Four methods to obtain Class instances
- Call the properties of the runtime class
- Call getClass() through the object of the runtime class
- Calling Class static method: the most commonly used method in forName(String classPath) development
- Loader using class: ClassLoader (just know)
package day_12_29;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname ReflectionTest
* @Description Four ways to get an instance of Class by reflection
* @Date 2021-12-29 20:44
*/
public class ReflectionTest {
//Get Person class
@Test
public void test() {
//1. Call the properties of the runtime class
Class<Person> clazz1 = Person.class;
System.out.println(clazz1);
//2. Call getClass() through the object of the runtime class
Person p1 = new Person();
Class<? extends Person> clazz2 = p1.getClass();
System.out.println(clazz2);
//3. Calling Class static method: the most commonly used method in forName(String classPath) development
Class<?> clazz3 = null;
try {
clazz3 = Class.forName("day_12_29.Person");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(clazz3);
//4. Loader using class: ClassLoader (just know it)
ClassLoader classLoader = ReflectionTest.class.getClassLoader();
Class<?> clazz4 = null;
try {
clazz4 = classLoader.loadClass("day_12_29.Person");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(clazz4);
}
}
//Class to get
class Person {
}
Define test structure
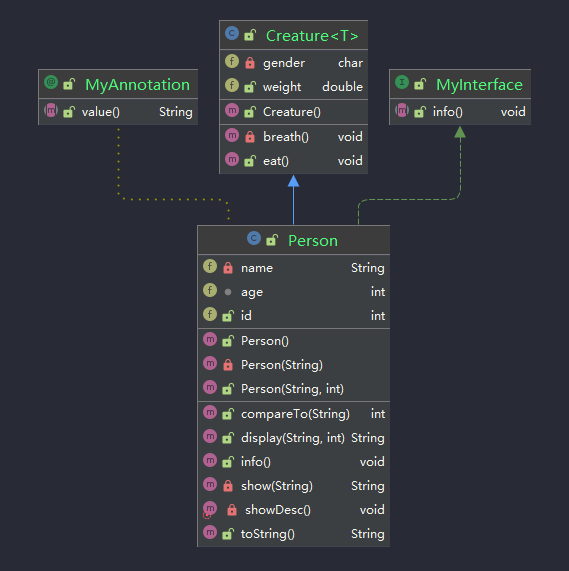
Get attribute structure
Get properties in class:
getFields(): get the attributes of the current runtime class and all parent classes declared as public access rights
Getdeclaraedfields(): get all the attributes declared in the current runtime class (independent of permission modification and excluding the attributes declared in the parent class)
Get the internal structure of the property:
1.getModifiers(): get the permission modifier. The return value is of type int, which corresponds to the value of the modifier. You can use modifier toString(...) get
2.getType(): data type, return Class type, can be passed getName() gets the full Class name
3.getName(): returns the variable name of String type
package day_12_30.reflection.test;
import day_12_30.reflection.java.Person;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname FieldTest
* @Description Gets the property structure of the current runtime class
* @Date 2021-12-30 14:54
*/
public class FieldTest {
//Gets the current runtime Class (Class instance)
Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;
@Test
public void test1(){
Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
/*
public int day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.id
public double day_12_30.reflection.java.Creature.weight
*/
}
System.out.println();
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
System.out.println(field);
/*
private java.lang.String day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.name
int day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.age
public int day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.id
*/
}
}
//Permission modifier data type variable name
@Test
public void test2(){
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : declaredFields) {
//1. Permission modifier
int modifier = f.getModifiers();
System.out.print(Modifier.toString(modifier) + "\t");
//2. Drama type
Class<?> type = f.getType();
System.out.print(type.getName() + "\t");
//3. Variable name
String name = f.getName();
System.out.print(name);
System.out.println();
}
/*
private java.lang.String name
int age
public int id
*/
}
}
Get method structure
Get methods in class:
getMethods(): get the methods declared as public access rights of the current runtime class and all parent classes
getDeclaredMethods(): get all the methods declared in the current runtime class (independent of permission modification and excluding those declared in the parent class)
Note: overridden methods can also be obtained
Get the internal structure of the method:
- @Xxxx
- Permission modifier return value type method name(Parameter type 1 parameter name 1,...) throws XxxException{}
1.getAnnotations() gets all declaration annotations of the method and returns them as an Annotation [] array
2.getModifiers() gets the permission modifier of the method
3.getReturnType() gets the return value type, which can be accessed through getName() gets the specific name
4.getName() method name
5.getParameterTypes(): parameter list. Returned as an array through Class [] getName() gets the specific name
6.getExceptkionTypes(): get the exception type that runs out. Returned as an array through Class [] getName() gets the specific name
package day_12_30.reflection.test;
import day_12_30.reflection.java.Person;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname MethodTest
* @Description Gets the method structure of the runtime class
* @Date 2021-12-30 15:05
*/
public class MethodTest {
Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;
@Test
public void test1(){
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method m : methods) {
System.out.println(m);
}
/*
public java.lang.String day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.toString()
public int day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.compareTo(java.lang.String)
public int day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.compareTo(java.lang.Object)
public void day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.info()
public java.lang.String day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.display(java.lang.String,int) throws java.lang.NullPointerException,java.lang.ClassCastException
public void day_12_30.reflection.java.Creature.eat()
public final void java.lang.Object.wait(long,int) throws java.lang.InterruptedException
public final void java.lang.Object.wait() throws java.lang.InterruptedException
public final native void java.lang.Object.wait(long) throws java.lang.InterruptedException
public boolean java.lang.Object.equals(java.lang.Object)
public native int java.lang.Object.hashCode()
public final native java.lang.Class java.lang.Object.getClass()
