1, Relational database and non relational database
1 relational database
Relational database is a structured database, which is created on the basis of relational model (two-dimensional table model) and is generally oriented to records.
SQL statement (standard data query language) is a language based on relational database, which is used to retrieve and operate the data in relational database.
Mainstream relational databases include Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, Microsoft Access, DB2, etc.
2 non relational database
NoSQL (NoSQL = Not Only SQL), which means "not just SQL", is the general name of non relational databases.
In addition to the mainstream relational database, all databases are considered to be non relational.
Mainstream NoSQL databases include Redis, MongBD, Hbase, Memcached, etc.
2, The difference between relational database and non relational database
1. Different data storage methods
The main difference between relational and non relational databases is the way of data storage. Relational data is naturally in table format, so it is stored in rows and columns of the data table. Data tables can be associated with each other, stored cooperatively, and data can be easily extracted.
On the contrary, non relational data is not suitable to be stored in rows and columns of the data table, but large blocks are combined together. Non relational data is usually stored in data sets, such as documents, key value pairs, or graph structures. Your data and its characteristics are the primary factors affecting the choice of data storage and extraction methods.
2. Different expansion modes
The biggest difference between SQL and NoSQL databases may be in the expansion mode. To support the growing demand, of course, it needs to be expanded.
To support more concurrency, the SQL database is vertically expanded, that is, to improve processing capacity and use faster computers, so that the same data set can be processed faster. Because the data is stored in relational tables, the performance bottleneck of operation may involve many tables, which needs to be overcome by improving computer performance. Although SQL database has a large expansion space, it will eventually reach the upper limit of vertical expansion.
NoSQL database is horizontally expanded. Because non relational data storage is naturally distributed, the expansion of NoSQL database can share the load by adding more common * * database servers (nodes) * * to the resource pool.
3. Different support for transactional
If the data operation needs high transaction or complex data query needs to control the execution plan, the traditional SQL database is your best choice in terms of performance and stability. SQL database supports fine-grained control over the atomicity of transactions and is easy to roll back transactions.
Although NoSQL databases can also use transaction operations, they cannot be compared with relational databases in terms of stability, so their real shining value is in the scalability of operations and large amount of data processing.
3, Background of non relational database
1. It can be used to deal with web2 0 three high problems of pure dynamic website type.
(1) High performance – high concurrent read and write requirements for the database
(2)HugeStorage – requirements for efficient storage and access of massive data
(3) High scalability & & high availability – requirements for high scalability and availability of database
Both relational database and non relational database have their own characteristics and application scenarios. The close combination of the two will give web2 0 database development brings new ideas. Let relational databases focus on relationships and non relational databases focus on storage. For example, in a MySQL database environment with separate reading and writing, frequently accessed data can be stored in a non relational database to improve access speed.

4, Introduction to redis

5, Redis installation, deployment and optimization
1. Installation and deployment
systemctl stop firewalld setenforce 0 yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ make tar zxvf redis-5.0.7.tar.gz -C /opt/ cd /opt/redis-5.0.7/ make make PREFIX=/usr/local/redis install #Since the Makefile file is directly provided in the Redis source package, there is no need to execute it first after decompressing the software package/ configure. You can directly execute the make and make install commands to install. #Execute the install provided by the software package in / utils_ server. SH script file sets the relevant configuration files required by Redis service cd /opt/redis-5.0.7/utils ./install_server.sh ...... #Keep returning Please select the redis executable path [/usr/local/bin/redis-server] /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-server #It needs to be manually modified to / usr / local / redis / bin / redis server. Pay attention to correct input at one time



Selected config: Port : 6379 #The default listening port is 6379 Config file : /etc/redis/6379.conf #Profile path Log file : /var/log/redis_6379.1og #log file path Data dir : /var/lib/redis/6379 #Data file path Executable : /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-server #Executable path Cli Executable : /usr/local/bin/redis-cli #Client command tool

