1, What is reflection?
(1) The core of Java reflection mechanism is to dynamically load classes and obtain class details when the program is running, so as to operate the properties and methods of classes or objects. The essence is that after the JVM obtains the class object, it decompiles it through the class object to obtain various information of the object.
(2) Java is a language that compiles first and then runs. The type of object in the program is determined at the compilation time. When the program runs, it may need to dynamically load some classes. These classes are not loaded into the JVM because they were not used before. Through reflection, you can dynamically create objects and call their properties at run time without knowing who the running object is at compile time in advance.
2, Why use reflection
First, we have an interface X and its method test, and two corresponding implementation classes A and B:
public class Test {
interface X {
public void test();
}
class A implements X{
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("I am A");
}
}
class B implements X{
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("I am B");
}
}
In general, we need to directly create a new implementation class. See the following code:
public class Test {
......
public static void main(String[] args) {
X a = create1("A");
a.test();
X b = create1("B");
b.test();
}
public static X create1(String name){
if (name.equals("A")) {
return new A();
} else if(name.equals("B")){
return new B();
}
return null;
}
}
According to the above description, if hundreds of different X implementation classes need to be created, don't we need to write thousands of if statements to return different X objects?
Let's look at how the reflection mechanism works:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
X a = create2("A");
a.test();
X b = create2("B");
b.testReflect();
}
// Use reflection mechanism
public static X create2(String name){
Class<?> class = Class.forName(name);
X x = (X) class.newInstance();
return x;
}
}
Pass in the package name and class name to the create2() method, dynamically load the specified class through the reflection mechanism, and then instantiate the object.
After reading the above example, I believe you have a certain understanding of reflection. Reflection has the following four functions:
- The class to which any object belongs is known at runtime (dynamic compilation).
- Construct an object of any class at run time.
- Know the member variables and methods of any class at run time.
- Call the methods and properties of any object at run time.
The above function of dynamically obtaining information and dynamically calling objects is called the reflection mechanism of Java language.
3, Class class
To understand reflection, we must first understand Class Class because Class Class is the foundation of reflection implementation.
During program running, the JVM always maintains a type ID called runtime for all objects. This information tracks the complete structure information of the class to which each object belongs, including package name, class name, implemented interface, owned methods and fields. You can access this information through a special Java class, which is the class class. We can understand a class class as a class type. A class object is called a class type object. A class object corresponds to a. Class file loaded into the JVM.
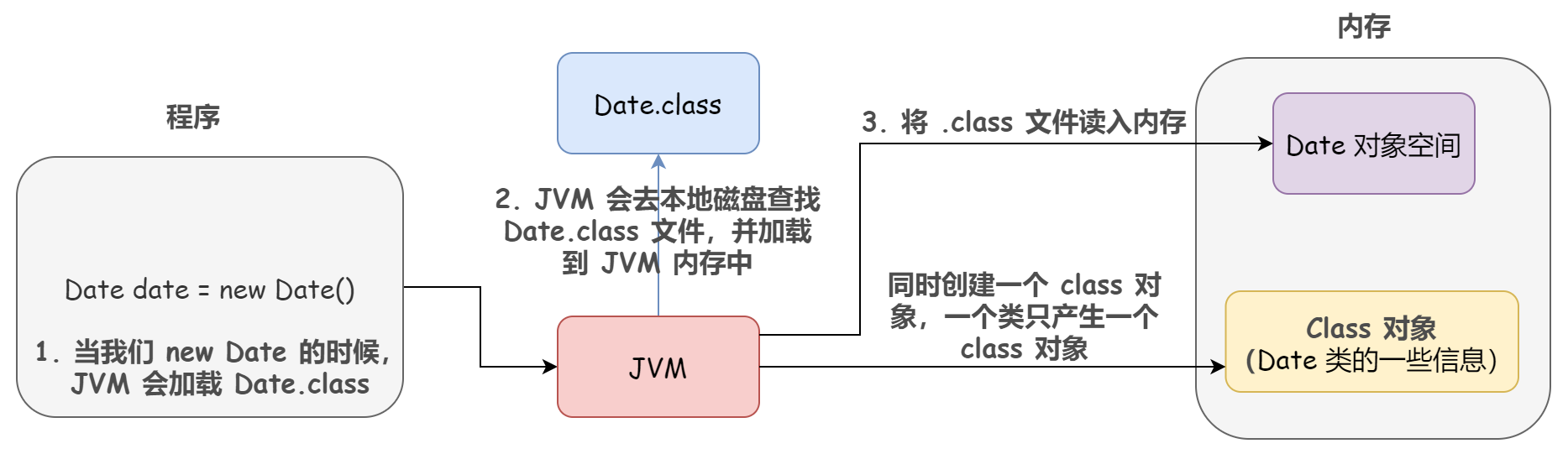
In general, there must be classes before objects. Taking the following code as an example, the normal loading process of a class is as follows:
import java.util.Date; // Prior class
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date(); // Object after
System.out.println(date);
}
}
First, the JVM will compile your code into a. Class bytecode file, and then load it into the memory of the JVM by the Class Loader. At the same time, it will create a class object of Date class and store it in the heap (note that this is not a new object, but a class type object). Before creating a Date object, the JVM will first check whether its class is loaded and find the class object corresponding to the class. If it is loaded, allocate memory for it, and then initialize new Date().
