Preface
Ribbon Load Balancer
Flow chart of Ribbon load balancer
Implementation Principle of Ribbon Load Balancer
Judging Service Availability
Choosing an available service based on load balancing strategy IRule
Initialize access to all service lists
Preface
What is load balancing? Simply speaking, an application can be supported by multiple services in the background, that is, to provide a single service by using multiple servers. When a service hangs up or the load is too high, the load balancer can choose other services to process requests to improve the high availability and high concurrent distribution of the application. In addition, when the user requests come in, the load balancer can select other services to process requests. At the same time, the load balancer will send the response of the request back to the load balancer. The load balancer will send the response to the user, which can prevent the user from accessing the back-end server directly and make the server more secure.
Reference Wikipedia-Load Balancing
Ribbon Load Balancer
Ribbon's load balancer is implemented by LoadBalancer Client. When the application starts, LoadBalancer Client defaults to get the list of services from EurekaClient and caches the list of registered services locally. When LoadBalancer Client's select () method is invoked, according to the load balancing policy IRule. To select an available service to achieve load balancing.
Of course, LoadBalancer Client can also not get the list of services from EurekaClient. This is the need to maintain a service registration list information by itself. The specific operation is as follows:
ribbon: eureka: enabled: false stores: ribbon: listOfServers: baidu.com, google.com
Flow chart of Ribbon load balancer
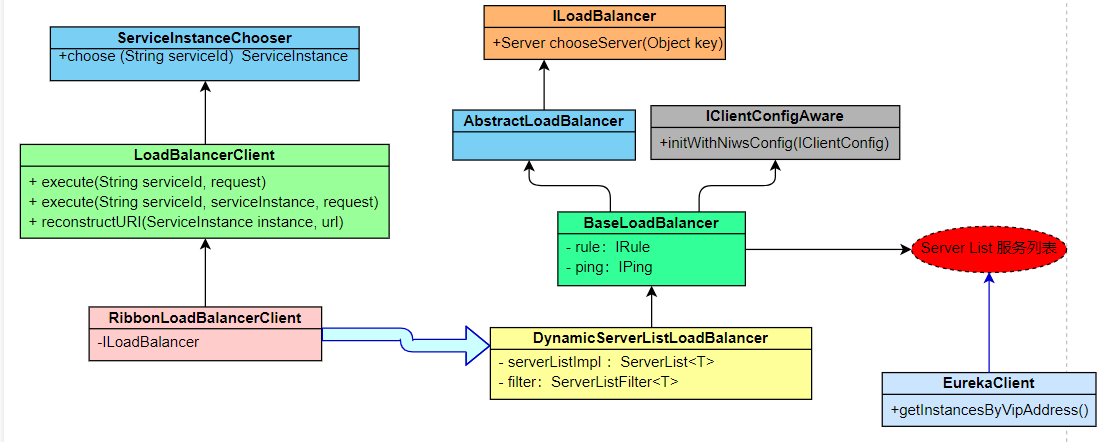
Main processes:
When the application starts, ILoadBalancer retrieves the list of services from the EurekaClient
2. Then send heartbeat detection to EurekaClient every 10 seconds. If the registration list changes, update the acquisition and retrieve it.
3. When LoadBalancerClient calls the select () method to select a service, it calls ILoadBalancer's chooseServer() to get a service that is available.
4. When ILoadBalancer obtains services, it chooses them according to the load balancing strategy IRule.
5. Return available services
Implementation Principle of Ribbon Load Balancer
Here's how each class works
RibbonLoadBalancerClient
Ribbon Load Balancer Client is an important class of Ribbon load balancing implementation. The final load balancing request processing is performed by Ribbon Load Balancer Client.