public final native void java.lang.Object.notify()
public final native void java.lang.Object.notifyAll()
*/
System.out.println();
Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m : declaredMethods) {
System.out.println(m);
}
/*
public java.lang.String day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.toString()
public int day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.compareTo(java.lang.String)
public int day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.compareTo(java.lang.Object)
public void day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.info()
public java.lang.String day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.display(java.lang.String,int) throws java.lang.NullPointerException,java.lang.ClassCastException
private static void day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.showDesc()
private java.lang.String day_12_30.reflection.java.Person.show(java.lang.String)
*/
}
/*
@Xxxx
Permission modifier return value type method name (parameter type 1, parameter name 1,...) throws XxxException{}
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m : declaredMethods) {
//1. Get comments
Annotation[] annotations = m.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation a : annotations) {
System.out.println(a);
}
//2. Permission modifier
System.out.print(Modifier.toString(m.getModifiers()) + "\t");
//3. Return value type
System.out.print(m.getReturnType().getName()+"\t");
//4. Method name
System.out.print(m.getName());
System.out.print("( ");
//5. Formal parameter list
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = m.getParameterTypes();
if(!(parameterTypes == null && parameterTypes.length == 0)){
for(int i = 0;i < parameterTypes.length;i++){
if(i == parameterTypes.length - 1){
System.out.print(parameterTypes[i].getName() + " args_" + i);
break;
}
System.out.print(parameterTypes[i].getName() + " args_" + i + ",");
}
}
System.out.print(" )");
//6. Exceptions thrown
Class<?>[] exceptionTypes = m.getExceptionTypes();
if(exceptionTypes.length > 0){
System.out.print("throws ");
for(int i = 0;i < exceptionTypes.length;i++){
if(i == exceptionTypes.length - 1){
System.out.print(exceptionTypes[i].getName());
break;
}
System.out.print(exceptionTypes[i].getName() + ",");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
/*
public java.lang.String toString( )
public int compareTo( java.lang.String args_0 )
public volatile int compareTo( java.lang.Object args_0 )
public void info( )
public java.lang.String display( java.lang.String args_0,int args_1 )throws java.lang.NullPointerException,java.lang.ClassCastException
@day_12_30.reflection.java.MyAnnotation("soberw")
private java.lang.String show( java.lang.String args_0 )
private static void showDesc( )
*/
}
}
Get constructor structure (including parent class generics)
Gets the constructor in the currently running class
1.getConstructors(): get the constructor declared as public in the current runtime class
2.getDelaredConstructors(): get all constructors declared in the current runtime class
Get the parent class (which can also be generic) - more commonly used
1.getSuperclass(): get the parent class of the runtime class
2.getGenericSuperclass(): get the generic parent class of the runtime
3. Get the generics of the parent class with generics of the runtime class. After the previous step, get a return value of Type
Call its getActualTypeArguments() method to obtain Type [], that is, the types of all generic types, which are obtained through getName()
Name
@Test
public void test1(){
Constructor<?>[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> c : constructors) {
System.out.println(c);
/*
public day_12_30.reflection.java.Person(java.lang.String,int)
public day_12_30.reflection.java.Person()
*/
}
System.out.println();
Constructor<?>[] declaredConstructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> d : declaredConstructors) {
System.out.println(d);
/*
public day_12_30.reflection.java.Person(java.lang.String,int)
private day_12_30.reflection.java.Person(java.lang.String)
public day_12_30.reflection.java.Person()
*/
}
}
/**
* Get parent class (including with generics and its generics)
*/
@Test
public void test3(){
Class<? super Person> superclass = clazz.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(superclass);
//class day_12_30.reflection.java.Creature
//Gets the generic parent of the runtime class
Type genericSuperclass = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();
System.out.println(genericSuperclass);
//day_12_30.reflection.java.Creature<java.lang.String>
//Gets the generic type of the generic parent class of the runtime class
//Convert to a parameterized type, which is a generic type
ParameterizedType paramType = (ParameterizedType) genericSuperclass;
//Get parameters for generic
Type[] actualTypeArguments = paramType.getActualTypeArguments();
for (Type a : actualTypeArguments) {
//Both are acceptable
//System.out.println(a.getTypeName());
System.out.println(((Class<?>)a).getName());
//java.lang.String
}
}
Get the implemented interface
Gets the interface (and generics) implemented by the runtime class
getInterfaces() returns all interfaces implemented by Class [], excluding those implemented by the parent Class
getGenericInterfaces(): returns the type of interface directly implemented by the runtime class
Gets the interface implemented by the parent class of the runtime class
getSuperclass().getInterfaces()
@Test
public void test4(){
//Gets the interface implemented by the runtime class
Class<?>[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> c : interfaces) {
System.out.println(c);
/*
interface day_12_30.reflection.java.MyInterface
interface java.lang.Comparable
*/
}
System.out.println();
//Gets the interface implemented by the parent class of the runtime class
Class<?>[] interfaces1 = clazz.getSuperclass().getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> c : interfaces1) {
System.out.println(c);
//interface java.io.Serializable
}
System.out.println();
//Returns the type of interface directly implemented by the runtime class.
