Reading guide
Set type is a set of string type, which is characterized by disordered and non repetitive set elements. Each set can store 232 - 1 elements (more than 4 billion) at most. Set type mainly has the following application scenarios.
1. Collection of friends / followers / fans / interested people
The unique feature of set type makes it suitable for storing the collection of friends / followers / fans / interested people. The number of elements in the collection may be many, and the cost of taking them all out each time is not small. Set type provides some practical commands for directly operating these collections, such as:
A. The sinter command can obtain the common friends of users A and B
b. The sismember command can determine whether A is A friend of B
c. The scard command can get the number of friends
d. When following, the smove command can transfer B from A's fan collection to A's friend collection
2. Random display
Generally, the display area of the app home page is limited, but it can not always display fixed content. One way is to determine a batch of content to be displayed, and then obtain it randomly. As shown in the figure below, there are 29 challenge songs on the day of kugou music K-song challenge arena, and 5 are randomly displayed on the home page; A total of 200 golden songs were played yesterday, and 30 were randomly displayed on the home page.
The set type is suitable for storing all the contents that need to be displayed, while the srandmember command can get several at random.
3. Blacklist / whitelist
Often, for security reasons, businesses need to set user blacklists, ip blacklists, device blacklists, etc. the set type is suitable for storing these blacklist data. The sismember command can be used to judge whether users, ip and devices are in the blacklist.
Create test class [demo12.py]
newly added
sadd(name,values)
name - adds an element to the corresponding set
import redis
r = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, decode_responses=True)
r.flushall()
r.sadd("myset","block A","Plum blossom A","heart A","spade A","king","Xiao Wang")
print(r.scard("myset"))#Set length
print(r.smembers("myset"))#Query all members 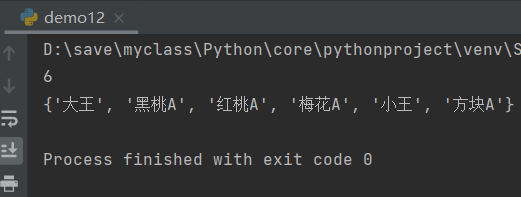
Tuple access
import redis
r = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, decode_responses=True)
r.flushall()
r.sadd("myset","block A","Plum blossom A","heart A","spade A","king","Xiao Wang")
scan=r.sscan("myset")#Get by tuple
print(scan)
print(r.sscan_iter("myset"))#Get iterator
#Ergodic iterator
for str in r.sscan_iter("myset"):
print(str)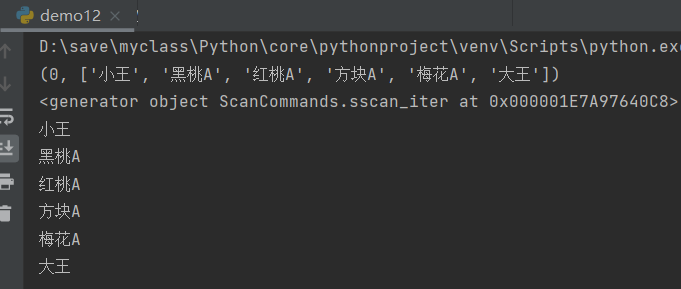
Difference set
import redis
r = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, decode_responses=True)
r.flushall()
r.sadd("myset1","block A","Plum blossom A","heart A","spade A","king","Xiao Wang")
r.sadd("myset2","Block 2","Plum blossom 2","Hearts 2","Spade 2","king","Xiao Wang")
print(r.smembers("myset1"))#myset1 all elements
print(r.smembers("myset2"))#myset2 all elements
print(r.sdiff("myset1","myset2"))#Difference set of myset1 to myset2
print(r.sdiff("myset2","myset1"))#Difference set of myset2 to myset1
r.sdiffstore("myset3","myset1","myset2")#Store the difference set between myset1 and myset2 in myset3
