SAMBA service overview
What is SAMBA?
-
SMB (Server Message Block) protocol realizes file sharing, also known as CIFS (Common Internet File System)
-
It is a protocol for sharing files between Windows and Unix like systems
-
The client is mainly Windows; Supports simultaneous mounting and concurrent writing of multiple nodes
-
It is mainly used for file sharing and printing sharing under windows and Linux
-
Realize anonymous file sharing with local users
SAMBA main process:
-
smbd process controls publishing shared directory and permissions, responsible for file transmission, port: TCP 139 445
-
nmbd process is used for name resolution. NETBIOS and port: UDP 137 138; Obtain the computer name based on NETBIOS protocol - > resolve it to the corresponding IP address to realize information communication
NetBIOS is the abbreviation of Network Basic Input/Output System, that is, Network Basic Input/Output System, which generally refers to a set of API s for LAN communication
samba service follows two protocols: smb protocol -- > TCP and nmb protocol -- > UDP
SAMBA service experiment
SAMBA environmental preparation
Step 1: clone a Linux server called SAMBA from the template machine
Step 2: change the host name and IP address
# hostnamectl set-hostname samba # su # vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 BOOTPROTO=none IPADDR=10.1.1.10 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=10.1.1.2 DNS1=8.8.8.8 DNS2=114.114.114.114 # systemctl restart network Expansion: it is recommended to use multiple network cards"ifdown ens33"as well as"ifup ens33"Restart network operation
Step 3: close the firewall and SELinux
# systemctl stop firewalld # systemctl disable firewalld # setenforce 0 # vim /etc/selinux/config SELINUX=disabled
Step 4: configure yum source
- If there is a network, you can directly use the official website source. The domestic yum source has been loaded in CentOS7. If there is no network, you need to mount the image source
# yum clean all # yum makecache
SAMBA software installation (server construction)
Step 1: install samba software
- Samba is also a C/S architecture software. The Client is mainly Windows, and Samba service is mainly used for file sharing between Windows and Linux systems
# yum install samba -y => Installing Samba services # rpm -qa |grep ^samba => Check which software is installed [root@samba ~]# rpm -qa |grep ^samba samba-common-tools-4.10.16-13.el7_9.x86_64 samba-common-4.10.16-13.el7_9.noarch samba-client-libs-4.10.16-13.el7_9.x86_64 samba-common-libs-4.10.16-13.el7_9.x86_64 # samba-4.10.16-13. el7_ 9.x86_ sixty-four => Server side samba-libs-4.10.16-13.el7_9.x86_64 samba-client-4.10.16-13.el7_9.x86_64
Configuration file for smb
- The samba service configuration file is set by default. We only need to write the share name option
# vim /etc/samba/smb.conf => Open Samba service configuration #l [global] => Global option, which all samba configurations need to follow workgroup = MYGROUP => definition samba The workgroup in which the server resides security = user => Authentication mode: share anonymous|user User password|server External server user password max log size = 50 => Maximum log size KB log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m = log file passdb backend = tdbsam => Password format,representative tdbsam Formatted server string = Samba Server Version %v => smb Description of the service load printers = yes => Load printer cups options = raw => Represents the printer's options #l [homes] => Local options (shared name) comment = Home Directories => describe browseable = no => Represents the hidden share name writable = yes => If the share has a directory, it represents readable and writable #l [printers] => Share name comment = All Printers => describe path = /var/spool/samba => Local shared directory browseable = no => Hide indicates whether to hide the shared name guest ok = no -> public = no => no The representative needs account and password access. There are two ways to write it writable = no -> read only =yes => no Represents non writable and read-only. There are two ways to write printable = yes => Print options Edit yourself samba Share name profile #l [share] => Share name path = /dir1 => Shared path guest ok = no => Account and password access required writable = yes => Writable
samba default profile:
