1, Introduction to Rancher
Rancher is a container management platform that helps organizations deploy and manage containers easily and quickly in a production environment. Rancher can easily manage kubernetes in various environments, meet IT needs and support DevOps teams. Kubernetes has not only become the standard for container orchestration, but also is rapidly becoming the standard infrastructure provided by various cloud and virtualization vendors. Rancher users can choose to use Rancher Kubernetes Engine(RKE) to create kubernetes clusters, or use cloud kubernetes services such as GKE, AKS and EKS.
Rancher users can also import and manage existing Kubernetes clusters. GKE: Google Kubernetes Engine, Google's k8s hosting service, AKS: Azure Kubernetes service (AKS), Microsoft's k8s hosting service. EKS: Amazon Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes, Amazon's k8s hosting service
2, Building k8s clusters using Rancher
1. Initialize the installer environment (three machines operate the same)
Modify the three host names, close selinux and firewall, and swap , time synchronization
192.168.4.11 rancher 2C 4G
192.168.4.12 master 2C 4G
192.168.4.13 node1 2C 2G
~]# systemctl set-hostname rancher ~]# swapoff -a ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service && systemctl disable firewalld.service && iptables -F &&setenforce 0 && swapoff -a ~]# date -R # View the current server time zone Mon, 27 Apr 2020 10:41:54 +0800 ~]# yum install ntpdate ~]# timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai ~]# ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com ~]# date -R #Check whether the new time has been synchronized
