study Uncover the secrets of React Technology
Render phase - Coordinator - Reconciler work
- Start at the workflow.syncformoncorrent phase
- Depends on whether the update is synchronous or asynchronous
// performSyncWorkOnRoot calls this method
function workLoopSync() {
while (workInProgress !== null) {
performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
}
// Performcurrentworkonroot calls this method
function workLoopConcurrent() {
while (workInProgress !== null && !shouldYield()) {
performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
}
- shouldYield: judge whether the browser currently has the remaining time
- workInProcess: represents the currently created workInProcess fiber
- performUnitOfWork:
- Create the next Fiber node and assign it to workInProcess
- The workInProcess is linked with the created fiber node to form a fiber tree
- Fiber Reconciler reconstructs Stack Reconciler and realizes interruptible recursion through traversal
- performUnitOfWork. Work is divided into "delivery" and "return"
- "Delivery" stage
- Start from rootFiber and traverse downward depth first Call the beginWork method for each fiber node
- This method creates a child Fiber node based on the incoming Fiber node and links the two Fiber nodes
- If there are sibling nodes, create sibling nodes in turn according to the nodes
- When traversing the leaf node, it will enter the return phase
- "Return" stage
- The return node calls the completeWork stage to process the fiber node
- A fiber node completes the completeWork
- If it has a sibling Fiber node, it will enter the delivery phase of the sibling node
- If there is no sibling fiber node, it will enter the homing phase of the parent fiber
- "Delivery" and "return" will be executed alternately until "return" to rootfiber The work of render phase is completed
Leaf nodes with single text will not execute beginWork/completeWork
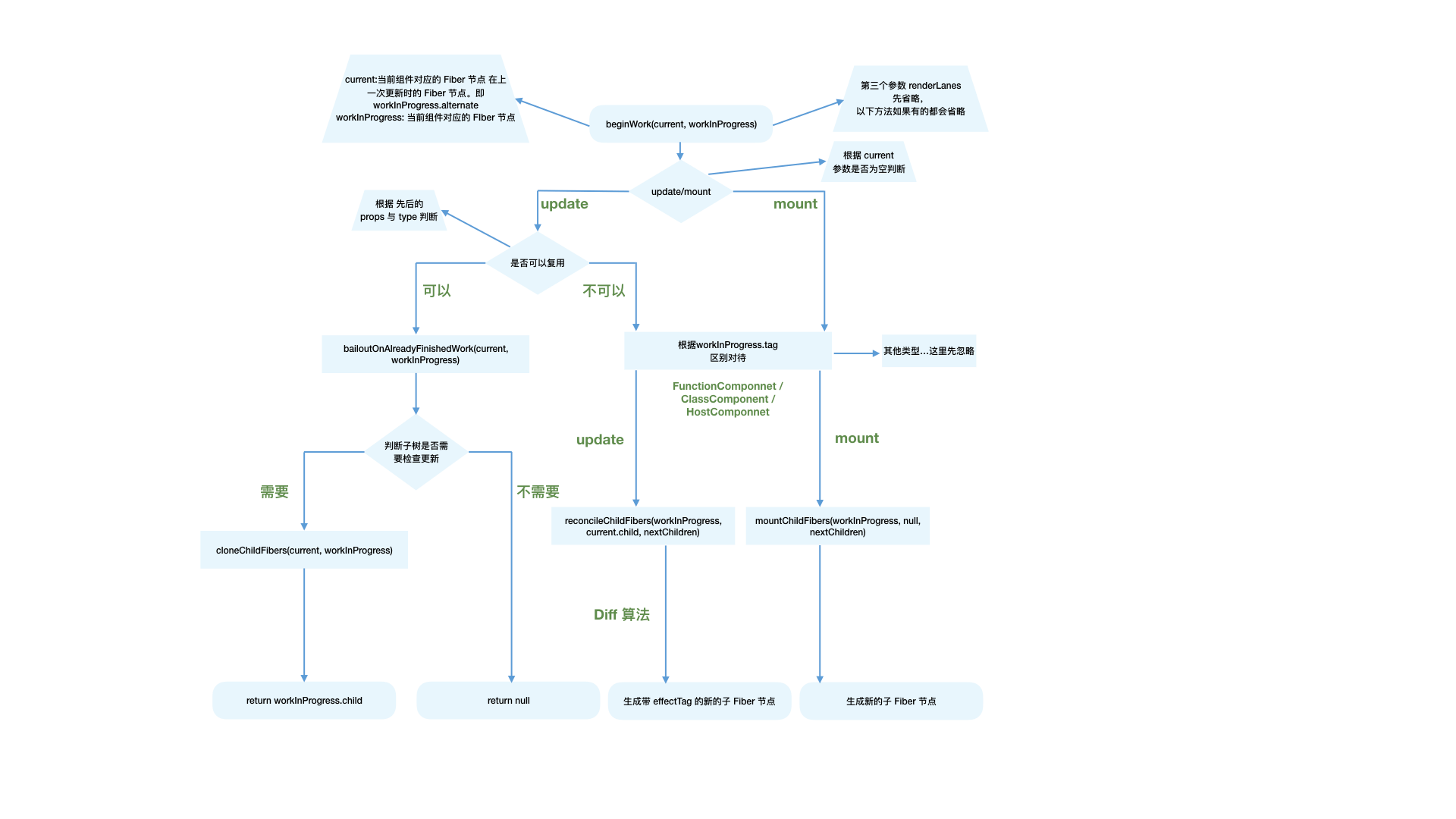
beginWork
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
// ... Omit function body
}
-
Current: the Fiber node corresponding to the current component at the time of last update workInProcess.alternate
-
workInProcess: fiber node corresponding to the current component
-
renderLanes: priority dependent
-
Distinguish between mount and update
- mount: current === null
- update: current== null
-
begin is divided into two parts:
- update: the current node exists and meets certain conditions for reuse Clone current Child to workinprocess child
- mount: except for fiberRootNode, current === null According to fiber Different tags create different types of sub fiber nodes
-
Update: the following conditions are met. - > didReceiveUpdate = false; Directly reuse the last fiber node
- oldProps === newProps && workInProcess. type === current. Type unchanged
- includesSomeLane(renderLanes, updateLanes). The priority of the current node is not enough
-
Mount:
- Enter the creation logic of different types of Fiber according to different types of tag s
- Eventually, reconcileChildren will be executed: create a child fiber node according to the fiber node
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes
): Fiber | null {
// During update: if there may be an optimization path, you can reuse current (that is, the last updated Fiber node)
