This article mainly refers to the Rest Framework official website documents: https://www.django-rest-framework.org/
And then I realize my own personal summary.
Development tools: Pycharm, python 3.7, Django 2.1, djangorest framework-3.9.4
Contents of this article
New project:
- Here, you can directly create a Django project through pycharm. The path is tutorial, and the App Name is quickstart (keep with the official website)
- You can also do this from the command line:
django-admin startproject tutorial . # Note the trailing '.' character cd tutorial django-admin startapp quickstart cd ..
- Initialize database, create initial user
python manage.py migrate python manage.py createsuperuser --email admin@example.com --username admin
Serializer:
First, we'll define some serializers. Let's create a new module called tutorial/quickstart/serializers.py, which we'll use for data representation.
The HyperlinkedModelSerializer class is similar to the ModelSerializer class, except that it uses hyperlinks to represent relationships rather than primary keys.
By default, the serializer will contain a url field instead of a primary key field.
The url field will be represented by the hyperlinkeddidentityfield serializer field, and any relationships on the model will be represented by the hyperlinkedrelatitedfield serializer field.
# serializers.py
from django.contrib.auth.models import User, Group
from rest_framework import serializers
class UserSerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = User
fields = ('url', 'username', 'email', 'groups')
class GroupSerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Group
fields = ('url', 'name')View:
Complete view writing in tutorial/quickstart/views.py
from django.contrib.auth.models import User, Group
from rest_framework import viewsets
# from tutorial.quickstart.serializers import UserSerializer, GroupSerializer
from quickstart.serializers import UserSerializer, GroupSerializer
class UserViewSet(viewsets.ModelViewSet):
"""
//User API node
"""
queryset = User.objects.all().order_by('-date_joined')
serializer_class = UserSerializer
class GroupViewSet(viewsets.ModelViewSet):
"""
//Group API node
"""
queryset = Group.objects.all()
serializer_class = GroupSerializerurls.py:
# tutorial/urls.py
from django.urls import include, path
from rest_framework import routers
# from tutorial.quickstart import views
from quickstart import views
# Automatically generate URL conf for our API by simply registering view sets with router classes
router = routers.DefaultRouter()
router.register(r'users', views.UserViewSet)
router.register(r'groups', views.GroupViewSet)
# Wire up our API using automatic URL routing.
# Additionally, we include login URLs for the browsable API.
urlpatterns = [
path('', include(router.urls)),
# Include default login and logout, authentication
path('api-auth/', include('rest_framework.urls', namespace='rest_framework'))
]Configure paging, app
Configure in tutorial/settings.py:
INSTALLED_APPS = (
...
'rest_framework',
)
# pagination
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.pagination.PageNumberPagination',
'PAGE_SIZE': 10
}Launch project test API
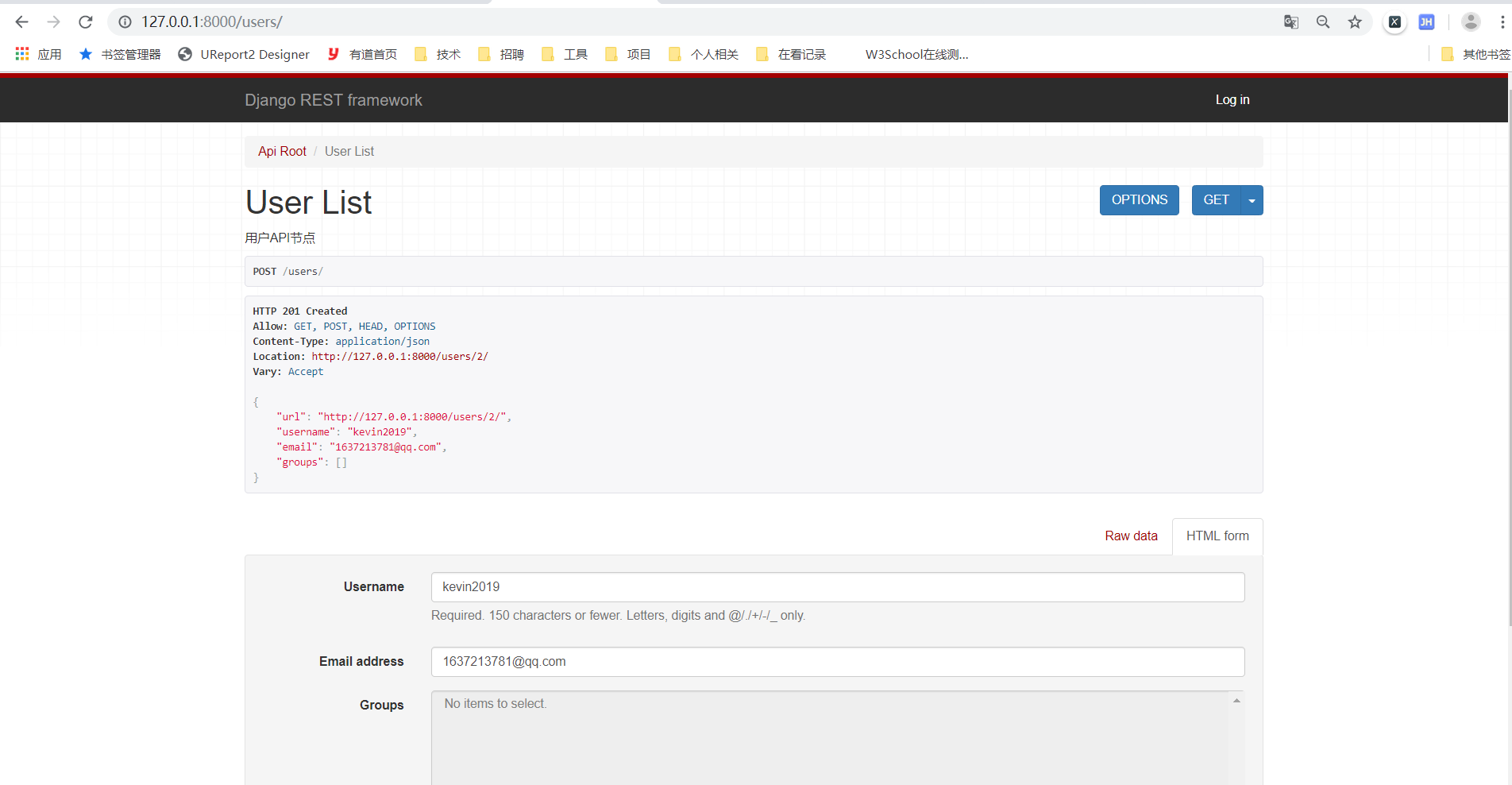
At this point, you can use the related interfaces of groups and users, get to get the data, and post to submit the data.
python manage.py runserver
*If there is any misunderstanding, please also point out