2. Add mirror source
~]# curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/docker.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo ~]# curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo ~]# yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
3. Install and start docker CE
~]# tee /etc/docker/daemon.json << EOF
{
"registry-mirrors":["http://e9yneuy4.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}
EOF
## tee will be displayed again after input, and it will be checked again with cat
# It is recommended to select alicloud source when using rancher
~]# systemctl enable docker.service --now && systemctl daemon-reload12.2.3 install rancher platform on rancher and start it
[root@rancher ~]# docker load -i rancher_257_v1.tar.gz #Do not import three is too laggy. [root@rancher ~]# gzip -dc rancher_257_v1.tar.gz |ssh root@192.168.4.12 'cat | docker load' Note: gzip Command parameters: -c Write the output to the standard output and keep the original file;-d Unzip. [root@rancher ~]# gzip -dc rancher_257_v1.tar.gz |ssh root@192.168.4.13 'cat | docker load' ##Shut down the three machines and create a snapshot, so that it is convenient to do the experiment again later. start-up rancher [root@rancher ~]# docker run -d --restart=unless-stopped -p 80:80 -p 443:443 --privileged rancher/rancher Note:--restart=unless-stopped ,Always restart the container when it exits, but do not consider Docker Container that has been stopped when the daemon starts
12.2.4 log in to Rancher to create k8s cluster
