Redis Fragmentation Technology
requirement analysis
- If all data is saved in a redis, if the server is damaged, all services will be affected.
- Using single Redis memory settings generally does not exceed 1G. However, some business data is very large. If memory is not modified, data cannot be stored.
Improvement scheme: Redis fragmentation technology is adopted.
Advantage:
- The dynamic expansion of memory data can be realized by redis fragmentation.
- Using fragmentation, each redis node saves as much as 1/n of data as possible to prevent data loss.
- For users, the whole redis fragmentation is a service.
Fragment construction
Copy configuration files
Note: Copy redis.conf file to shards, and copy three copies with the name of
redis-6379.conf/redis-6380.conf/redis-6381.conf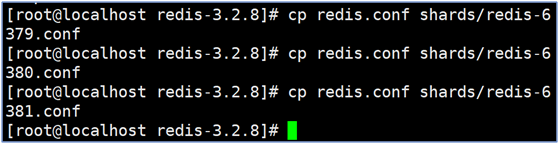
Modify port number
Note: Modify the configuration file 6380/6381 to the specified port.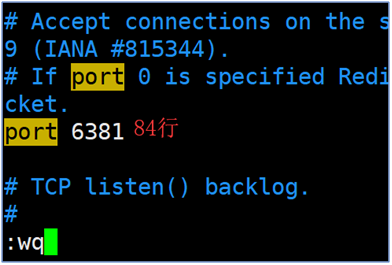
Restart Redis Service
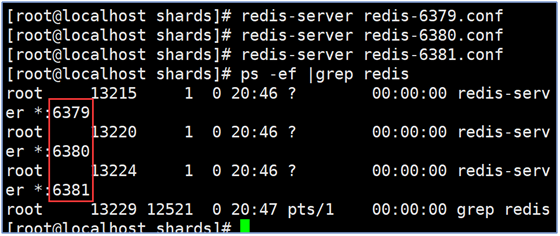
Fragmentation test
@Test publicvoidtestShard(){ /** * Create fragmented objects * 1.poolConfig Identification pool size * 2.shardsredis Fragmented node information */ JedisPoolConfigpoolConfig = newJedisPoolConfig(); poolConfig.setMaxTotal(1000); poolConfig.setTestOnBorrow(true); //Detection before getting links List<JedisShardInfo>shards = newArrayList<>(); shards.add(newJedisShardInfo("192.168.126.166",6379)); shards.add(newJedisShardInfo("192.168.126.166",6380)); shards.add(newJedisShardInfo("192.168.126.166",6381)); ShardedJedisPoolpool = newShardedJedisPool(poolConfig, shards); //Get redis links ShardedJedisjedis = pool.getResource(); jedis.set("shards","Save fragmented data"); System.out.println(jedis.get("shards")); //Return the link back to the pool pool.returnResource(jedis); }
Hash Consistency Algorithms
How to save data
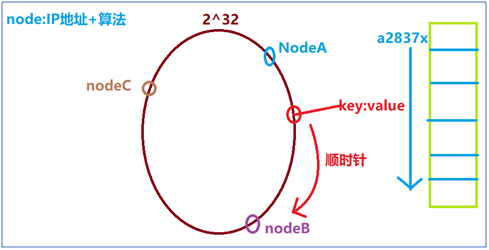
- The node's IP + algorithm determines the unique hash value, and then the node's location is determined in memory.
- When data is saved, hash operations are performed according to Key to determine the only location.
- Find the nearest node clockwise according to the current key location for mounting.
Equilibrium
Description: According to the number of redis nodes, the data should be evenly divided as much as possible. The data in each node should be guaranteed as much as 1/n.
Promotion: In order to ensure balance, hash consistency algorithm introduces the concept of virtual nodes. In order to balance data, if one node is not enough, it generates multiple nodes.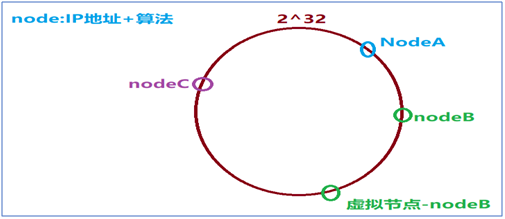
Monotonicity
Note: If node nodes are added, data migration can be dynamically implemented. This feature is called monotonicity.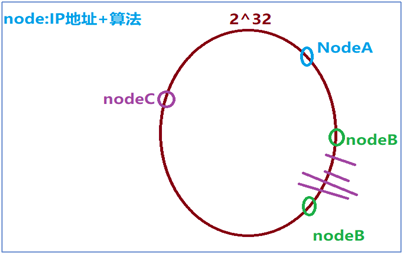
Dispersivity
Features: Due to distributed reasons, users can not get all the memory space when using memory, resulting in a key corresponding to multiple locations.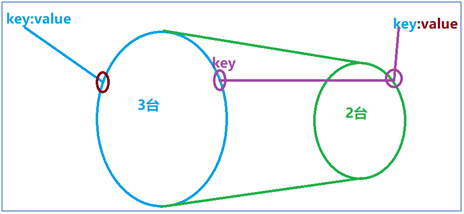
load
Note: Load considers decentralization from another perspective
Features: One location corresponds to multiple key s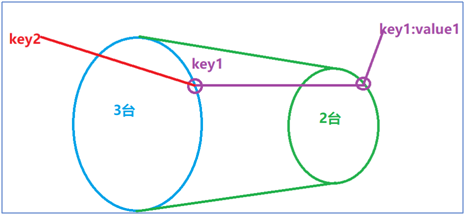
How to solve this problem: When designing the architecture, we need to use all the memory space.