#Put the executable program file of redis into the directory of path environment variable for system identification ln -s /usr/local/redis/bin/* /usr/local/bin/ #When install_ server. After the SH script runs, the Redis service has been started. The default listening port is 6379 netstat -natp | grep redis

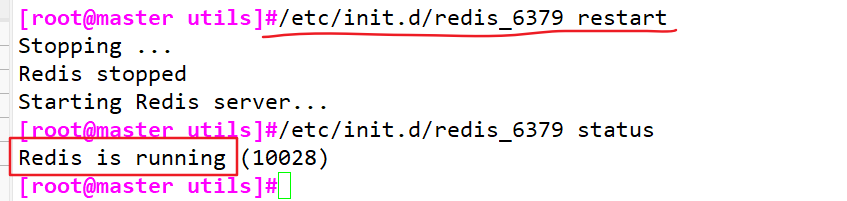
2. Redis service control
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 stop #stop it /etc/init.d/redis_6379 start #start-up /etc/init.d/redis_6379 restart #restart /etc/init.d/redis_6379 status #state
3. Modify / etc / redis / 6379 Conf parameter
#Modify the configuration / etc / redis / 6379 Conf parameter vim /etc/redis/6379.conf bind 127.0.0.1 192.168.238.10 #Line 70, add the listening host address port 6379 #Line 93: Redis's default listening port daemonize yes #Line 137, enable the daemon pidfile /var/run/redis_6379.pid #Line 159, specify PID file loglevel notice #167 lines, log level logfile /var/log/redis_6379.log #172 line, specify log file /etc/init.d/redis_6379 restart







6, Redis related command tools
1. Redis cli command line tool
Syntax: redis-cli -h host -p port -a password -h: Specify remote host -p: appoint Redis Port number of the service -a: Specify the password. If the database password is not set, it can be omitted-a option If no option representation is added, 127 is used.0.0.1:6379 Connect the on this machine Redis database redis-cli -h 192.168.40.50 -p 6379

2. Redis benchmark test tool
Redis benchmark is the official redis performance testing tool, which can effectively test the performance of redis services.
Basic test syntax: redis-benchmark [option] [Option value]. -h: Specify the server host name. -p: Specify the server port. -s: Specify server socket -c: Specifies the number of concurrent connections. -n: Specify the number of requests. -d: Specified in bytes SET/GET The data size of the value. -k: 1=keep alive 0=reconnect. -r: SET/GET/INCR Use random key,SADD Use random values. -P: Transmission through pipeline<numreq>Request. -q: forced return redis. Show only query/sec Value. --csv: with CSV Format output. -l: Generate a loop and permanently execute the test. -t: Run only a comma separated list of test commands. -I: Idle pattern. Open only N individual idle Connect and wait.
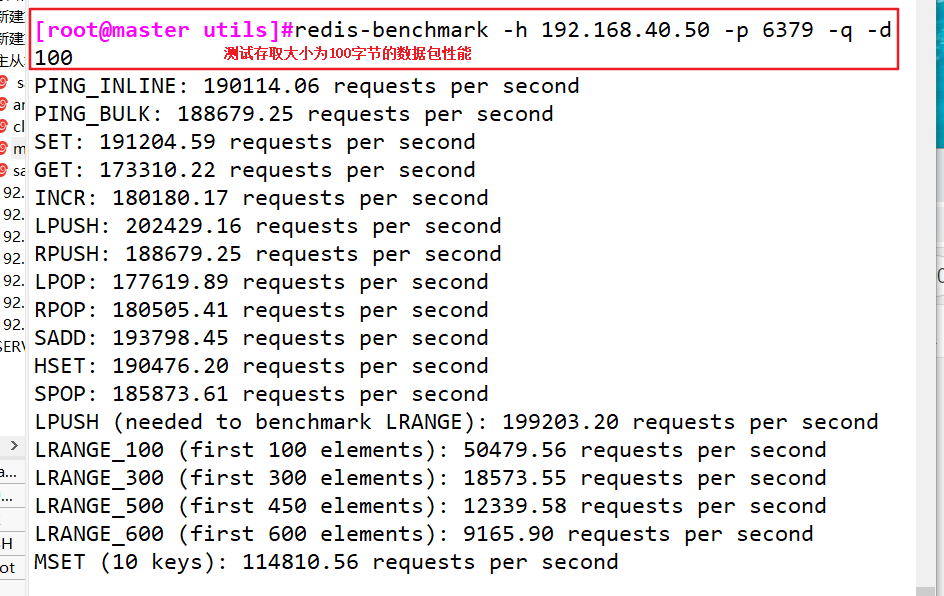
- Send 5-minute concurrent connection and 10W request tests to Redis server with IP address 192.168.40.50 and port 6379