Type[] genericInterfaces = clazz.getGenericInterfaces();
for (Type g : genericInterfaces) {
System.out.println(g.getTypeName());
/*
day_12_30.reflection.java.MyInterface
java.lang.Comparable<java.lang.String>
*/
}
}
Get the package
getPackage()
@Test
public void test5(){
Package aPackage = clazz.getPackage();
System.out.println(aPackage);
//package day_12_30.reflection.java
}
Get annotation
To get annotations through reflection, the lifecycle must be the RUNTIME runtime annotation
getAnnotations() returns an array because there may be more than one Annotation []
@Test
public void test6(){
Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation a : annotations) {
System.out.println(a);
//@day_12_30.reflection.java.MyAnnotation("soberw")
}
}
Gets and creates the specified constructor
There are three steps:
- Get the specified Constructor getdeclaraedconstructor(): parameter: the parameter list of the specified Constructor (we usually call parameterless here), and the return value is of Constructor type
- Ensure that the constructor is accessible setAccessible(true): set to true and private can also be called
- Call the constructor to create the object newInstance() of the runtime class: deformable parameter, which is null by default
Gets the specified property
First step: you must declare an object of a runtime class through the constructor
Get properties declared public (not commonly used)
getField(String name) get property (must be public)
Set (two parameters): the first is the specified object and the second is the set value
Get (a parameter) gets the current property value of the specified object
Get and operate the specified properties in the runtime class (more commonly used)
The same three steps:
-
Get the property getdeclaraedfield() of the variable name specified in the runtime class, and the return value is Field type
-
Ensure that the current property is accessible: setAccessible(true)
-
Gets or sets the property value of the specified object
Set (two parameters): the first is the specified object and the second is the set value
Get (a parameter) gets the current property value of the specified object
Gets and runs the specified method
The data obtained through getMethod(String name,Class c) is not commonly used in actual development, because only public data can be obtained, so I won't elaborate
Gets and operates the specified method of the runtime class (more commonly used)
First step: you must declare an object of a runtime class through the constructor
Next four steps:
-
getDeclaredMethod(): parameter 1: indicates the name of the Method. Parameter 2: indicates the Method parameter list (because of overload), and the return value is Method type
-
Ensure that the current property is accessible: setAccessible(true)
-
invoke() is called to run this method. Parameter 1: the caller of the method (usually the declared object) parameter 2: the method argument (pass in the parameter, or null if there is no parameter)
-
Return value. The invoke() method can have a return value of Object type
If the original method has no return value (void), null is returned
If the original method has a return value, invoke() returns the specified type
Also note
- If we call a static method of a class, we also need to declare the object first, and then get the corresponding method by name
- Only when the caller is specified, it can no longer be specified as a declared object, but run the class itself or write it as null
package day_12_30.reflection.test;
import day_12_30.reflection.java.Person;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname ReflectionTest
* @Description Call the structure specified in the runtime class: property, method, constructor
* @Date 2021-12-30 15:52
*/
public class ReflectionTest {
Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;
//constructor
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
Constructor<Person> constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
Person person = constructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(person);
//Person{name='null', age=0, id=0}
//Get private constructor
Constructor<Person> declaredConstructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
//Open access
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Person soberw = declaredConstructor.newInstance("soberw");
System.out.println(soberw);
//Person{name='soberw', age=0, id=0}
}
//attribute
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
//Step 1: be sure to create the object first
Person person = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
Field pname = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");
pname.setAccessible(true);
pname.set(person, "soberw");
System.out.println(pname.get(person));
//soberw
}
//method
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
Person person = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show", String.class);
show.setAccessible(true);
Object invoke = show.invoke(person, "China");
//My nationality is Chinese
System.out.println(invoke);
//China
//Call static method
Method showDesc = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("showDesc");
showDesc.setAccessible(true);
Object val1 = showDesc.invoke(null);
//I am a lovely person
Object val2 = showDesc.invoke(clazz);
//I am a lovely person
Object val3 = showDesc.invoke(Person.class);
//I am a lovely person
System.out.println(val1);
//null
System.out.println(val2);
//null
System.out.println(val3);
//null
}
}