After learning rh124, rh134 and rh254, you can take the certification examination.
This is part of rh124
Chapter 1 accessing the command line
1.1 log in to the Linux system and run simple commands
There are two ways to physically access Linux: tty (terminal) and console (control).
There is also a concept of virtual terminal (ctrl + Alt + F {1... 6}) in the Linux system, which allows us to better access the Linux system.
When the software side accesses Linux, it can execute commands and call resources through the shell. Bash shell (GNU Bourne again shell) is the default shell for many Linux distributions.
Several shell conventions:

1.2 launching applications in GNOME environment
Workspace toggle Ctrl+ Alt + up and down arrows
1.3 practice using the bash shell to execute commands
Several simple command examples
date # Display date passwd #Change Password file # View file types head # Look at the file from the beginning tail #View at the end of the file wc ##Number of line characters ## Historical command history # View history commands !num Or! str #View the running echo of the corresponding number of the history command Esc + . # Quickly complete the parameters of the previous command
There are some shortcut keys in the bash command line to make us use the shell more efficiently

Chapter 2 managing files from the command line
2.1 Linux file system hierarchy
| position | purpose |
|---|---|
| /usr | Installed software, shared libraries, including files and static read-only program data. Important subdirectories are: -/ usr/bin: user command -/ usr/sbin: system management command -/ usr/local: local customization file |
| /etc | Configuration files specific to this system |
| /var | Variable data specific to this system remains permanent between system startup. Dynamically changing files (such as databases, cache directories, log files, printer spooling documents, and website content). Can be found under / var. |
| /run | Runtime data for processes started since the last system startup. This includes ID files, lock files, and so on. The contents of this directory are recreated on restart |
| /home | The home directory where ordinary users store their personal data and configuration files. |
| /root | The home directory of the super administrator user root. |
| /tmp | Global writable space for temporary files. Files that have not been accessed, changed or modified within 10 days will be automatically deleted from the directory. There is also a temporary directory / var/tmp. If the files in this directory have not been accessed, changed or modified within 30 days, they will be automatically deleted. |
| /boot | Files required to start the startup process |
| /dev | Contains special device files for the system to access hardware. |
2.2 find files by name
Find out the absolute path and relative path. Those starting with / are absolute paths. There's nothing to say.
2.3 managing files using command line tools
Objective: to be able to create, copy, link, move and delete files and subdirectories in various directories.
## cp mv rm mkdir cp file1 file2 file3 dir ## Copy multiple files to dir mv and rm at one time. The same is true ## The - r parameter is usually added to handle directory related operations
2.4 using pathname extension to match files
Objective: use metacharacters and extension techniques to improve file management efficiency
- Document general configuration

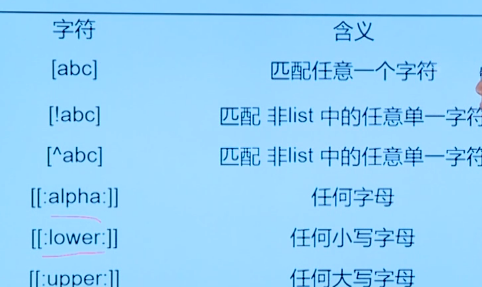



get help
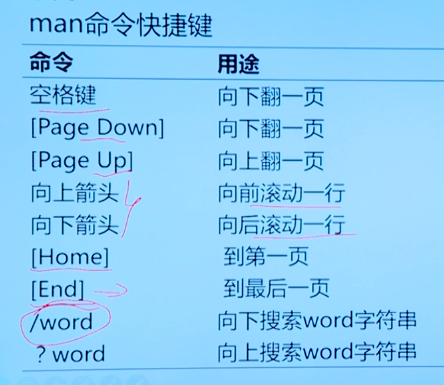
3.1 obtaining local help information
man [-k] [-K] string
-k keyword