- Test the performance of accessing packets with a size of 100 bytes
redis-benchmark -h 192.168.40.50 -p 6379 -q -d 100
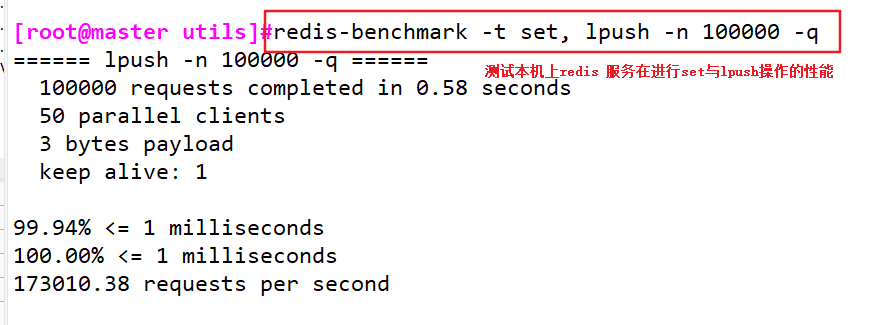
- Test the performance of Redis service on this machine when performing set and lpush operations
redis-benchmark -t set, lpush -n 100000 -q
7, Common commands of Redis database
1.get and set read / write key value pair commands
set: Store data, and the command format is set key value get: Get data, command format is get key
192.168.40.50:6379> set key2 drop OK 192.168.40.50:6379> get key2 " drop"

2. The keys command is used in combination with symbols


3. The command is followed by + nx. If it does not exist, it will be executed; if it exists, it will not be executed


4. The Del command can delete the specified key of the current database

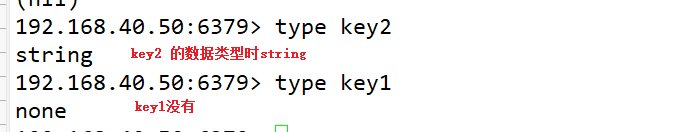
5. The type command can obtain the value type corresponding to the key
192.168.40.50:6379> type k2 string
6. The rename command renames an existing key. (overlay)
Command format: rename source key target key


- The renamenx command is used to rename the existing key and check whether the new name exists. If the target key exists, it will not be renamed. (not covered)

7 the dbsize command is used to view the number of key s in the current database
192.168.40.50:6379> dbsize

8. Use the config set requirepass yourpassword command to set the password

9. Use the config get requirepass command to view the password (once the password is set, the password must be verified first, otherwise all operations are unavailable)

