redux Chinese document https://www.redux.org.cn/
redux official website https://redux.js.org/
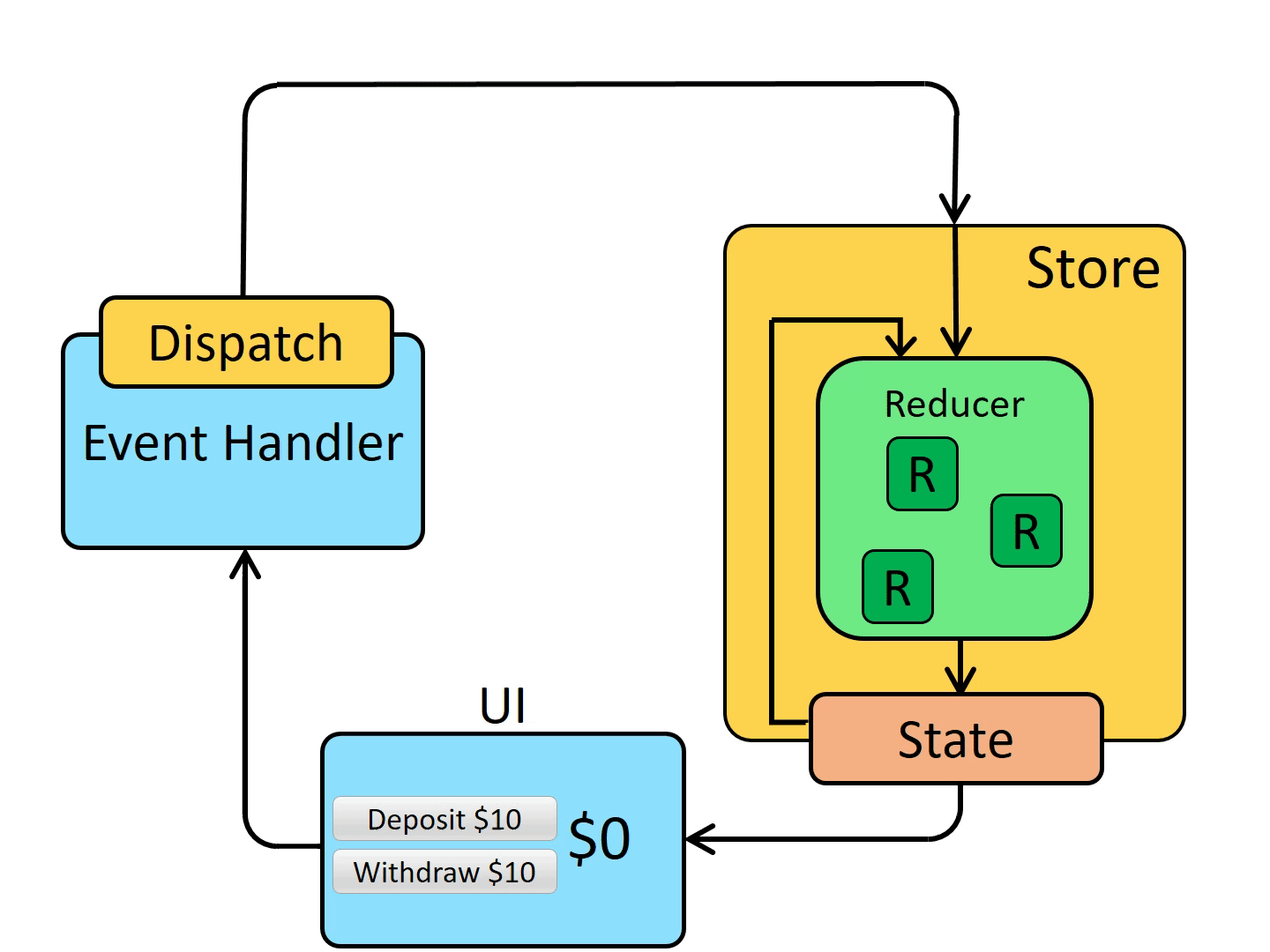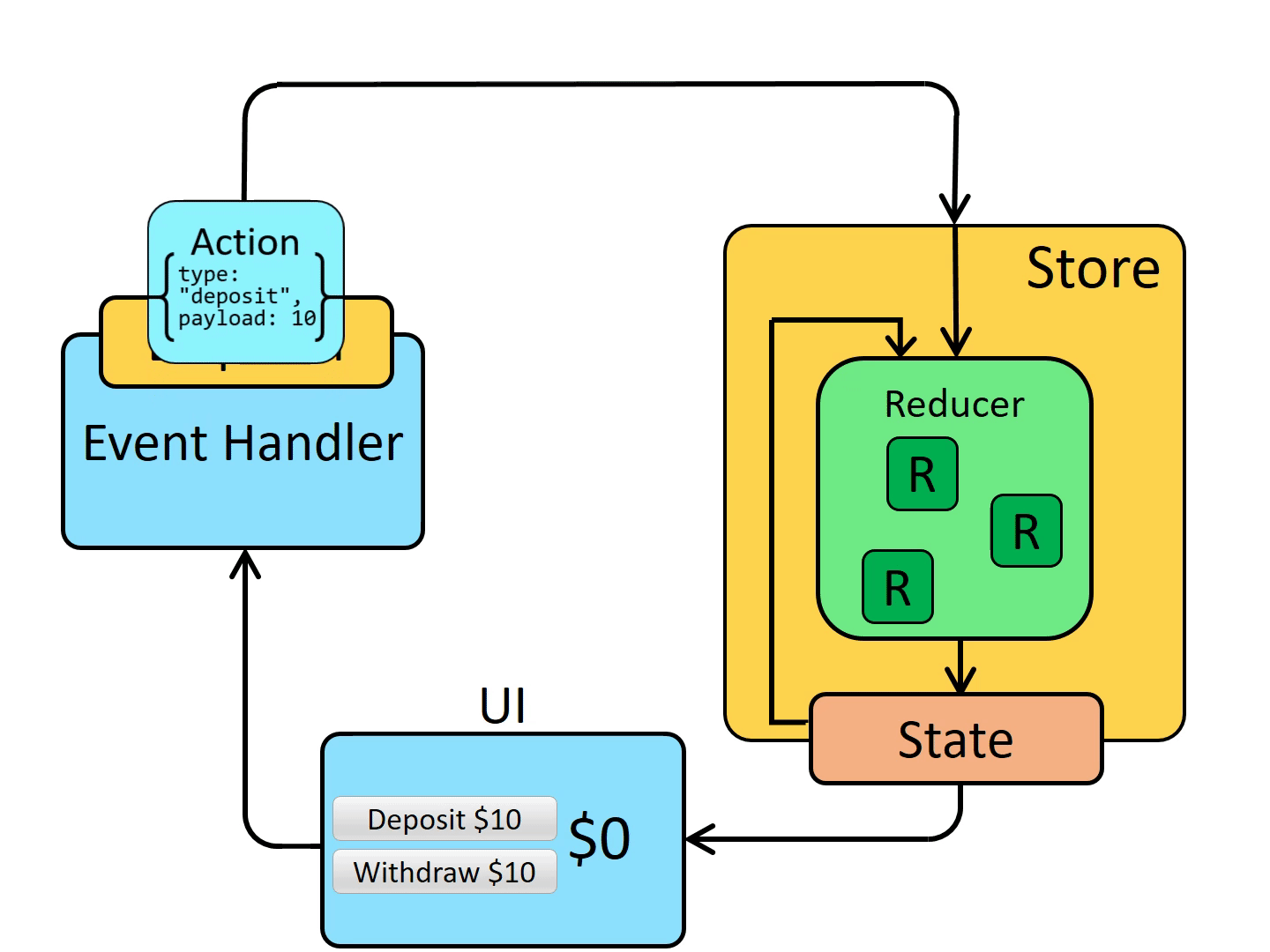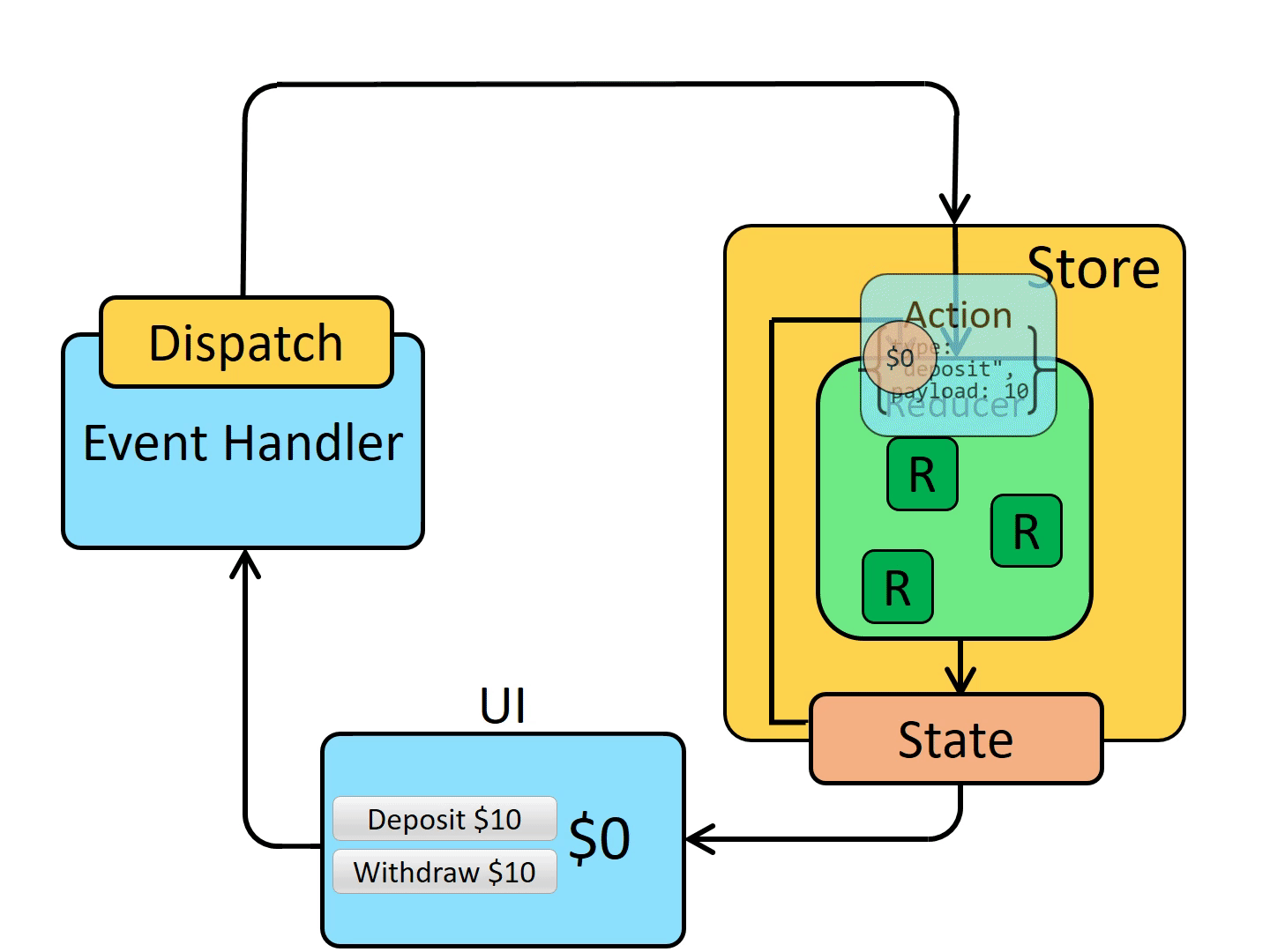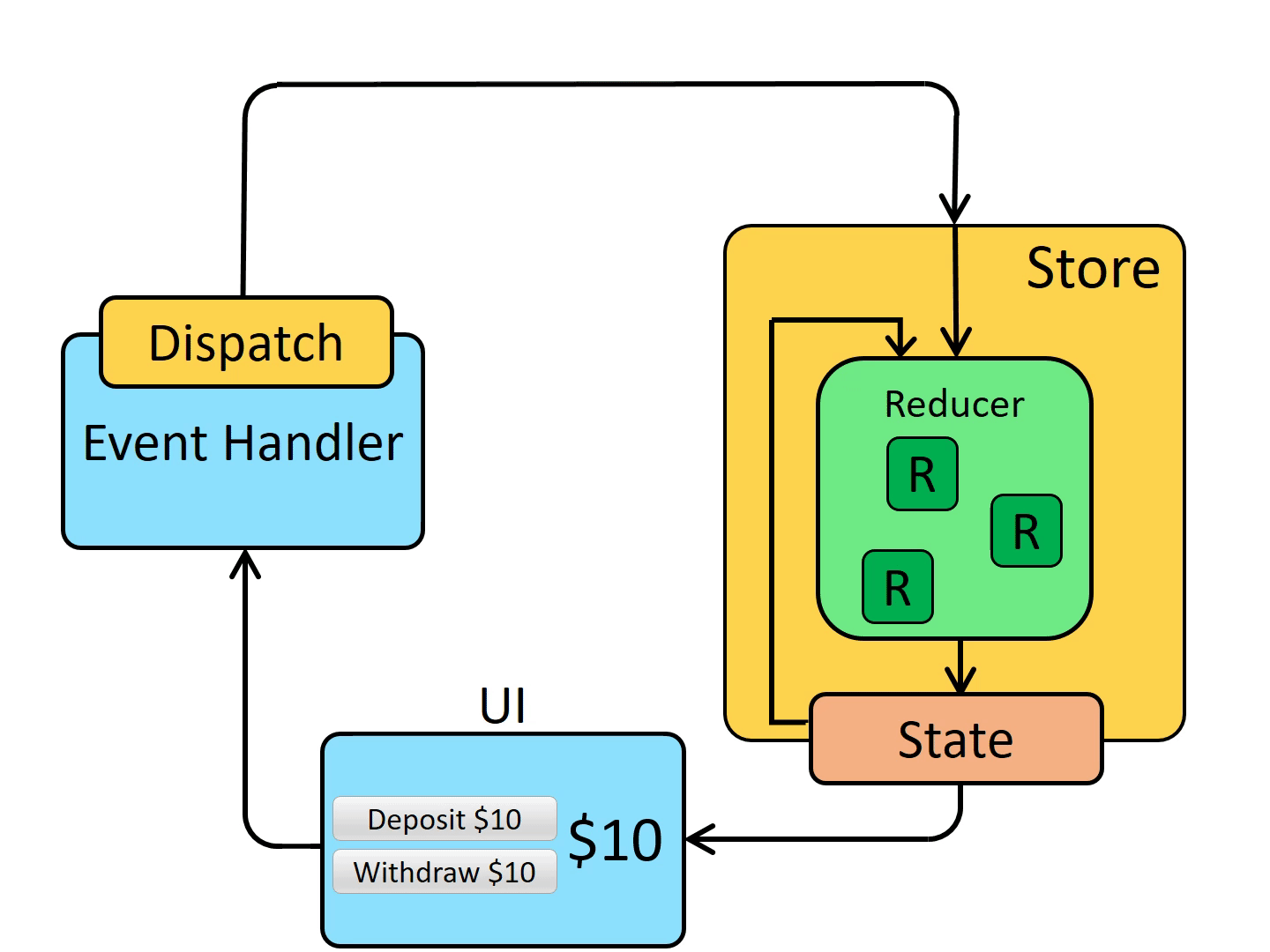
The so-called state management is to manage the data in the application.
Concept: almost all projects with chaotic data flow management can't go online. A good project must have very good data flow management.
How to use Redux? Remember "three threes".
- the first three: three APIs, createStore, combineReducers, applymeddleware
- the second and third: three features: the store is a single data source, the store is read-only, and the store can only be modified through the reducer pure function.
- the third three: three concepts: store, action and reducer.
Basic concepts:
-state contains all data and is used to provide data to the store
-store is the state management data, the data that can be shared by React, the data container, and the place where the data is saved
-action is a signal that can be used to modify the signal of state. It has a fixed format: {type,payload}. It can be understood that type is the email title and payload is the email content
Example: create a new store folder under src directory and a new index js
// store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'redux'
// The data defined in redux can be shared by Reac components
const initState = {
count: 1,
msg: 'hello world'
}
// The state parameter is the state management data, which can be shared by React