It implements the LoadBalancerClient interface, while the LoadBalancerClient interface implements the Service Instance Chooser interface:
ServiceInstanceChooser
This interface is used to obtain an available service from the load balancer. There is only one way:
public interface ServiceInstanceChooser { /** * @param serviceId: Service ID * @return Available service instances */ ServiceInstance choose(String serviceId); }
LoadBalancerClient
A client representing load balancing is an interface that inherits the Service Instance Chooser interface and has three methods:
public interface LoadBalancerClient extends ServiceInstanceChooser { /** * Execution of requests * @param serviceId : Service ID for finding LoadBalancer * @param request: Allow implementation to perform before and after operations */ <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException; /** * Execution of requests * @param serviceId : Service ID for finding LoadBalancer * @param serviceInstance : Services to execute requests * @param request: Allow implementation to perform before and after operations */ <T> T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException; /** * Create the correct URI with the real host and port. Some systems use the URL with the logical service name as the host. Calling this method will use host:port to replace the logical service name. * @param instance : Service instances for reconstructing URI s * @param original : URL with logical service name * @return A reconstructed URI. */ URI reconstructURI(ServiceInstance instance, URI original); }
Ribbon Load Balancer Client is implemented as follows:
Look at the interface method implemented from Service Instance Chooser, Load Balancer Client
public class RibbonLoadBalancerClient implements LoadBalancerClient { // Factory: Mainly used to create client, create load balancer, client configuration, etc. // For each client name, a Spring Application Context is created from which the required bean s can be retrieved. private SpringClientFactory clientFactory; protected ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer(String serviceId) { return this.clientFactory.getLoadBalancer(serviceId); } .................. } public class SpringClientFactory extends NamedContextFactory<RibbonClientSpecification> { // Get Client public <C extends IClient<?, ?>> C getClient(String name, Class<C> clientClass) { return getInstance(name, clientClass); } // Obtaining Load Balancer public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer(String name) { return getInstance(name, ILoadBalancer.class); } //Get Client Configuration public IClientConfig getClientConfig(String name) { return getInstance(name, IClientConfig.class); } // Get Ribbon Load Balancer Context public RibbonLoadBalancerContext getLoadBalancerContext(String serviceId) { return getInstance(serviceId, RibbonLoadBalancerContext.class); } // Get the corresponding bean public <T> T getInstance(String name, Class<T> type) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = getContext(name); ..... return context.getBean(type); ..... } }
Select () method
This method is mainly used to obtain an available service instance.
public ServiceInstance choose(String serviceId, Object hint) { Server server = getServer(getLoadBalancer(serviceId), hint); if (server == null) { return null; } // Ribbon Server implements Service Instance return new RibbonServer(serviceId, server, isSecure(server, serviceId), serverIntrospector(serviceId).getMetadata(server)); } // Getting the load balancer based on the service ID calls the Spring ClientFactory method for acquisition protected ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer(String serviceId) { return this.clientFactory.getLoadBalancer(serviceId); } // Obtain available services based on load balancer protected Server getServer(ILoadBalancer loadBalancer, Object hint) { if (loadBalancer == null) { return null; } return loadBalancer.chooseServer(hint != null ? hint : "default"); }
Finally, ILoadBalancer.chooseServer is invoked to obtain the available services, and then ILoadBalancer.
execute() method
This method executes requests
public <T> T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException { Server server = null; if (serviceInstance instanceof RibbonServer) { server = ((RibbonServer) serviceInstance).getServer(); } RibbonLoadBalancerContext context = this.clientFactory.getLoadBalancerContext(serviceId); // A status logger that records the status of a service RibbonStatsRecorder statsRecorder = new RibbonStatsRecorder(context, server); ........... T returnVal = request.apply(serviceInstance); statsRecorder.recordStats(returnVal); return returnVal; ........... } // apply method calls as follows, and eventually returns ClientHttpResponse public ListenableFuture<ClientHttpResponse> intercept(final HttpRequest request, final byte[] body, final AsyncClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException { final URI originalUri = request.getURI(); String serviceName = originalUri.getHost(); return this.loadBalancer.execute(serviceName, new LoadBalancerRequest<ListenableFuture<ClientHttpResponse>>() { @Override public ListenableFuture<ClientHttpResponse> apply( final ServiceInstance instance) throws Exception { HttpRequest serviceRequest = new ServiceRequestWrapper(request, instance, AsyncLoadBalancerInterceptor.this.loadBalancer); return execution.executeAsync(serviceRequest, body); } }); }
This is the principle of the left part of the load balancer flow chart. Next, look at the right part.
