.3
1, Operation effect
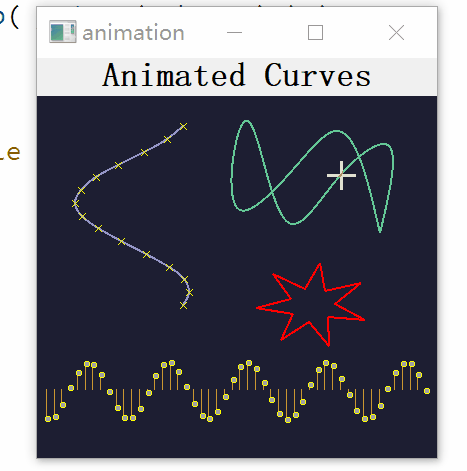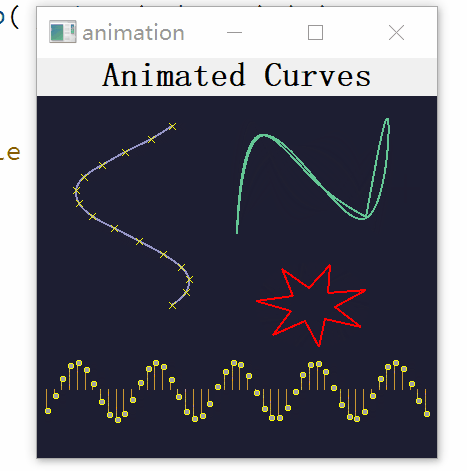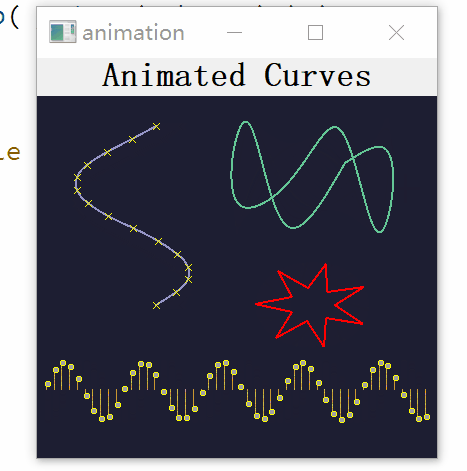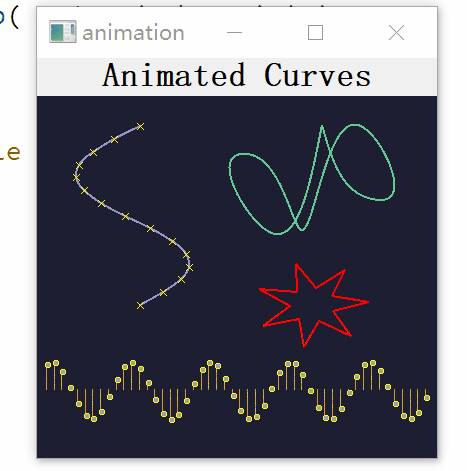
2, Engineering structure
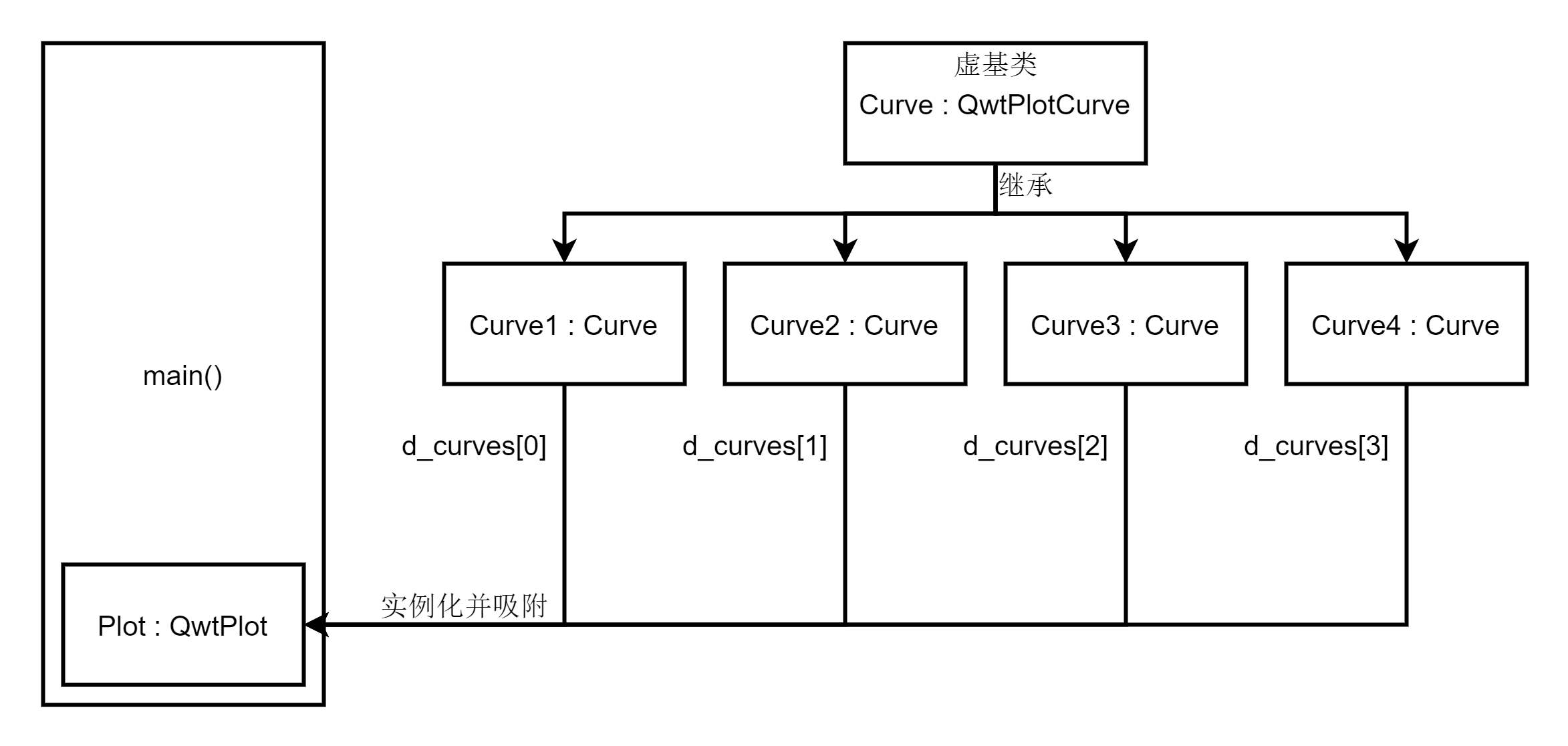
The structure of this project is very simple. It defines the Plot class inherited from QwtPlot, defines a virtual base class Curve inherited from QwtPlotCurve, and derives four classes from the virtual base class Curve: Curve1, Curve2, Curve3 and Curve4
3, Code analysis
main.cpp
#include <qapplication.h>
#include "plot.h"
#ifndef QWT_NO_OPENGL
#define USE_OPENGL 1
#endif
#if USE_OPENGL
#include <qgl.h>
#include <qwt_plot_glcanvas.h>
#else
#include <qwt_plot_canvas.h>
#endif
int main ( int argc, char **argv )
{
#if USE_OPENGL
#if QT_VERSION >= 0x040600 && QT_VERSION < 0x050000
// on my box QPaintEngine::OpenGL2 has serious problems, f.e:
// the lines of a simple drawRect are wrong.
