catalogue
Use size to get the display resolution of the screen
Use position to get the current position of the mouse
moveTo: move the mouse to a position on the screen
moveRel (move): move based on the current position
doubleclick: double click the mouse
mouseDown and mouseUp: mouse press and release
screenshot: full screen capture
locateOnScreen: find the location of the screenshot
keyDown and keyUp: keyboard press and keyboard release
press: release immediately after pressing the key
typewrite(): continuous typing
The following is my study and arrangement of pyautogui, one of the most important libraries for scripting in python. I hope it will be helpful to share with you
Tip: during the initial use of pyautogui, I found that the click on Google browser failed, and others have not been found yet
Installation of pyautogui
You can use cmd to enter pip install pyautogui to install the library
mouse
The control of the mouse is based on the position on the screen. For example, the display resolution of my computer is 1920 ✖ 1080, that is, starting from the upper left corner of the screen, the horizontal direction to the right represents x, 1920 small pixel blocks in a row, and the vertical direction down represents y, and 1080 pixel blocks in a column, just like a large coordinate system, except that there is only the first quadrant in the whole screen
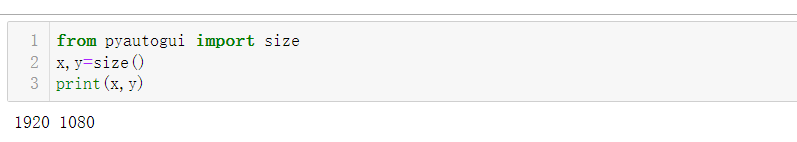
Use size to get the display resolution of the screen
Examples are as follows:
from pyautogui import size x,y=size() print(x,y)
Use position to get the current position of the mouse
from pyautogui import position x,y=position() print(x,y)

Mouse movement
moveTo: move the mouse to a position on the screen
It can be seen from the above that the coordinates of the upper left corner are (0, 0) and the lower right corner is (19201080). An example is as follows
from pyautogui import moveTo moveTo(1684,1059,duration=3)#1684 and 1059 are the positions to be moved, and duration represents the time to perform the move, in seconds
moveRel (move): move based on the current position
from pyautogui import moveTo,moveRel moveRel(100,200,duration=2) #Move from the current mouse position to 100 to the right and 200 to the down, and the process time is set to 2 seconds
Mouse click
Click: click the mouse
from pyautogui import click #click specifies the coordinates. You can also set the duration from execution to clicking this location, as well as the left, middle or right buttons click(100,200,button='left',duration=2) click(100,200,button='middle') click(100,200,button='right')
doubleclick: double click the mouse
from pyautogui import doubleClick #The parameters are the same as clicking, except now double-click the mouse doubleClick(100,200,button='left',duration=2) doubleClick(100,200,button='middle') doubleClick(100,200,button='right')
mouseDown and mouseUp: mouse press and release
from pyautogui import mouseDown,mouseUp mouseDown() # Mouse down mouseUp() # Mouse release
Mouse drag
dragTo: drag the mouse to a position
dragRel: drag according to the logarithm table of the current position
Dragging the mouse is similar to moving the mouse, but compared with moving the window, a difference test is done
from pyautogui import moveTo,mouseDown,mouseUp mouseDown(button='left') moveTo(1000,500) mouseUp(button='left')
from pyautogui import dragTo,mouseDown,mouseUp mouseDown(button='left') dragTo(1000,500) mouseUp(button='left')
During the test, it was found that the combination of moveTo and mouse press can drag a window, but dragTo can't
Mouse scrolling
from pyautogui import scroll scroll(300)#Pass in an integer. A positive number means sliding the roller up scroll(-300)#Slide the roller down
Screen processing
screenshot: full screen capture
The screenshot will be saved in the same directory where the script is saved
from pyautogui import screenshot
screenshot().save('Screenshot.png')#jpg format is also supported. Please try other formatsCrop captures screenshots of any size, such as crop((
locateOnScreen: find the location of the screenshot
Find the screenshot location here is to find the location that matches the saved screenshot on the screen
from pyautogui import locateOnScreen
print(locateOnScreen('Screenshot.png'))keyboard entry
keyDown and keyUp: keyboard press and keyboard release
Multiple keys can be pressed at the same time by pressing and releasing the keyboard, such as ctrl+v pasting. In order to achieve multiple keys at the same time, we also have hotkey('ctrl','c '), which can accept multiple parameters, press them in the incoming order, and then release them in the opposite order
from pyautogui import keyDown,keyUp
keyDown('space') # Press the spacebar
keyUp('space') # Release the spacebar
keyDown('ctrl')
keyDown('c')
keyUp('c')
keyUp('ctrl')
hotkey('ctrl','c')
press: release immediately after pressing the key
It can be regarded as a combination of press and release. For example, if we want to send a message, press enter, and it will be released after pressing. Therefore, press is widely used
The case of letters does not affect the keys. For example, Enter can be written as press ('Enter ') and press ('end')
There are two key positions, such as Shift, followed by left or right, press('shiftleft ')
It should be emphasized that the Enter key is recognized as line feed and can be replaced by \ n, that is, press('enter')=press('\n '), and the tab key can be replaced by \ t
The up, down, left and right keys are up, down, left and right respectively
typewrite(): continuous typing
typewrite here can recognize case
from pyautogui import typewrite
typewrite('ceshi',0.5)
#The first parameter is the content to be entered, and the second parameter is the interval between each key press
typewrite(['c','e','s','h','i'])
#You can also pass in a list of individual strings
typewrite(['S','u','n'])#typewrite('Sun',0.5)
#An uppercase S will be enteredPrompt information
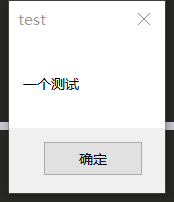
prompt box
from pyautogui import alert print(alert(text='A test',title='test')) #Click OK to return to OK
Selection box
from pyautogui import confirm
print(confirm('Please select gender',buttons=['male','female']))
#Your hits will be output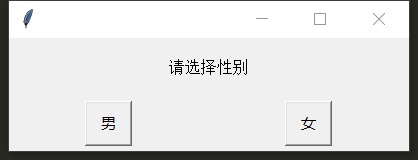
Input password
from pyautogui import password
print(password('Please enter your password'))
#The password just entered will be output
Enter common content
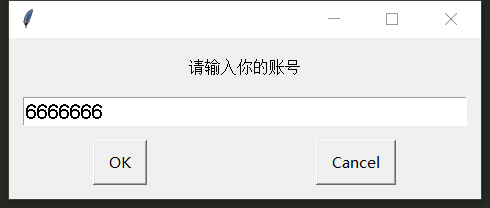
from pyautogui import prompt
print(prompt('Please enter your account number'))
#The content just entered will be returned