Note: just after running the docker run command, you need to wait about 1 minute until the container is started successfully. Browser access to rancher: http://192.168.4.11 , The password is defined as 123456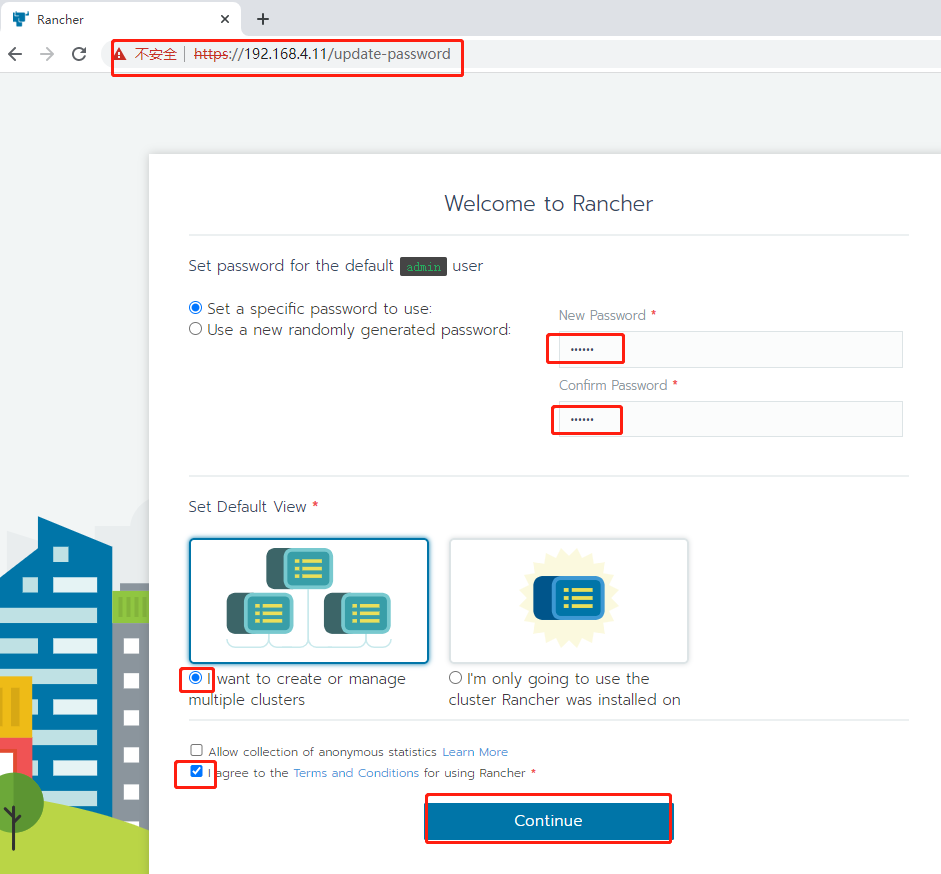
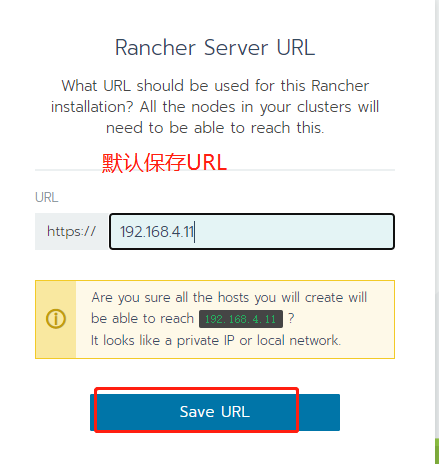
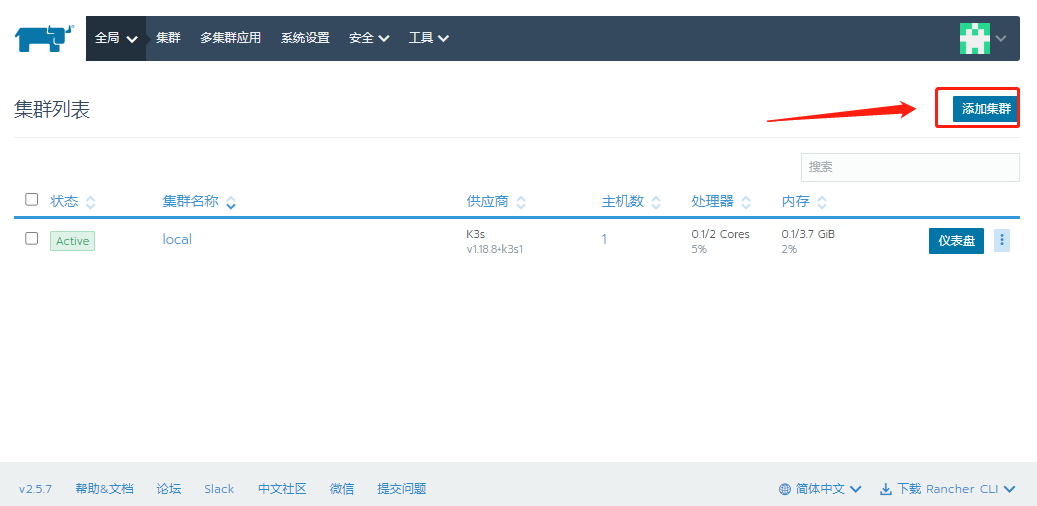
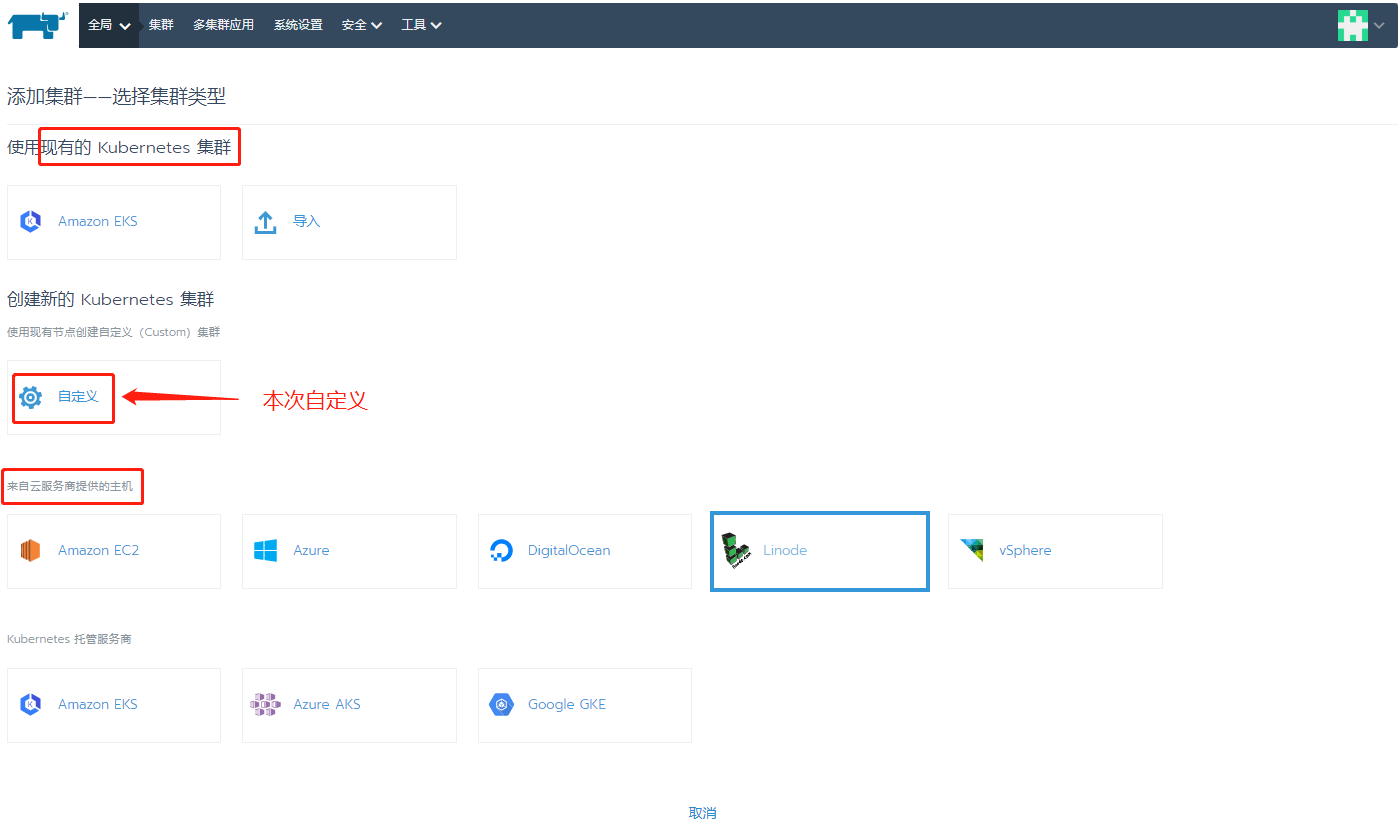
The mirror version of this experiment is v1.20.4-ranger1-1. If it does not match, please modify yaml to v1.20.4-ranger1-1
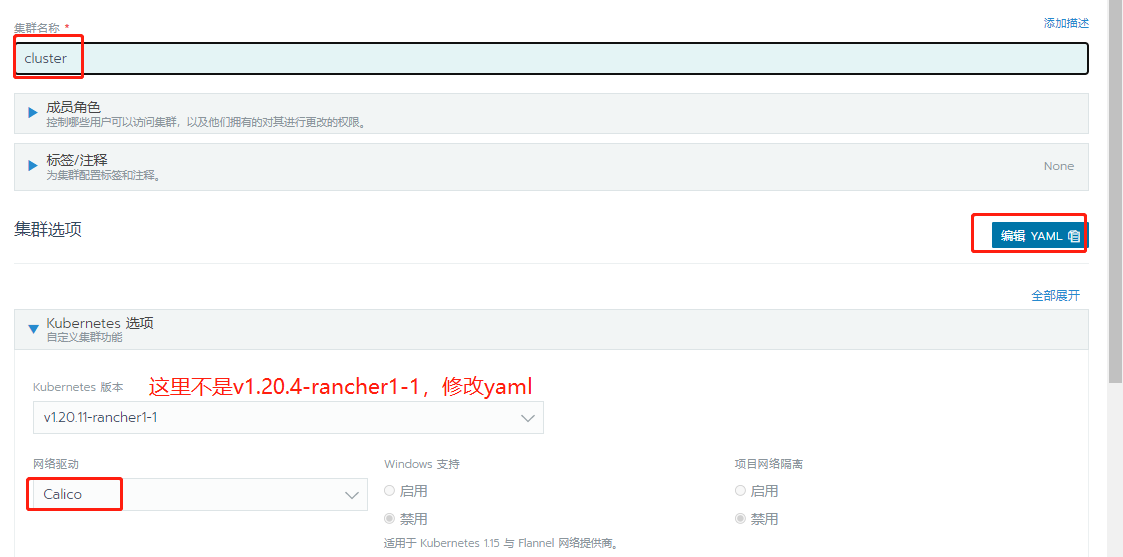
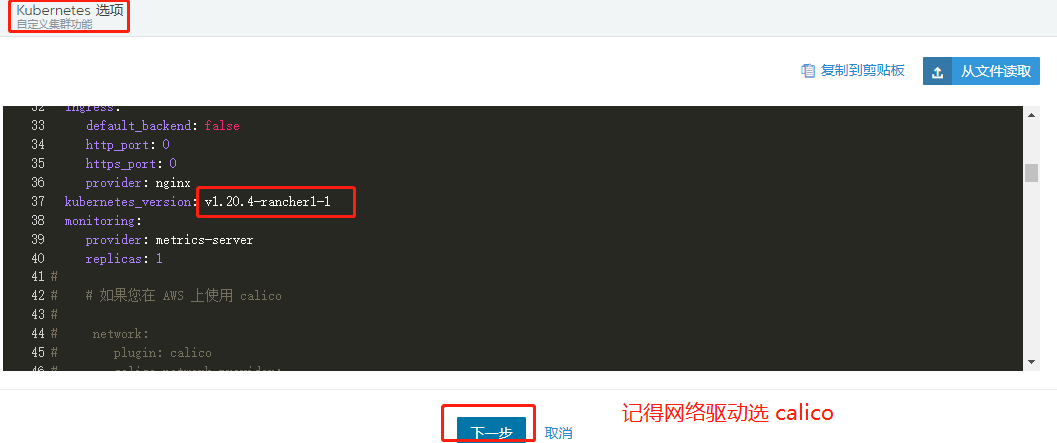
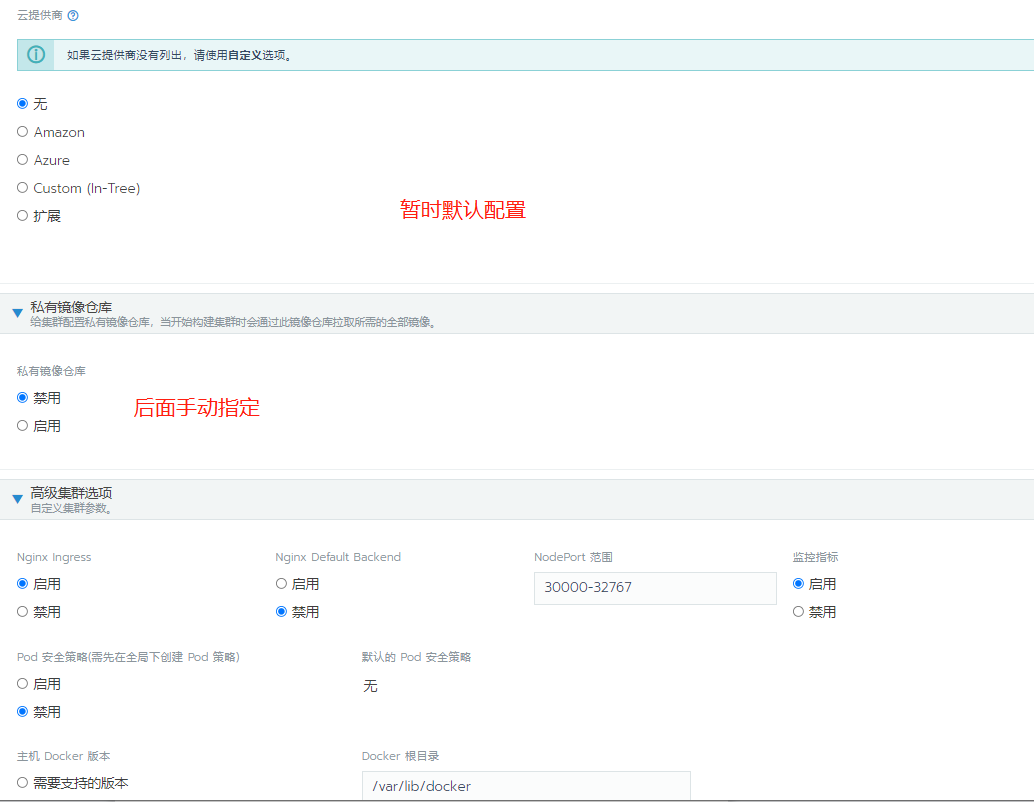
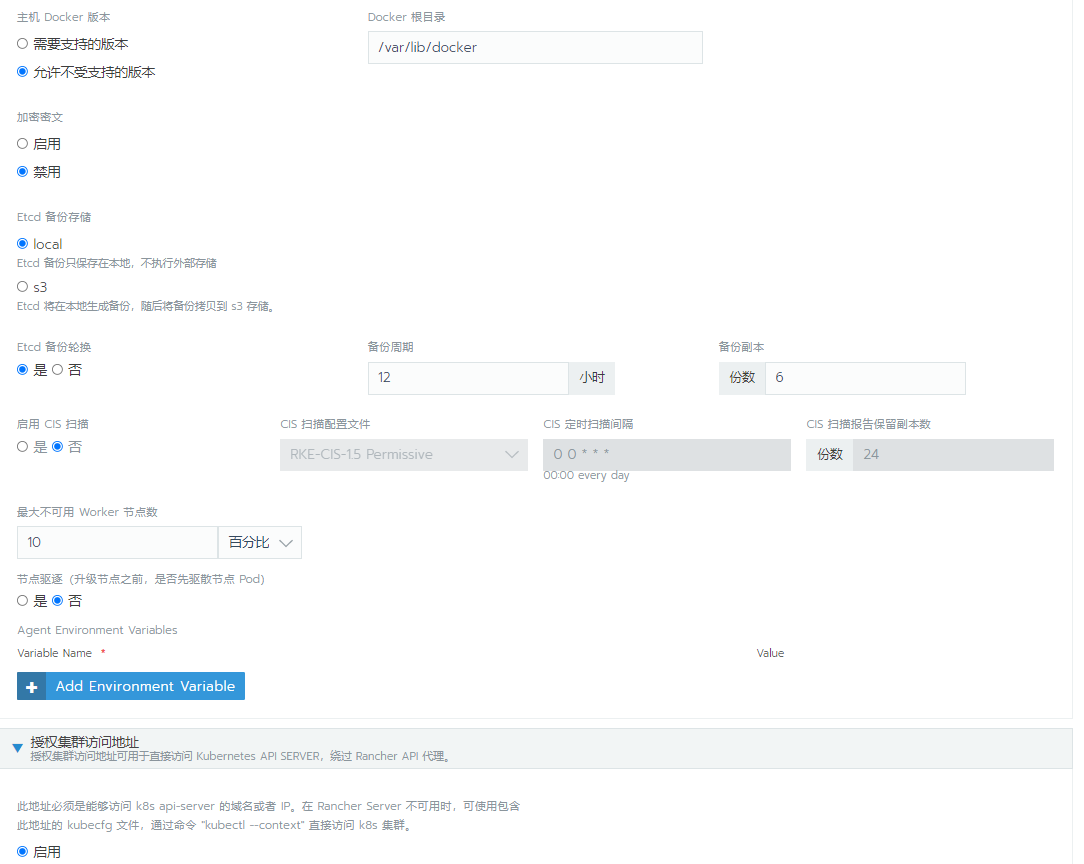
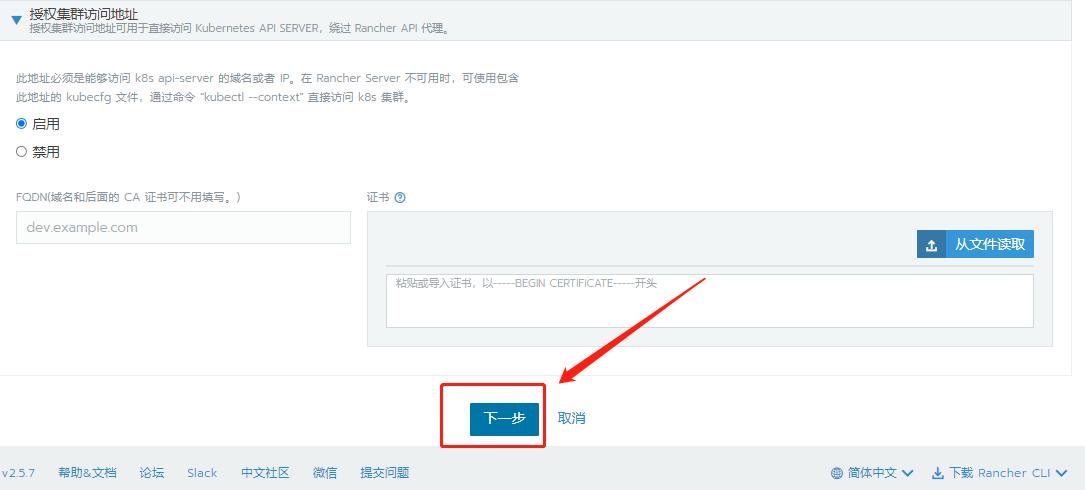
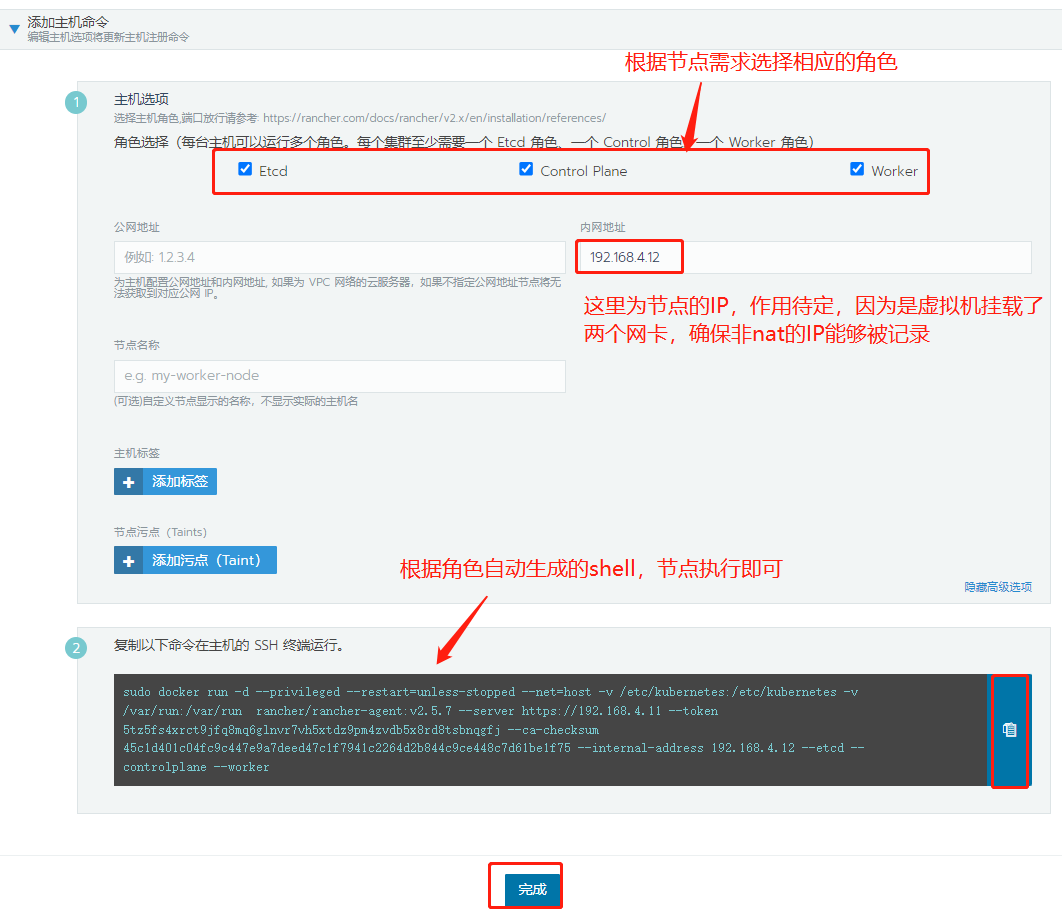
This time, 4.12 is used as the master etcd configured control plane Worker role
