1, Brief introduction of theoretical knowledge
1. Serial communication protocol and RS-232 standard
(1) Brief description of serial communication protocol
Serial communication refers to sending and receiving bytes by bit. Although the serial communication of bits and bytes is slow, the serial port can use one line to send data and another line to receive data. Serial communication protocol refers to the relevant specifications that specify the content of data packet, including start bit, main data, check bit and stop bit. Both parties need to agree on a consistent data packet format to send and receive data normally. In serial communication, common protocols include RS-232, RS-422 and RS-485.
(2) Principle of serial communication protocol
Serial port is an important data communication interface in embedded system. Its essential function is to act as an encoding converter between CPU and serial equipment. When the data is sent from the CPU through the serial port, the byte data is converted into serial bits; When receiving data, serial bits are converted to byte data. If the application wants to use the serial port for communication, it must submit a resource application request to the operating system before use (open the serial port), and release the resources after communication (close the serial port). Typically, a serial port is used for the transmission of ASCII characters. Three lines are used for communication: ① ground wire, ② sending data line and ③ receiving data line. The most important parameters of serial communication are baud rate, data bit, stop bit and parity. For two ports for traffic, these parameters must match: baud rate is a parameter to measure the communication speed, which represents the number of bits transmitted per second; Data bit is a parameter to measure the actual data bit in communication. When the computer sends a packet, the standard values are 5, 7 and 8 bits. How to set it depends on your needs; The stop bit is used to represent the last bit of a single packet. The typical values are 1, 1.5 and 2 bits. The stop bit not only represents the end of transmission, but also provides an opportunity for the computer to correct clock synchronization; Parity bit is a simple error detection method in serial communication. There are four error detection methods - even, odd, high and low, or there can be no parity bit.