ILoadBalancer
Through the above analysis, the load balancer obtains an available service and eventually calls ILoadBalancer's chooseServer method. Here's how ILoadBalancer works.
First, let's look at the overall class diagram of ILoadBalancer:
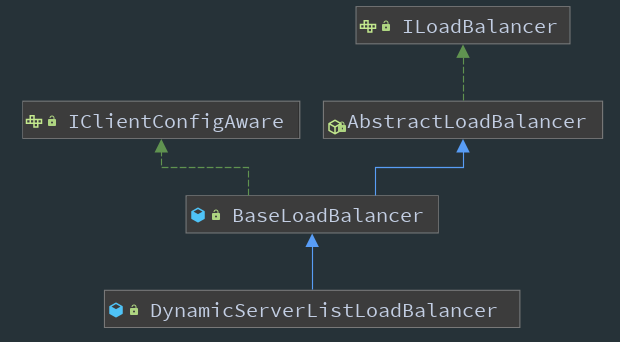
In the above class diagram, the main logic is implemented in BaseLoadBalancer, while DynamicServerListLoadBalancer mainly provides the ability to dynamically obtain service lists.
ILoadBalancer
Let's first look at ILoadBalancer, which represents a load balancer interface.
public interface ILoadBalancer { // Adding services public void addServers(List<Server> newServers); //Access to services public Server chooseServer(Object key); //Mark a service offline public void markServerDown(Server server); //Get a list of all available services with UP status public List<Server> getReachableServers(); //Get a list of all services, including available and unavailable public List<Server> getAllServers(); }
AbstractLoadBalancer
Implement the ILoadBalancer interface and provide some default implementations
public abstract class AbstractLoadBalancer implements ILoadBalancer { public enum ServerGroup{ALL, STATUS_UP, STATUS_NOT_UP} public Server chooseServer() { return chooseServer(null); } public abstract List<Server> getServerList(ServerGroup serverGroup); // Get status public abstract LoadBalancerStats getLoadBalancerStats(); }
IClientConfigAware
Client Configuration
public interface IClientConfigAware { public abstract void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig); }
BaseLoadBalancer
The main implementation logic of the load balancer is that in this class, the available services are obtained according to the load balancing policy IRule, and the availability of services is detected through IPing. In addition, when the service list is obtained from EurkaClient, it will be saved in this class and all the service lists and available services will be maintained. Business List.
Let's first look at some of its attributes, and then at each of its corresponding methods.
public class BaseLoadBalancer extends AbstractLoadBalancer implements PrimeConnections.PrimeConnectionListener, IClientConfigAware { // Default load balancing strategy: polling to select service instances private final static IRule DEFAULT_RULE = new RoundRobinRule(); protected IRule rule = DEFAULT_RULE; // The default ping policy calls IPing to detect whether the service is available private final static SerialPingStrategy DEFAULT_PING_STRATEGY = new SerialPingStrategy(); protected IPingStrategy pingStrategy = DEFAULT_PING_STRATEGY; protected IPing ping = null; // List of all services protected volatile List<Server> allServerList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Server>()); // List of services with status up protected volatile List<Server> upServerList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Server>()); // lock protected ReadWriteLock allServerLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); protected ReadWriteLock upServerLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); // Timing Tasks, Is the ping Service Available protected Timer lbTimer = null; // ping interval, 10 seconds protected int pingIntervalSeconds = 10; // Maximum number of ping protected int maxTotalPingTimeSeconds = 5; // State of Load Balancer protected LoadBalancerStats lbStats; // Client Configuration private IClientConfig config; // Service List Change Monitor private List<ServerListChangeListener> changeListeners = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<ServerListChangeListener>(); // Service State Change Monitor private List<ServerStatusChangeListener> serverStatusListeners = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<ServerStatusChangeListener>(); // Constructor, which uses default configuration to create a load balancer, and other overloaded constructors that can be used to create a load balancer as needed public BaseLoadBalancer() { this.name = DEFAULT_NAME; this.ping = null; setRule(DEFAULT_RULE); setupPingTask(); lbStats = new LoadBalancerStats(DEFAULT_NAME); } ..................... }
In the above properties, Ribbon provides some default configurations:
IClientConfig represents the configuration of the client. The implementation class is DefaultClientConfigImpl, in which default values are configured.