[root@master ~]# sudo docker run -d --privileged --restart=unless-stopped --net=host \ -v /etc/kubernetes:/etc/kubernetes -v /var/run:/var/run rancher/rancher-agent:v2.5.7 --server https://192.168.4.11 --token \ 5tz5fs4xrct9jfq8mq6glnvr7vh5xtdz9pm4zvdb5x8rd8tsbnqgfj --ca-checksum \ 45c1d401c04fc9c447e9a7deed47c1f7941c2264d2b844c9ce448c7d61be1f75 --internal-address 192.168.4.12 --etcd --controlplane --worker
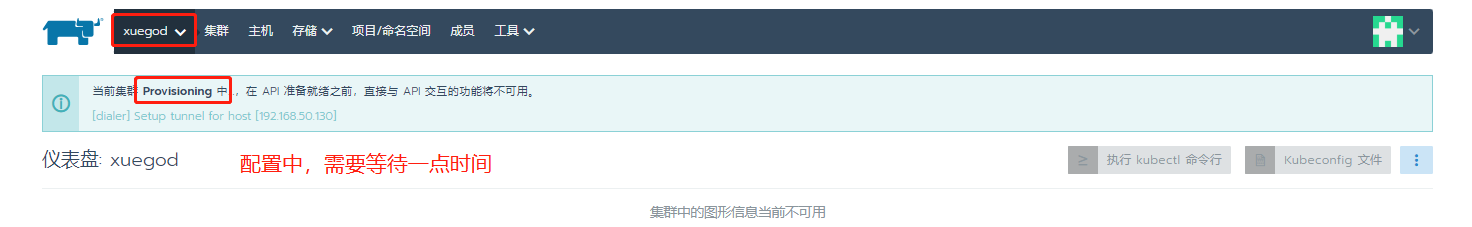
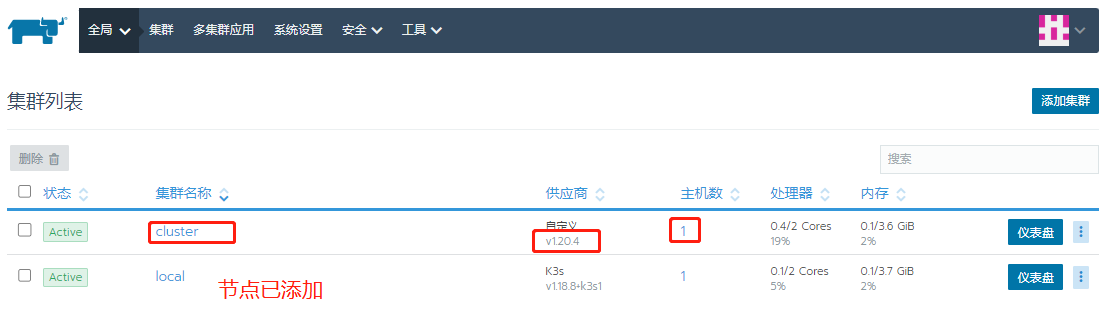
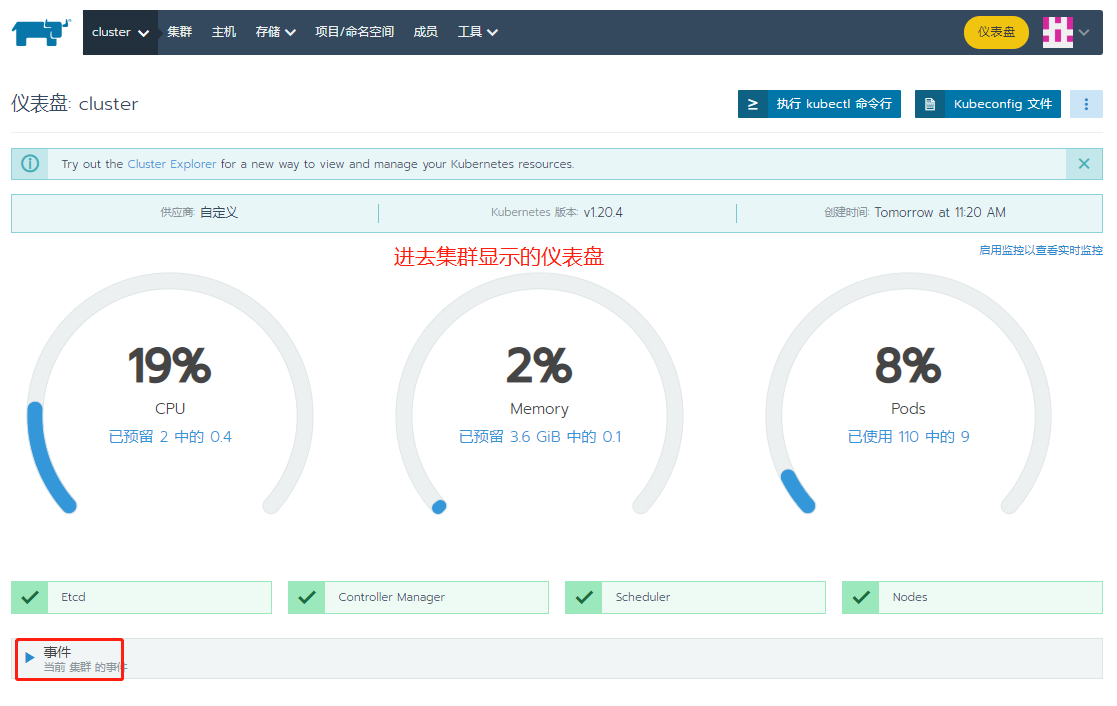
Continue adding members
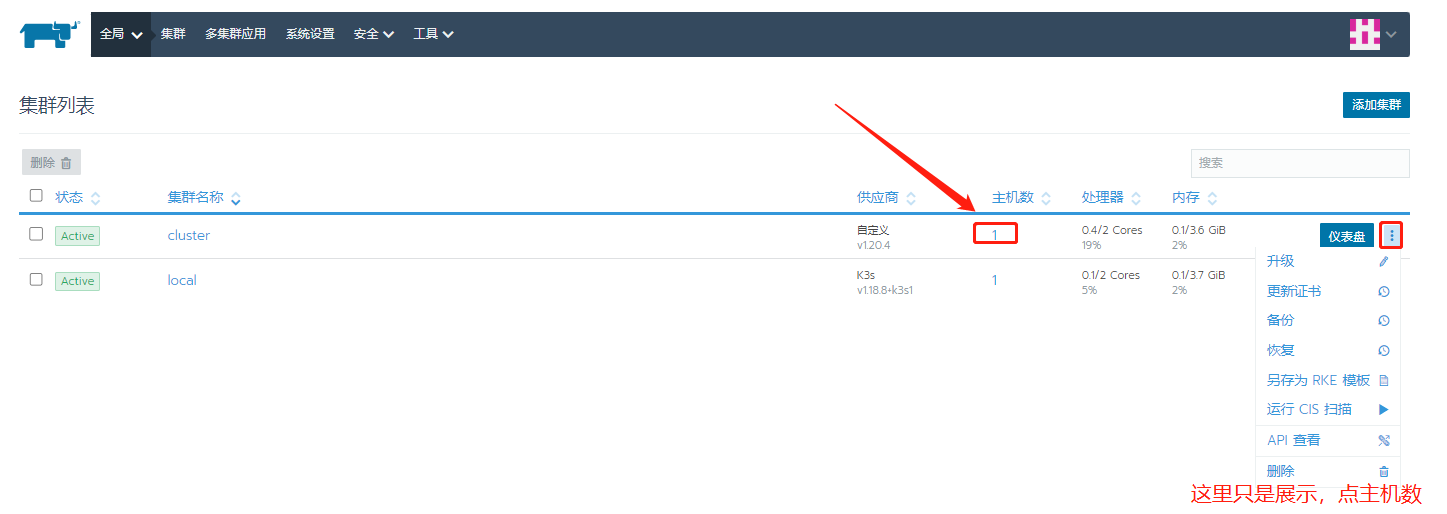
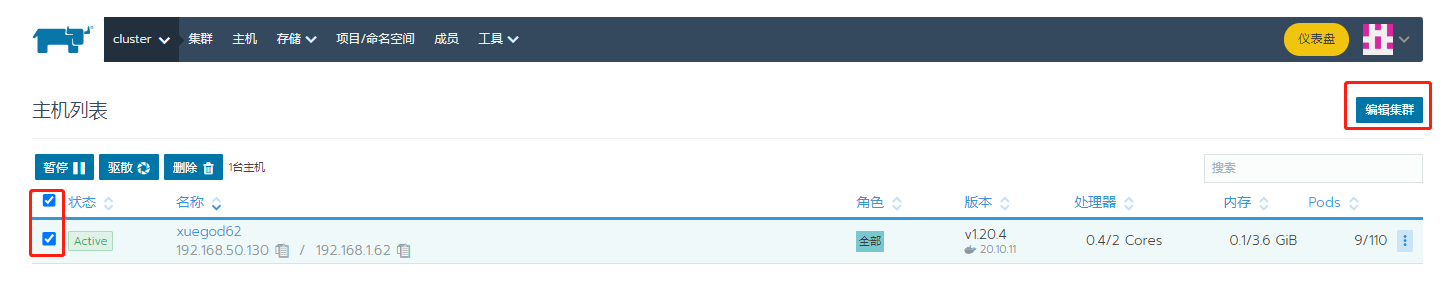
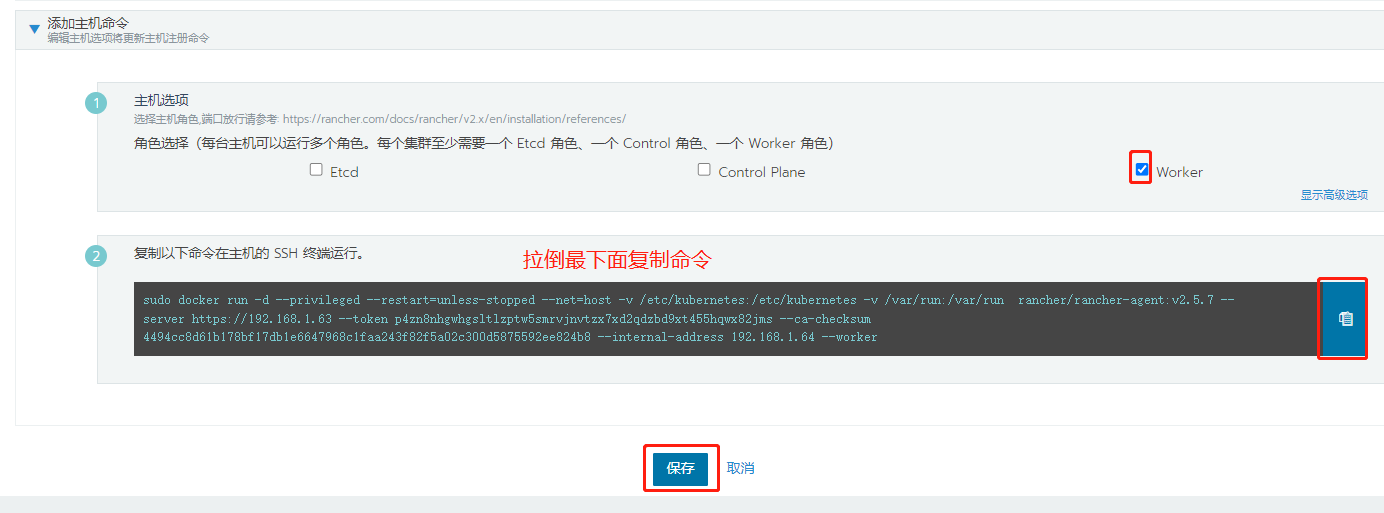
Here I write the intranet address in the display advanced item, because the nat address of the 192.168.50.0 network segment is used when joining the cluster
