Redis Learning 09 - Multi-database and Server Command
I. Multi-database
A Redis instance can contain multiple databases. Each client can specify which database to connect to a Redis instance, just like creating multiple databases in a mysql, and the client can specify which database to connect to.
A Redis instance can provide up to 16 databases with subscripts ranging from 0 to 15. The client defaults to database 0, or can select which database to connect to, as follows
Select Library 1
127.0.0.1:6379> select 1
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
(empty list or set)
Select Library 0
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> select 0
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "mysortedset"
2) "myset3"
3) "mylist2"
4) "mylist"
5) "myset2"
6) "username"
7) "myset4"
8) "myset1"
9) "mylist3"
10) "myhash"
11) "mysorted"
Two. Move library
Order:
move key dbMeaning:
Move the key of the current library to the db Library
Example
127.0.0.1:6379> select 1
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
(empty list or set)
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> select 0
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> move mysorted 1
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> select 1
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
1) "mysorted"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> zrange mysorted 0 -1
1) "wiming"
2) "xiaoming"
3. Server commands
3.1 ping
Order:
ping [message]Meaning:
Test whether the connection survives
Example
127.0.0.1:6379> ping
PONG
127.0.0.1:6379> ping xiaoming
"xiaoming"
Now let's turn off the server to test it.
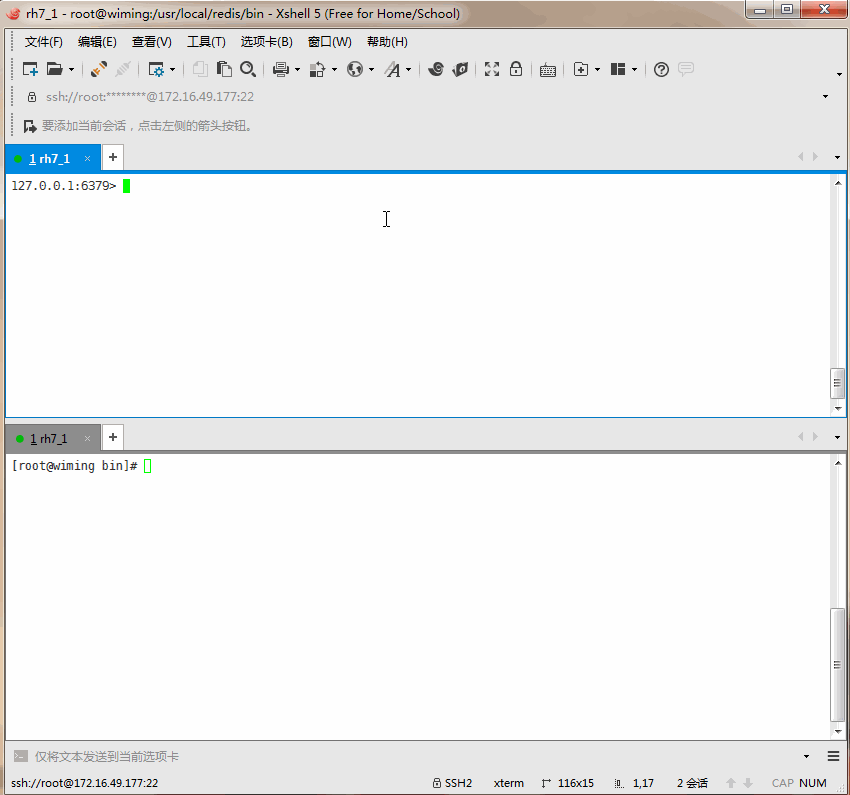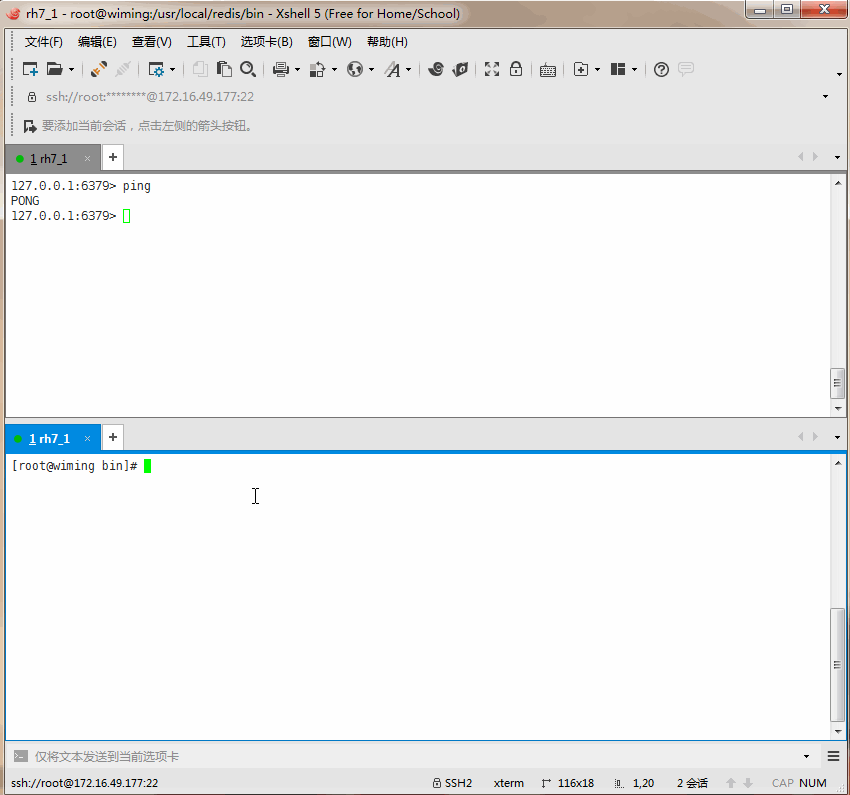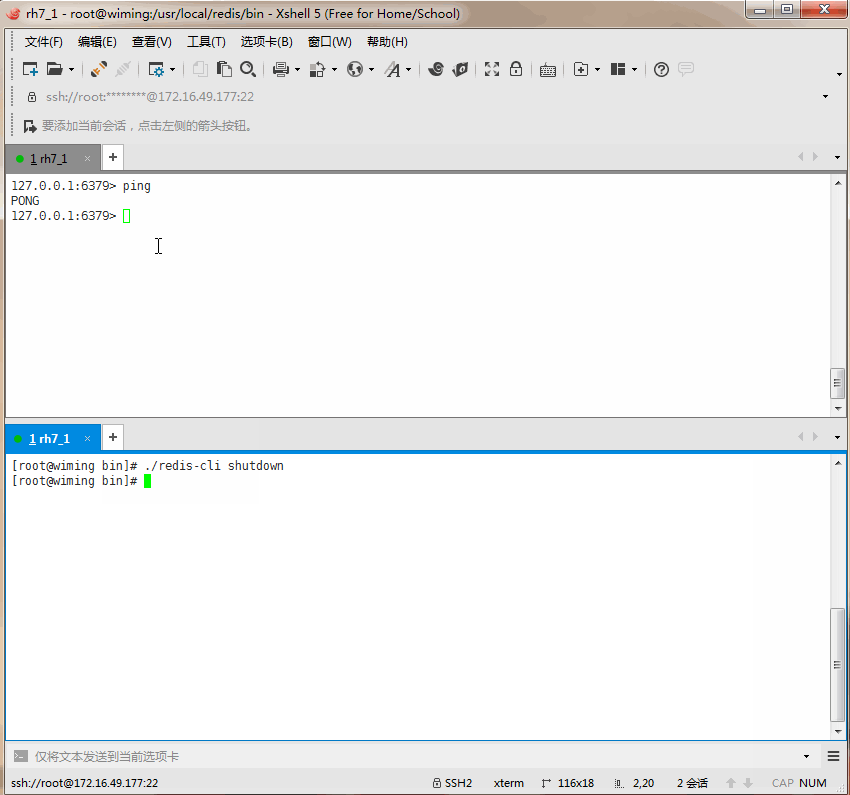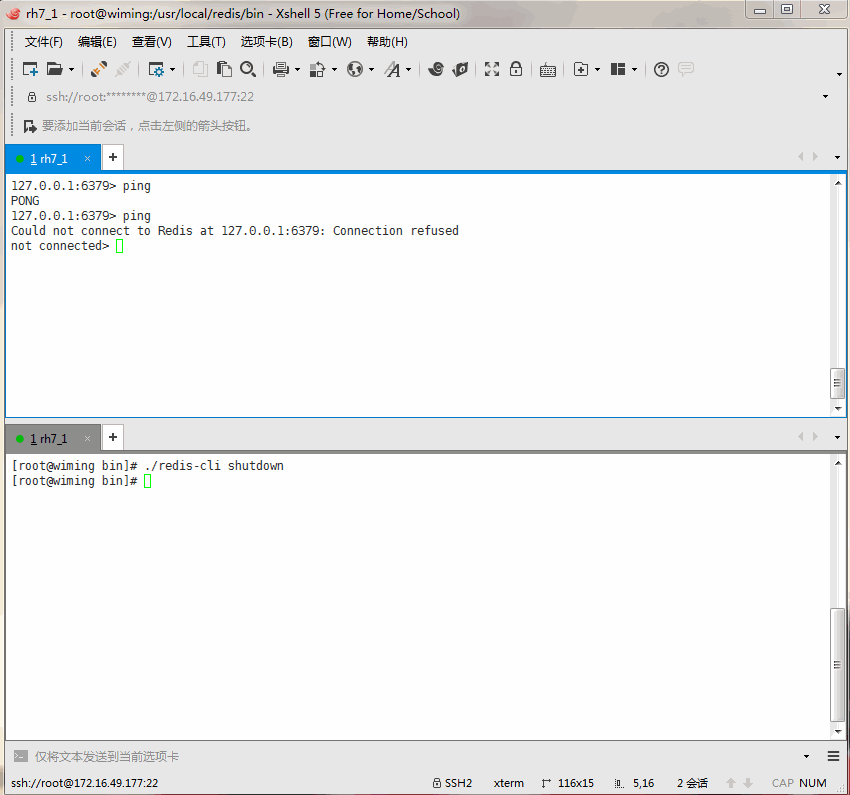
127.0.0.1:6379> ping
Could not connect to Redis at 127.0.0.1:6379: Connection refused
3.2 echo
Order:
echo messageMeaning:
Print something on the command line
Example
127.0.0.1:6379> echo wiming
"wiming"
3.3 select
Order:
select dbMeaning:
Select the database, numbered from 0-15
Example
127.0.0.1:6379> select 2
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[2]> select 0
OK
3.4 quit
Order:
quitMeaning:
Exit connection
Example
127.0.0.1:6379> quit
[root@wiming bin]#
3.5 dbsize
Order:
dbsize
Meaning:
Get the number of key s in the current database
Example
127.0.0.1:6379> dbsize
(integer) 10
3.6 info
Order:
info
Meaning:
Access to server information and statistics
Example
127.0.0.1:6379> info
# Server
redis_version:4.0.2
redis_git_sha1:00000000
redis_git_dirty:0
redis_build_id:17ae9636a5224df7
redis_mode:standalone
os:Linux 3.10.0-123.el7.x86_64 x86_64
arch_bits:64
multiplexing_api:epoll
atomicvar_api:atomic-builtin
gcc_version:4.8.2
process_id:17733
run_id:b09701789073b432652ef68cb5c7ecd5b6fd9a5c
tcp_port:6379
uptime_in_seconds:404
uptime_in_days:0
hz:10
lru_clock:13443152
executable:/usr/local/redis/bin/./redis-server
config_file:/usr/local/redis/bin/redis.conf
.......Output is omitted.........
3.7 flushdb
Order:
flushdb
Meaning:
Delete all key s in the current database
Example
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
1) "mysorted"
2) "name"
3) "age"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> flushdb
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
(empty list or set)
3.8 flushall
Order:
flushall
Meaning:
Get all key s in all databases
Example
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> set name wiming
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> set age 18
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
1) "age"
2) "name"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> select 0
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "mylist3"
2) "mylist"
3) "myset4"
4) "myset2"
5) "mysortedset"
6) "myset3"
7) "myhash"
8) "myset1"
9) "mylist2"
10) "username"
127.0.0.1:6379> flushall
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
(empty list or set)
127.0.0.1:6379> select 1
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
(empty list or set)