public class DefaultClientConfigImpl implements IClientConfig { // The default policy of ping: DummyPing public static final String DEFAULT_NFLOADBALANCER_PING_CLASSNAME = "com.netflix.loadbalancer.DummyPing"; // DummyPing.class.getName(); public static final String DEFAULT_NFLOADBALANCER_RULE_CLASSNAME = "com.netflix.loadbalancer.AvailabilityFilteringRule"; public static final String DEFAULT_NFLOADBALANCER_CLASSNAME = "com.netflix.loadbalancer.ZoneAwareLoadBalancer"; public static final int DEFAULT_MAX_TOTAL_TIME_TO_PRIME_CONNECTIONS = 30000; public static final int DEFAULT_MAX_RETRIES_PER_SERVER_PRIME_CONNECTION = 9; ............................................. }
IRule represents the load balancing strategy, that is, how to select service instances, default to Round Robin Rule, that is, to select services by polling. Ribbon offers seven by default.
IPing denotes policies for detecting whether services are available. Ribbon also provides many strategies, five of which are defaulted to Dummy Ping.
The strategies of IRule and IPing will be studied later.
In BaseLoadBalancer, in addition to providing a parametric construction method (using the default configuration), there are also many overloaded construction methods. Let's look at creating BaseLoadBalancer according to the configuration of the client:
// Create BaseLoadBalancer based on client configuration public BaseLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config) { initWithNiwsConfig(config); } @Override public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig) { // Load Balancing Strategy String ruleClassName = (String) clientConfig.getProperty(CommonClientConfigKey.NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName); // ping strategy String pingClassName = (String) clientConfig.getProperty(CommonClientConfigKey.NFLoadBalancerPingClassName); IRule rule = (IRule) ClientFactory.instantiateInstanceWithClientConfig(ruleClassName, clientConfig); IPing ping = (IPing) ClientFactory.instantiateInstanceWithClientConfig(pingClassName, clientConfig); // state LoadBalancerStats stats = createLoadBalancerStatsFromConfig(clientConfig); // Initialization configuration initWithConfig(clientConfig, rule, ping, stats); } void initWithConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule, IPing ping, LoadBalancerStats stats) { this.config = clientConfig; String clientName = clientConfig.getClientName(); this.name = clientName; // Period of ping int pingIntervalTime = Integer.parseInt(clientConfig.getProperty(CommonClientConfigKey.NFLoadBalancerPingInterval,Integer.parseInt("30"))); // Number of maximum ping int maxTotalPingTime = Integer.parseInt(clientConfig.getProperty(CommonClientConfigKey.NFLoadBalancerMaxTotalPingTime,Integer.parseInt("2"))); setPingInterval(pingIntervalTime); setMaxTotalPingTime(maxTotalPingTime); setRule(rule); setPing(ping); setLoadBalancerStats(stats); rule.setLoadBalancer(this); if (ping instanceof AbstractLoadBalancerPing) { ((AbstractLoadBalancerPing) ping).setLoadBalancer(this); } ................. // Registration monitoring/negligible init(); }
In the above construction method, a BaseLoad Balancer can be created according to the information of client configuration, such as the client can configure load balancing strategy, ping strategy, ping interval and maximum number of times, etc.