Spring integrated fragmentation
Editing properties files
redis.host=192.168.126.166 redis.port.a=6379 redis.port.b=6380 redis.port.c=6381 redis.maxTotal=1000
Edit Spring configuration file
<!--Realization spring Integration fragmentation --> <bean id="poolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig"> <property name="maxTotal" value="${redis.maxTotal}"/> </bean> <!--Define three redis node --> <bean id="shardInfoA" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisShardInfo"> <constructor-arg name="host" value="${redis.host}"/> <constructor-arg name="port" value="${redis.port.a}"/> </bean> <bean id="shardInfoB" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisShardInfo"> <constructor-arg name="host" value="${redis.host}"/> <constructor-arg name="port" value="${redis.port.b}"/> </bean> <bean id="shardInfoC" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisShardInfo"> <constructor-arg name="host" value="${redis.host}"/> <constructor-arg name="port" value="${redis.port.c}"/> </bean> <!--Define connection pool --> <bean id="jedisPool" class="redis.clients.jedis.ShardedJedisPool"> <constructor-arg name="poolConfig" ref="poolConfig"/> <constructor-arg name="shards"> <list> <ref bean="shardInfoA"/> <ref bean="shardInfoB"/> <ref bean="shardInfoC"/> </list> </constructor-arg> </bean>
Editing Tool API
@Service publicclassRedisService { //Some projects need, some projects need not. Set required=false, inject if you have it, and inject if you haven't. @Autowired(required = false) privateShardedJedisPoolshardedJedisPool; publicvoidset(String key,Stringvalue){ ShardedJedisjedis = shardedJedisPool.getResource(); jedis.set(key, value); shardedJedisPool.returnResource(jedis); } //Add timeout time publicvoidset(String key,Stringvalue,intseconds){ ShardedJedisjedis = shardedJedisPool.getResource(); jedis.setex(key, seconds, value); shardedJedisPool.returnResource(jedis); } //Edit get method public String get(String key){ ShardedJedisjedis = shardedJedisPool.getResource(); String result = jedis.get(key); shardedJedisPool.returnResource(jedis); returnresult; } }
Note: After editing the API, package common.
Modifying the Business Layer Method
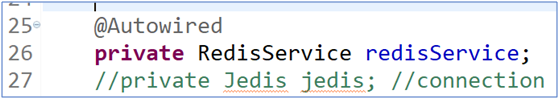
Handover Business Method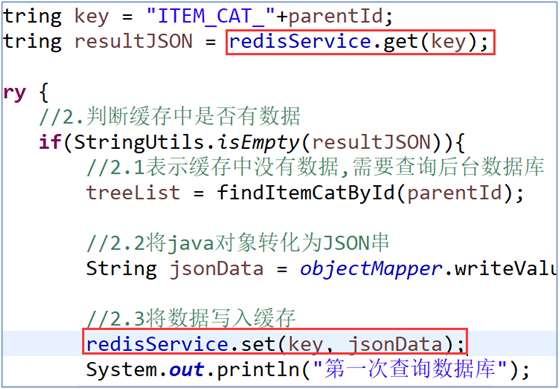
Redis Sentinel
Business needs
Memory expansion can be achieved by using redis fragmentation technology, but if one of the machines goes down, the whole redis fragmentation will not work properly.