if (current !== null) {
const oldProps = current.memoizedProps;
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
if (
oldProps !== newProps ||
hasLegacyContextChanged() ||
(__DEV__ ? workInProgress.type !== current.type : false)
) {
didReceiveUpdate = true;
} else if (!includesSomeLane(renderLanes, updateLanes)) {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
// Omit processing
}
// Reuse current
return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(
current,
workInProgress,
renderLanes,
);
} else {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
}
} else {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
}
// mount: create different sub Fiber nodes according to different tag s
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent:
// ... ellipsis
case LazyComponent:
// ... ellipsis
case FunctionComponent:
// ... ellipsis
case ClassComponent:
// ... ellipsis
case HostRoot:
// ... ellipsis
case HostComponent:
// ... ellipsis
case HostText:
// ... ellipsis
// ... Omit other types
}
}
- reconcileChildren work:
- mount: create a new child fiber node
- update: the current fiber node will be compared with the last updated fiber node (diff), and a new fiber node will be generated
- Finally, a new sub fiber node will be generated and assigned to workinprocess Child, as the return value of this beginWork
- And as the parameter of workInProcess in the next execution of performinunitofwork
- reconcileChildFibers will bring the effectTag attribute to the generated Fiber node
export function reconcileChildren(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
nextChildren: any,
renderLanes: Lanes
) {
if (current === null) {
// For mount components
workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(
workInProgress,
null,
nextChildren,
renderLanes,
);
} else {
// For update components
workInProgress.child = reconcileChildFibers(
workInProgress,
current.child,
nextChildren,
renderLanes,
);
}
}
- effectTag
- render(Reconciler) phase works in memory After the work is accepted, notify the Renderer to perform dom operation
- The operation of dom is saved in effectTag
- Notify the Renderer to insert the dom corresponding to the Fiber node into the page. Two conditions need to be met
- fiber.stateNode exists, that is, the fiber node saves the corresponding dom node
- Placement effectTag exists on Fiber node
- fiber.stateNode will be completed in completeWork
- When mount ing, only rootFiber will be assigned placement effecttag The commit phase is inserted at one time
commitWork
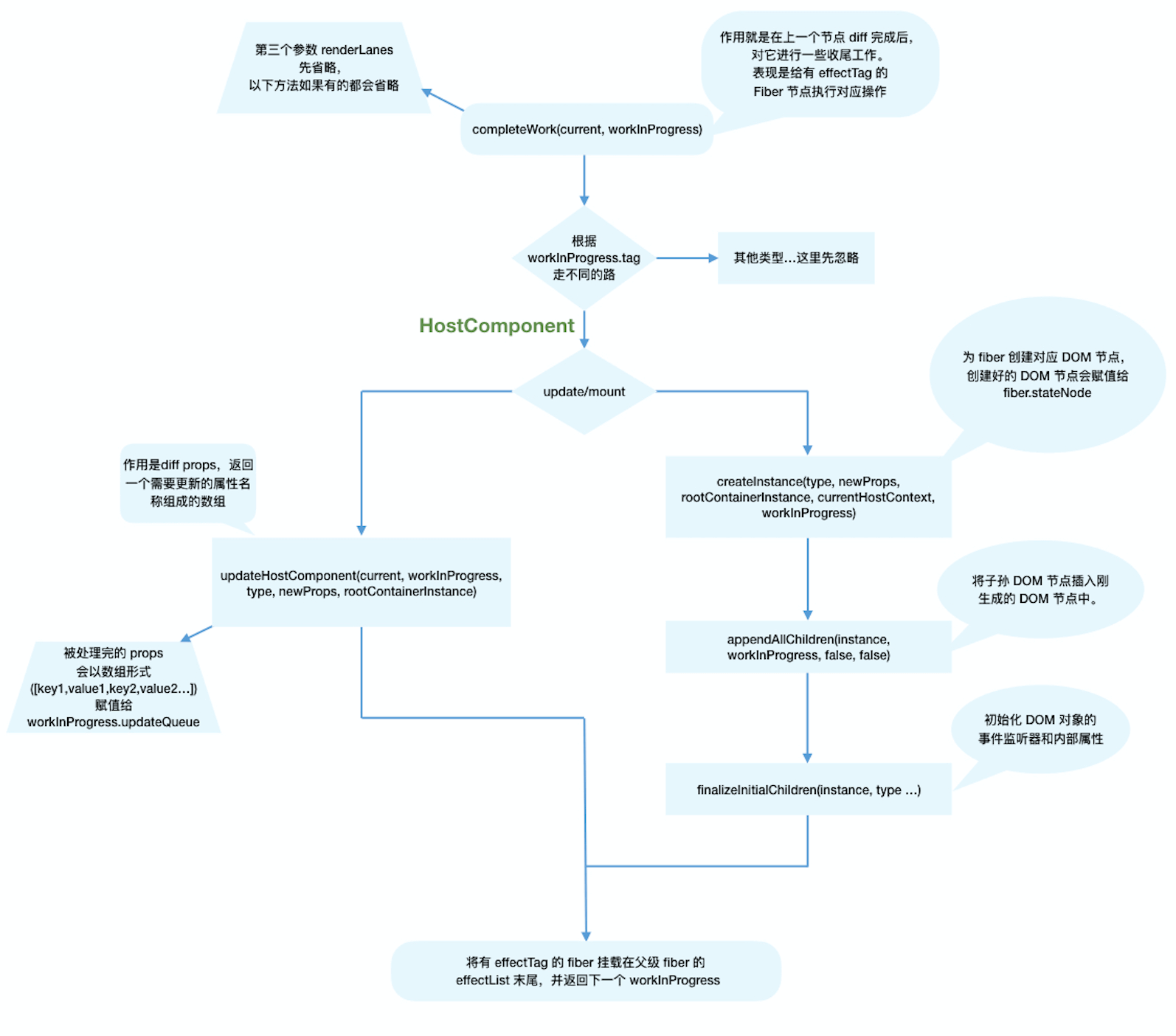
function completeWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent:
case LazyComponent:
case SimpleMemoComponent:
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case Fragment:
case Mode:
case Profiler:
case ContextConsumer:
case MemoComponent:
return null;
case ClassComponent: {
// ... ellipsis
return null;
}
case HostRoot: {
// ... ellipsis
updateHostContainer(workInProgress);
return null;
}
case HostComponent: {
// ... ellipsis
return null;
}
// ... ellipsis
- HostComponent: the fiber node corresponding to the native component
- When updating:
- The dom node corresponding to the Fiber node already exists. There is no need to generate a dom node. It mainly deals with props