(3) Basic protocol (mainly introduces RS-232)
RS-232 (ANSI/EIA-232 standard) is a serial connection standard on IBM-PC and its compatible computers. It can be used for many purposes, such as connecting mouse, printer or Modem, and industrial instruments. For the improvement of drive and connection, the transmission length or speed of RS-232 often exceeds the standard value in practical application. RS-232 is limited to point-to-point communication between PC serial port and equipment. The maximum distance of RS-232 serial communication is 50 feet.
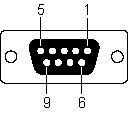
DB-9-pin connector
From the computer serial port section.
Functions of RS-232 pin:
① Data:
TXD (pin 3): serial port data output (Transmit Data)
RXD (pin 2): serial port data input (Receive Data)
② Handshake:
RTS (pin 7): request to send
CTS (pin 8): clear to send
DSR (pin 6): data send ready
DCD (pin 1): data carrier detect
DTR (pin 4): data terminal ready
③ Ground wire:
GND (pin 5): ground wire
④ Others
RI (pin 9): ring indication
2. Difference between RS232 level and TTL level
(1) TTL level signals are widely used because we usually use binary to represent data. Moreover, it is specified that + 5V is equivalent to logic "1" and 0V is equivalent to logic "0". Such data communication and level specification mode is called TTL (transistor transistor logic level) signal system. This is the standard technology of communication between various parts of equipment controlled by computer processor.
(2) RS232 is one of the communication interfaces on personal computer. It is an asynchronous transmission standard interface formulated by Electronic Industries AssociaTIon (EIA). Generally, RS-232 interfaces appear in the form of 9 pins (DB-9) or 25 pins (DB-25). Generally, there are two groups of RS-232 interfaces on personal computers, called COM1 and COM2 respectively. The level standard of RS232 is + 12V is logic negative, - 12 is logic positive, TTL level is 5V is logic positive, and 0 is logic negative
