strings
String type is the most basic data type of redis. Other types are based on it. In short, the value of string type means string. We can store simple and complex types of strings (json, xml), numbers, binary files (pictures, audio, etc.). But not more than 512M.
Common commands
Set value
set key value [ex] [px] [nx|xx] redis>set hello world redis>ok
ex: you can set the expiration time of seconds for the key
px: sets the elapsed time in milliseconds for the key
nx: the key cannot be set successfully until it does not exist. It is used to add
xx: the key must exist before it can be successfully set for adding
redis also provided us with setnx
setnx key value
set, setnx difference
When the key does not exist: return 0
redis>exists hello redis>0
Set the key to hello and the value to world
redis>set hello world redis>ok
Because the key hello exists, setnx returns 0
redis>setnx hello world redis>0
Setnx can also be used as a distributed lock, which is implemented by redis+lua script. Due to the redis single thread command processing mechanism, if multiple users purchase goods or clients execute setnx key value at the same time, only one setnx can be set successfully.
Get value
get key
Get value
redis>get hello redis>"world"
If it does not exist, nil is returned
redis>get helloo redis>nil
Batch setting value
mset key value [key value...]
redis>mset a 1 b 2 c 3 redis>ok
Batch get value
mset key [key...]
redis>mget a b c redis>"1" redis>"2" redis>"3"
If some of the obtained values do not exist, nil will be returned
redis>mget a c b d redis>"1" redis>"2" redis>"3" redis>nil
Batch operation commands can effectively improve the efficiency of development. If there are no mget and mset, the data operation needs to execute the get get set command n times. Think about the time it takes to get if there is 10000 or more data in the set.
Although redis can support 10000 read and write operations per second, this refers to the processing capacity of the redis server, which consumes command time and network time for the client.
Note that batch operation commands may cause redis congestion.
count
incr key
The incr command is used to increase the value automatically.
be careful:
The value is not an integer and an error is returned.
The value is an integer and returns the result of self increment.
If the value is 0, the self increment is 1
redis>exists key redis>0 ############################## redis>incr key redis>1
And incrby, decr and decrby
Usage scenario
Cache function
The most common usage scenarios are for caching. Redis is used as the data caching layer. mysql is used as the data storage layer. Because redis supports high concurrency, caching in seckill and other scenarios can reduce the pressure on mysql.
Counting function
Generally, the reading volume of praise is increased by 1 at a time,
hashes
Hash is also a key value pair data structure in redis.
Note that the key value of the string is not the same as the hash here
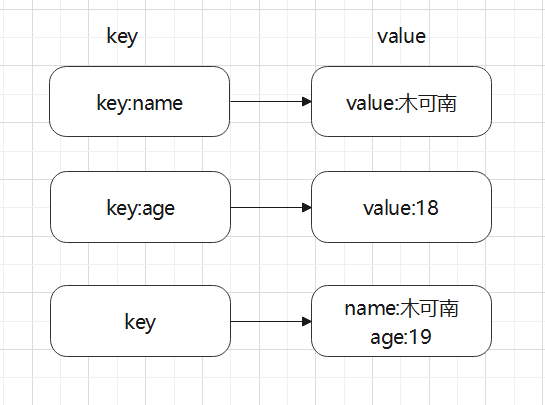
Common commands
Set value
hset key field value
redis>hset key:1 name mukenan redis>1
If the setting is successful, it will return 1, otherwise it will return 0. redis also provides hsetnx. The relationship between them is the same as set and setnx
Get value
hget key field
redis>hget key:1 name redis>mukenan
nil if field does not exist
redis>key:2 name redis>nil ############## redis>key:1 age redis>nil
Delete value
hdel key field [field...]
If one or more fields are deleted, the number of fields will be returned if the deletion is successful
redis>hdel key:1 name redis>1
Calculated value
hlen key
redis>hlen key:1 redis>1
Batch setting or obtaining
hmset key field value [field value...] hmget key field [field...]
redis>hmset key:1 name mukenan age 18 redis>ok ################### redis>hmget key:1 name age redis>"mikenan" redis>"18"
Determine whether the field exists
hexists key field
redis>hexists key:1 name redis>1 ############ redis>hexists key:1 sex redis>0
Returns 1 if it exists, or 0 if it does not
Specify setting value
hincrby key field 1
redis> hincrby key:1 age 10 redis>20
Sets the specified value for the value and returns
The usage scenario has not been encountered yet, so I don't know how to write it
lists
A list type is used to store multiple ordered strings
List types have two characteristics:
First: the elements in the list are ordered, that is, a value can be obtained by index subscript.
Second: the elements in the list can be repeated.
Common commands
Add operation
Insert element from right
rpush key value [value...]
redis>rpush key c b a redis>3
Get value
lrange key 0 -1
redis>lrange key 0 -1 redis>"c" redis>"b" redis>"a"
LRANGE requires two indexes, the first and last elements of the range to be returned. Both indexes can be negative numbers, telling Redis to count from the end: so - 1 is the last element, - 2 is the penultimate element of the list, and so on.