[root@samba ~]# vim /etc/samba/smb.conf
# See smb.conf.example for a more detailed config file or
# read the smb.conf manpage.
# Run 'testparm' to verify the config is correct after
# you modified it.
[global]
workgroup = SAMBA
security = user
passdb backend = tdbsam
printing = cups
printcap name = cups
load printers = yes
cups options = raw
[homes]
comment = Home Directories
valid users = %S, %D%w%S
browseable = No
read only = No
inherit acls = Yes
[printers]
comment = All Printers
path = /var/tmp
printable = Yes
create mask = 0600
browseable = No
[print$]
comment = Printer Drivers
path = /var/lib/samba/drivers
write list = @printadmin root
force group = @printadmin
create mask = 0664
directory mask = 0775
SAMBA comprehensive case
Task requirements
Build a SAMBA service and share a directory / samba/share. The client can use user01/123 to create files and delete files in this directory through windows or Linux
Solution
Environment configuration
Step 1: SAMBA server environment preparation
Change host name, IP address, turn off firewall, SELinux, configure YUM source
Step 2: install SAMBA software
# yum install samba -y => Install Samba service software # rpm -aq|grep ^samba => Check which Samba service software is installed
Step 3: query SAMBA generated file list (rpm -ql)
- Because samba service follows two protocols: smb protocol -- > TCP and nmb protocol -- > UDP
- SMB Service and NMB Service two services
# rpm -ql samba => Query SAMBA generated file list /usr/sbin/smbd => Binary files, representing commands /usr/sbin/nmbd => Binary files, representing commands /usr/lib/systemd/system/smb.service => smb service /usr/lib/systemd/system/nmb.service => nmb service #l note: with these two services, you can manage them through systemctl start|restart|stop service
Step 4: create a shared directory on the server side
# mkdir /samba/share -p
Step 5: edit / etc / SMB Conf configuration file to realize SAMBA sharing
- The original configuration options remain unchanged. Edit the shared directory at the bottom of the configuration file