- Registration of callback functions such as onclick and onchange
- Handling style prop
- Handling DANGEROUSLY_SET_INNER_HTML prop
- Dealing with children prop
- It mainly calls updateHostComponent
- Assign the processed props to workinprocess updateQueue
- And will eventually render on the page in the commit phase (Renderer)
- workInProgress.updateQueue = (updatePayload: any);
- updatePayload is an array, the even number is the changed prop key, and the odd number is prop value
- The dom node corresponding to the Fiber node already exists. There is no need to generate a dom node. It mainly deals with props
- Mount time
- Main logic:
- Add the corresponding dom node for the fiber node
- Insert the descendant dom node into the newly generated dom node
- The props process is similar to the updateHostComponent in update
- Main logic:
- The completeWork stage belongs to the return stage function Every time appendAllChildren is called, the generated descendant dom node will be inserted under the currently generated dom node
- When "returning" to rootFiber, there is already a built dom tree in memory
case HostComponent: {
popHostContext(workInProgress);
const rootContainerInstance = getRootHostContainer();
const type = workInProgress.type;
if (current !== null && workInProgress.stateNode != null) {
// update
updateHostComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
type,
newProps,
rootContainerInstance,
);
} else {
// mount
// ... Omit the logic related to server-side rendering
const currentHostContext = getHostContext();
// Create corresponding DOM node for fiber
const instance = createInstance(
type,
newProps,
rootContainerInstance,
currentHostContext,
workInProgress,
);
// Insert the descendant DOM node into the newly generated DOM node
appendAllChildren(instance, workInProgress, false, false);
// The DOM node is assigned to fiber stateNode
workInProgress.stateNode = instance;
// The process of processing props is similar to that of updateHostComponent in update logic
if (
finalizeInitialChildren(
instance,
type,
newProps,
rootContainerInstance,
currentHostContext,
)
) {
markUpdate(workInProgress);
}
}
return null;
}
- effectList
- All fiber nodes are needed to solve the problem. Find the fiber marked effectTag
- In the upper level function completeUnitOfWork of completeWork:
- Every time the completeWork is executed and the fiber node of effectTag exists, it will be saved in the one-way linked list of effectList
- The first node is saved in fiber firstEffect
- The last node is saved in fiber lastEffect
- In the "return" stage, all Fiber nodes of effectTag will be added to this linked list
- Finally, a rootfiber effectList with firsteffect as the starting point
- The commit phase only needs to traverse the effectList
nextEffect nextEffect rootFiber.firstEffect -----------> fiber -----------> fiber
-
After the render phase is completed
- In the performSyncWorkRoot function, fiberNode is passed to commitRoot
- Start the work of the commit phase
-
Commit phase - Renderer - Renderer works
- fiberRootNode as a parameter
- fiberRootNode. A unidirectional linked list of Fiber nodes that need to perform side effects is saved on firsteffect