QGL::setPreferredPaintEngine( QPaintEngine::OpenGL );
#endif
#endif
QApplication a( argc, argv );
Plot plot; //Create window
#if USE_OPENGL
QwtPlotGLCanvas *canvas = new QwtPlotGLCanvas(); //Instantiate canvas
canvas->setFrameStyle( QwtPlotGLCanvas::NoFrame );
#else
QwtPlotCanvas *canvas = new QwtPlotCanvas();
canvas->setFrameStyle( QFrame::NoFrame );
canvas->setPaintAttribute( QwtPlotCanvas::BackingStore, false );
#endif
plot.setCanvas( canvas ); //Window settings canvas
plot.setCanvasBackground( QColor( 30, 30, 50 ) ); //Set background color for window canvas
plot.resize( 400, 400 );
plot.show();
return a.exec();
}
plot.h
#include <qwt_plot.h>
#include <qdatetime.h>
class Curve;
class Plot: public QwtPlot
{
public:
Plot( QWidget * = NULL);
protected:
virtual void timerEvent( QTimerEvent * ); //timer event
private:
void updateCurves();
enum { CurveCount = 4 };
Curve *d_curves[CurveCount]; //Curve object array
QTime d_time; //timer
};
plot.cpp
#include <qapplication.h>
#include <qwt_math.h>
#include <qwt_symbol.h>
#include <qwt_curve_fitter.h>
#include <qwt_plot_curve.h>
#include <qwt_plot_canvas.h>
#include <qwt_plot_layout.h>
#include <qevent.h>
#include "plot.h"
class Curve: public QwtPlotCurve
{
public:
void setTransformation( const QTransform &transform )
{
d_transform = transform;
}
virtual void updateSamples( double phase )
{
setSamples( d_transform.map( points( phase ) ) );
}
private:
virtual QPolygonF points( double phase ) const = 0; //Pure virtual function, point set interface
private:
QTransform d_transform;
};
class Curve1: public Curve
{
public:
Curve1()
{
//Set curve style
setPen( QColor( 150, 150, 200 ), 2 );
setStyle( QwtPlotCurve::Lines );
//QwtCurveFitter attempts to interpolate / smooth the curve before drawing
QwtSplineCurveFitter *curveFitter = new QwtSplineCurveFitter();
curveFitter->setSplineSize( 150 );
setCurveFitter( curveFitter );
setCurveAttribute( QwtPlotCurve::Fitted, true ); //Set curve attributes
//Set sample point flag
QwtSymbol *symbol = new QwtSymbol( QwtSymbol::XCross );
symbol->setPen( Qt::yellow );
symbol->setSize( 7 );
setSymbol( symbol );
//Set coordinate system conversion
QTransform transform;
transform.scale( 1.5, 1.0 );
transform.translate( 1.5, 3.0 );
setTransformation( transform );
}
virtual QPolygonF points( double phase ) const
{
QPolygonF points;
const int numSamples = 15;
for ( int i = 0; i < numSamples; i++ )
{
const double v = 6.28 * double( i ) / double( numSamples - 1 );
points += QPointF( qSin( v - phase ), v );
}
return points;
}
};
class Curve2: public Curve
{
public:
Curve2()
{
setStyle( QwtPlotCurve::Sticks );
setPen( QColor( 200, 150, 50 ) );
setSymbol( new QwtSymbol( QwtSymbol::Ellipse,
QColor( Qt::gray ), QColor( Qt::yellow ), QSize( 5, 5 ) ) );
}
private:
virtual QPolygonF points( double phase ) const
{
QPolygonF points;
const int numSamples = 50;
for ( int i = 0; i < numSamples; i++ )
{
const double v = 10.0 * i / double( numSamples - 1 );
points += QPointF( v, qCos( 3.0 * ( v + phase ) ) );
}
return points;
}
};
class Curve3: public Curve
{
public:
Curve3()
{
setStyle( QwtPlotCurve::Lines );
setPen( QColor( 100, 200, 150 ), 2 );
QwtSplineCurveFitter* curveFitter = new QwtSplineCurveFitter();
curveFitter->setFitMode( QwtSplineCurveFitter::ParametricSpline );
curveFitter->setSplineSize( 200 );
setCurveFitter( curveFitter );
setCurveAttribute( QwtPlotCurve::Fitted, true );
// somewhere in the top right corner
QTransform transform;
transform.translate( 7.0, 7.5 );
transform.scale( 2.0, 2.0 );
setTransformation( transform );
}
private:
virtual QPolygonF points( double phase ) const
{
QPolygonF points;
const int numSamples = 9;
for ( int i = 0; i < numSamples; i++ )
{
const double v = i * 2.0 * M_PI / ( numSamples - 1 );
points += QPointF( qSin( v - phase ), qCos( 3.0 * ( v + phase ) ) );