3. Working principle of "USB / TTL to 232" module (taking CH340 chip module as an example)


2, Using stm32CubeMX to realize water lamp
1. Installation and configuration of stm32CubeMX
(1) Installation address https://www.st.com/en/development-tools/stm32cubemx.html
(2) Click download, fill in the registration information and email, and then check the download information in the email
(3) Unzip the installation package and click to install
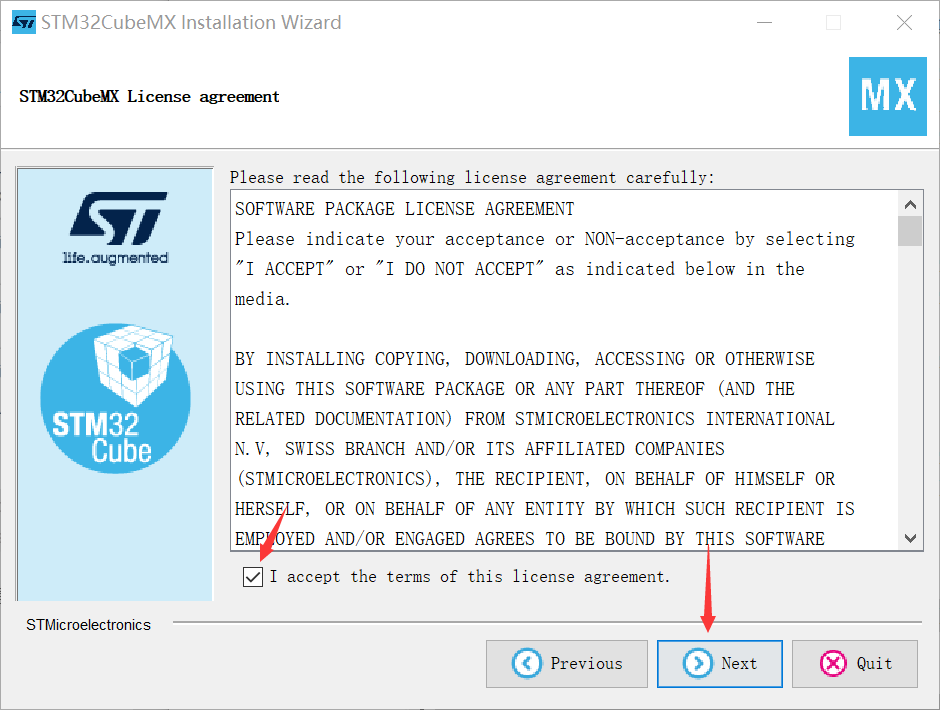
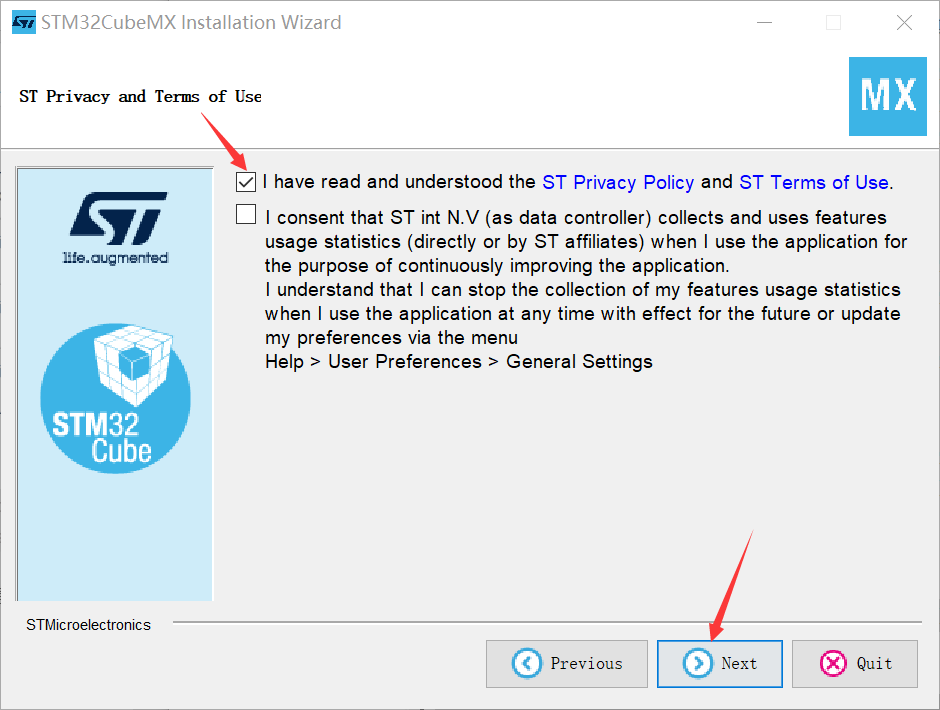
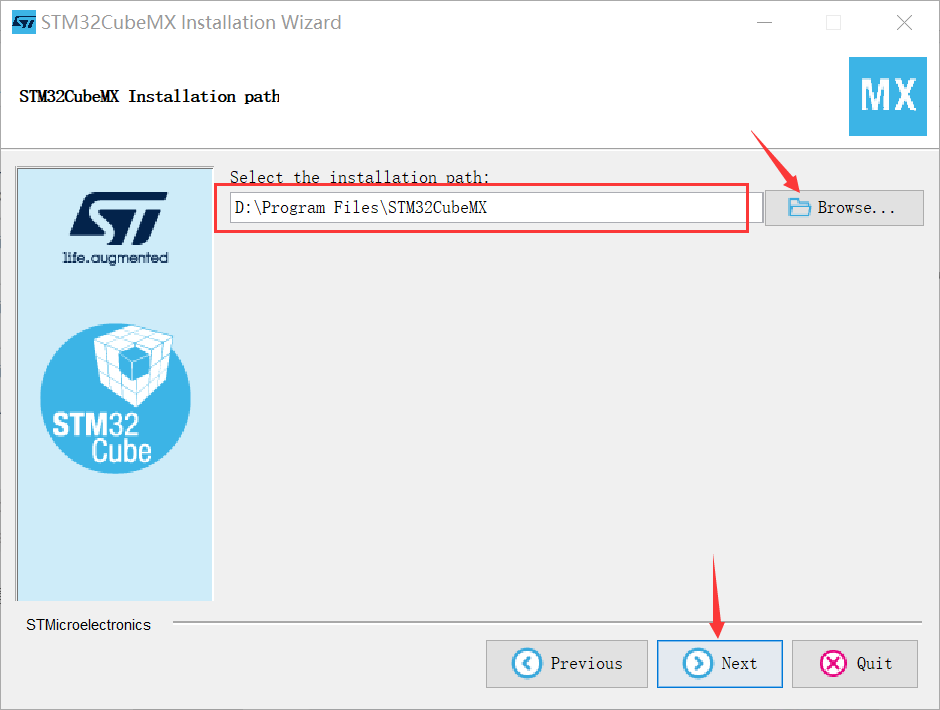
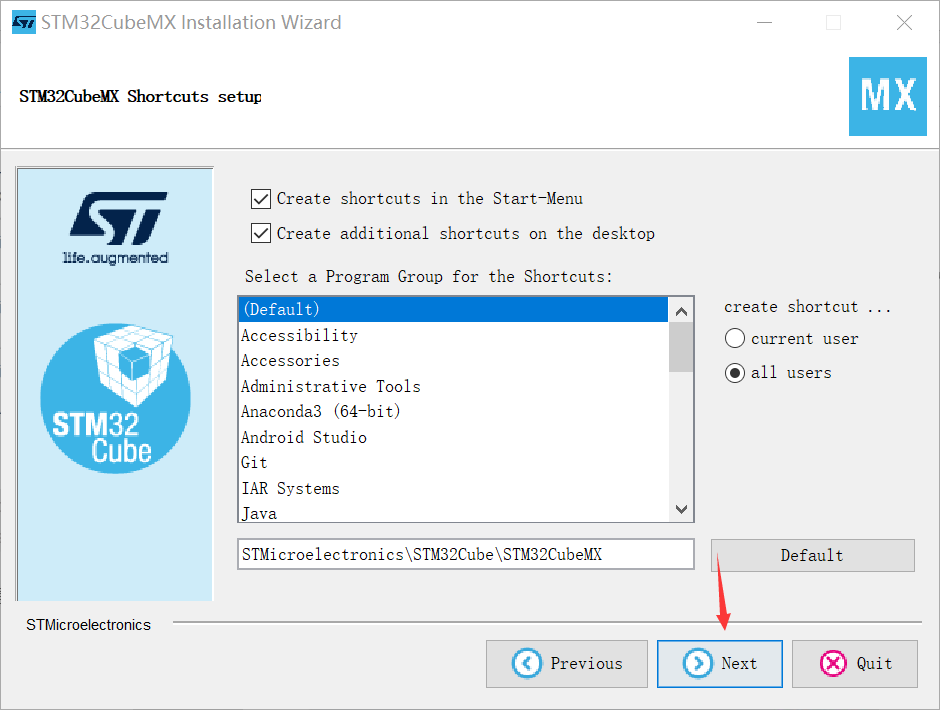
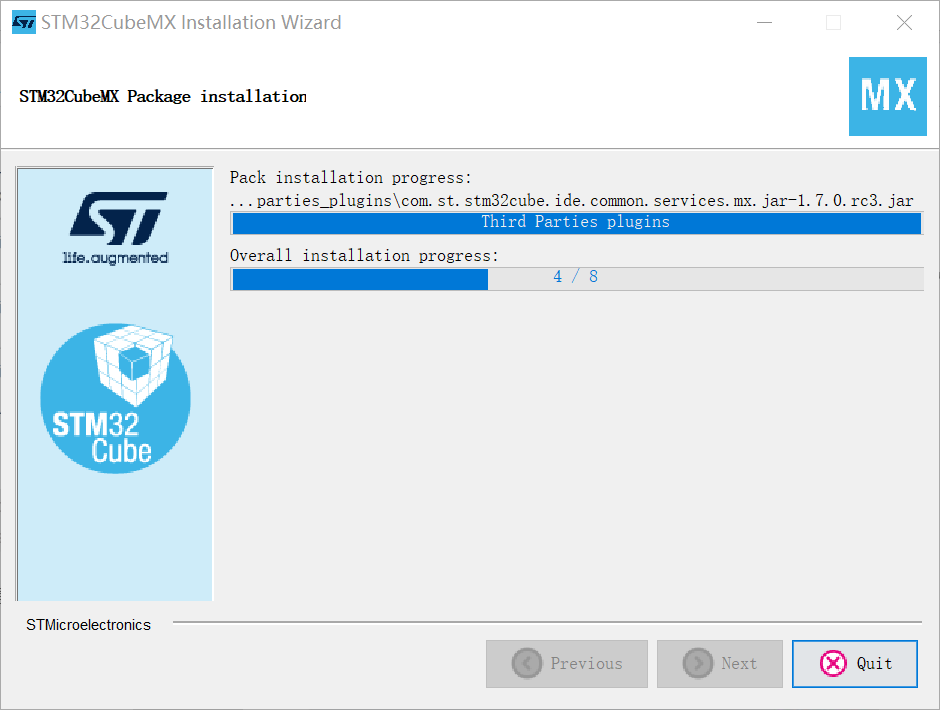

(4) Open the Cube and install the dependent package
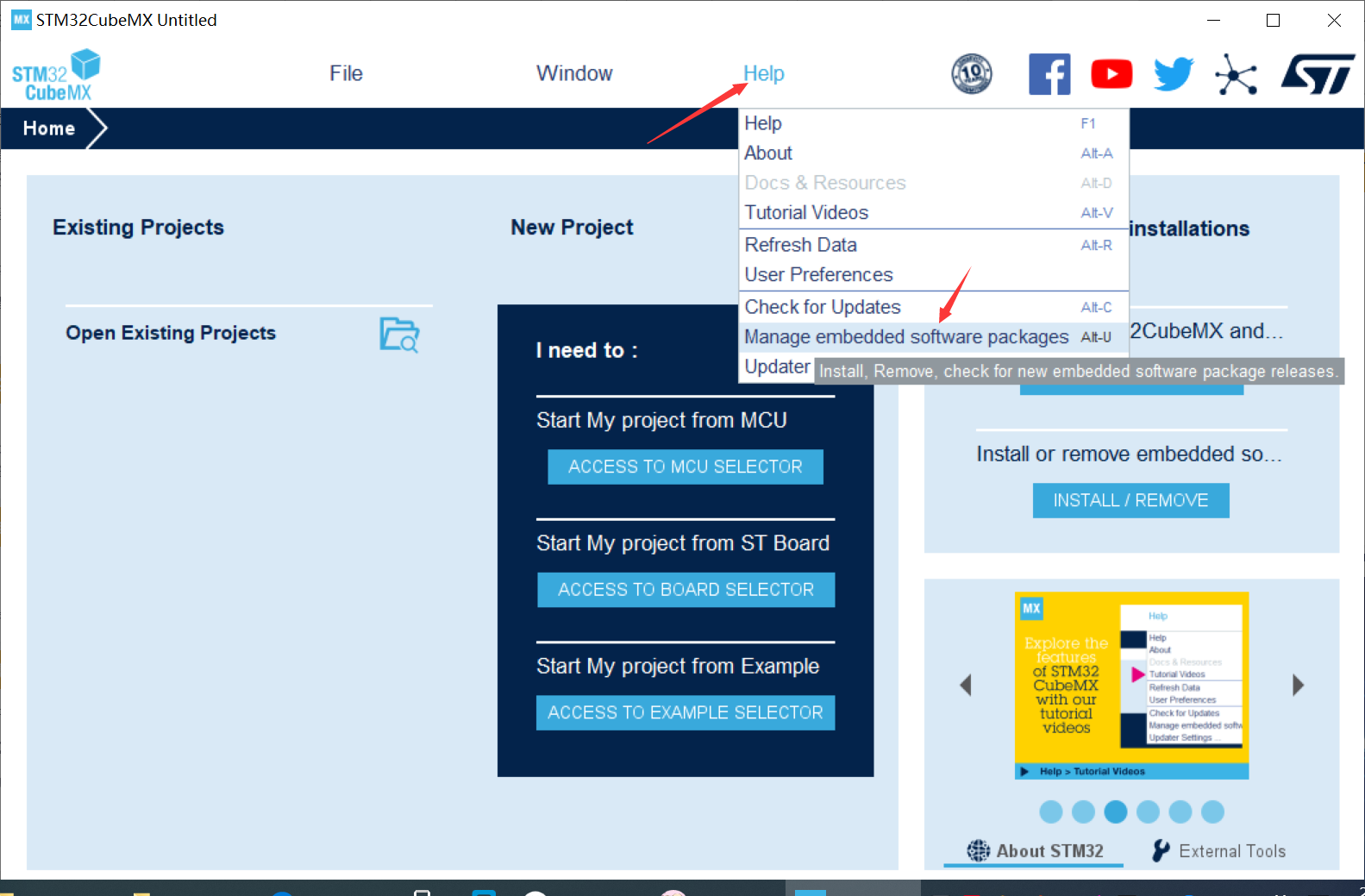
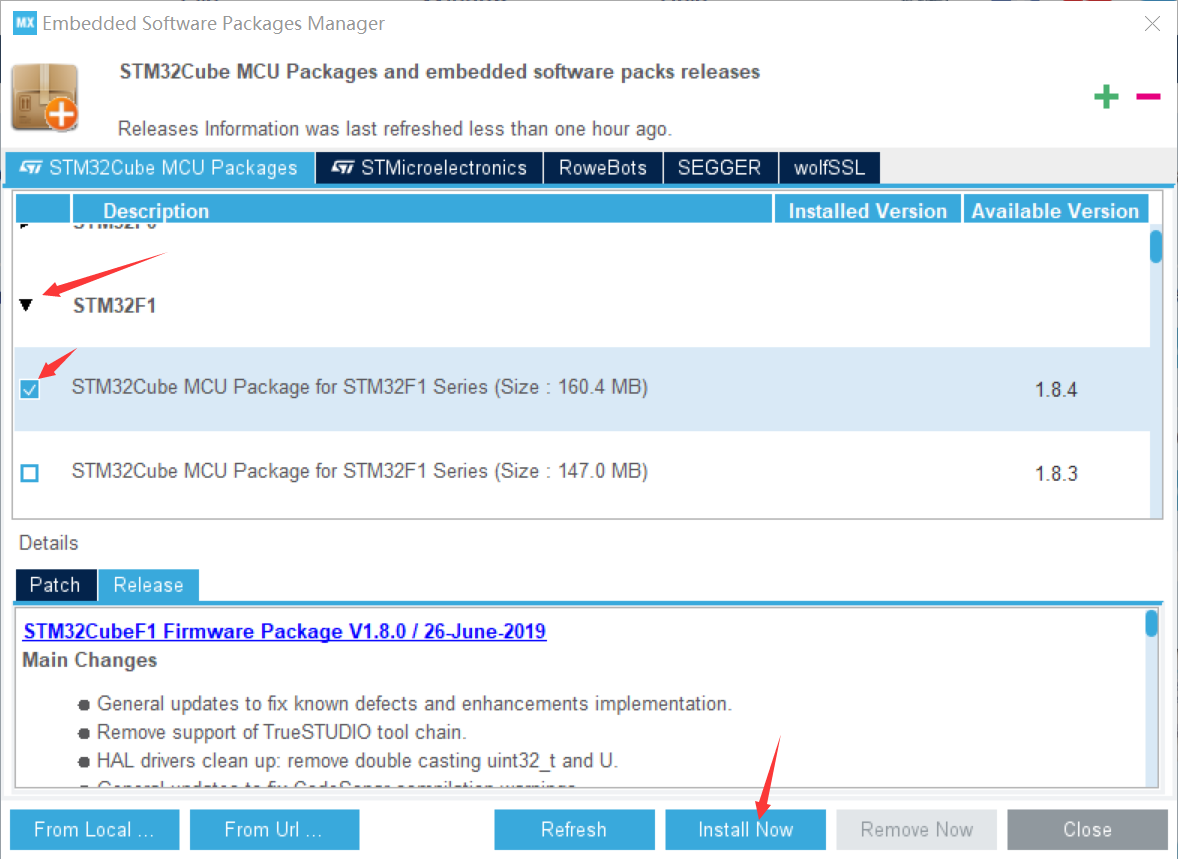
2. Use GPIO port to complete LED traffic light cycle flashing
(1) Modify stm32CubeMX code
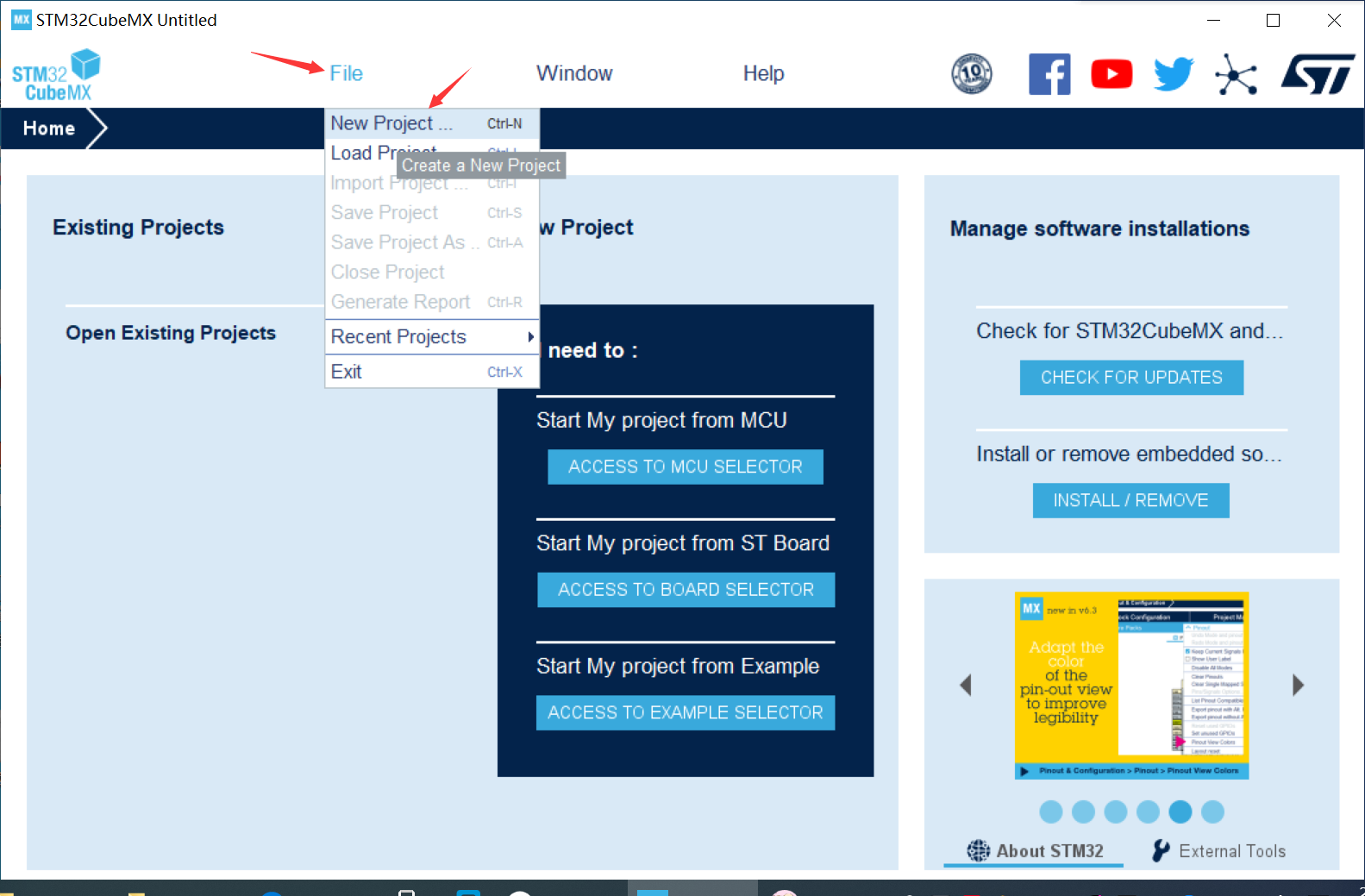
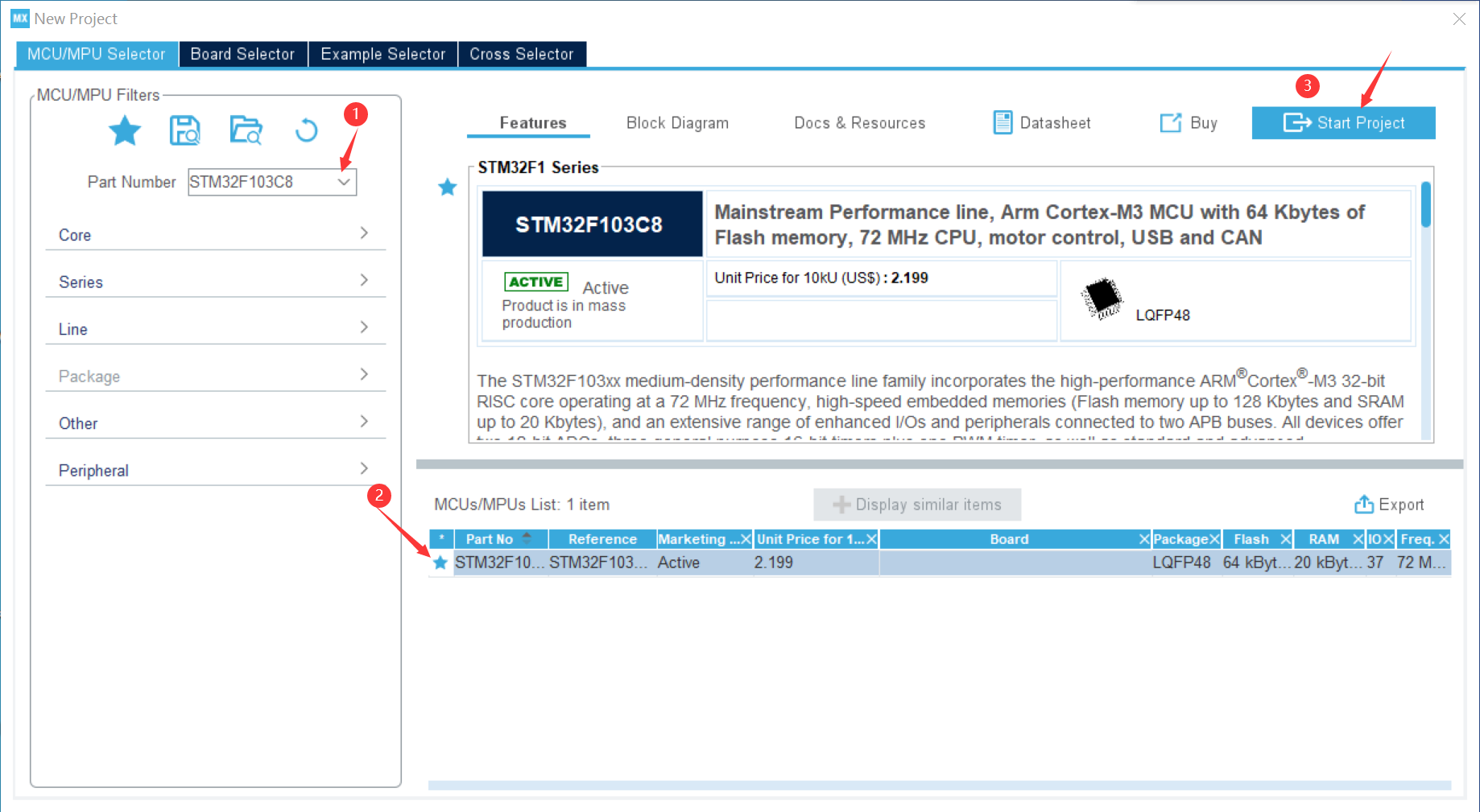
① Create a new project in stm32CubeMX
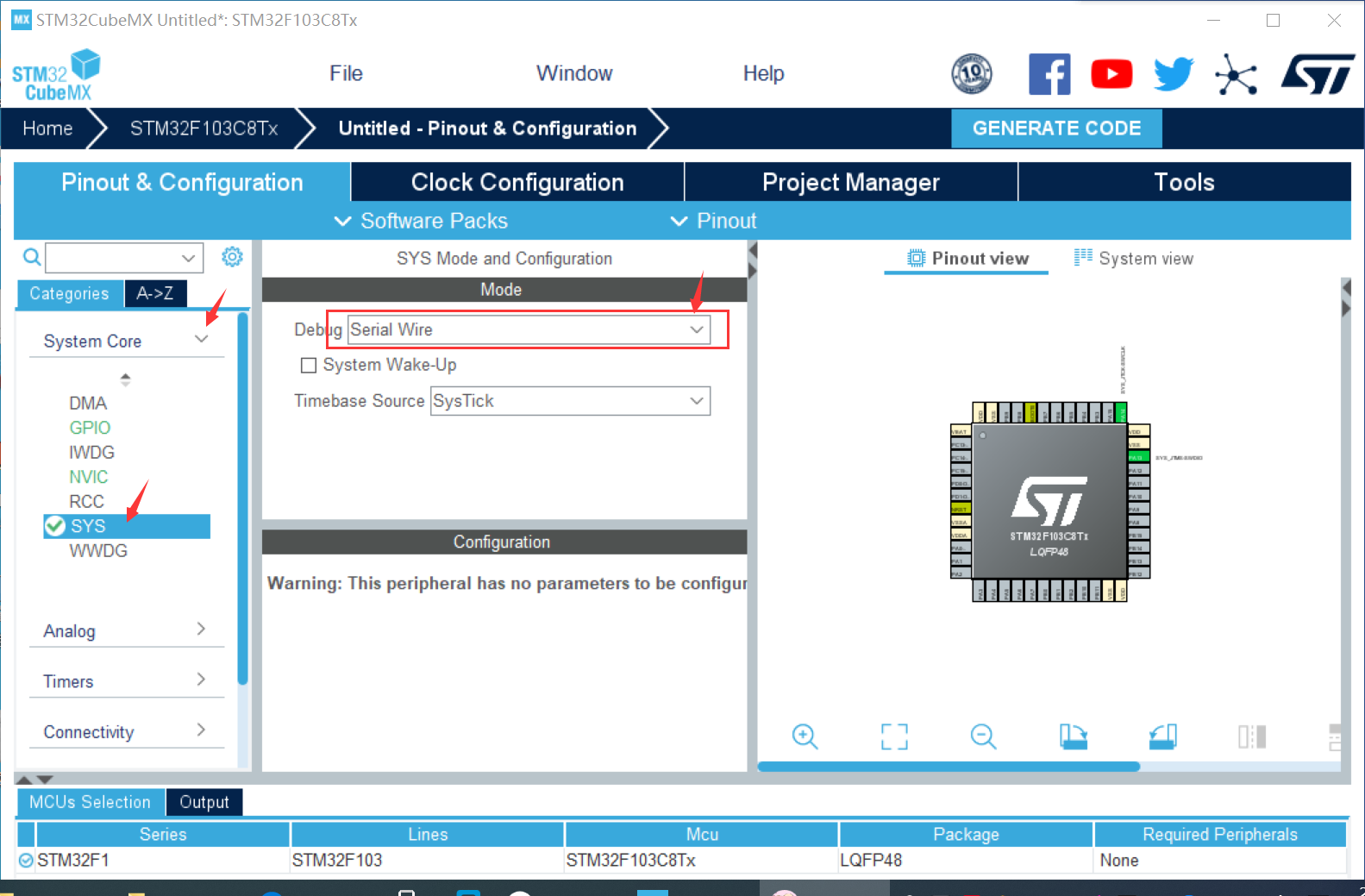
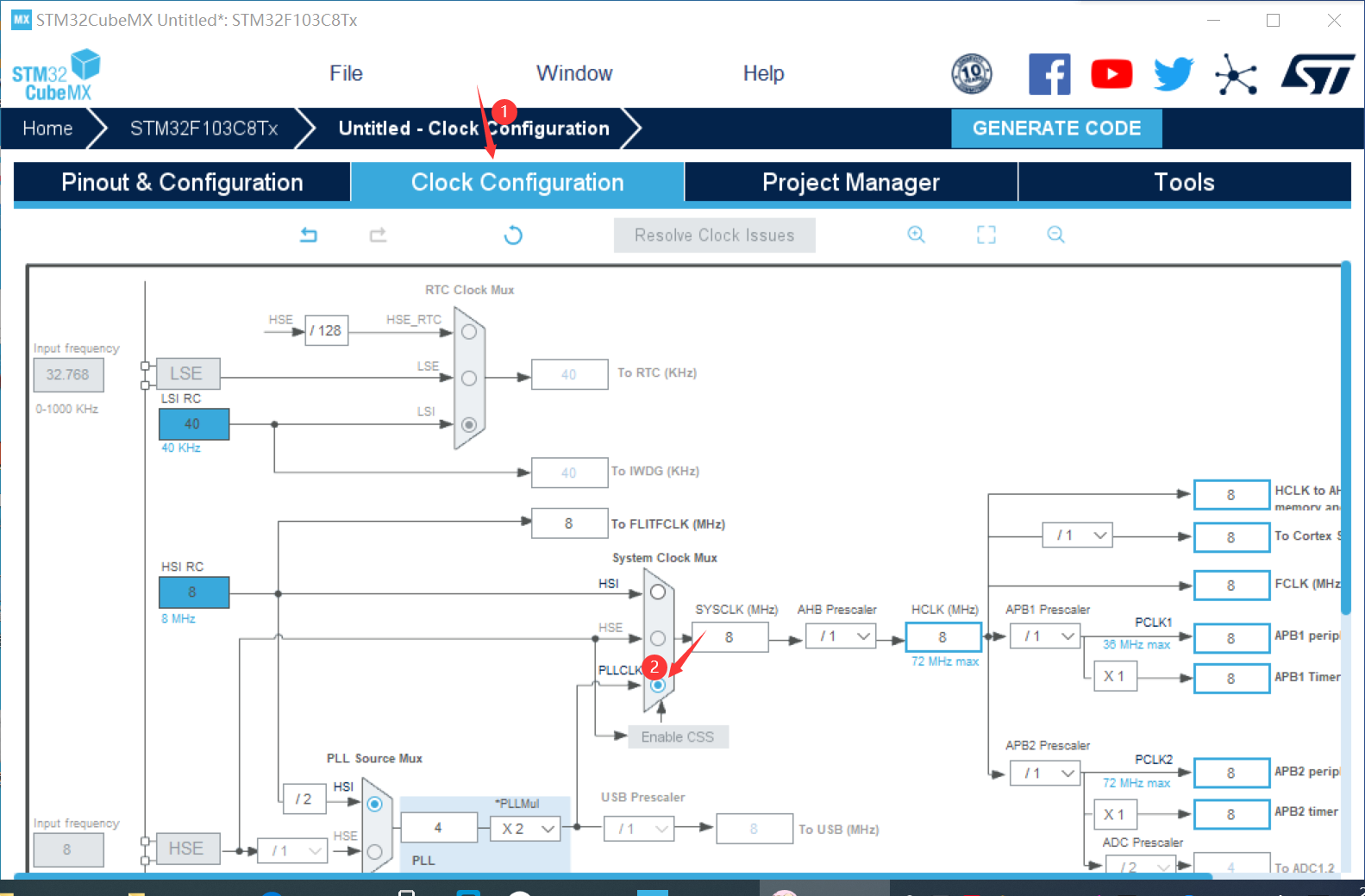
② Complete configuration
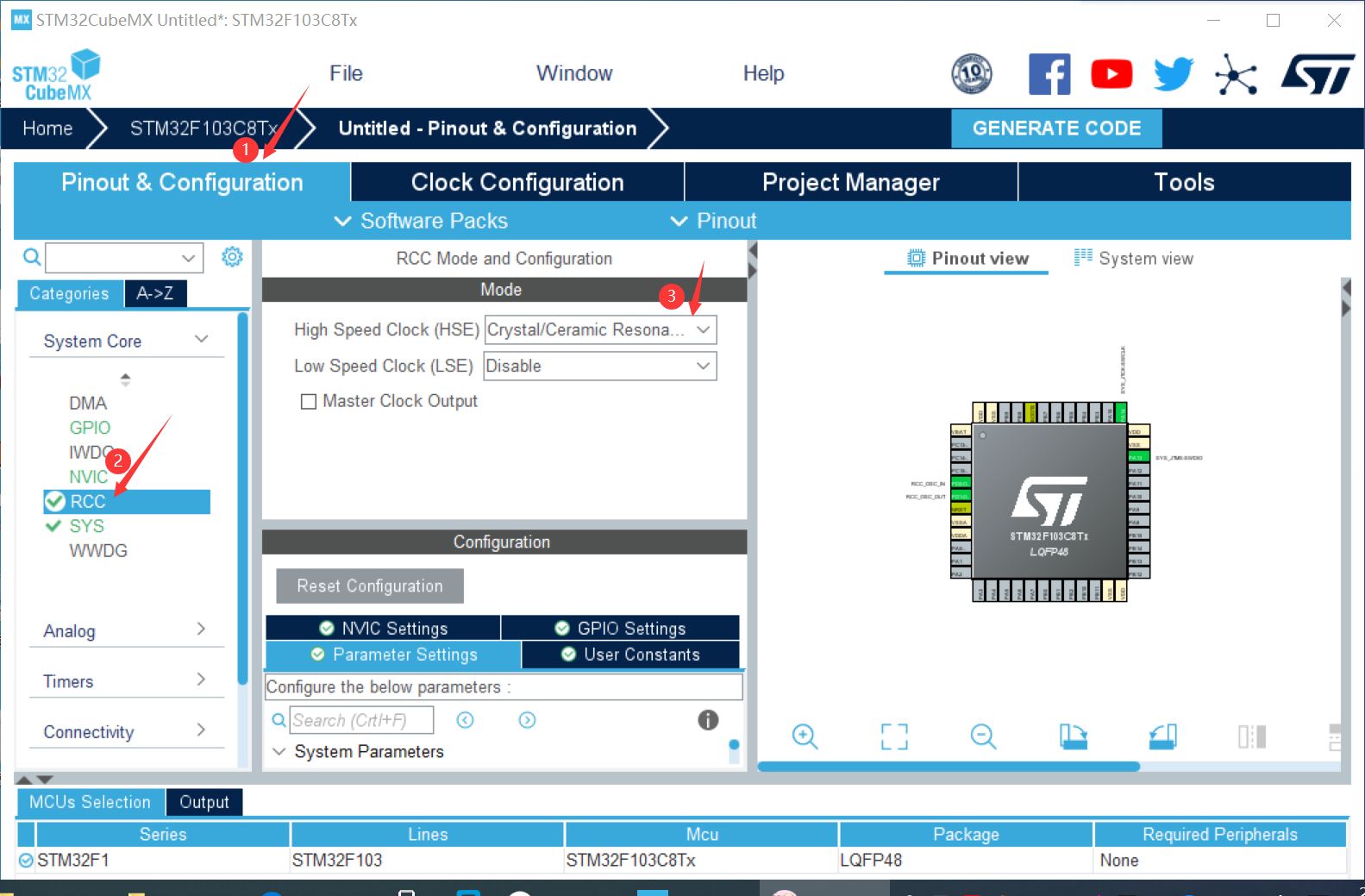
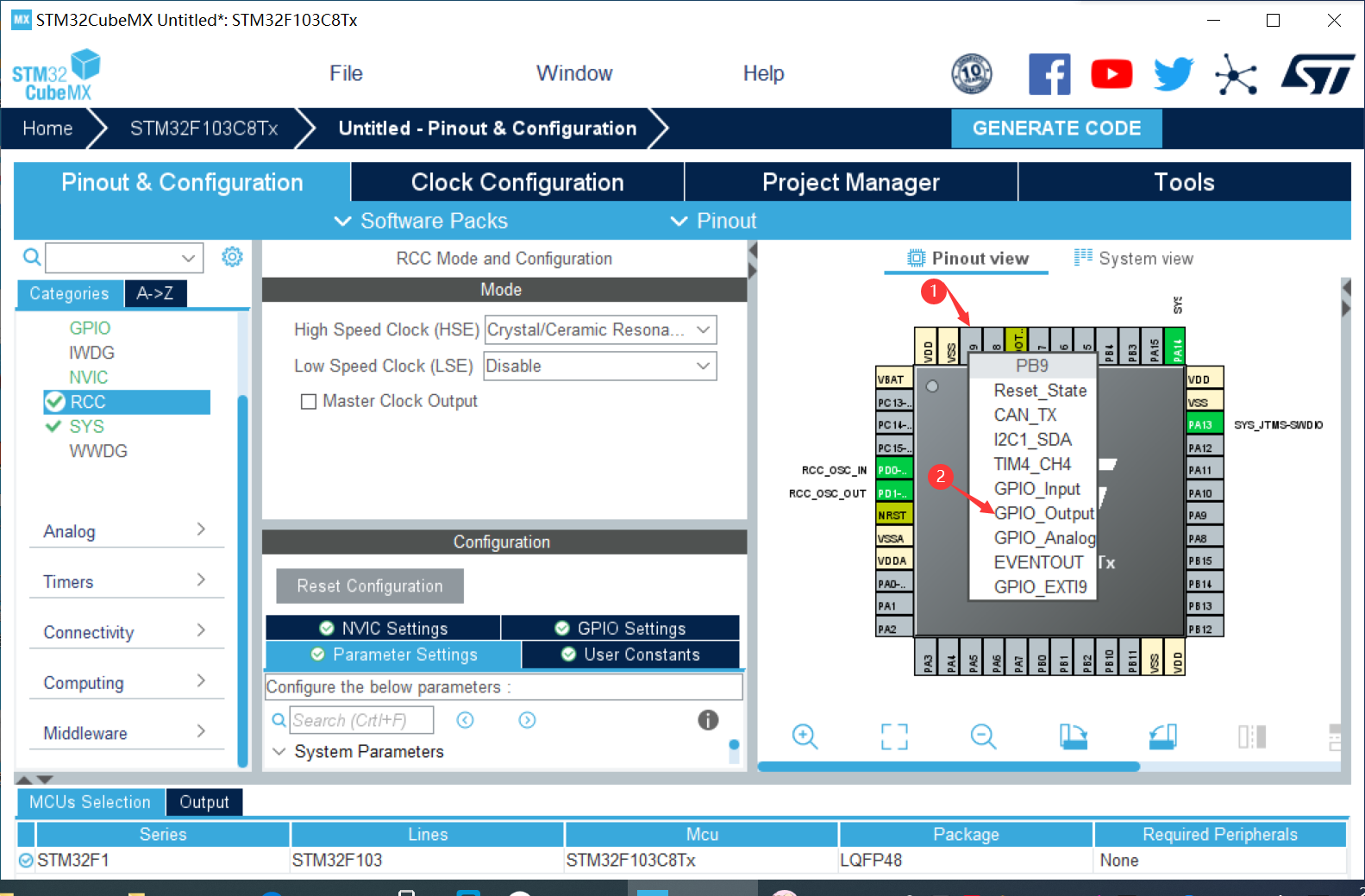
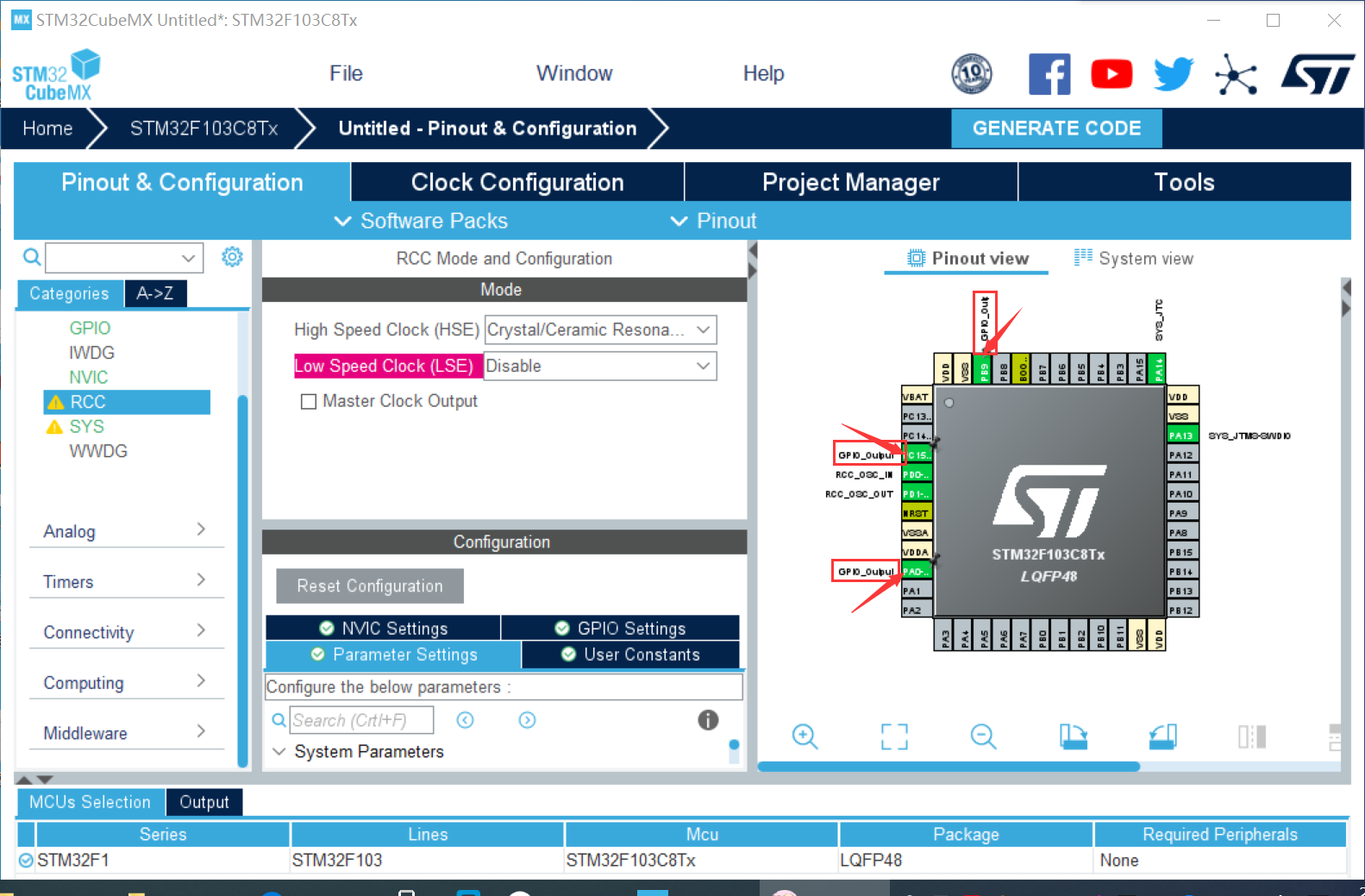
③ Right click to select output and select pin to set output register (PAO, PB9, PC15)
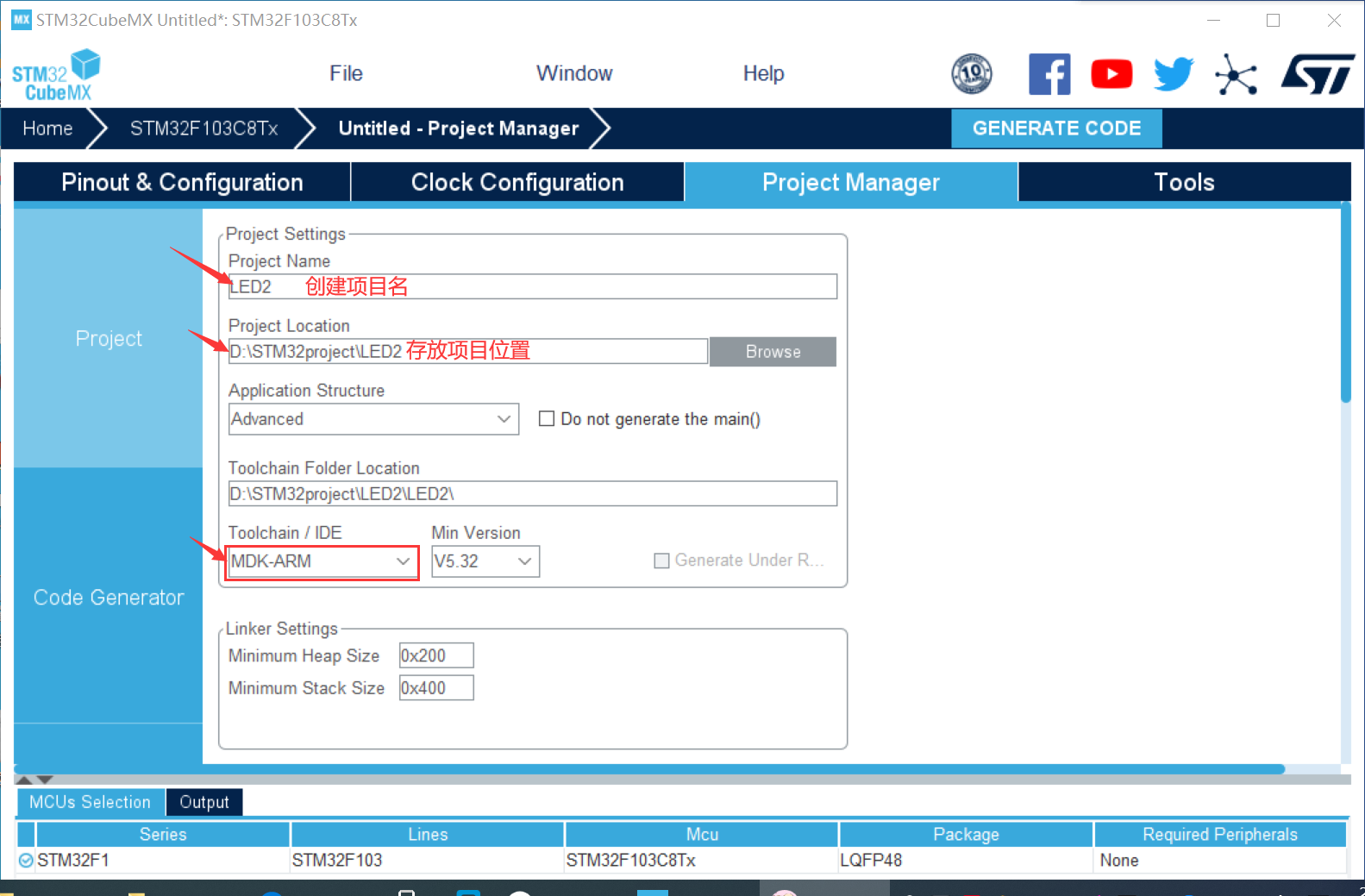
④ Create a project and open it in keli to run
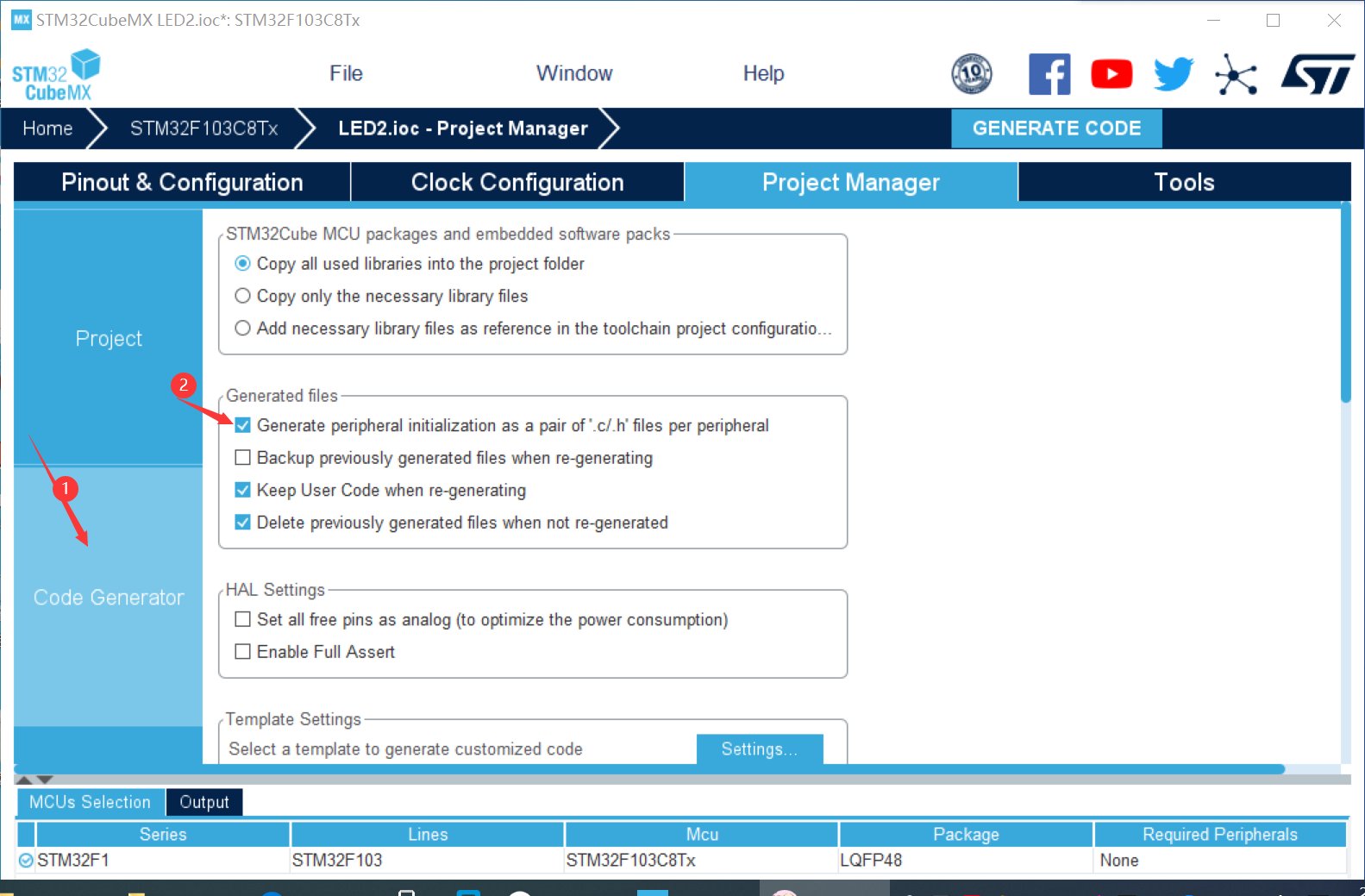
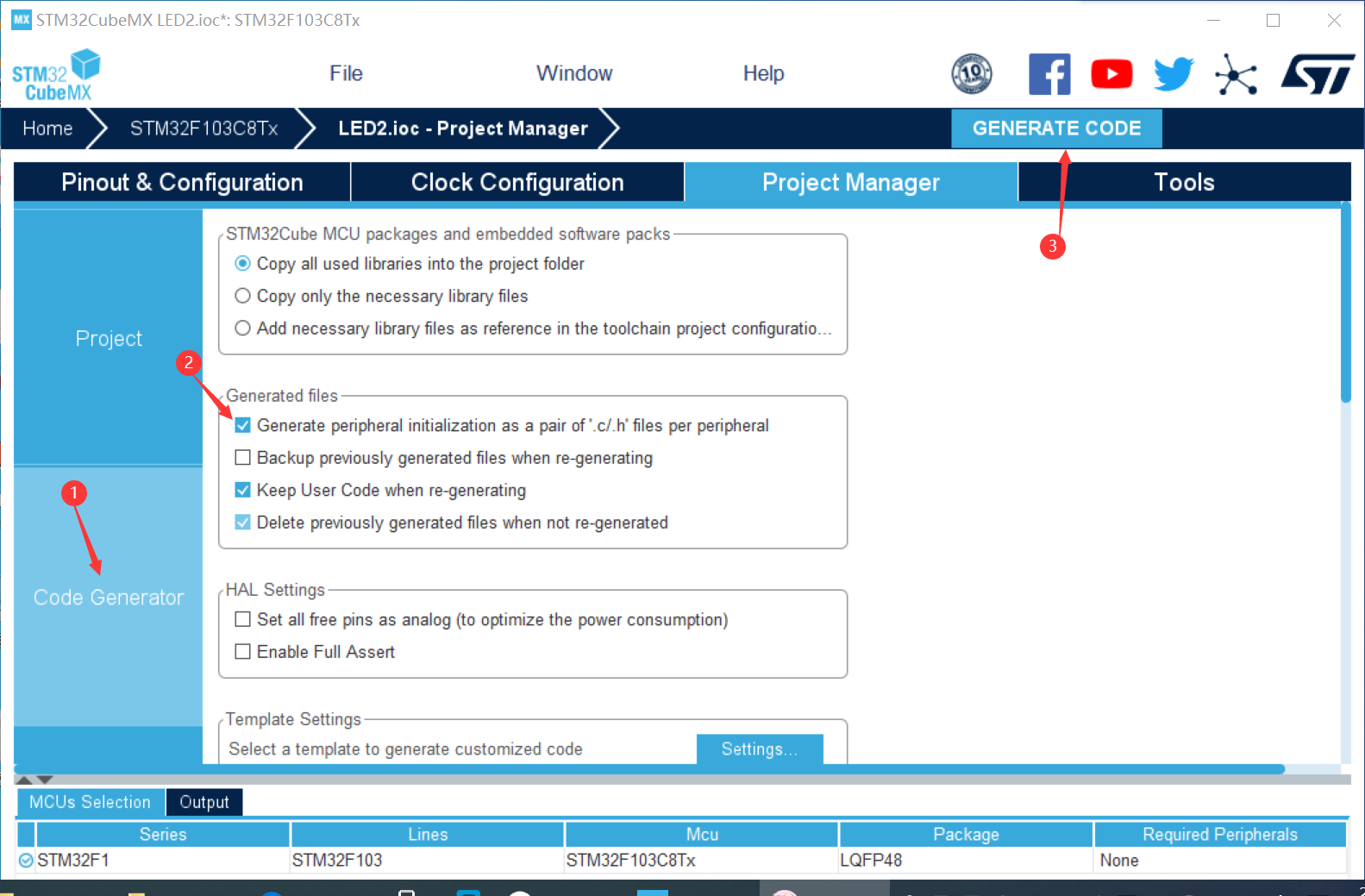
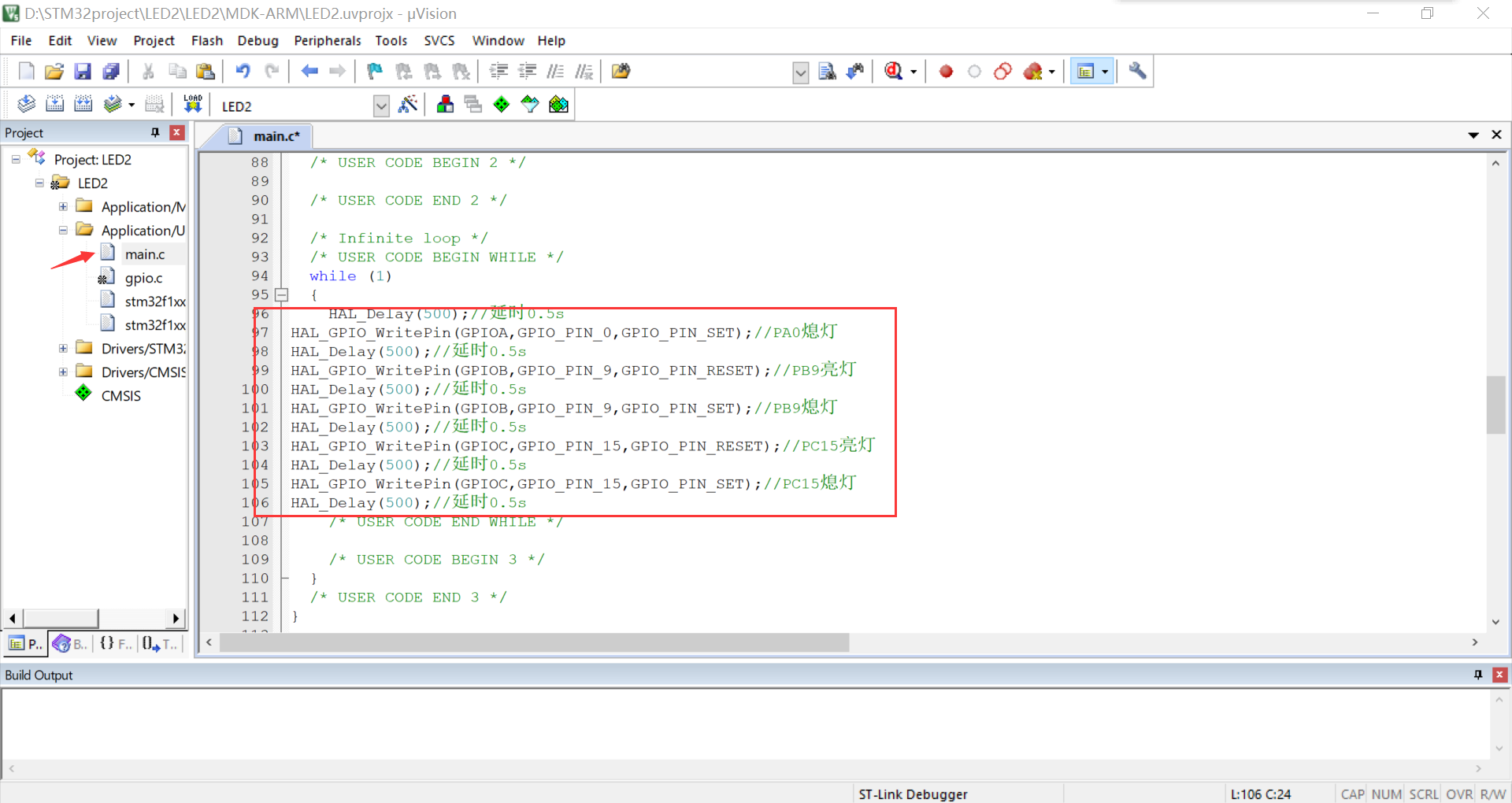
⑤ Find main in keil C file while function, add
HAL_Delay(500);//Delay 0.5s HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA,GPIO_PIN_0,GPIO_PIN_SET);//PA0 lights out HAL_Delay(500);//Delay 0.5s HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB,GPIO_PIN_9,GPIO_PIN_RESET);//PB9 on HAL_Delay(500);//Delay 0.5s HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB,GPIO_PIN_9,GPIO_PIN_SET);//PB9 lights out HAL_Delay(500);//Delay 0.5s HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOC,GPIO_PIN_15,GPIO_PIN_RESET);//PC15 on HAL_Delay(500);//Delay 0.5s HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOC,GPIO_PIN_15,GPIO_PIN_SET);//PC15 lights out HAL_Delay(500);//Delay 0.5s