- The changed props are saved on the updateQueue of these fiber nodes
- The dom operations corresponding to these side effects are executed in the commit phase
- Some declaration cycle hook functions (componentdidxxx) and hook (useeffect) are executed in the commit phase
- Main work in the commit phase
- before mutation stage: before dom operation
- mutation phase: execute dom operation
- layout phase: after dom operation
- There is still some work before mutation and after layout
- Trigger of useEffect
- Priority dependent reset
- Unbinding of ref
- before mutation
- Variable assignment, status reset
- Finally, a firsteffect will be assigned, which will be used in the three sub phases of commit
- After layout
- useEffect related processing
- Performance tracking correlation
- Starting from commit, some life cycle functions, hook
before mutation
- Traverse the effectList and call the commitBeforeMutationEffects function for processing
// Save the previous priority, execute with the synchronization priority, and restore the previous priority after execution const previousLanePriority = getCurrentUpdateLanePriority(); setCurrentUpdateLanePriority(SyncLanePriority); // Mark the current context as CommitContext as the flag of the commit phase const prevExecutionContext = executionContext; executionContext |= CommitContext; // Processing focus status focusedInstanceHandle = prepareForCommit(root.containerInfo); shouldFireAfterActiveInstanceBlur = false; // Main function of beforeMutation stage commitBeforeMutationEffects(finishedWork); focusedInstanceHandle = null;
- commitBeforeMutationEffects
- Deal with the logic of autofocus and blur after DOM node rendering / deletion
- Call getSnapshotBeforeUpdate lifecycle hook
- Scheduling useEffect
function commitBeforeMutationEffects() {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
if (!shouldFireAfterActiveInstanceBlur && focusedInstanceHandle !== null) {
// ... focus blur
}
const effectTag = nextEffect.effectTag;
// Call getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
if ((effectTag & Snapshot) !== NoEffect) {
commitBeforeMutationEffectOnFiber(current, nextEffect);
}
// Scheduling useEffect
if ((effectTag & Passive) !== NoEffect) {
if (!rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) {
rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = true;
// Call a callback function at a certain priority
scheduleCallback(NormalSchedulerPriority, () => {
// Calling useEffect
flushPassiveEffects();
return null;
});
}
}
nextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect;
}
}
- Call getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
- The task in the render phase may be interrupted and restarted, and the componentWillXXX hook may be triggered multiple times Become unsafe
- Using the new getSnapshotBeforeUpdate, it is executed synchronously in the commit phase, so it will only be triggered once
- Asynchronous scheduling
- The flushpassive effects method obtains the effectList from the global variable rootwithpendingpassive effects
- The effectList contains the Fiber node that needs to perform side effects
- Insert dom node (PLACEMENT)
- Update dom node (UPDATE)
- Delete dom node (DELETION)