It should be noted that each Class has only one Class object, that is, if we have the second new Date() statement, the JVM will not generate another Class object of Date because one already exists. This also allows us to use the = = operator to compare two Class objects:
System.out.println(date.getClass() == Date.getClass()); // true
After loading a Class, a Class object is generated in the method area of the heap memory. This object contains the complete Class structure information. We can see the Class structure through this Class object, just like a mirror. So we call it reflection.
Say it in more detail and explain it again. As mentioned above, under normal circumstances, there must be classes before objects. We call this normal situation "positive". Then the "anti" in reflection can be understood as finding the class to which the object belongs (the source of the object) according to the object
Date date = new Date(); System.out.println(date.getClass()); // "class java.util.Date"
Through reflection, that is, after calling the getClass() method, we get the Class object corresponding to the Date Class, see the structure of the Date Class, and output the full name of the Class to which the Date object belongs, that is, we find the source of the object. Of course, there is more than one way to get Class objects.
4, Four ways to get Class objects
From the source code of Class, we can see that its constructor is private, that is, only the JVM can create Class objects. We can't directly new a Class object like an ordinary Class.
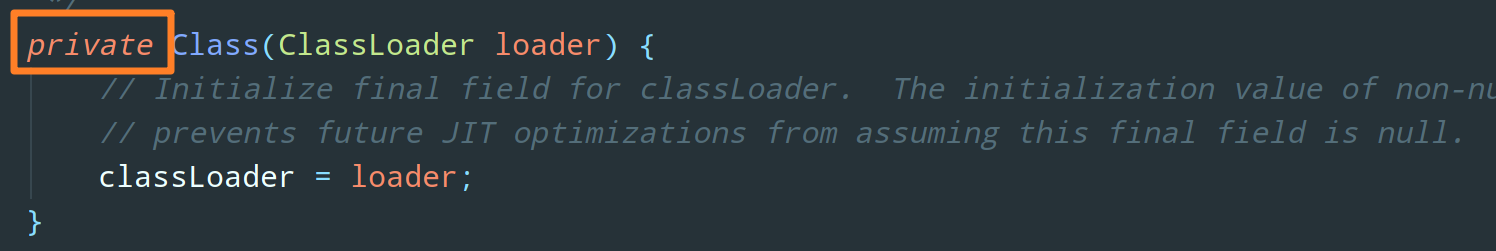
We can only get a Class object from an existing Class. Java provides four ways:
The first type: you can use when you know the specific class:
Class alunbarClass = TargetObject.class;
However, we generally do not know the specific Class. We basically obtain the Class object by traversing the Class under the package. The Class object obtained in this way will not be initialized.
The second method: pass in the full class name through Class.forName() to obtain:
Class alunbarClass1 = Class.forName("com.xxx.TargetObject");
The actual call inside this method is forName0:

The second boolean parameter indicates whether the class needs to be initialized. By default, it needs to be initialized. Once initialized, the static block code execution of the target object will be triggered, and the static parameter will be initialized again.