10. Common commands of redis multi database

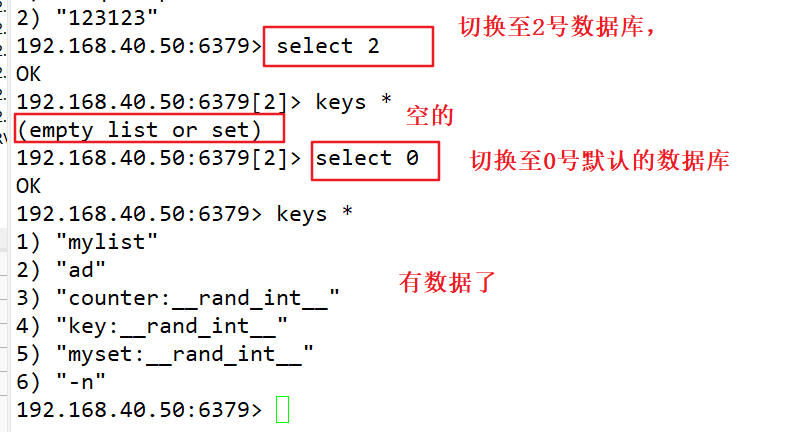
11.move instruction movement of key value pairs between multiple databases
move Key value serial number
192.168.40.50:6379> set k1 66 OK 192.168.40.50:6379> get k1 "66" 192.168.40.50:6379> select 5 OK 192.168.40.50:6379[5]> get k1 (nil) 192.168.40.50:6379[5]> select 0 OK 192.168.40.50:6379> move k1 5 (integer) 1 192.168.40.50:6379> select 5 OK 192.168.40.50:6379[5]> get k1 "66" 192.168.40.50:6379[5]> select 0 OK 192.168.40.50:6379> get k1 (nil)

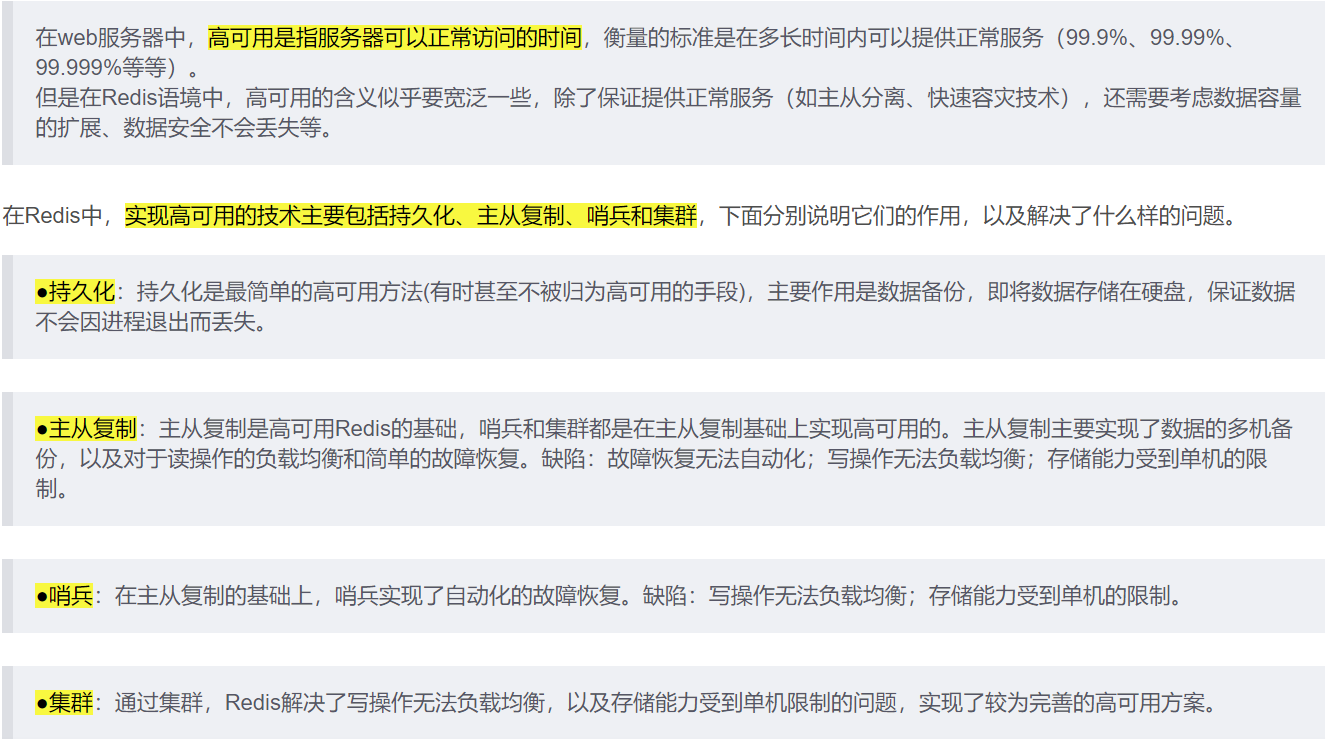
8, Redis high availability
9, Redis persistence