// action is a signal that can be used to modify the signal of state
// The format of action is fixed {type,payload}
function reducer(state = initState, action) {
return state
}
const store = createStore(reducer)
export default storeUnder src, create a new directory views, good, goodlist js
// views/good/GoodList.js
export default props => {
console.log('GoodList props', props);
return (
<div>
<h1>Product list page</h1>
</div>
)
}App.js
// Introduce Provider to provide data
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
import store from '@/store';
import GoodList from '@/views/good/GoodList';
// store is state
function App() {
return (
<Provider store={store}>
<GoodList />
</Provider>
);
}
export default App;Print GoodList props is empty. You can't get data directly using props
Question: how to associate with redux in this functional component
Answer: 1 Connect high-level component, which puts the data and methods related to redux on props. 2.hooks, which is direct access and has nothing to do with props
-Connect # syntax: connect(mapStateToProps,mapDispatchToProps)
Understanding: mapStateToProps is used to put store data on props, and mapDispatchToProps is used to put the method of modifying store on props
Transform views / good / goodlist js:
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
// Syntax: connect(mapStateToProps,mapDispatchToProps)(UI component)
// Understanding: mapStateToProps is used to put store data on props, and mapDispatchToProps is used to put the method of modifying store on props
function mapStateToProps(state) {
console.log('In context store', state);
// return the obtained data and props will receive it
return {
count: state.count,
msg: state.msg
}
}
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch) {
// dispatch is used to send an action, which can modify the store
console.log('dispatch', dispatch);
return {
// Requirement: add a method to make the count increase or decrease automatically
add: function () {
// Here, send a 'self increasing' signal to the store through dispatch
const action = { type: 'add', payload: 1 }
dispatch(action)
},
sub: function () {
const action = { type: 'sub', payload: 1 }
dispatch(action)
}
}
}
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(
props => {
console.log('GoodList props', props);
return (
<div>
<h1>Product list page</h1>
<h1>{props.count}</h1>
<button onClick={props.add}>Self increasing</button>
<button onClick={props.sub}>Self subtraction</button>
</div>
)
}
)
The store will receive the signal and transform the store / index js:
// store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'redux'
// The data defined in redux can be shared by Reac components
const initState = {
count: 1,
msg: 'hello world'
}
// The state parameter is the state management data, which can be shared by React
// action is a signal that can be used to modify the signal of state
// The format of action is fixed {type,payload}
function reducer(state = initState, action) {
console.log('signal', action);
// Since the store is read-only, modifying the state directly will not update the view