- When a FunctionComponent contains useEffect or useLayoutEffect, its fiber node will also contain Passive effectTag
- flushPassiveEffect internally traverses the effectList and executes the effect callback function
- useEffect is divided into three steps:
- before mutation stage scheduling flushPassiveEffects in scheduleCallback
- After the layout phase, assign the effectList to rootwidth pending passive effects
- scheduleCallBack triggers flushpassive effects, which traverses rootwidth pending passive effects internally
- reason:
- After the browser finishes rendering and drawing, the function passed to useEffect will delay the call
- This makes it applicable to many common side-effect scenarios of browsers, such as setting subscriptions and event handling
- Therefore, you should not block the browser from updating the screen in the function
- Prevent browser rendering from being blocked during synchronous execution
mutation stage
- Similarly, traverse the effectList, execute the function, and commitMutationEffects
nextEffect = firstEffect;
do {
try {
commitMutationEffects(root, renderPriorityLevel);
} catch (error) {
invariant(nextEffect !== null, 'Should be working on an effect.');
captureCommitPhaseError(nextEffect, error);
nextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect;
}
} while (nextEffect !== null);
- commitMutationEffects
- Reset the text node according to ContentRest effectTag
- Update ref
- Process respectively according to the effectTag, where the effectTag includes placement | update | deletion | hydration
function commitMutationEffects(root: FiberRoot, renderPriorityLevel) {
// Traverse the effectList
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const effectTag = nextEffect.effectTag;
// Reset the text node according to ContentReset effectTag
if (effectTag & ContentReset) {
commitResetTextContent(nextEffect);
}
// Update ref
if (effectTag & Ref) {
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
if (current !== null) {
commitDetachRef(current);
}
}
// Process according to the effectTag
const primaryEffectTag = effectTag & (Placement | Update | Deletion | Hydrating);
switch (primaryEffectTag) {
// Insert DOM
case Placement: {
commitPlacement(nextEffect);
nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Placement;
break;
}
// Insert Dom and update DOM
case PlacementAndUpdate: {
// insert
commitPlacement(nextEffect);
nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Placement;
// to update
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
commitWork(current, nextEffect);
break;
}
// SSR
case Hydrating: {
nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Hydrating;
break;
}
// SSR
case HydratingAndUpdate: {
nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Hydrating;
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
commitWork(current, nextEffect);
break;
}
// Update DOM
case Update: {
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
commitWork(current, nextEffect);
break;
}
// Delete DOM
case Deletion: {
commitDeletion(root, nextEffect, renderPriorityLevel);
break;
}
}
nextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect;
}
}
- Placement effect: the dom node corresponding to the fiber node needs to be inserted into the page
- Get parent dom node