3.2 get online help
Enter sosreport under root to generate a tar XZ file (tar -xvJf), you can use md5sum to verify the file hash and cat to read the file content
4 create, view and edit text files
4.1 output redirection to file or program
Standard input, standard output and standard error
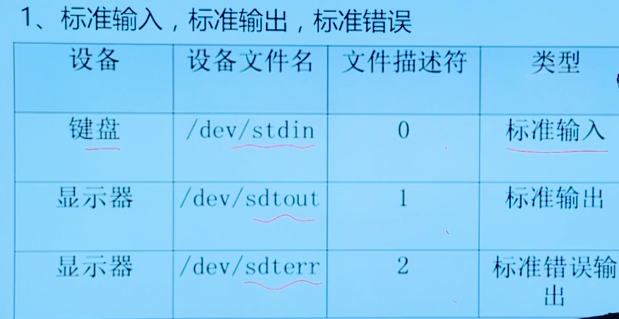
Other documents start with signal 3.
> file # Redirect stdout to overwrite files >> file # Redirect stdout to append files 2>file # Redirect stderr overwrite file 2> /dev/null # /dev/null black hole >file 2>&1 # stderr and stdout overwrite the same file, the same & > file >>file 2>&1 # stderr and stdout append the same file, the same as & > > file
Pipe symbol
The pipe character connects the standard output of the first command to the standard input of the next command
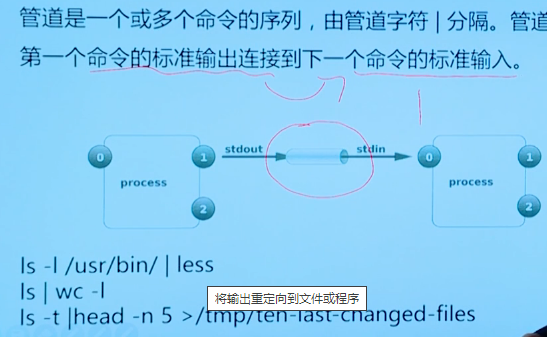
When both pipeline characters and redirection commands exist, the shell will give priority to commands inside the pipeline, such as commands
ls > /tmp/saved-output | less
There will be no output after execution, because the result of ls has been redirected to the file instead of being piped to the next command.
To solve this problem, you can use the tee command to write the file in the form of - i overwrite and - a append
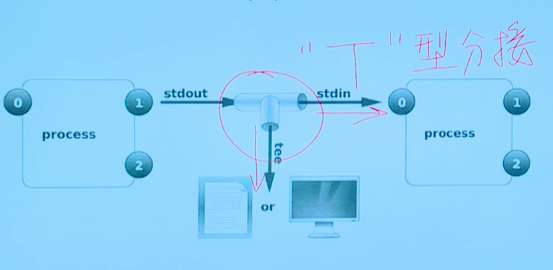
Example
ls -l |tee /tmp/saved-output |less
4.2 editing text files from the shell prompt
vim use, you can search the Internet for detailed tutorials
Compensation is noted that in the command mode, hjkl can be used as up, down, left and right buttons, and o can be inserted in the next line
4.3 editing text files with graphic editor
There's nothing to remember about the use of gedit
ctrl +o open file
ctrl + n new file
Manage local linux users and groups
5.1 users and groups
The configuration files for users and groups are / etc/passwd and / etc/group
id # Display user id and group id ps # Display instantaneous dynamic [common parameter - aux] newgrp # Switch the user group command and log in to another group
The relationship between users and groups can be 1 to 1, 1 to many, many to one, and many to many
5.2 obtaining super user access rights
It is recommended to switch to super user only when necessary
The su command directly switches to other user identities. su username starts the non login shell and will not switch to the corresponding user's home directory. The sudo command requires the user to configure in / etc/sudoers. Sudo is to enter the current user password to ensure the security of the root password.
5.3 manage local linux users and account groups
useradd # Add user usermod # It can be used to modify user accounts userdel # Without the option, only the user is deleted, and the related files are not deleted. Generally, the - r parameter is added to delete all the files related to the user at the same time passwd # Set the password. root can modify the passwords of all users
uid

5.4 manage local group accounts
groupadd [-g gid] [-r System group] groupname groupmod [-g gid] [-n name] groupdel # / etc/group and / etc/gshadow will be modified. If the current group is a user's primary group, it cannot be deleted. You need to modify the user group first
5.5 managing users and passwords