10, Two persistence modes of Redis RDB and AOF
1.RDB persistence
- rdb: refers to saving the generated snapshot of the data in the current process in the memory to the hard disk within the specified time interval (so it is also called snapshot persistence), and storing it in binary compression. The suffix of the saved file is rdb; Redis can restart reading data when the snapshot is started.
1.1 manual trigger and automatic trigger
(1) Manual trigger

(2) Automatic trigger

vim /etc/redis/6379.conf #---------Line 219 bgsave will be called when any of the following three save conditions are met----- save 900 1 : When the time reaches 900 seconds, if redis If the data has changed at least once, execute bgsave save 300 10 : When the time reaches 300 seconds, if redis If the data has changed at least 10 times, execute bgsave save 60 10000 : When the time reaches 60 seconds, if redis If the data has changed at least 10000 times, execute bgsave #---------Line 242 whether RDB file compression is enabled--------------------------------------- rdbcompression yes #---------Line 254 specifies the RDB file name---------------------------------------------- dbfilename dump.rdb #---------Line 264 specifies the directory where the RDB file and AOF file are located------------------------------- dir /var/lib/redis/6379

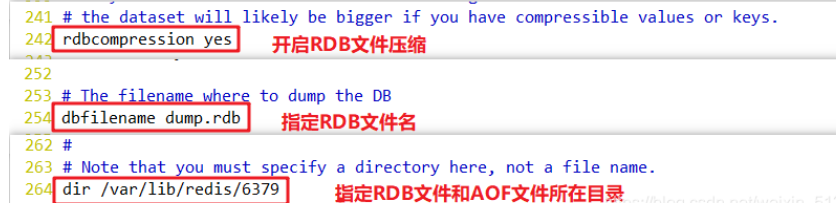
1.2 process
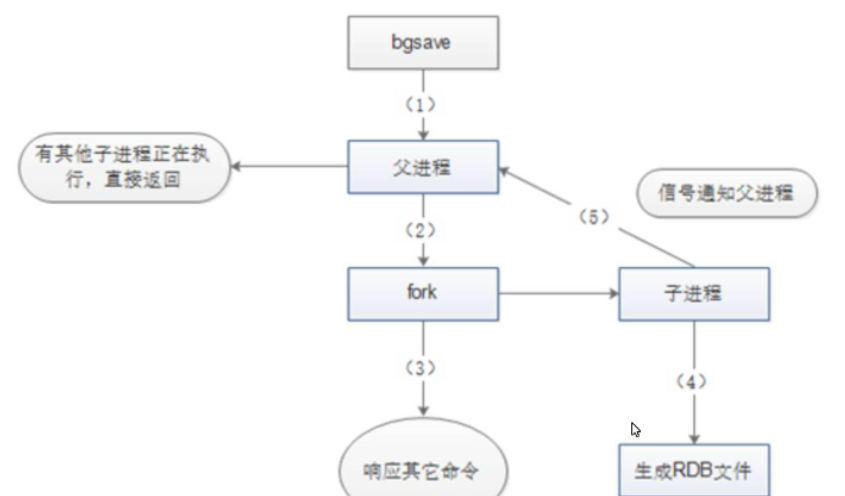