}
return points;
}
};
class Curve4: public Curve
{
public:
Curve4()
{
setStyle( QwtPlotCurve::Lines );
setPen( Qt::red, 2 );
initSamples();
// somewhere in the center
QTransform transform;
transform.translate( 7.0, 3.0 );
transform.scale( 1.5, 1.5 );
setTransformation( transform );
}
private:
virtual QPolygonF points( double phase ) const
{
const double speed = 0.05;
const double s = speed * qSin( phase );
const double c = qSqrt( 1.0 - s * s );
for ( int i = 0; i < d_points.size(); i++ )
{
const QPointF p = d_points[i];
const double u = p.x();
const double v = p.y();
d_points[i].setX( u * c - v * s );
d_points[i].setY( v * c + u * s );
}
return d_points;
}
void initSamples()
{
const int numSamples = 15;
for ( int i = 0; i < numSamples; i++ )
{
const double angle = i * ( 2.0 * M_PI / ( numSamples - 1 ) );
QPointF p( qCos( angle ), qSin( angle ) );
if ( i % 2 )
p *= 0.4;
d_points += p;
}
}
private:
mutable QPolygonF d_points;
};
Plot::Plot( QWidget *parent ):
QwtPlot( parent)
{
setAutoReplot( false ); //Set canvas auto redraw
setTitle( "Animated Curves" ); //Set window title
//Hide all axes
for ( int axis = 0; axis < QwtPlot::axisCnt; axis++ )
enableAxis( axis, false );
plotLayout()->setCanvasMargin( 10 ); //Set the canvas outer margin to 10
d_curves[0] = new Curve1(); //Initialize Curve Object
d_curves[1] = new Curve2();
d_curves[2] = new Curve3();
d_curves[3] = new Curve4();
updateCurves(); //Update curve
for ( int i = 0; i < CurveCount; i++ ) //Attach curves to canvas
d_curves[i]->attach( this );
d_time.start();
( void )startTimer( 40 ); //Start timer, 40ms
}
void Plot::timerEvent( QTimerEvent * )
{
updateCurves();
replot();
}
void Plot::updateCurves()
{
const double speed = 2 * M_PI / 25000.0; // One cycle every 25 seconds
const double phase = d_time.elapsed() * speed;
for ( int i = 0; i < CurveCount; i++ )
d_curves[i]->updateSamples( phase );
}
4, Additional knowledge points
1,virtual void timerEvent( QTimerEvent * );
-
timerEvent events can easily make objects do certain things regularly;
-
timerEvent is a built-in event of QObject, which can be used by all classes inherited from QObject;
-
int startTimer(delaytime); Generate timerEvent and return the timer Id number of the object;
-
killTimer(timerId); A timer whose ID number of the object is timerid;
-
An object can have multiple timers. You can distinguish which timer triggered the event by E - > timerid(), for example;
class MainWindow : public QMainWindow
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit MainWindow(QWidget *parent = 0);
~MainWindow();
protected:
void timerEvent(QTimerEvent* event);
private:
Ui::MainWindow *ui;
int id1;
int id2;
int id3;
};
//============================================================
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent),
ui(new Ui::MainWindow)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
id1 = startTimer(1000); //Start a 1-second timer and return its ID
id2 = startTimer(1500); //Start a 1.5 second timer and return its ID
id3 = startTimer(2200); //Start a 2-second timer and return its ID
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
delete ui;
}
void MainWindow::timerEvent(QTimerEvent *event)
{
if(event->timerId() == id1) {
qDebug()<<"timer1";
}else if(event->timerId() == id2) {
qDebug()<<"timer2";
}else{
qDebug()<<"timer3";
}
}
2. QTime timing class
- start(): counting starts;
- Restart(): the timing restarts and returns the number of milliseconds elapsed since the last call to start() or restart();
- elapsed(): the timing ends and returns the result since the last call
3,QTransform
QTransform is a conversion class recommended in Qt. The conversion specifies how to translate, scale, cut, rotate or project the coordinate system. It is usually used when rendering graphics.