# vim /etc/samba/smb.conf
...
[smb_share] => Share name
comment = samba service => Remark information, optional
path = /samba/share => share directory
guest ok = no => The representative needs an account and password to log in
writable = yes => Represents that this shared directory is readable and writable
perhaps
[samba_share] => Share name
path = /samba/share
public = no
writable = yes
#l remarks:
guest ok === public The two are equivalent
writable Represents readable and writable
Step 6: create a user01 user, add it to samba authentication, and set the password to 123
- After the following operations are completed, a user01 account and password 123 are added to SAMBA service
# useradd user01 => Create account # which smbpasswd => Query smb password command to create directory [root@samba ~]# which smbpasswd /usr/bin/smbpasswd # smbpasswd -a user01 => - A stands for add. Add an account and set a password for smb service New SMB password:123 Retype new SMB password:123 Added user user01. => This message represents increased success
Step 7: start nmb and smb services
# systemctl start nmb # systemctl start smb
samba service sharing based on Windows and Linux server
Step 1: install samba client
-
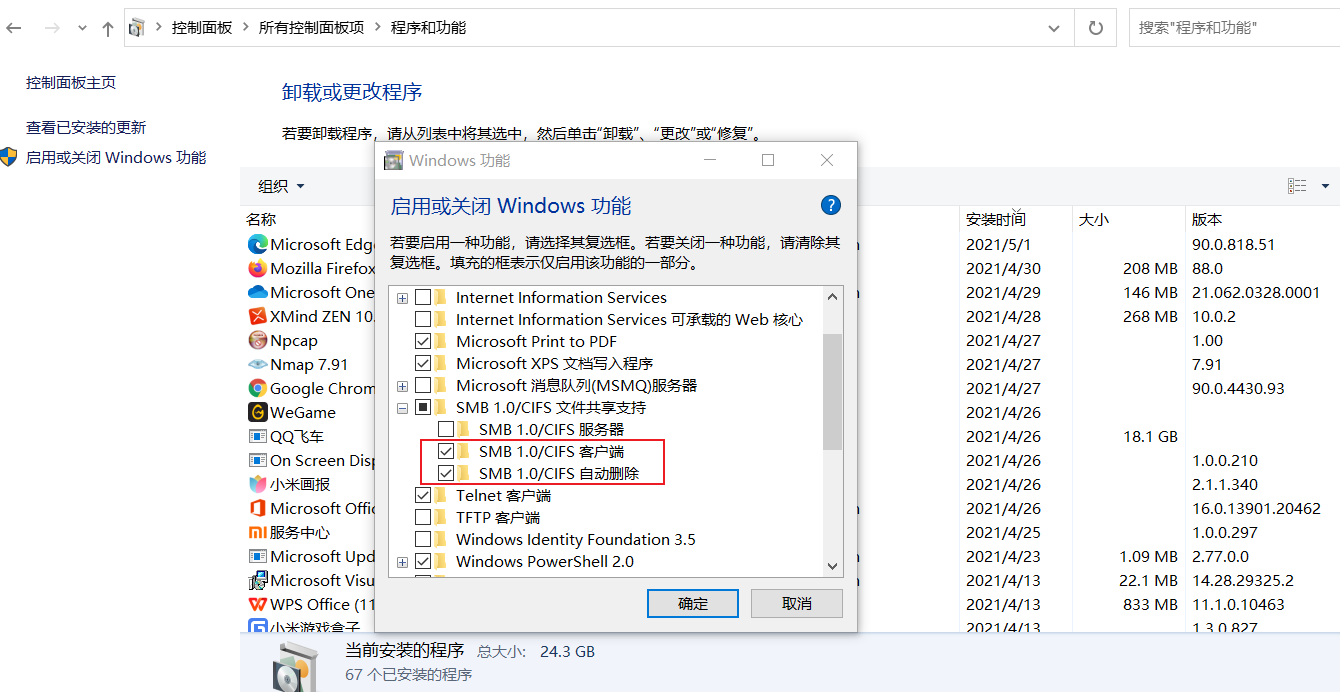
Control panel = > programs and features = > turn Windows features on or off
-
Find the following two options to install
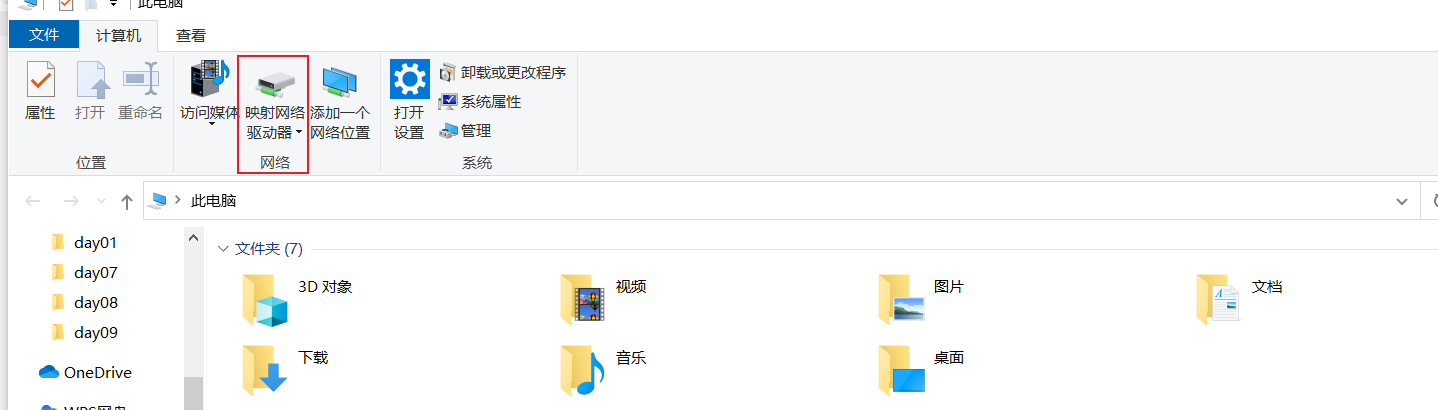
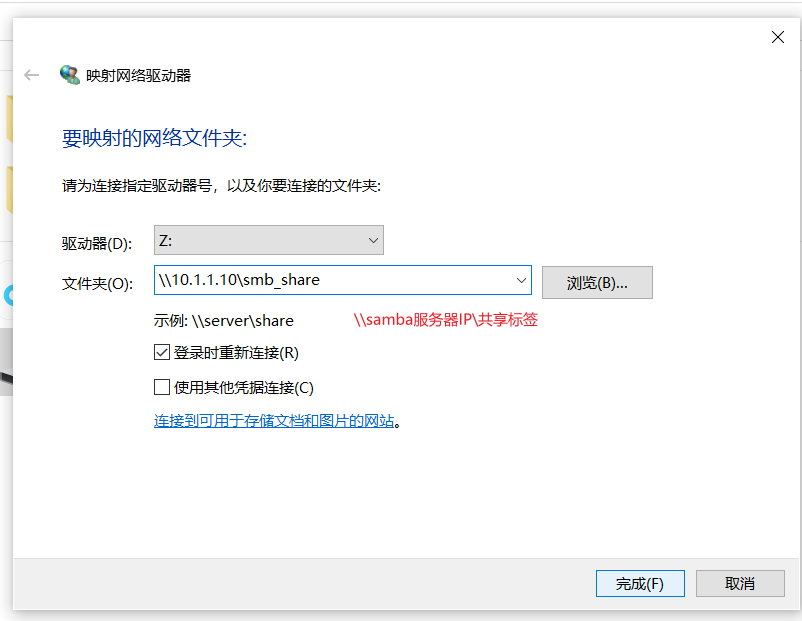
Step 2: enter the computer (my computer) and find the mapped network drive
- Specify a drive (choose any one) enter: \ \ SAMBA server IP \ shared directory label
- Then enter the account and password
Step 3: through acl policy, give user01 user read, write and execute permission in samba shared directory
-
After the mount is completed, the directory cannot be written? A: the main reason is that the / samba/share directory does not have write permission
-
You can have upload and download permissions on the / samba/share directory