chage # Change password period
# example chage -m 0 -M 90 -W 7 -l 14 student modify student The minimum password period of the account is 0 days, and the maximum password period is 90 days # Remind to change the password 7 days before the period, and extend it for 14 days
usermod -L -U username # Lock user or unlock user
usermod -s /sbin/nologin username # User login is restricted through nologin shell, but resource access is not restricted
6 using linux file system permissions to control system permissions
6.1 Linux file permission system
rwx read, write, execute. It's very basic to find out kogn Chu's main genus, group and other
6.2 managing file system permissions from the command line
chmod [u,g,o,a] [+,-,=][r,w,x] filename # Change file permissions. It can also be used as chmod 755 filename, - R recursive directory chown [-R] user:group file/dir # Change primary group chgrp [-R] group filename # Change file group
6.3 manage default permissions and file access
Manage special permissions and default umask. linux has three special permissions
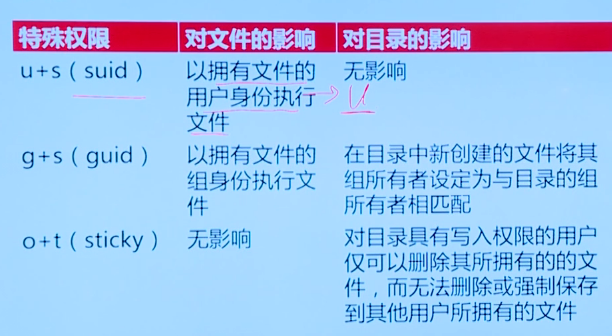
Example of setting special permissions
chmod u+s filename chmod 2750 filename # Here is setgid, setuid=4, setgid=2, sticky=1
redhat has a default file permission of 666 and a directory permission of 777. Umask is used to set a mask to restrict the permission of a new file. When a new file is created, its initial permission is determined by the file creation mask. Every time a user registers and enters the system, the umask command will be executed. You can modify the permission through umask, such as umask 007. All the rwx permissions of the newly created file permission other group will be removed.
Initial permissions for files (or directories) = Maximum default permissions for files (or directories) - umask jurisdiction
Permanently change umask through Add umask command after bashrc file or modify / etc/bashrc and / etc/profile configuration files directly through root user.
7 monitoring and managing linux processes
7.1 process
Process status can be divided into running, sleep, zombie, etc
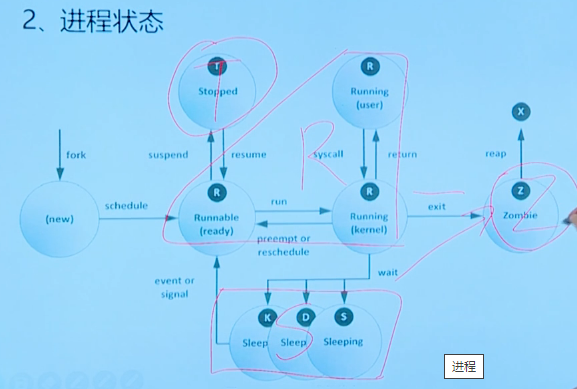
systemd is the parent of all linux processes.
ps [aux][lax][-ef] #Lists the process status of the current system
The processes in square brackets are usually kernel processes. ps is only displayed once. top can continuously observe the processes
7.2 control operation
A session can be understood as a terminal
A job can be understood as a command or a collection of commands. It may be a process group, including pipeline characters
jobs fg %1 bg %1 ctrl+z ctrl+c
7.3 interrupt process
You can send signals to the foreground to stop the process, such as ctrl+c, ctrl+z, ctrl + / and so on
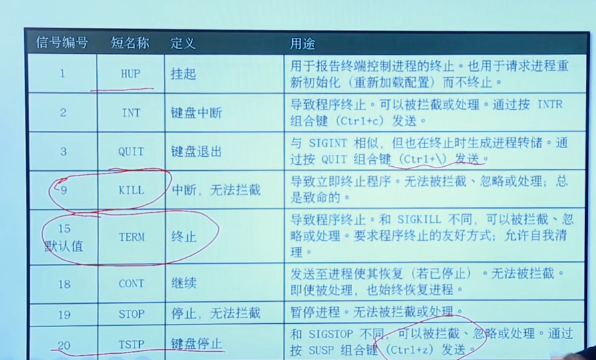
kill -l # List common signals killall [-signal] [-u] comman_pattern# Using the process name to kill a process can kill a group of processes with the same name pkill [-signal][-U][-G][-P][-t] command_pattern #Use the name of the process to kill the process, similar to kill
Log off user as administrator (pkill)
w # You can view the users currently logged in to the system and the cumulative activities pstree # You can view the parent-child relationship and use the parent process to terminate the process
The following figure shows how to log off a user by killing a process