⑥ Click compile and run it in FlyMcu
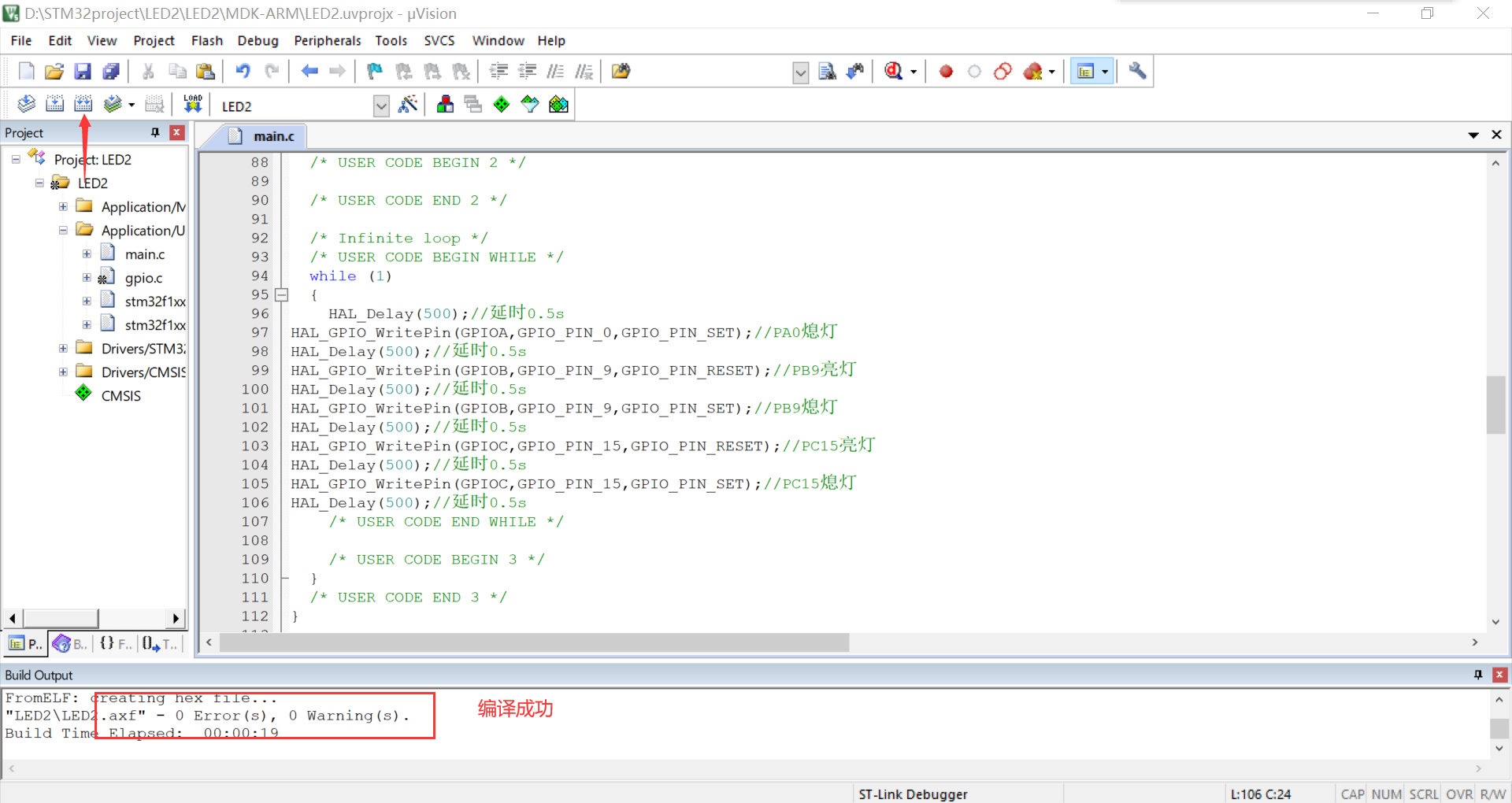
3. Observe the output waveform of three GPIO ports
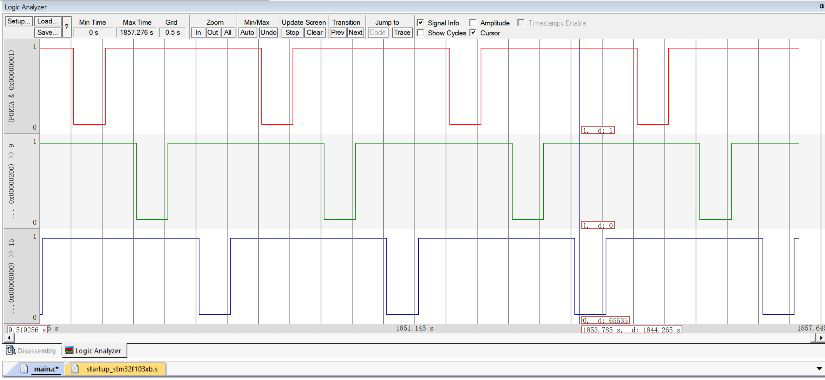
3, USART serial communication program of STM32
1.USART Brief
USART:(Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) universal synchronous / asynchronous serial receiver / transmitter USART is a full duplex universal synchronous / asynchronous serial transceiver module, and the interface is a highly flexible serial communication device.

2. Compilation implementation
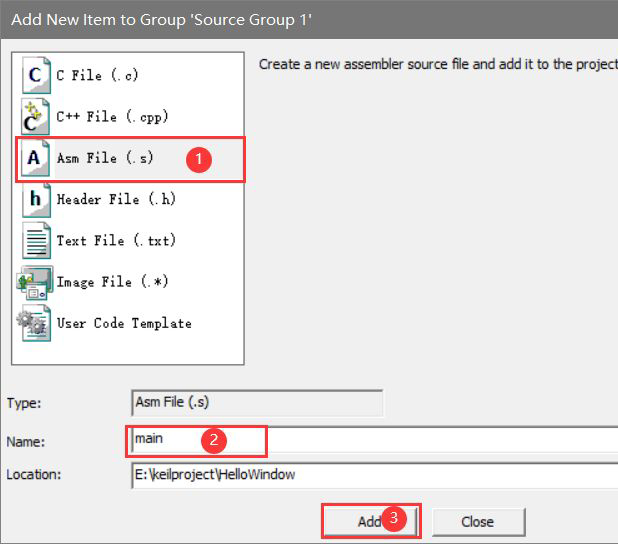
(1) Create project
Create a new project, select chip STM32F103C8, and add one in it s file
 Write code
Write code
;RCC Register address mapping
RCC_BASE EQU 0x40021000
RCC_CR EQU (RCC_BASE + 0x00)
RCC_CFGR EQU (RCC_BASE + 0x04)
RCC_CIR EQU (RCC_BASE + 0x08)
RCC_APB2RSTR EQU (RCC_BASE + 0x0C)
RCC_APB1RSTR EQU (RCC_BASE + 0x10)
RCC_AHBENR EQU (RCC_BASE + 0x14)
RCC_APB2ENR EQU (RCC_BASE + 0x18)
RCC_APB1ENR EQU (RCC_BASE + 0x1C)
RCC_BDCR EQU (RCC_BASE + 0x20)
RCC_CSR EQU (RCC_BASE + 0x24)
;AFIO Register address mapping
AFIO_BASE EQU 0x40010000
AFIO_EVCR EQU (AFIO_BASE + 0x00)
AFIO_MAPR EQU (AFIO_BASE + 0x04)
AFIO_EXTICR1 EQU (AFIO_BASE + 0x08)
AFIO_EXTICR2 EQU (AFIO_BASE + 0x0C)
AFIO_EXTICR3 EQU (AFIO_BASE + 0x10)
AFIO_EXTICR4 EQU (AFIO_BASE + 0x14)
;GPIOA Register address mapping
GPIOA_BASE EQU 0x40010800
GPIOA_CRL EQU (GPIOA_BASE + 0x00)
GPIOA_CRH EQU (GPIOA_BASE + 0x04)
GPIOA_IDR EQU (GPIOA_BASE + 0x08)
GPIOA_ODR EQU (GPIOA_BASE + 0x0C)
GPIOA_BSRR EQU (GPIOA_BASE + 0x10)
GPIOA_BRR EQU (GPIOA_BASE + 0x14)
GPIOA_LCKR EQU (GPIOA_BASE + 0x18)
;GPIO C Mouth control
GPIOC_BASE EQU 0x40011000
GPIOC_CRL EQU (GPIOC_BASE + 0x00)
GPIOC_CRH EQU (GPIOC_BASE + 0x04)
GPIOC_IDR EQU (GPIOC_BASE + 0x08)
GPIOC_ODR EQU (GPIOC_BASE + 0x0C)
GPIOC_BSRR EQU (GPIOC_BASE + 0x10)
GPIOC_BRR EQU (GPIOC_BASE + 0x14)