Note: QTransform conversion is for coordinate system
The QTransform object contains a 3 * 3 matrix as follows:
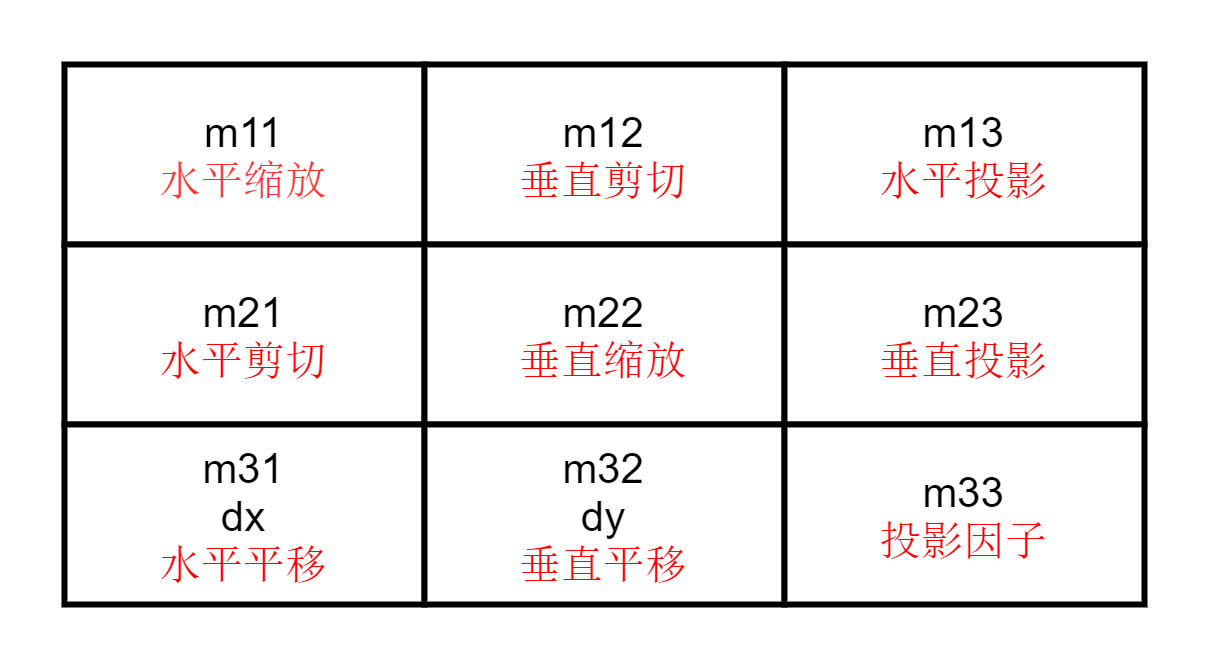
- m31 (dx) and m32 (dy) specify horizontal and vertical translation;
- The m11 and m22 elements specify horizontal and vertical scaling;
- m21 and m12 elements specify horizontal and vertical cuts;
- The m13 and m23 elements specify horizontal and vertical projections, with m33 as the additional projection factor;
How qtransform can realize various transformations through matrix operation can refer to this article: Coordinate transformation matrix of Qt coordinate system (QTransform class)
Common functions:
- Qtransform & translate (qreal dx, qreal dy): move the coordinate system dx along the x axis and Dy along the y axis, and return the reference to the matrix;
- Qtransform & Scale (qreal sx, qreal SY): scale the coordinate system horizontally and vertically by sx and sy, and return the reference to the matrix;
- Qtransform & rotate (qreal angle, QT:: axis, axis = QT:: zaxis): rotates the coordinate system counterclockwise around the specified axis and returns a reference to the matrix;
- Qtransform & shear (qreal sh, qreal sv): horizontal shear horizontal axis, vertical shear horizontal axis sv, and return a reference to the matrix;