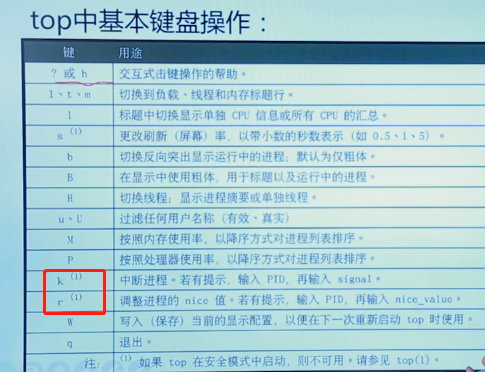
7.4 monitoring process activities
Load balancing value: the linux kernel calculates the average load index based on the exponential moving draw of the load (the cumulative number of CPUs requested by active system resources). The calculation result is expressed as the average number of processes running the process queue in the past 1 minute, 5 minutes and 15 minutes
cat /proc/loadavg 0.00 0.01 0.05 2/199 30259
top # Similar to windows process management uptime w #Number of login users
Generally, if the load balancing value is less than 1, it indicates that the resource utilization is reasonable, and if it is greater than 1, it indicates that there are resources waiting.
8 control services and Daemons
8.1 identify automatically started system processes
The system daemon and network service started by systemd service and socket word unit can be listed
systemd unit
systemctl -t help can list the available units of systemd. The focus is on service
systemclt status servicename.service # View service status

systemctl list-units --type=service # List servcie service units systemctl status sshd # View specific services systemclt is-enabled sshd # Check whether a service is started or not
8.2 control system services
It can control system daemons and network services through systemctl

Unit dependency

9 configuring and protecting openssh
9.1 accessing the remote command line Using ssh
ssh remotehostname # Log in as current user ssh root@remotehostname # Log in as root ssh root@remotehostname command # Run a single instruction remotely
9.2 configure authentication of ssh key
ssh password free login
ssh-keygen # Generate public-private key ssh-copy-id root@remotehost # Add the public key to the machine to which you want to log in without secret
9.3 customize ssh service configuration
The ssh configuration file is placed in / etc/ssh/sshd_config
# Disable root login PermitRootLogin no # Only the root user is allowed to authenticate with the key PermitRootLogin without-passwd # Password login is prohibited. You can only log in through a key PassWordAuthentication no
The ssh service needs to be restarted for the configuration to take effect
10 analyzing and storing logs
10.1 log system architecture and log system files
The system D-JOURNAL daemon provides an improved log management service
The rsyslog service is an enhanced version of syslog. Write them to a permanent file in the / var/log directory
/var/log/messages # Log, system, other /var/log/secure # Authentication, security related /var/log/maillog # Mail and mail related logs /var/log/cron # System time related to planned tasks /var/log/boot.log # Log files generated during system startup
For system log priority, classification and details, please refer to the help manual
man 5 rsyslog.conf
10.2 viewing log system files
Configuration file / etc / rsyslog Conf, each five-day to file location is configured under the #####RULES### field
Log file rotate prevents the file system in / var/log from filling up. It is usually done in combination with cron.
tail -f log file # Show the last 10 and scroll, f = follow logger -p user.notice hello # Send log p= priority, which is usually used to test the correctness of rsyslog configuration
10.3 viewing systemd log entries
journalctl find events
The systemd log stores the log data in a structured binary file with an index and cannot be read directly by a text editor. It should be viewed with journalctl
Note that each restart will clear the systemd log

journalctl -o verbose displays log details
10.4 save systemd log
You can configure systemd journal to store logs on disk instead of memory. By default, systemd logs are stored in / run/log/journal, and permanently retained logs are placed in / var/log/journal. At the same time, it supports log rotation mechanism to clear every month
mkdir /var/log/journal chown root:systemd-journal /var/log/journal chmod 2775 /var/log/journal reboot # Or send the special signal USR1 to the system D-JOURNAL process as root journalctl -b -1 # View the systemd log of the last time the system was started
10.5 keep the system time accurate
Time synchronization is very important for analyzing logs between multiple systems
timedatectl # Displays the current time related system settings timedatectl list-timezones # List available time zones timedatectl set-timezone # Set time zone timedatectl set-time "2021-06-18 15:00: 00" # Set time timedatectl set-ntp true/false #Set ntp switch
Configuring and monitoring chronyd
The chronyd service is usually an imprecise local hardware clock (rtc keeps accurate) by synchronizing with the configured ntp server