The third method: obtain the following information through the object instance instance instance.getClass():
Date date = new Date(); Class alunbarClass2 = date.getClass(); // Gets the Class object of the object instance
The fourth method is to pass in the classpath through the classloader xxclassloader. Loadclass()
class clazz = ClassLoader.LoadClass("com.xxx.TargetObject");
The Class object obtained through the Class loader will not be initialized, which means that static blocks and static objects will not be executed without some steps including initialization. Here's a comparison with forName.
4. Construct an instance of a class through reflection
We introduced the method of obtaining Class objects above. After successful acquisition, we need to construct an instance of the corresponding Class. Here are three methods. The first one is the most common, and the last one can be understood by everyone.
① Use Class.newInstance
for instance:
Date date1 = new Date(); Class alunbarClass2 = date1.getClass(); Date date2 = alunbarClass2.newInstance(); // Create an instance with the same class type as alunbarClass2
Created an instance with the same class type as alunbarClass2.
It should be noted that the newInstance method calls the default constructor (parameterless constructor) to initialize the newly created object. If this class does not have a default constructor, an exception will be thrown.

② Get the constructor first and then call it through reflection
Since not all classes have parameterless constructors or class constructors are private, Class.newInstance cannot satisfy if we still want to instantiate objects through reflection.
At this time, we can use the newInstance method of Constructor to obtain the Constructor first, and then execute the Constructor.
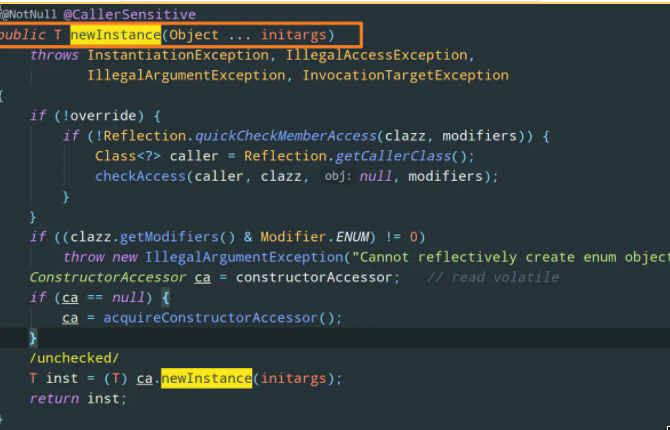
It is easy to see from the above code that Constructor.newInstance can carry parameters, while Class.newInstance is parameterless, which is why it can only call parameterless constructors.
Don't confuse the two newInstance methods. If the constructor of the called class is the default constructor, Class.newInstance() is a better choice. One sentence of code is OK; If you need to call the class's parameterized constructor, private constructor, etc., you need to use constructor. newInstance()
Constructor.newInstance is the method that executes the constructor. Let's take a look at the channels through which the constructor can be obtained. The following methods are easy to remember and understand. The return values are received through the Cnostructor type.
Batch get constructor:
1) Gets all "public" constructor methods
public Constructor[] getConstructors() { }
2) Get all construction methods (including private, protected, default and public)
public Constructor[] getDeclaredConstructors() { }
Single get constructor:
1) Gets a public constructor of the specified parameter type
public Constructor getConstructor(Class... parameterTypes) { }
2) Gets a constructor of a specified parameter type, which can be private, protected, default, or public
public Constructor getDeclaredConstructor(Class... parameterTypes) { }
for instance:
package fanshe;
public class Student {
//(default construction method)
Student(String str){
System.out.println("(default)Construction method of s = " + str);
}
// Nonparametric construction method
public Student(){
System.out.println("The public and parameterless construction method is called to execute...");
}
// Construction method with one parameter
public Student(char name){
System.out.println("full name:" + name);
}
// Construction method with multiple parameters
public Student(String name ,int age){
System.out.println("full name:"+name+"Age:"+ age);//There is a problem with the implementation efficiency of this, which will be solved later.
}
// Protected construction method
protected Student(boolean n){
System.out.println("Protected construction method n = " + n);
}
// Private construction method
private Student(int age){
System.out.println("Private construction method age:"+ age);
}
}
----------------------------------
public class Constructors {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Load Class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("fanshe.Student");
// Get all public constructor methods
Constructor[] conArray = clazz.getConstructors();
for(Constructor c : conArray){
System.out.println(c);
}
// Get all construction methods (including: private, protected, default, public)
conArray = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
for(Constructor c : conArray){
System.out.println(c);
}
// Get public and parameterless construction methods
// Because it is a parameterless construction method, the type is null and can be written without writing: what is needed here is the type of a parameter. Remember that it is a type
// The class object that describes the parameterless constructor is returned.