GPIOC_LCKR EQU (GPIOC_BASE + 0x18)
;Serial port 1 control
USART1_BASE EQU 0x40013800
USART1_SR EQU (USART1_BASE + 0x00)
USART1_DR EQU (USART1_BASE + 0x04)
USART1_BRR EQU (USART1_BASE + 0x08)
USART1_CR1 EQU (USART1_BASE + 0x0c)
USART1_CR2 EQU (USART1_BASE + 0x10)
USART1_CR3 EQU (USART1_BASE + 0x14)
USART1_GTPR EQU (USART1_BASE + 0x18)
;NVIC Register address
NVIC_BASE EQU 0xE000E000
NVIC_SETEN EQU (NVIC_BASE + 0x0010)
;SETENA Starting address of register array
NVIC_IRQPRI EQU (NVIC_BASE + 0x0400)
;Start address of interrupt priority register array
NVIC_VECTTBL EQU (NVIC_BASE + 0x0D08)
;Address of vector table offset register
NVIC_AIRCR EQU (NVIC_BASE + 0x0D0C)
;Address of application interrupt and reset control register
SETENA0 EQU 0xE000E100
SETENA1 EQU 0xE000E104
;SysTick Register address
SysTick_BASE EQU 0xE000E010
SYSTICKCSR EQU (SysTick_BASE + 0x00)
SYSTICKRVR EQU (SysTick_BASE + 0x04)
;FLASH Buffer register address image
FLASH_ACR EQU 0x40022000
;SCB_BASE EQU (SCS_BASE + 0x0D00)
MSP_TOP EQU 0x20005000
;Starting value of main stack
PSP_TOP EQU 0x20004E00
;Process stack start value
BitAlias_BASE EQU 0x22000000
;Bit alias area start address
Flag1 EQU 0x20000200
b_flas EQU (BitAlias_BASE + (0x200*32) + (0*4))
;Bit address
b_05s EQU (BitAlias_BASE + (0x200*32) + (1*4))
;Bit address
DlyI EQU 0x20000204
DlyJ EQU 0x20000208
DlyK EQU 0x2000020C
SysTim EQU 0x20000210
;Constant definition
Bit0 EQU 0x00000001
Bit1 EQU 0x00000002
Bit2 EQU 0x00000004
Bit3 EQU 0x00000008
Bit4 EQU 0x00000010
Bit5 EQU 0x00000020
Bit6 EQU 0x00000040
Bit7 EQU 0x00000080
Bit8 EQU 0x00000100
Bit9 EQU 0x00000200
Bit10 EQU 0x00000400
Bit11 EQU 0x00000800
Bit12 EQU 0x00001000
Bit13 EQU 0x00002000
Bit14 EQU 0x00004000
Bit15 EQU 0x00008000
Bit16 EQU 0x00010000
Bit17 EQU 0x00020000
Bit18 EQU 0x00040000
Bit19 EQU 0x00080000
Bit20 EQU 0x00100000
Bit21 EQU 0x00200000
Bit22 EQU 0x00400000
Bit23 EQU 0x00800000
Bit24 EQU 0x01000000
Bit25 EQU 0x02000000
Bit26 EQU 0x04000000
Bit27 EQU 0x08000000
Bit28 EQU 0x10000000
Bit29 EQU 0x20000000
Bit30 EQU 0x40000000
Bit31 EQU 0x80000000
;Vector table
AREA RESET, DATA, READONLY