Insert element from left
Use the same method as above
lpush key value [value...]
Insert an element before or after an element
linsert key before|after pivot value
redis>linsert key before b mukenan redis>4
redis>lrange key 0 -1 redis>"c" redis>"mukenan" redis>"b" redis>"a"
Gets the element of the index subscript specified in the list
lindex key index
redis>lindex key 0 redis>"c"
lindex needs an index to tell Redis to count from the end: so - 1 is the last element, - 2 is the penultimate element of the list, and so on.
Gets the length of the list
llen key
redis>llen key redis>4
Pop up elements from the left side of the list
lpop key
redis>lpop key redis>"c" ########### redis>lrange key 0 -1 redis>"mukenan" redis>"b" redis>"a"
Pop up elements is equivalent to deleting elements, so we will only find three elements when querying
Pop up elements from the right side of the list
rpop key
Same as above
Delete elements by index
ltrim key start end
redis>lpush key c redis>lrange key 0 -1 redis>"c" redis>"mukenan" redis>"b" redis>"a" ############## redis>ltrim key 0 2 redis>"c" redis>"mukenan" redis>"b"
Only get the list elements from index 0 to 2, and all other elements will be discarded.
Delete the specified element
lrem key count value
count is divided into three cases:
Count > 0, delete up to count elements from left to right
Count < 0, from right to left, delete up to count absolute value elements, all >
count=0, delete
Blocking operation
blpop key [key...] timeout brpop key [key...] timeout
blpop and brpop are basically the same as lpop and rpop. Timeout: the blocking time, but when timeout=0, it will be blocked until there is data
Usage scenario
It can be used as a message queue, which will be introduced later
sets
The collection is also used to save multiple string elements, but unlike the list, duplicate values are not allowed in the collection, and the elements in the collection are unordered, so the elements cannot be obtained through index subscript.
Common commands
Intra collection operation
Add element
sadd key element [element...]
The returned result is the number of successfully added elements
redis>sadd mykey a b c d e redis>4
Delete element
srem key element [element...]
The returned result is the number of elements deleted successfully
redis>srem mykey a b redis>2
Calculate the number of elements
scard key
The time complexity of scard is O(1). Instead of traversing all the elements of the collection, he directly uses the variables inside redis.
redis>scard mykey redis>2
Determine whether the element is in the collection
sismember key element
Returns 1 if the given element exists in the collection, otherwise returns 0
redis>sismember mykey c redis>1
Returns a specified number of elements from a collection at random
srandmember key [count]
[count] defaults to 1
redis>srandmember myket 2 redis>"c" redis>"d"
Random pop-up elements
spop key
redis>spop mykey redis>"e"
Note: the pop-up elements of spop will be deleted
Get all elements
smembers key
redis>smemebers mykey redis>"d" redis>"c" redis>"e"
Note: the returned elements are unordered
Ordered sets
An ordered set has the characteristics of a set, but the difference is that the elements in the set can be sorted. Another difference is that unlike a list, it can use index subscripts to obtain elements, but will give each element a score.
Common commands
Set element
zadd key score member [score member...]
redis>zadd key:king 123 mukenan redis>1
The returned result represents the number of successfully added elements
redis also adds nx, xx, ch and incr to the zadd command
- nx: member must not exist before it can be set successfully for adding
- xx: member must exist before it can be successfully set for update
- ch: returns the number of ordered set elements and scores changed after this operation
- incr: add score
It should be noted that ordered sets provide sorting fields than sets, but they also produce corresponding costs. The time complexity of zadd is O(log(n)), and the time complexity of sadd is O(1)
Calculate the number of members
zcard key
redis>zcard key:king redis>1
Calculate a member's score
zcard key member
redis>zcard key:king mukenan redis>"123"
Calculate the ranking of members
zrank key member zrevrank key member
zrank returns the ranking from low to high, zrevran vice versa
Delete member
zrem key member
redis>zrem key:king mukenan redis>1
The returned result is the number of successfully deleted
Increase members' scores
zincrby key increment member
redis>zincrby key:king 10 mikenan redis>"133"
Usage scenario
Suitable for ranking system
Common commands
View all keys
keys *
Total number of keys
dbsize
Dbsize does not traverse all keys when calculating the total number of keys, but directly obtains the total number of keys variable built in redis. Therefore, the time complexity of dbsize is O(1), while the keys command will traverse all keys, so its time complexity is O(n)
Check whether the key exists
exists
If the key exists, it returns 1; if it does not exist, it returns 0
Delete key
del key [key ...]
Key expiration
expire key seconds
redis supports adding an expiration time to the key. When the expiration time is exceeded, the key will be deleted automatically.
ttl command returns the remaining time of the key. There are three return values:
- Integer greater than or equal to 0: the remaining expiration time of the key.
- -1: Key has no expiration time set.
- -2: The key does not exist.
Data structure type of key
type key
The result of this command is the data type of the key
Key rename
rename key newkey
Random return of a key
randomkey
Only for your own study and use. If there is infringement, please contact me in time to delete it