1.3 loading at startup

2.AOF persistence
- Aof persistence: records every write and delete command executed by Redis in a separate log file, and the query operation will not be recorded; When Redis restarts, execute the command in the AOF file again to recover the data.
- Compared with RDB, AOF has better real-time performance, so it has become the mainstream persistence scheme.
(1) Turn on AOF
- Redis server turns on RDB and turns off AOF by default; To enable AOF, you need to configure in the configuration file:
vim /etc/redis/6379.conf #700 lines; Modification; Turn on AOF appendonly yes #704 lines; Specify AOF file name appendfilename "appendonly.aof" #Does line 796 ignore the last instruction that may have a problem aof-load-truncated yes /etc/init.d/redis_6379 restart

(2) Execution process

(1) Command append

(2) File write and file sync

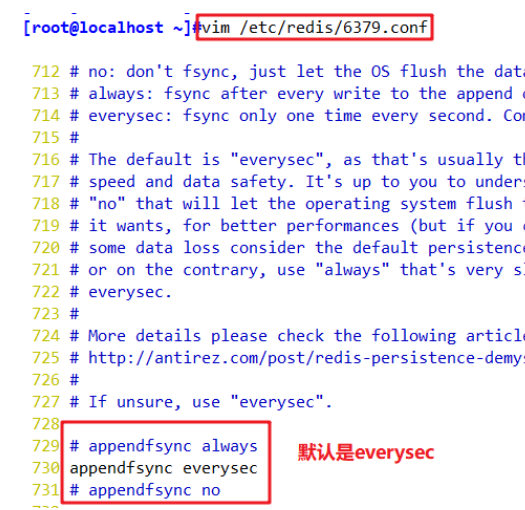
There are three synchronization methods for the synchronization file policy of AOF cache, which are:

vim /etc/redis/6379.conf #----------Line 729---------- #appendfsync always appendfsync everysec #appendfsync no
(3) File rewrite
- With the passage of time, the Redis server executes more and more write commands, and the AOF file will become larger and larger; Too large AOF files will not only affect the normal operation of the server, but also cause the data recovery to take too long.

(4) Process of file rewriting

(5) Load on startup

3. Advantages and disadvantages of RDB and AOF

11, Redis performance management
1. View Redis memory usage

2. Memory fragmentation rate
Memory value allocated by the operating system used_memory_rss divide Redis Memory value used used_memory Calculated; Memory fragmentation is an inefficient allocation by the operating system/Caused by reclaiming physical memory (discontinuous physical memory allocation)

3. Memory utilization
- The memory utilization of redis instance exceeds the maximum available memory, and the operating system will start exchanging memory and swap space.

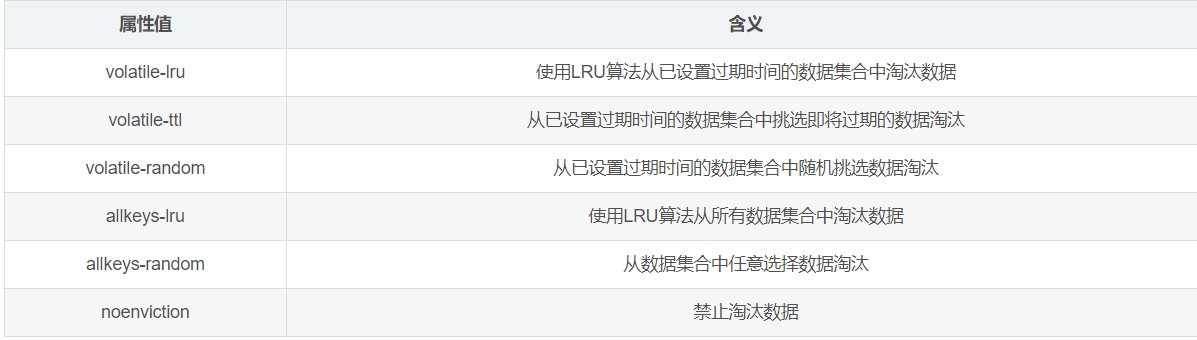
4. Internal recycling key
Ensure reasonable distribution redis Limited memory resources.

vim /etc/redis/6379.conf #---------598 uncomment--------------------------------------------------------------------------- maxmemory-policy noenviction