[root@node1~]# sudo docker run -d --privileged --restart=unless-stopped --net=host -v /etc/kubernetes:/etc/kubernetes -v /var/run:/var/run rancher/rancher-agent:v2.5.7 --server https://192.168.1.63 --token p4zn8nhgwhgsltlzptw5smrvjnvtzx7xd2qdzbd9xt455hqwx82jms --ca-checksum 4494cc8d61b178bf17db1e6647968c1faa243f82f5a02c300d5875592ee824b8 --internal-address 192.168.4.13 --worker
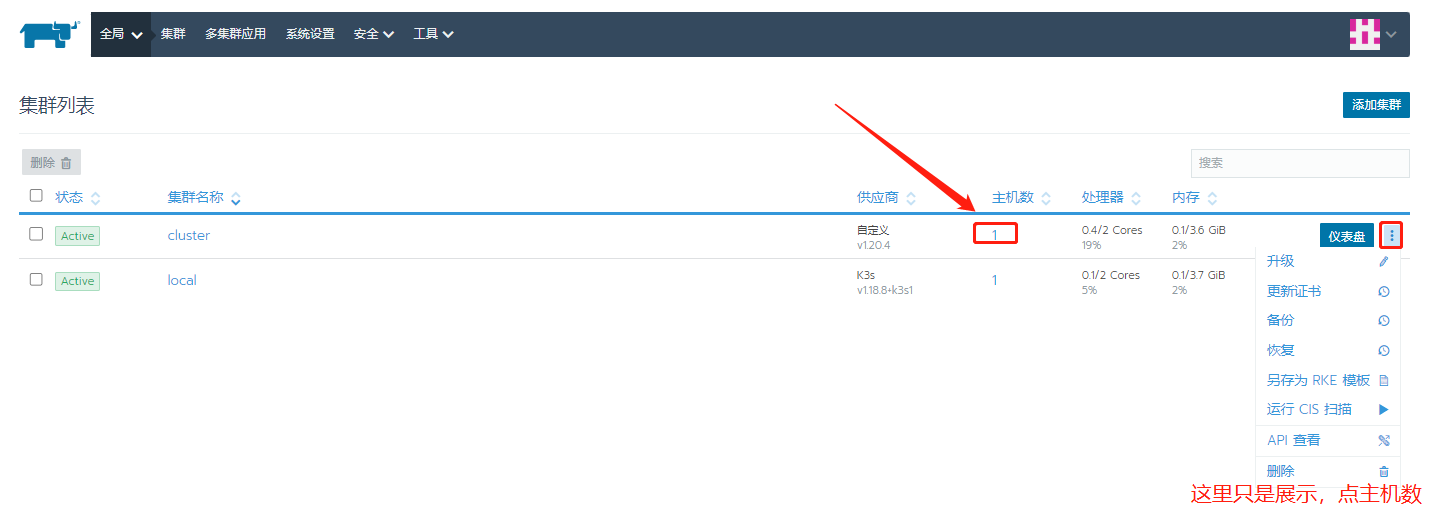
Wait until the resources in the cluster are created and our node nodes are added
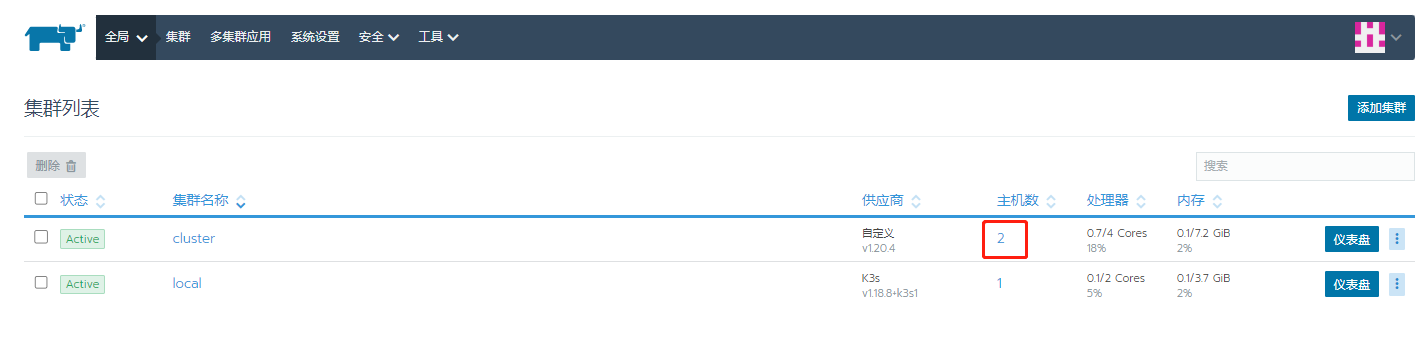
Note: there will be red error messages in the process of creating resources. We can wait for the creation to succeed.
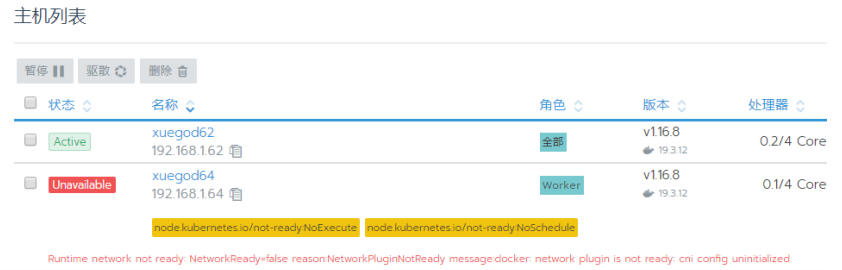
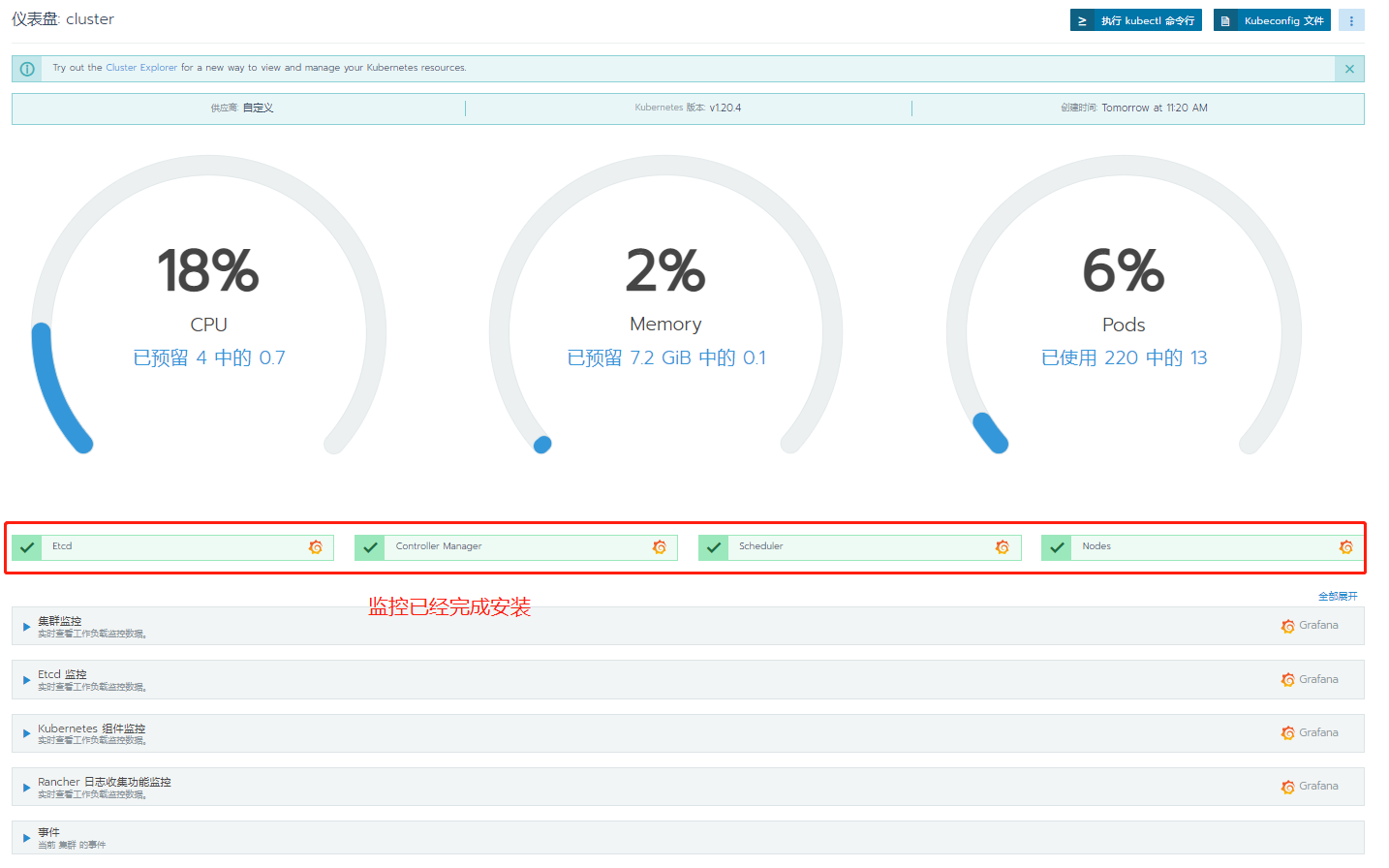