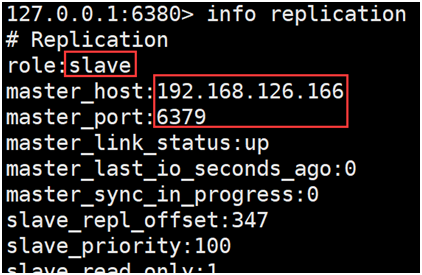
Implementing master-slave mounting
Role division: 6379 master 6380/6381 slave
- Check node status info replication
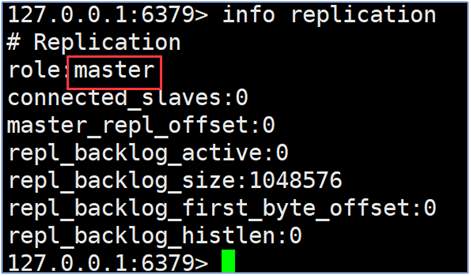
- Implementing master-slave mounting
Order:
127.0.0.1:6380> SLAVEOF 192.168.126.166 6379
- Check state
Sentinel implementation
Sentinel principle
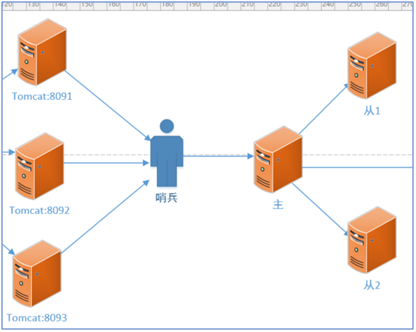
- Sentinel monitors the status of the host and gets all the information of the host, including slave information.
- Through the heartbeat detection mechanism, if three connections do not respond, it is concluded that the host is down and the Sentry will elect a slave from the slave to act as the host.
At the same time, another slave (old host) is modified to mount to the current host. - When the old mainframe is repaired, act as a slave and wait for the next election.
Editing Sentinel Profile
- Save the document in its original name
cp sentinel.conf sentinel - Turn off protection mode

- Modifying Sentinel Monitoring Node Information
sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6379 1
mymaster host variable name
IP: Port Host Information
2 Number of electoral votes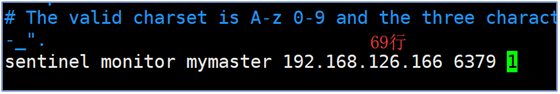
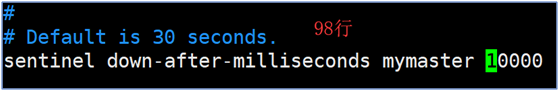
- Modify the selection time
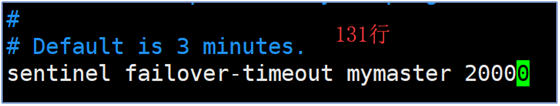
- Modify selection failure time
sentinel test
- Start Sentinel
redis-sentinel sentinel.conf - Startup Test
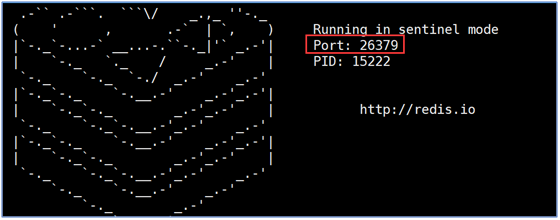
- Turn off the main engine and check whether the Sentry can be selected.
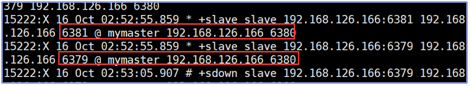
Spring Integrated Sentinel
Introductory case
//IP: port Set<String>sentinels = new HashSet<>(); sentinels.add("192.168.126.166:26379"); JedisSentinelPoolpool = newJedisSentinelPool("mymaster", sentinels); //new JedisSentinelPool(masterName, sentinels, poolConfig) Jedisjedis = pool.getResource(); jedis.set("shaobing","sentinel test"); System.out.println("get data:"+jedis.get("shaobing")); pool.returnResource(jedis);
Editing properties files
redis.maxTotal=1000 redis.sentinel=192.168.126.166:26379 redis.mastername=mymaster
Editing configuration files
<bean id="sentinelPool" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisSentinelPool"> <constructor-arg name="masterName" value="${redis.mastername}"/> <constructor-arg name="sentinels"> <set> <value>${redis.sentinel}</value> </set> </constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="poolConfig" ref="poolConfig"/> </bean> <!--Define pool objects --> <bean id="poolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig"> <property name="maxTotal" value="${redis.maxTotal}"/> </bean>
Defining Tool Classes
@Service publicclassRedisService { //Introduction of Sentinel Configuration @Autowired(required=false) privateJedisSentinelPoolsentinelPool; publicvoidset(String key,Stringvalue){ Jedisjedis = sentinelPool.getResource(); jedis.set(key, value); sentinelPool.returnResource(jedis); } publicvoidset(String key,Stringvalue,intseconds){ Jedisjedis = sentinelPool.getResource(); jedis.setex(key, seconds, value); sentinelPool.returnResource(jedis); } public String get(String key){ Jedisjedis = sentinelPool.getResource(); String result = jedis.get(key); sentinelPool.returnResource(jedis); returnresult; } }