Constructor con = clazz.getConstructor(null);
Object obj = con.newInstance(); // Call constructor
// Get private constructor
con = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class);
System.out.println(con);
con.setAccessible(true); // In order to call the private method / domain, we need to cancel the security check
obj = con.newInstance(12); // Call constructor
}
}
③ Using the open source library Objenesis
Objenesis is an open source library. Like the second method above, you can call any constructor, but the encapsulation is relatively simple:
public class Test {
// No parameterless constructor exists
private int i;
public Test(int i){
this.i = i;
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("test..." + i);
}
}
------------------------
public static void main(String[] args) {
Objenesis objenesis = new ObjenesisStd(true);
Test test = objenesis.newInstance(Test.class);
test.show();
}
It is very simple to use. Objenesis is implemented by the subclass objenesisobjenesistd. The detailed source code will not be studied here. Just understand it.
5. Get member variables through reflection and use
Similar to obtaining constructors, obtaining member variables is also divided into batch obtaining and single obtaining. The return value is received through the Field type.
Batch acquisition:
1) Get all public fields
public Field[] getFields() { }
2) Get all fields (including private, protected and default)
public Field[] getDeclaredFields() { }
Single acquisition:
1) Gets a public field with the specified name
public Field getField(String name) { }
2) Gets a field with a specified name, which can be private, protected and default
public Field getDeclaredField(String name) { }
After getting the member variables, how to modify their values?
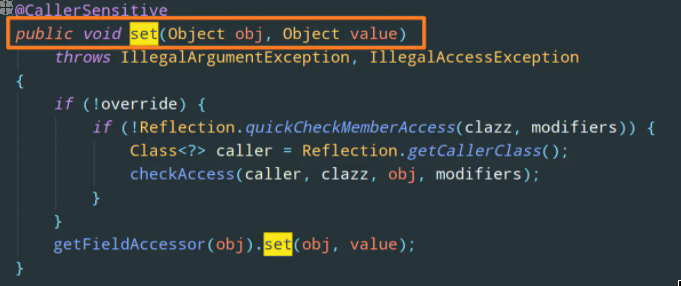
The set method contains two parameters:
- obj: which object needs to modify this member variable
- Value: to which value
for instance:
package fanshe.field;
public class Student {
public Student(){
}
public String name;
protected int age;
char sex;
private String phoneNum;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", sex=" + sex
+ ", phoneNum=" + phoneNum + "]";
}
}
----------------------------------
public class Fields {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Get Class object
Class stuClass = Class.forName("fanshe.field.Student");
// Get public parameterless constructor
Constructor con = stuClass.getConstructor();
// Get private constructor
con = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class);
System.out.println(con);
con.setAccessible(true); // In order to call the private method / domain, we need to cancel the security check
obj = con.newInstance(12); // Call constructor
// Get all public fields
Field[] fieldArray = stuClass.getFields();
for(Field f : fieldArray){
System.out.println(f);
}
// Get all fields (including private, protected and default)
fieldArray = stuClass.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field f : fieldArray){
System.out.println(f);
}
// Gets the public field of the specified name
Field f = stuClass.getField("name");
Object obj = con.newInstance(); // Call the constructor to create an instance of the class
f.set(obj, "Lau Andy"); // Assign a value to the name attribute in the Student object
// Get private field
f = stuClass.getDeclaredField("phoneNum");
f.setAccessible(true); // Violent reflex, lifting private restrictions
f.set(obj, "18888889999"); // Assign a value to the phoneNum property in the Student object
}
}
6. Get member methods through reflection and call
Similarly, the Method of obtaining members can be divided into batch acquisition and single acquisition. The return value is received through the Method type.
Batch acquisition:
1) Get all "public methods" (including the methods of the parent class and, of course, the Object class)
public Method[] getMethods() { }
2) Get all member methods, including private (excluding inherited)
public Method[] getDeclaredMethods() { }
Single acquisition:
Gets a member method with the specified method name and parameter type:
public Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)
How do I call methods after I get them?