# setfacl -m u:user01:rwx /samba/share
samba service sharing based on Linux and Linux server
Step 1: File Sharing Based on Linux or Linux
- Install samba client
- Using smbclient command to view directory information
# smbclient -L 10.1.1.10 -U user01 => View directory information
[root@client ~]# smbclient -L 10.1.1.11 -U user01
Enter SAMBA\user01's password:
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
print$ Disk Printer Drivers
# smb_share Disk samba service => Shared directory of disk type
IPC$ IPC IPC Service (Samba 4.10.16)
user01 Disk Home Directories
Reconnecting with SMB1 for workgroup listing.
Server Comment
--------- -------
SAMBA Samba 4.10.16
Workgroup Master
--------- -------
SAMBA SAMBA
Note: input required user01 User password
- Viewing directory information using smbclient
- When it is not writable, use the ACL command to increase user permissions
# smbclient //10.1.1.10/smb_share -U user01
Step 2: Mount SAMBA to Linux system (similar to NFS)
# mkdir /u01 => Create mount directory for Linux client # mount.cifs -o user=user01,pass=123 //10.1.1.10/smb_share /u01 => mount
Access control Description:
Control read and write permissions writable = yes/no readonly = yes/no If the resource is writable, but only some users are allowed to write, others are read-only write list = admin, root, @staff(User group) read list = mary, @students Control access object valid users = tom,mary,@itcast invalid users = tom Note: only one of the above two options can exist Network access control: hosts deny = 192.168.0. Reject a segment hosts allow = 192.168.0.254 Allow a IP hosts deny = all Reject all hosts allow = 192.168.0. EXCEPT 192.168.0.254 Allow a network segment, but reject a single IP be careful: deny and allow At the same time, allow first
summary
1. ftp, LAN and extranet are OK
2. Access mount.com via NFS LAN mount NFS focuses on the relationship between Linux and Linux
3. samba LAN direct access (smbline) mount CIFS focuses on the relationship between Windows and Linux