Reference Textbook: Proficiency in C++ (9th Edition)
Recursive function: a self-calling function
Functions can also call themselves
Example:
#include<iostream>
void message(int times)
{
if (times > 0)
std::cout << "You are pretty beautiful!!!\n" <<std:: endl;
message(times - 1);//control power
}
int main()
{
message(3);
return 0;
}
Functions are called four times, so the depth of recursion is: 4;
Direct Recursion and Indirect Recursion: One calls its own function directly, the other calls indirectly. A calls B,B calls C,C calls A.
Example: Recursive factorial calculation: Receiving an integer parameter and calculating its factorial
Factorial (n)=n*factorial(n-1); if n > 1;
=1;n=1
#include<iostream>
//#include<string>
int factorial(int arg)
{
if (arg == 1)
return 1;
else
return arg * factorial(arg - 1);
}
int main()
{
int number;
std::cout << "Enter an number and I will dispaly it's factorial:\n";
std::cin >> number;
std::cout << "It is equal to " << factorial(number) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Recursive calculation of maximum common divisions: greastest common divisior,GCD
Rolling phase division
Rotary phase division: Rotary phase division is a method of finding the greatest common divisor of two natural numbers, also known as Euclidean algorithm.
Come from https://baike.baidu.com/item/maximum common divisor
gcd(x,y)=y; if y is divided by x, there is no remainder
= gcd(y,x/y remainder)
#include<iostream>
//#include<string>
int gcd(int x, int y)
{
if ( x% y== 0)
return y;
else
return gcd(y, x % y);
}
int main()
{
int x, y;
std::cout << "Enter two integers:\n";
std::cin >> x >> y;
std::cout << "The two integers' greatest common divisor is " << gcd(x, y) << std::endl;
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
//#include<string>
int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 0)
return 0;
else if (n == 1)
return 1;
else
return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}
int main()
{
std::cout << "The first Fibonacci numbers are: \n";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
std::cout << fib(i) << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
Example: Recursive Binary Search Function: Binary Search can be defined as a Recursive Function
int binarySearch(const int array[], int first ,int last ,int value)
Main parts:
int middle;
if(first>last)
return -1;
if(array[middle]<value)
return binarySearch( const int array[], int middle+1 ,int last ,int value)
if(array[middle]>value)
return binarySearch( const int array[], int first ,int middle-1 ,int value)
Array is an array to search for. The first and last parameters retain the search scope. value finds the target.
#include<iostream>
int binarySearch(const int list[], int first, int last, int value)
{
int middle=(first+last)/2;
bool found = false;
if (first > last)
return -1;
if (list[middle] == value)
return middle;
if (list[middle] > value)
return binarySearch(list, first, middle - 1, value);
else
return binarySearch(list, middle + 1, last, value);
}
const int SIZE = 20;
int main()
{
int array[SIZE] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,89,99,100 };
int number, results;
std::cout << "Enter an integer to search in the list\n";
std::cin >> number;
results = binarySearch(array, 0,SIZE-1, number);
if (results == -1)
std::cout << "That's number isn't exist in the array\n";
else
std::cout << "the number " << number << " you had search, is on the position" << results + 1 << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Example: Programming and Programming: Quick Sorting Algorithms
Use recursion to sort lists effectively:
A recursive function, usually with three parameters, that defines a part of the array to be sorted.
An array arr containing a list of items
Two subscripts start and end
Pseudo-code:
void Quick Sorting( int arr[],int start, int end)
{
If(start<end)
{
Int p=partition(arr,start,end);//Partitioning the array and obtaining the pivot
//Sort less than base elements
//Quick sort (arr,start,p-1);
//Sort larger than base elements
//Quick sort (arr,p+1,end)
}
}
Difficulty: Understand the split array arr[start... end] process,
The partitioning algorithm chooses arr[start] as the base element, and constructs two sub-elements on the left side and right side of the base element in stages.
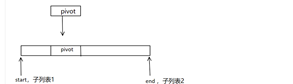
Repeat partitioning, sorting: row x just at the end of sublist 2, assuming x < pivot, to be added to sublist 1 of the start group
Method: Add it to the end of sublist 1 and place it on the left of pivot.
Strategy: Store x in a temporary location, move the elements of sublist 2 to the right, and then put x in the position vacated by pivot, which is inefficient.
The first exchange places y (>= pivot) at the end of sublist 2, while the second exchange places x adjacent to pivot, and the second exchange places x on the left of pivot.