// So make a deep copy of the store
let newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state))
if (action.type === 'add') {
newState.count += action.payload
}
if (action.type === 'sub') {
newState.count -= action.payload
}
// console.log('newState',newState)
return newState
}
const store = createStore(reducer)
export default storeFinal effect:

Of course, there are many improvements in the code. For example, we usually use the Hooks function instead of connect to directly access the data in the store without props
-useSelector() is used to access redux data in the context
-useDispatch() gets the dispatch method, which can be sent to redux
Put views / good / goodlist JS is transformed into hooks function writing method, which greatly reduces the amount of code
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from "react-redux";
// Note: Hooks can only be used in functional components
// -useSelector() is used to access redux data in the context
// -useDispatch() gets the dispatch method and can send action to redux
export default () => {
// Access the count in the study sub module in the root state
const count = useSelector(state => state.count)
const dispatch = useDispatch()
const add = (payload) => dispatch({ type: 'add', payload })
const sub = (payload) => dispatch({ type: 'sub', payload })
return (
<div>
<h1>Product list page</h1>
<h1>{count}</h1>
<button onClick={() => add(1)}>Self increasing</button>
<button onClick={() => sub(1)}>Self subtraction</button>
</div>
)
}And we can also realize deep replication through produce: Produce: the first parameter is to pass in the old state. After internal deep replication, we can get the result of deep replication in the second function; Modify (process) the result of deep copy in the callback function, and the final modified result is the return value of produce,
Store / index JS transformation is as follows:
import { produce } from 'immer'
// The data defined in redux can be shared by Reac components
const initState = {
count: 1,
msg: 'hello world'
}
function reducer(state = initState, action) {
// immer deep copy
// Produce: the first parameter is to pass in the old state. After internal deep replication, the result of deep replication can be obtained in the second function; Modify (process) the result of deep copy in the callback function, and the final modified result is the return value of produce
return produce(state, (newState) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'add':
newState.count += action.payload
break
case 'sub':
newState.count -= action.payload
break
default:
}
})
}
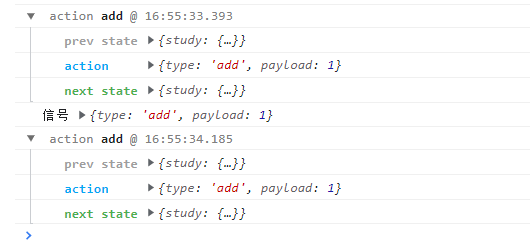
export default reducerYou can also use logger middleware to view the data flow more intuitively
import { createStore, combineReducers, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import logger from 'redux-logger'
const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(logger))
export default store
The use effect is shown in the figure:
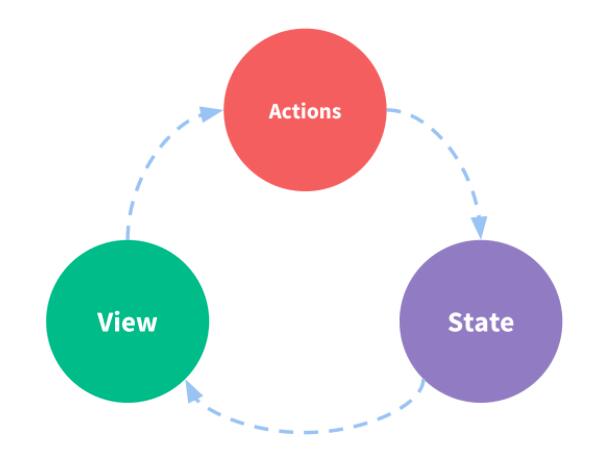
Schematic diagram of redux working principle