Judging Service Availability
In Ribbon, how long does it take the load balancer to update the access list? In the BaseLoadBalancer class, there is a setupPingTask method. Inside this method, a PingTask timer task is created to detect the availability of the service, while PingTask creates a Pinger object. In the runPinger() method of the Pinger object, the pingServers (ping, all Se) of the pingerStrategy are based on the Ping strategy. The main logic for rver to obtain service availability is as follows:
void setupPingTask() { if (canSkipPing()) { return; } // If a timed task already exists, cancel it if (lbTimer != null) { lbTimer.cancel(); } // The second parameter, true, indicates that it is a deamon thread lbTimer = new ShutdownEnabledTimer("NFLoadBalancer-PingTimer-" + name, true); // Create PingTask, which inherits from TimerTask and executes the run method on a regular basis lbTimer.schedule(new PingTask(), 0, pingIntervalSeconds * 1000); ...... } class PingTask extends TimerTask { public void run() { // Default Ping Strategy = new Serial Ping Strategy () new Pinger(pingStrategy).runPinger(); } } public void runPinger() throws Exception { // If ping, return if (!pingInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) { return; // Ping in progress - nothing to do } // All services, including unavailable services Server[] allServers = null; boolean[] results = null; Lock allLock = null; Lock upLock = null; try { allLock = allServerLock.readLock(); allLock.lock(); allServers = allServerList.toArray(new Server[allServerList.size()]); allLock.unlock(); // Number of all services int numCandidates = allServers.length; // Results of all service ping results = pingerStrategy.pingServers(ping, allServers); // List of services available in status final List<Server> newUpList = new ArrayList<Server>(); // List of services with status changes final List<Server> changedServers = new ArrayList<Server>(); for (int i = 0; i < numCandidates; i++) { // Update boolean isAlive = results[i]; Server svr = allServers[i]; // The state of old age boolean oldIsAlive = svr.isAlive(); // Update status svr.setAlive(isAlive); // If the state changes, it is put into the collection and retrieved. if (oldIsAlive != isAlive) { changedServers.add(svr); } // Status Available Services if (isAlive) { newUpList.add(svr); } } upLock = upServerLock.writeLock(); upLock.lock(); upServerList = newUpList; upLock.unlock(); // Abnormal Change Monitor notifyServerStatusChangeListener(changedServers); } finally { // ping completion pingInProgress.set(false); } } // Detect the status of the service @Override public boolean[] pingServers(IPing ping, Server[] servers) { int numCandidates = servers.length; boolean[] results = new boolean[numCandidates]; for (int i = 0; i < numCandidates; i++) { results[i] = false; if (ping != null) { results[i] = ping.isAlive(servers[i]); } } return results; }
In the above logic, Ribbon sends a ping to EurekaClient every 10 seconds to determine the availability of the service. If the availability of the service changes or the number of services does not match the previous one, the service will be updated or retrieved. With these services, an available service is selected according to the load balancing strategy IRule.
Choosing an available service based on load balancing strategy IRule
When the Ribbon client Ribbon Load Balancer Client chooses a service, it eventually calls ILoadBalancer.chooseServer to select a service. Next, let's look at this method:
public Server chooseServer(Object key) { ....... //rule= new RoundRobinRule() return rule.choose(key); .... }
Regarding Ribbon's load balancing strategy IRule, Ribbon provides seven kinds, which will be analyzed later. Now you just need to know how to select services through IRule.
Initialize access to all service lists
In the above analysis, Ribbon will check the availability of services every 10 seconds at regular intervals, retrieve if the service status changes, and then select an available service according to the load balancing strategy IRule; however, where to get the list of services at initialization? Here's an analysis of this problem.