Repeat until the entire list partition
partition function code for executing partitions (incomplete)
int partition(int arr[],int start, int end)
{
int pivotValue=arr[start];
int pivotposition=start;
//The elements from start to end in the rearrangement region, except the reference elements
for(int pos=start+1;pos<=end;pos++)
{
If(arr[pos]<pivotValue)
{
Swap(arr[pivotPosition+1],arr[pos];//Change of position
Swap(arr[pivotPosition],arr[pivotPosition+1];
pivotPosition++;
}
}
return pivotPosition;
}
Code:
#include<iostream>
#Include < algorithm >//swap function
using namespace std;
int quicksort(int[], int, int);//Quick sort
int partition(int[], int, int);//partition
int main()
{
const int SIZE = 10;
int array[SIZE] = { 17,45,6,89,65,33,83,24,45,76 };
for (int k = 0; k < SIZE; k++)
{
cout << array[k] << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
quicksort(array, 0, SIZE);
for (int k = 0; k < SIZE; k++)
{
cout << array[k] << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
int partition(int arry[], int start, int end)
{
int pivotValue = arry[start];
int pivotPosition = start;
//The elements from start to end in the rearrangement region, except the reference elements
for (int pos = start + 1; pos <= end; pos++)
{
if(arry[pos] < pivotValue)
{
swap(arry[pivotPosition + 1], arry[pos]);//Change of position
swap(arry[pivotPosition], arry[pivotPosition + 1]);
pivotPosition++;
}
}
return pivotPosition;
}
int quicksort(int arry[], int start, int end)
{
if (start < end)
{
int p = partition(arry, start, end);//Give the array partition and get the reference point
quicksort(arry, start, p - 1);//Obtain intervals smaller than base elements
quicksort(arry, p + 1, end);//Obtain intervals larger than base elements
}
return 0;
}
ps: It seems that I have a little bug running out with vs, but dev has no problem running out.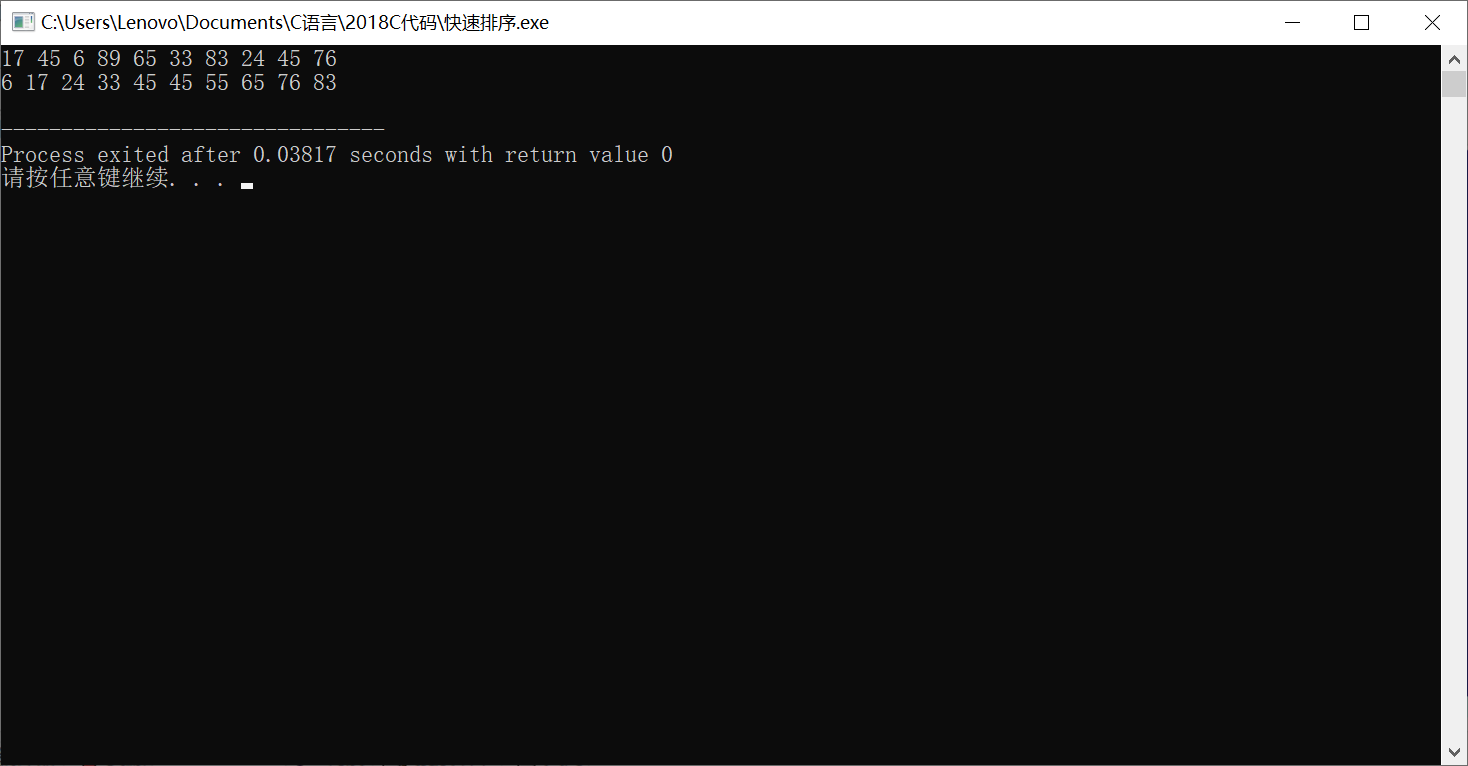
Example: Tower of Hanoi
cheer up!