print("myset3:",r.smembers("myset3"))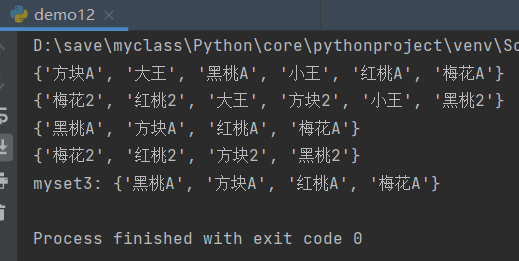
intersection
import redis
r = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, decode_responses=True)
r.flushall()
r.sadd("myset1","block A","Plum blossom A","heart A","spade A","king","Xiao Wang")
r.sadd("myset2","Block 2","Plum blossom 2","Hearts 2","Spade 2","king","Xiao Wang")
print(r.smembers("myset1"))#myset1 all elements
print(r.smembers("myset2"))#myset2 all elements
print(r.sinter("myset1","myset2"))#Intersection of myset1 and myset2
print(r.sinter("myset2","myset1"))#Intersection of myset2 and myset1
r.sinterstore("myset3","myset1","myset2")#Save the intersection of myset2 to myset3
print("myset3:",r.smembers("myset3"))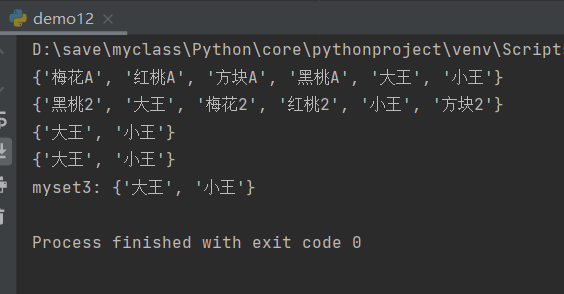
Union
import redis
r = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, decode_responses=True)
r.flushall()
r.sadd("myset1","block A","Plum blossom A","heart A","spade A","king","Xiao Wang")
r.sadd("myset2","Block 2","Plum blossom 2","Hearts 2","Spade 2","king","Xiao Wang")
print(r.smembers("myset1"))#myset1 all elements
print(r.smembers("myset2"))#myset2 all elements
print(r.sunion("myset1","myset2"))#Union of myset1 and myset2
print(r.sunion("myset2","myset1"))#Union of myset2 and myset1
r.sunionstore("myset3","myset1","myset2")#Store the union of myset1 and myset2 in myset3
print("myset3:",r.smembers("myset3"))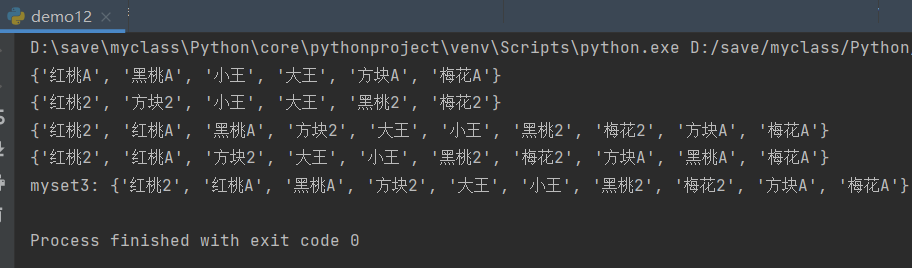
Determine whether it is a member of the collection
import redis
r = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, decode_responses=True)
r.flushall()
r.sadd("myset1","block A","Plum blossom A","heart A","spade A","king","Xiao Wang")
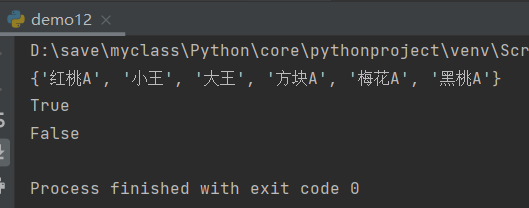
print(r.smembers("myset1"))#myset1 all elements
print(r.sismember("myset1","heart A"))#Judge whether heart A is A member of the set
print(r.sismember("myset1","Hearts 2"))#Determine whether heart 2 is a member of the set
move
smove(src, dst, value)
Move a member from one set to another
import redis
r = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, decode_responses=True)
r.flushall()
r.sadd("myset1","block A","Plum blossom A","heart A","spade A","king","Xiao Wang")
r.sadd("myset2","Block 2","Plum blossom 2","Hearts 2","Spade 2","king","Xiao Wang")
print(r.smembers("myset1"))#myset1 all elements
print(r.smembers("myset2"))#myset2 all elements
r.smove("myset1", "myset2", "block A")
print(r.smembers("myset1"))#myset1 all elements
print(r.smembers("myset2"))#myset2 all elements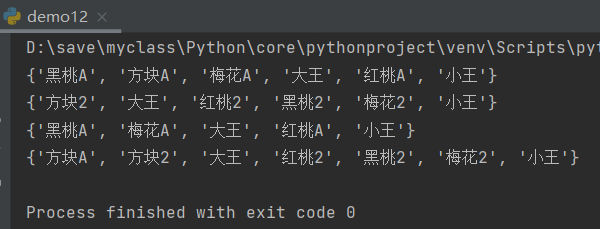
Delete · can be deleted randomly or specified
import redis
r = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, decode_responses=True)
r.flushall()
r.sadd("myset1","block A","Plum blossom A","heart A","spade A","king","Xiao Wang")
r.sadd("myset2","Block 2","Plum blossom 2","Hearts 2","Spade 2","king","Xiao Wang")
print(r.smembers("myset1"))#myset1 all elements
print(r.smembers("myset2"))#myset2 all elements
print("Random deletion:",r.spop("myset1"))
print("Specify delete",r.srem("myset2","Xiao Wang"))
print(r.smembers("myset1"))#myset1 all elements
print(r.smembers("myset2"))#myset2 all elements
I hope it can help you. Welcome to triple CLICK