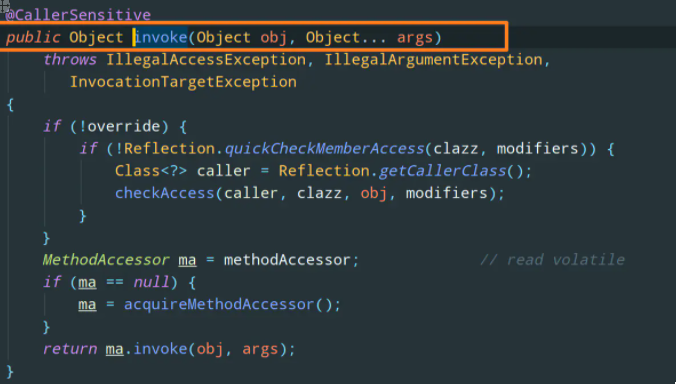
The invoke method contains two parameters:
- obj: which object will call this method
- args: the argument passed when the method is called
for instance:
package fanshe.method;
public class Student {
public void show1(String s){
System.out.println("Called: public, String Parametric show1(): s = " + s);
}
protected void show2(){
System.out.println("Called: protected, parameterless show2()");
}
void show3(){
System.out.println("Called: default, parameterless show3()");
}
private String show4(int age){
System.out.println("Called, private, and with a return value, int Parametric show4(): age = " + age);
return "abcd";
}
}
-------------------------------------------
public class MethodClass {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Get Class object
Class stuClass = Class.forName("fanshe.method.Student");
// Get public parameterless constructor
Constructor con = stuClass.getConstructor();
// Get all public methods
stuClass.getMethods();
Method[] methodArray = stuClass.getMethods();
for(Method m : methodArray){
System.out.println(m);
}
// Get all methods, including private
methodArray = stuClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method m : methodArray){
System.out.println(m);
}
// Get public show1() method
Method m = stuClass.getMethod("show1", String.class);
System.out.println(m);
Object obj = con.newInstance(); // Call the constructor to instantiate a Student object
m.invoke(obj, "veal");
// Get private show4() method
m = stuClass.getDeclaredMethod("show4", int.class);
m.setAccessible(true); // Lifting private restrictions
Object result = m.invoke(obj, 20);
System.out.println("Return value:" + result);
}
}
7. Advantages and disadvantages of reflection mechanism
Advantages: it is flexible and can dynamically obtain class instances at run time.
Disadvantages:
1) Performance bottleneck: reflection is equivalent to a series of interpretation operations to inform the JVM of what to do. The performance is much slower than that of direct Java code.
2) Security problem: reflection mechanism destroys encapsulation, because private methods and fields of a class can be obtained and called through reflection.
8. Classic application scenarios of reflection
Reflection is not directly used in our actual programming, but in fact, many designs are related to the reflection mechanism, such as:
- Dynamic agent mechanism
- Connect to the database using JDBC
- Spring / Hibernate Framework (in fact, it is related to reflection mechanism because dynamic proxy is used)
Why dynamic proxy uses reflection mechanism will be explained in detail in the next article.
JDBC connection database
In JDBC operation, if you want to connect to the database, you must follow the following steps:
- Load the driver of the database through Class.forName() (load through reflection)
- Connect to the database through the DriverManager class. The parameters include the connection address, user name and password of the database
- Receive connections through the Connection interface
- Close connection
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection con = null; // Database connection object
// 1 \. Load driver through reflection
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2 \. Connect to the database
con = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test","root","root");
// 3 \. Close database connection
con.close();
}
Spring framework
Reflection mechanism is the soul of Java framework design. The interior of the framework has been encapsulated, and we basically don't need to write it ourselves. In addition to Hibernate, Spring also uses many reflection mechanisms. The most typical is that Spring loads beans (creates objects) through xml configuration files, that is, Spring's IoC. The process is as follows:
- Load the configuration file and get the Spring container
- Use the reflection mechanism to obtain the Class instance of a Class according to the incoming string
// Get the IoC container of Spring and get the object according to the id
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. Use the ApplicationContext interface to load the configuration file and get the spring container
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
// 2 \. Use the reflection mechanism to obtain the Class instance of a Class according to this string
IAccountService aService = (IAccountService) ac.getBean("accountServiceImpl");
System.out.println(aService);
}