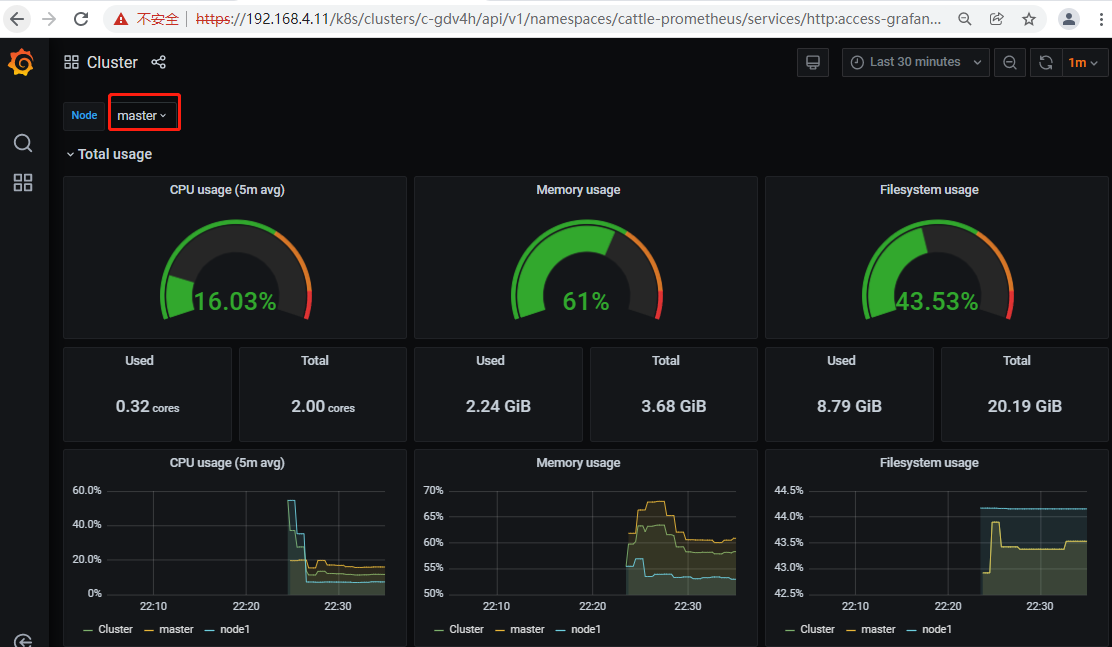
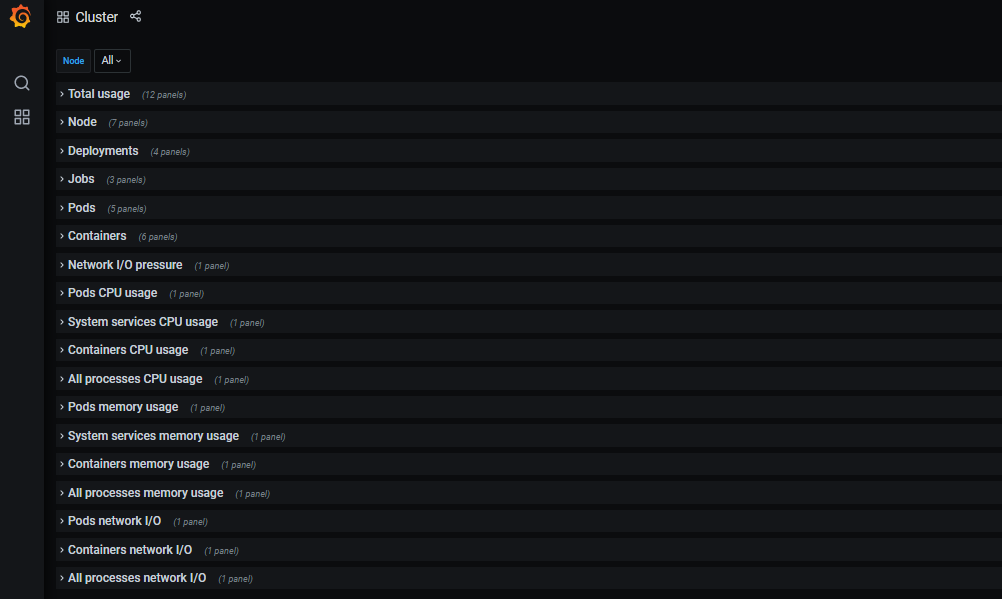
Check k8s cluster operation status by using the monitoring function in Rancher
Enable Rancher cluster level monitoring, start monitoring and view real-time monitoring indicators. The default setting is temporarily set
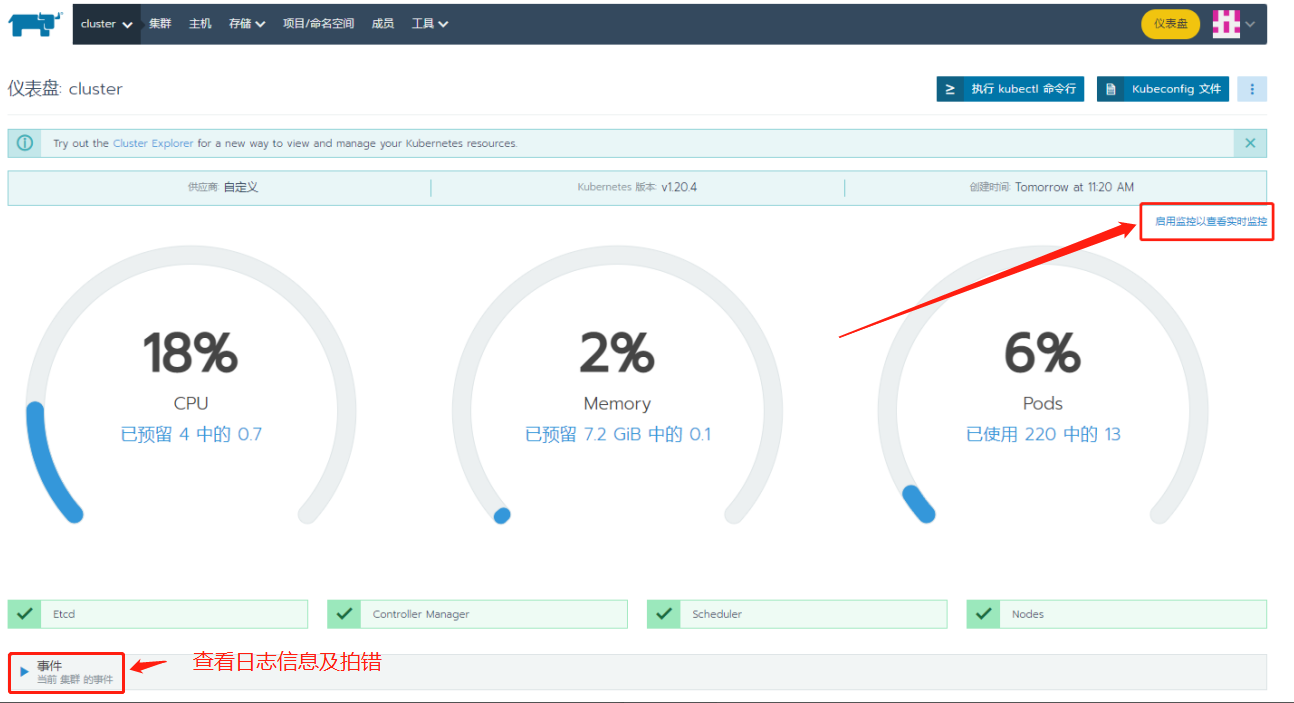
The default is OK. Click last: enable monitoring
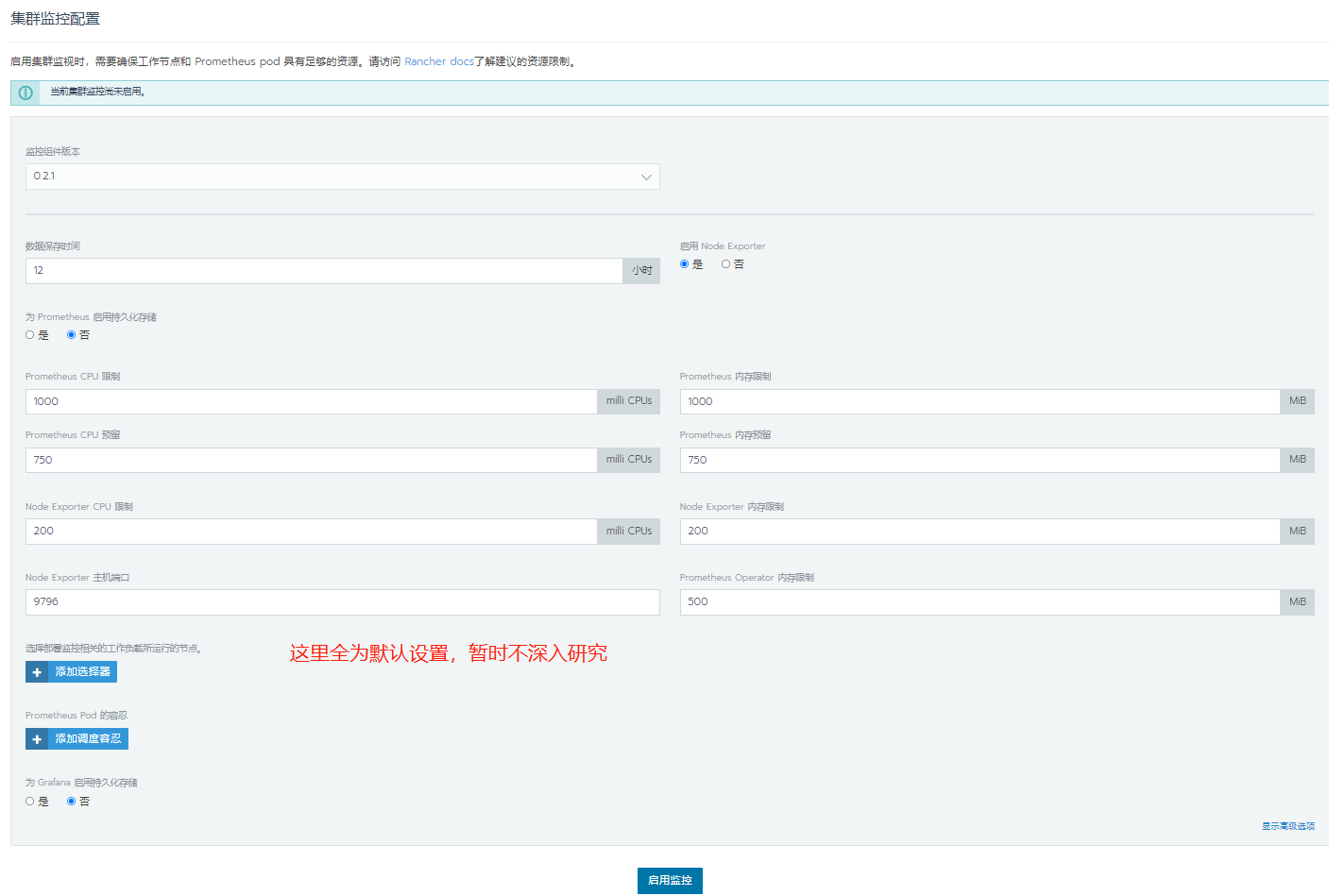
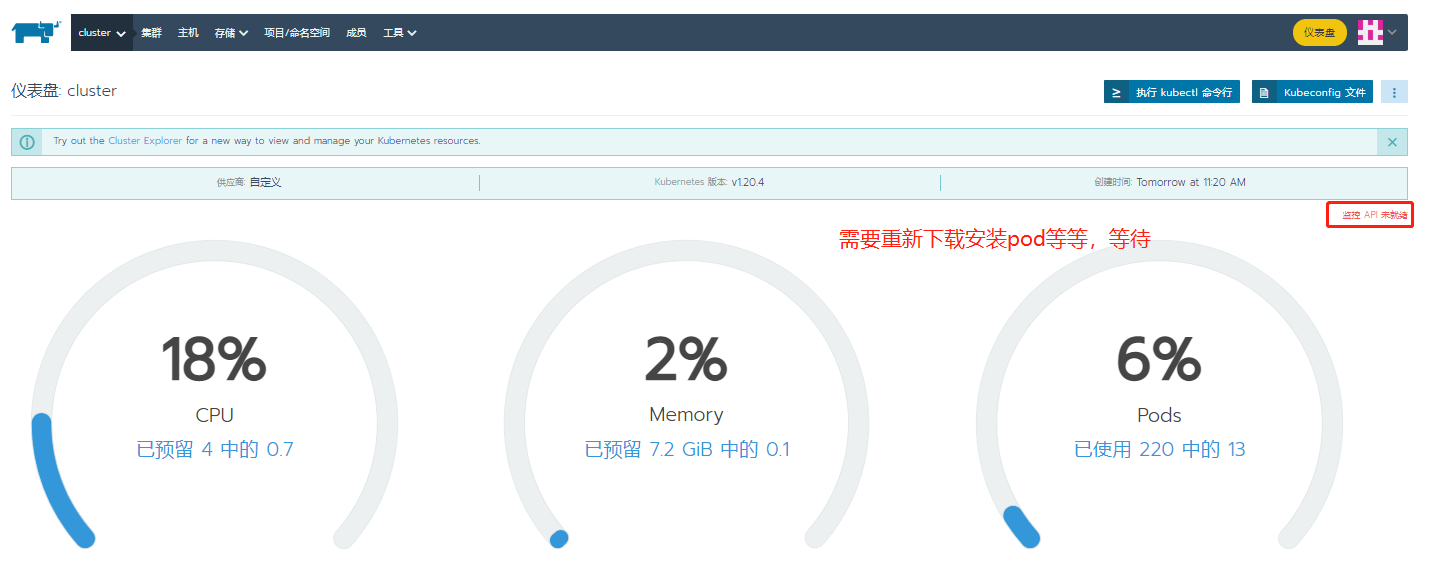
Here, you need to wait 20 minutes for the cluster to install the monitoring API. If there is not enough memory, an error will be reported
Note: when installing the monitoring plug-in, you should pay attention to whether the hardware resources are sufficient. If it is not enough, the installation will not succeed.