DCD MSP_TOP ;Initialize main stack
DCD Start ;Reset vector
DCD NMI_Handler ;NMI Handler
DCD HardFault_Handler ;Hard Fault Handler
DCD 0
DCD 0
DCD 0
DCD 0
DCD 0
DCD 0
DCD 0
DCD 0
DCD 0
DCD 0
DCD 0
DCD SysTick_Handler ;SysTick Handler
SPACE 20 ;Reserved space 20 bytes
;Code snippet
AREA |.text|, CODE, READONLY
;Main program start
ENTRY
;Instructs the program to execute from here
Start
;Clock system settings
ldr r0, =RCC_CR
ldr r1, [r0]
orr r1, #Bit16
str r1, [r0]
;Enable external crystal oscillator
;Start external 8 M Crystal oscillator
ClkOk
ldr r1, [r0]
ands r1, #Bit17
beq ClkOk
;Wait for the external crystal oscillator to be ready
ldr r1,[r0]
orr r1,#Bit17
str r1,[r0]
;FLASH Buffer
ldr r0, =FLASH_ACR
mov r1, #0x00000032
str r1, [r0]
;set up PLL The PLL magnification is 7,HSE Input no frequency division
ldr r0, =RCC_CFGR
ldr r1, [r0]
orr r1, #(Bit18 :OR: Bit19 :OR: Bit20 :OR: Bit16 :OR: Bit14)
orr r1, #Bit10
str r1, [r0]
;start-up PLL Phase locked loop
ldr r0, =RCC_CR
ldr r1, [r0]
orr r1, #Bit24
str r1, [r0]
PllOk
ldr r1, [r0]
ands r1, #Bit25
beq PllOk
;choice PLL Clock as system clock
ldr r0, =RCC_CFGR
ldr r1, [r0]
orr r1, #(Bit18 :OR: Bit19 :OR: Bit20 :OR: Bit16 :OR: Bit14)
orr r1, #Bit10
orr r1, #Bit1
str r1, [r0]
;other RCC Related settings
ldr r0, =RCC_APB2ENR
mov r1, #(Bit14 :OR: Bit4 :OR: Bit2)
str r1, [r0]
;PA9 Serial port 0 transmitting pin
ldr r0, =GPIOA_CRH
ldr r1, [r0]
orr r1, #(Bit4 :OR: Bit5)
;PA.9 Output mode,Maximum speed 50 MHz
orr r1, #Bit7
and r1, #~Bit6
;10: Multiplexing function push-pull output mode
str r1, [r0]
ldr r0, =USART1_BRR
mov r1, #0x271
str r1, [r0]
;Configure baud rate-> 115200
ldr r0, =USART1_CR1
mov r1, #0x200c
str r1, [r0]
;USART Module total enable send and receive enable
;71 02 00 00 2c 20 00 00
;AFIO Parameter setting
;Systick Parameter setting
ldr r0, =SYSTICKRVR
;Systick Initial installation value
mov r1, #9000
str r1, [r0]
ldr r0, =SYSTICKCSR
;set up,start-up Systick
mov r1, #0x03
str r1, [r0]
;Switch to user level line program mode
ldr r0, =PSP_TOP
;Initialize thread stack
msr psp, r0
mov r0, #3
msr control, r0
;initialization SRAM register