11 manage Red Hat Enterprise linux Network
11.1 network concept
Four layer network model and osi model

11.2 verifying network configuration
ip addr show eth0 # Display ip address ip -s link show eth0 # See eth0 connection status ip route ping -c3 172.25.0.253 # c3 means sending three packets tracepath #Link tracking
Ports and services
Common port names and services are listed in / etc/services
ss and nestat
ss -ta # display all tcp socket netstat -ta
11.3 configuring the network using nmcli
NetworkManager is a daemon that monitors and manages network settings. The configuration file directory of network configuration is / etc / sysconfig / network scripts

11.4 edit network profile
Configuration file storage location / etc / sysconfig / network scripts / ifcfg-

After the configuration is completed, the configuration can take effect by reboot ing the machine or reloading the connection
nmcli con reload nmcli con down "ID" nmcli con up "ID" ## Reconnecting the network one by one may result in failure to connect to the host. Be careful to confirm whether the configuration is correct or reboot is safer
11.5 configuration host name and name interpretation
hostname # Same as cat /etc/hostname hostnamectl set-hostname # Set static hostname hostnamectl status
Configure host name resolution / etc/hosts
getent hosts hostname # Test hosts file host resolution
If a host name is not found in the hosts file, the system will resolve / etc / resolvs conf. Generally, you can modify the configuration file directly or update the configuration file through network manager
nmcli con mod ID ipv4.dns IP # ID is the network interface configuration nmcli con mod ID +ipv4.dns IP # Add configuration host [hostname] # Test dns connection

12 archive files and copy files between systems
12.1 manage compressed tar archives
tar supports gzip, bzip2 and xz compression or decompression
Usage can refer to
https://www.runoob.com/linux/linux-comm-tar.html
12.2 copy files securely between systems
scp
scp file1 file2 root@server2:/root/ # Copy file1 and file2 to the remote / root directory scp -r root@server2:/var/log /tmp # -r
The disadvantage of sftp is that folders cannot be transferred
sftp [user@]host ##Download or synchronize files through push and get
12.3 secure synchronization of files between systems
rsync
rsync -nav /var/log /tmp # n the parameter executes null operation, and the simulation operation will not be changed. Ensure that the file is not overwritten or deleted rsync -av /var/log /tmp # Copy directory to destination directory rysnc -av /var/log/ /tmp # Copy files in directory to target directory
Installing and updating software packages
13.1 RPM package and yum
rpm
Yum is the rpm package manager, which can automatically handle dependencies. Yum configuration file / etc / yum conf. Yum repository / etc / yum.com repos. d/*
cat /etc/yum.repos.d/xxx.repo #Viewing the configuration, gpgcheck=0 means that gpgkey, baseurl, name, enabled, etc. are not verified yum repolist # Warehouse list yum list all |less # Get installed packages
13.2 update using yum management software
yum help yum list all httpd yum info httpd yum search keyword yum provides /var/www/html yum whatprovides # What package is the anti query command in. yum provides # Inverse query what package the file is in. yum install httpd -y # install httpd, assume yes yum update yum remove httpd
yum group

View historical operation records
All installation logs are placed in / var / log / yum log
yum history # yum installation history yum history undo 3 # Installation with undo number 3
13.3 enable yum software repository
yum repolist all # Current yum enabled yum-config-manager -enable "repo name" # Enable or disable yum warehouse yum-config-manager -add-repo="http://xxxxx "# or create a new file in / etc/yum.repos.d / # rpm configuration package for repository rpm -import http://xxxxxx yum localinstall http://xxxx/xxx.rpm
13.4 check rpm package file
The rpm user program can obtain information about the contents of the software package file and the installed software package from the local database or the package file itself
rpm -q -a # Query all installed packages rpm -q pkgname # pkgname is currently installed rpm -q -p pkgfile.rpm rpm -q -f filename # Equivalent to yum provides, which package provides the query file