- Getting the sibling node of fiber, getHostSibling, is very time-consuming, because the same fiber node contains more than HostComponent*
- Determine whether to execute parentnode according to the existence of dom node InsertBefore or parentnode appendChild
- Update effect: the fiber node needs to be updated. Call commitWork
- FunctionComponent mutation
- When fiber If the tag is a FunctionComponent, commitHookEffectListUnmount will be called
- Traverse the effectList and execute the destruction function of all uselayouteeffect hooks
- HostComponent mutation
- Call commitUpdate
- Finally, in updateDOMProperties, render the content corresponding to the updateQueue assigned to the fiber node in the render stage completeWork on the page
- FunctionComponent mutation
for (let i = 0; i < updatePayload.length; i += 2) {
const propKey = updatePayload[i];
const propValue = updatePayload[i + 1];
// Processing style
if (propKey === STYLE) {
setValueForStyles(domElement, propValue);
// Handling DANGEROUSLY_SET_INNER_HTML
} else if (propKey === DANGEROUSLY_SET_INNER_HTML) {
setInnerHTML(domElement, propValue);
// Dealing with children
} else if (propKey === CHILDREN) {
setTextContent(domElement, propValue);
} else {
// Process remaining props
setValueForProperty(domElement, propKey, propValue, isCustomComponentTag);
}
}
- Deletion Effect: when the fiber node contains effectTag, call commitDeletion
- Recursively call fiber nodes and descendant fiber nodes Call fiber Componentwillsubcomponent with tag as ClassComponent
- Remove the dom node corresponding to the fiber node from the page
- Unbind ref
- Scheduling the destruction function of useEffect
layout
- The code is executed after dom rendering is completed
- The life cycle hooks and hooks triggered by this stage can directly access the changed dom
- Traverse the effectList and execute the function
function commitLayoutEffects(root: FiberRoot, committedLanes: Lanes) {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const effectTag = nextEffect.effectTag;
// Call lifecycle hooks and hooks
if (effectTag & (Update | Callback)) {
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
commitLayoutEffectOnFiber(root, current, nextEffect, committedLanes);
}
// Assignment ref
if (effectTag & Ref) {
commitAttachRef(nextEffect);
}
nextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect;
}
}
-
commitLayoutEffects
- commitLayoutEffectOnFiber calls life cycle hook and hook related operations
- ClassComponent calls ComponentDidMount/ComponentDidUpdate
- Call this State() second parameter function
- FunctionComponent calls the uselayouteeffect callback function to schedule the destruction and callback function of useEffect
- Uselayouteeffect(): from the destruction of the last update to the execution of this update, it is executed synchronously
- useEffect(): it needs to be scheduled first, and then executed asynchronously after the execution is completed in the Layout phase
- Committatchref: assign ref: get dom instance and update dom
- commitLayoutEffectOnFiber calls life cycle hook and hook related operations
-
After the mutation phase is executed and before the layout starts, switch to root current = finishWork
-
Because the lifecycle functions executed by layout and hook need to get new dom information