mov r1, #0
ldr r0, =Flag1
str r1, [r0]
ldr r0, =DlyI
str r1, [r0]
ldr r0, =DlyJ
str r1, [r0]
ldr r0, =DlyK
str r1, [r0]
ldr r0, =SysTim
str r1, [r0]
;Main cycle
main
ldr r0, =Flag1
ldr r1, [r0]
tst r1, #Bit1
;SysTick Generate 0.5s,Set bit 1
beq main ;0.5s The flag is not set yet
;0.5s The flag has been set
ldr r0, =b_05s
;Bit band operation reset 0.5s sign
mov r1, #0
str r1, [r0]
mov r0, #'H'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'e'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'l'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'l'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'o'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #' '
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'W'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'i'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'n'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'d'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'o'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'w'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'\n'
bl send_a_char
b main
Mountain demon ladder 2:26:52
;Main cycle
main
ldr r0, =Flag1
ldr r1, [r0]
tst r1, #Bit1
;SysTick Generate 0.5s,Set bit 1
beq main ;0.5s The flag is not set yet
;0.5s The flag has been set
ldr r0, =b_05s
;Bit band operation reset 0.5s sign
mov r1, #0
str r1, [r0]
mov r0, #'H'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'e'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'l'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'l'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'o'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #' '
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'W'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'i'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'n'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'d'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'o'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'w'
bl send_a_char
mov r0, #'\n'
bl send_a_char
b main
--------