Install the local package files using yum or up2date
yum localinstall # Same as RPM -ivh * RPM, use yum to keep yumhistory # Extract files from rpm package rpm2cpio xxx.rpm|cpio -id "*txt" # Extract the txt suffix file in the software package
14 accessing linux file system
14.1 identify file systems and devices
Mount, unmount, mount point / mnt/
Partition, block device
ll /dev/sda #
Logical volume management (LVM)
Physical storage media, physical volume, volume group, logical volume
df -h # Look at the partition du -h # catalogue
14.2 mounting and unmounting file systems
Manually mount the file system
The root user is required to mount
blkid # View block device uuid mkdir /mnt/mydata mount /dev/vda1 /mnt/mydata/ #mount blkid /dev/vdb1/ # see mount uuid="xxxxxxx-xxxxxxx-xxxxxxx-xxxx" /mnt/mydata
Default manual mount to directory / mnt
If there are files in the directory used for mounting, the original file cannot be accessed after mounting, and the original file can be accessed only after uninstallation
Uninstall is available through
umount /mnt/mydata # umount [mount point] lsof /mnt/mydata # See what processes are currently using mount points
If the mount point is being used by a process and cannot be unloaded, you can process the corresponding process through the lsof command and try again
After usb flash memory is inserted, it can be automatically mounted on the graphical interface at / run/media//
14.3 connection between production documents
Hard links and soft links can be referred to https://www.jianshu.com/p/dde6a01c4094
Hard link
ln file1 /tmp/file2 # Create a hard link for file1 ls -li file1 /tmp/file2 #When viewing two files, the innode value and attribute are the same, and the storage space is shared rm -f file1 # Delete file1 cat /tmp/file2 # After deleting file1, the hard link file2 is still unaffected #Hard links can only link files, not directories
Soft links are equivalent to windows shortcuts
ln -s file1 /tmp/file2 ls -l /tmp/fiel #File attributes are lrwxrwxrwx such rm -f file1 cat /tmp/file2 # After deleting file1, file2 will become a dead link #Directories can create soft links
14.4 finding files in the system
The locate command searches for results based on file names or paths in the locate database
locate -i # Case insensitive locate -n 5 # Return the number of results. For example, 5 results are output here # The locate database will be updated automatically every day through scheduled tasks. root can update the database through the updatedb command
find real-time search in file system
find / -name # Search by file name, wildcards are supported find / -iname # Case insensitive find / -user student -group mail -perm 777 -size [10k,+10k,-10k,M,G] -type [f,d,l,b] -links [+1 Number of links] #Other attributes can be deleted
15 using virtualization
15.1 managing local virtual machine hosts
KVM kernalbased virtual machine

libvirt package provides the function of managing virtual machines, which can be managed through the graphical interface virtual manager
Command line tool virsh
15.2 installing a new virtual machine
Mainly the use of virtual manager and graphical operation. slightly
rh134
1 use kickstart to install automatically
Can refer to https://blog.csdn.net/mpu_nice/article/details/107922312
Without environmental practice, the meaning of learning is to know such a function when needed
1.1 define Anaconda Kickstart system

1.2 creating and editing kickstart files
System config kickstar & call the graphical tool for configuration and follow the steps.
Or edit the configuration file through a text file.

You can check whether the kickstart configuration file is correct through ksvalidator. If correct, no results are returned.
1.3 deploying a new virtual system using kickstart
Create configuration file -- > -- > configuration file sent to installer -- > -- > Anaconda points to the configuration file to install the system
2 using regular expressions through grep
2.1 fundamentals of regular expressions
2.2 matching text with grep
grep (global search regular expression and print out the line) prints matching regular expressions
grep -i 'cat$' file # Case insensitive ps aux | grep '^student' # Pipeline parameter ### grep common parameters -v # Invert the selection to print lines that are not included -r # A data search that recursively matches regular expressions is applied to a set of files or directories -A <Number> # Displays the number of rows after regular matches -B <Number> # Displays the number of rows before regular matches -e # Multiple - e options provide multiple regular expressions and will be used with logical or grep -e 'cat' -e 'dog' file -A 1 # Displays the line containing cat or dog and the line following it
3 creating and editing files using vim
In the command mode, hjkl you can move the cursor up, down, left and right, ^ to the beginning of the line, $to the end, gg to the first line of the document, and G to the last line of the document.
Command line mode: help can get help documents. In the shell environment, you can use vmtutor to view the tutorial