BaseLoadBalancer has a subclass, DynamicServerListLoadBalancer, which has the function of using dynamic sources to obtain server lists. That is, the server list may change at runtime. In addition, conditions can be used to filter out services that do not meet the requirements.
public class DynamicServerListLoadBalancer<T extends Server> extends BaseLoadBalancer { // Is the list of services being updated? protected AtomicBoolean serverListUpdateInProgress = new AtomicBoolean(false); // Service List volatile ServerList<T> serverListImpl; // Service filter volatile ServerListFilter<T> filter; }
1. Get all services at initialization
In DynamicServerListLoadBalancer, there is a restOfInit method that is called at initialization, in which all service lists are pulled from the Eureka client:
void restOfInit(IClientConfig clientConfig) { ............. updateListOfServers(); ........ } public void updateListOfServers() { List<T> servers = new ArrayList<T>(); if (serverListImpl != null) { // Get a list of all services servers = serverListImpl.getUpdatedListOfServers(); // Conditional filtering services if (filter != null) { servers = filter.getFilteredListOfServers(servers); } } updateAllServerList(servers); } protected void updateAllServerList(List<T> ls) { if (serverListUpdateInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) { try { for (T s : ls) { s.setAlive(true); // State set to available } setServersList(ls); super.forceQuickPing(); // Forced detection of service status } finally { serverListUpdateInProgress.set(false); } } }
Get all service list servers = serverListImpl.getUpdatedListOfServers(); eventually call the Discovery Enabled NIWSServerList method:
servers = serverListImpl.getUpdatedListOfServers(); public List<DiscoveryEnabledServer> getUpdatedListOfServers(){ return obtainServersViaDiscovery(); } private List<DiscoveryEnabledServer> obtainServersViaDiscovery() { List<DiscoveryEnabledServer> serverList = new ArrayList<DiscoveryEnabledServer>(); ........ // Get the list of registered services through eurekaClient EurekaClient eurekaClient = eurekaClientProvider.get(); if (vipAddresses!=null){ for (String vipAddress : vipAddresses.split(",")) { List<InstanceInfo> listOfInstanceInfo = eurekaClient.getInstancesByVipAddress(vipAddress, isSecure, targetRegion); for (InstanceInfo ii : listOfInstanceInfo) { if (ii.getStatus().equals(InstanceStatus.UP)) { ..... DiscoveryEnabledServer des = createServer(ii, isSecure, shouldUseIpAddr); serverList.add(des); } } ...... } } return serverList; }
Through the analysis of the above methods, Ribbon will eventually get the list of services through EurekaClient, and the implementation class of EurekaClient is DiscoveryClient. In Eureka, the DiscoveryClient class has the functions of registering, discovering, renewing and obtaining the list of services.
In addition, filters can also be used to obtain services that do not meet the requirements.
This is one of the implementation principles of Ribbon load balancer. Finally, let's take a look at the following flow chart to deepen our impression:
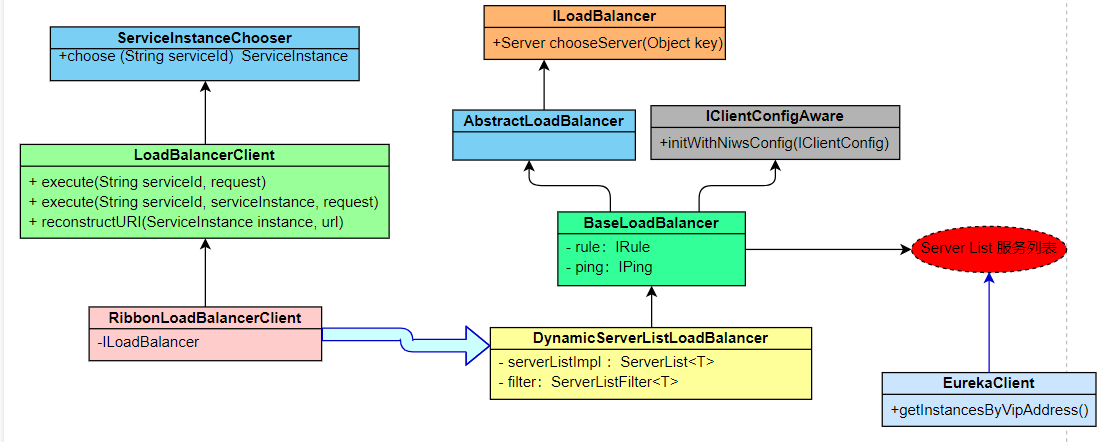
The next article is about IRule and Ping strategies for load balancing.