Copyright notice: This article is CSDN Blogger「Did you wake up」Original articles, follow CC 4.0 BY-SA Copyright agreement, please attach the original source link and this statement.
Original link: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_61682562/article/details/120931199
Mountain demon ladder 2:27:14
;Subroutine serial port 1 sends a character
send_a_char
push {r0 - r3}
ldr r2, =USART1_DR
str r0, [r2]
b1
ldr r2, =USART1_SR
ldr r2, [r2]
tst r2, #0x40
beq b1
;Send complete(Transmission complete)wait for
pop {r0 - r3}
bx lr
;Abnormal program
NMI_Handler
bx lr
HardFault_Handler
bx lr
SysTick_Handler
ldr r0, =SysTim
ldr r1, [r0]
add r1, #1
str r1, [r0]
cmp r1, #500
bcc TickExit
mov r1, #0
str r1, [r0]
ldr r0, =b_05s
;The clock tick counter is set to 0 when it is greater than or equal to 500 times of clearing.5s Flag bit
;Bit band operation set 1
mov r1, #1
str r1, [r0]
TickExit
bx lr
ALIGN
;By using zero or null instructions NOP fill,Aligns the current position with a specified boundary
END
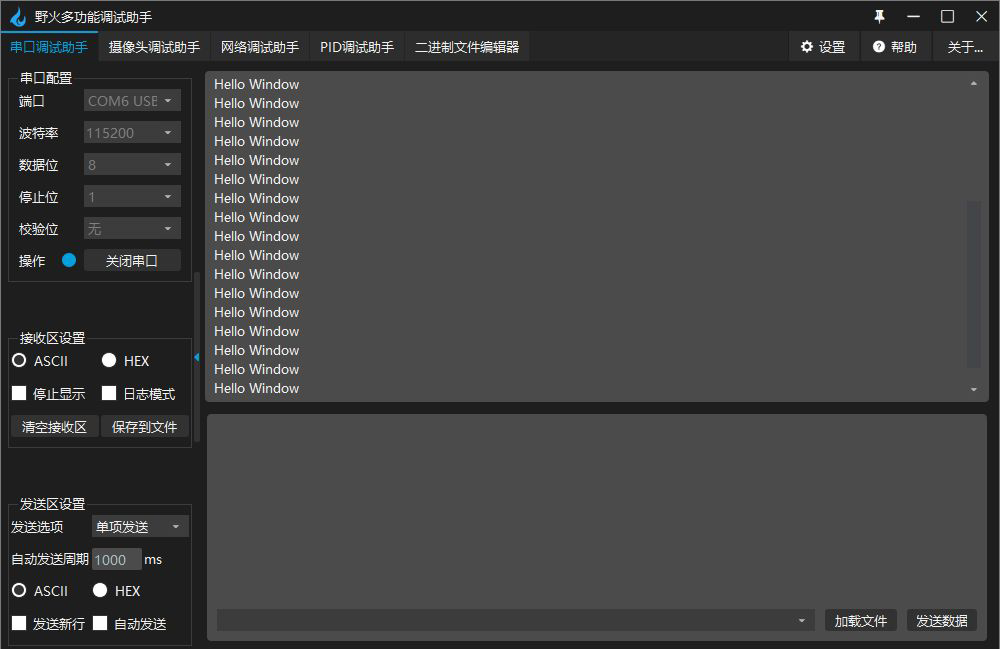
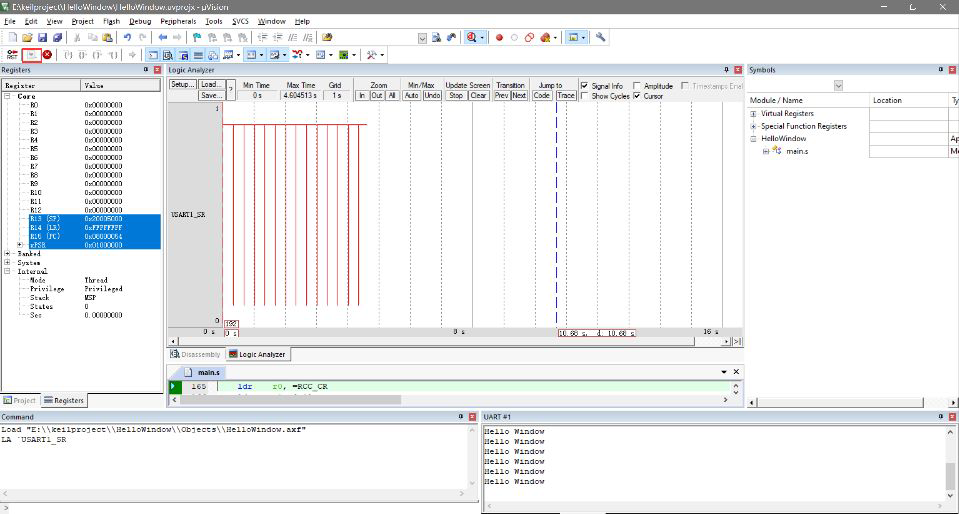
Compile and burn. Open the serial port with the wildfire debugging assistant to view the output
(2) Observe the timing waveform of discipline
Add register
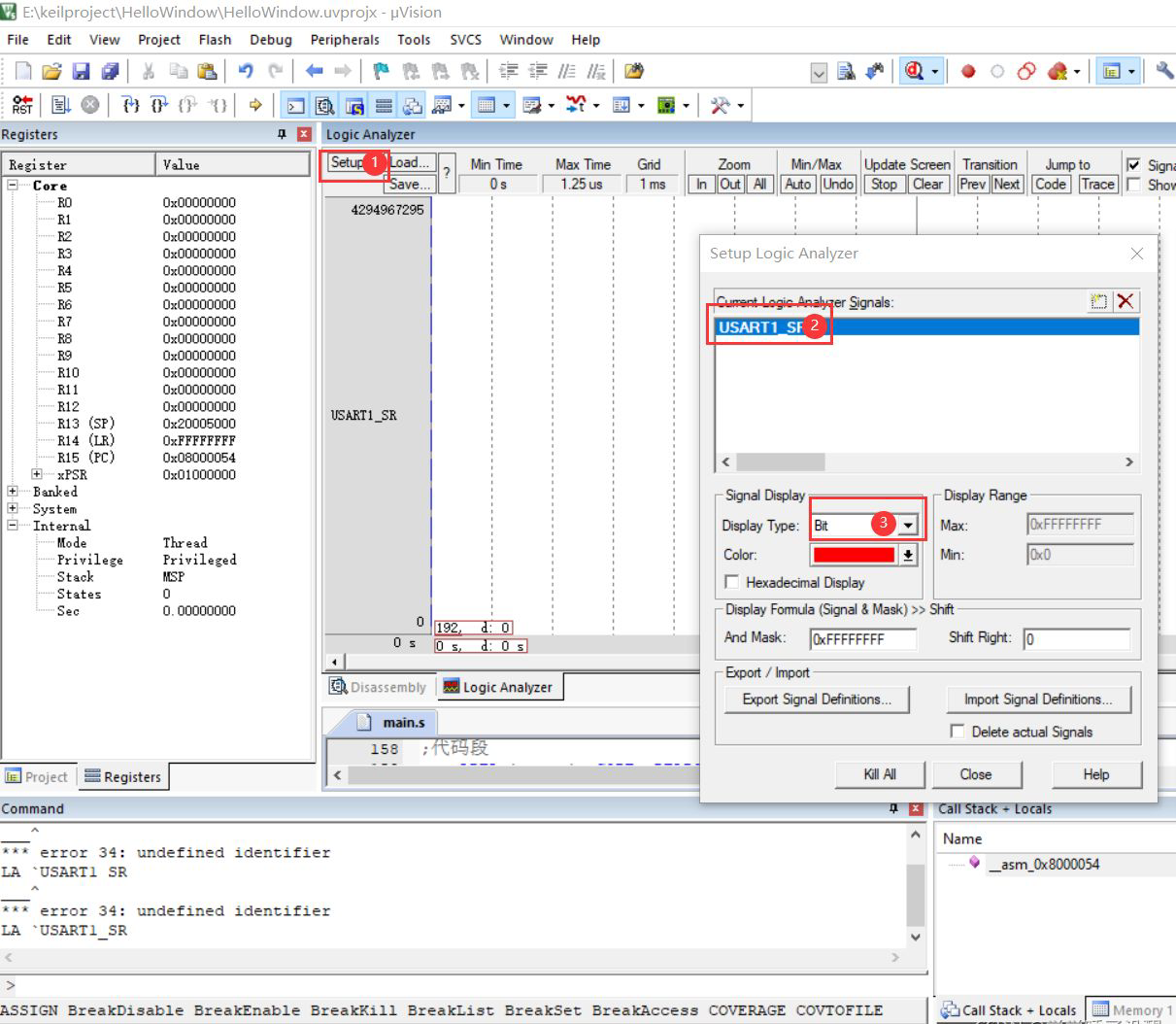
Click Run
3. Using hel Library
(1) Then create a new project in CubeMX and configure it
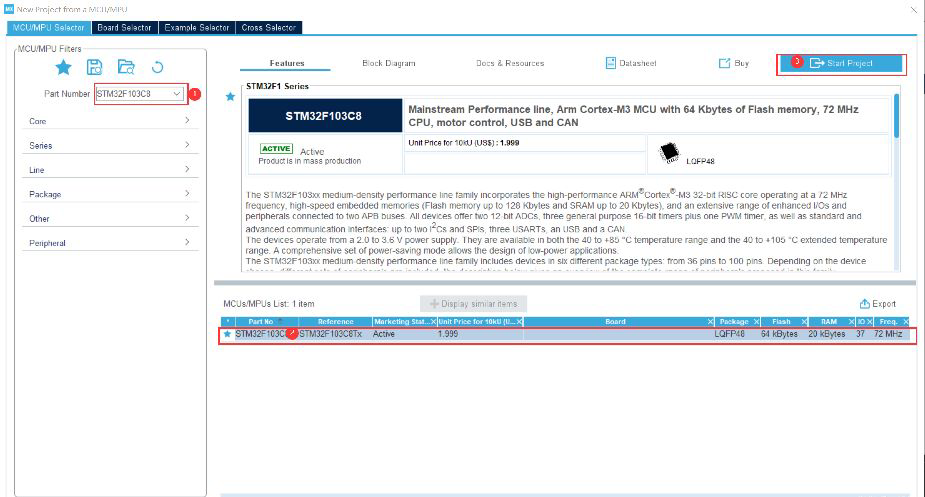
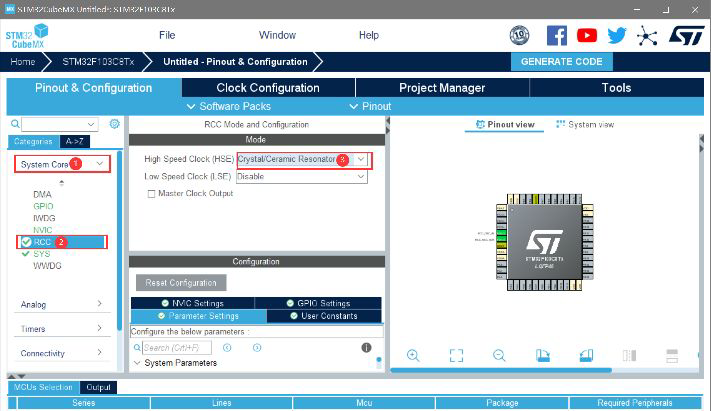
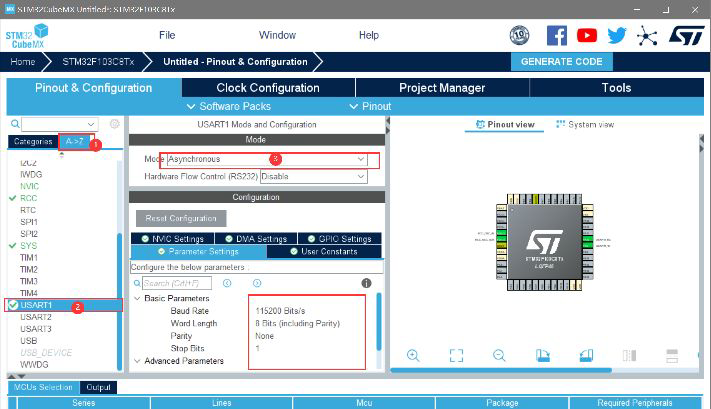
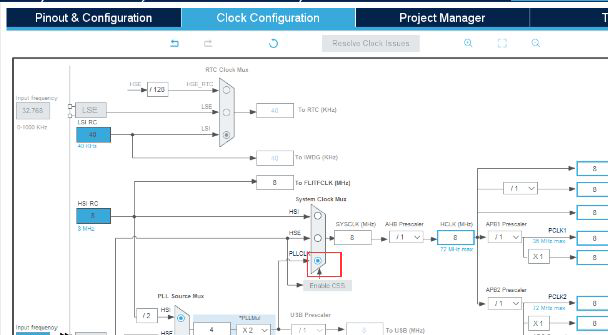
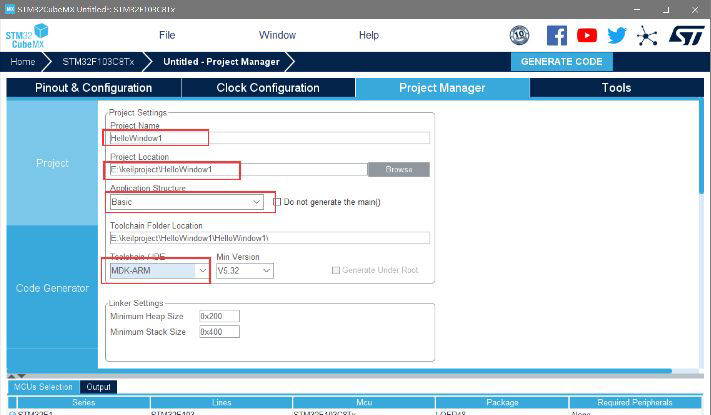
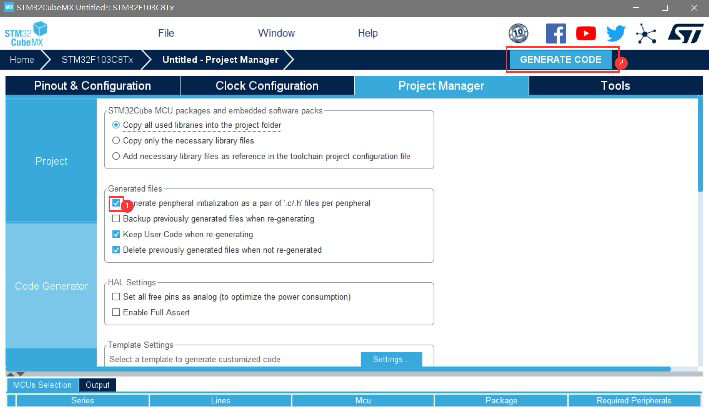
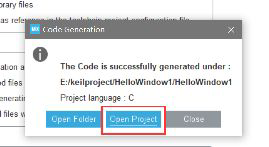
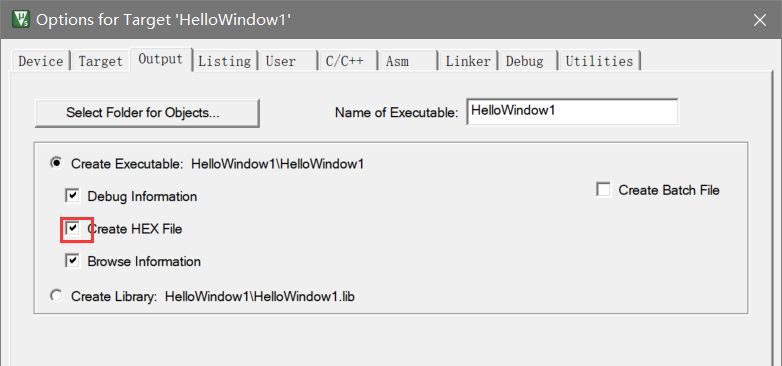
Set to generate HEX files
In main Add the code of while function to C file to realize the function
char data[]="hello windows!\n"; HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, (uint8_t *)data, 15, 0xffff); HAL_Delay(1000);
Compile and burn, and view the output results through the wildfire debugging assistant
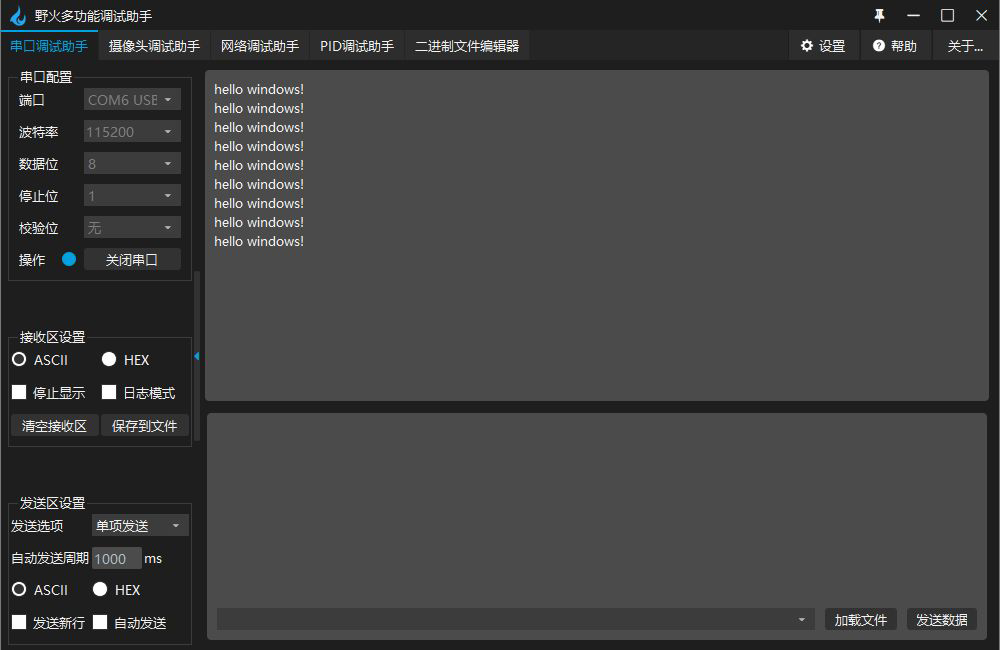
(2) Observe the timing waveform of the pin
Adjust real machine simulation parameters
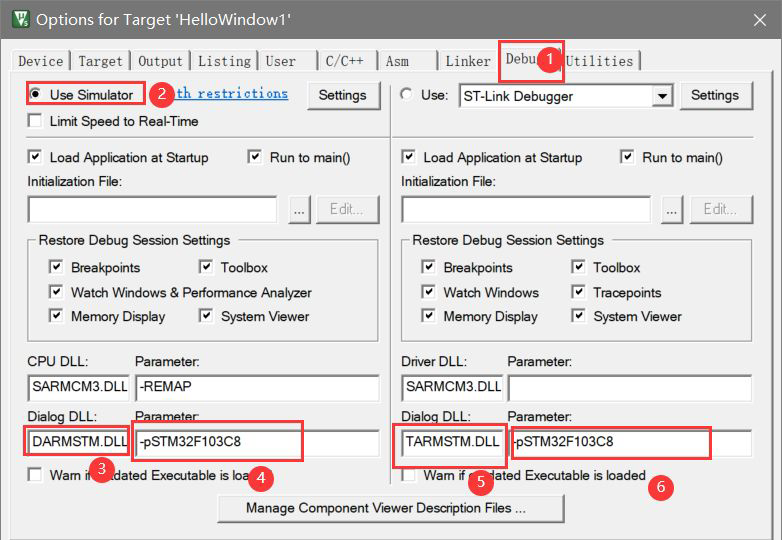
Add pin
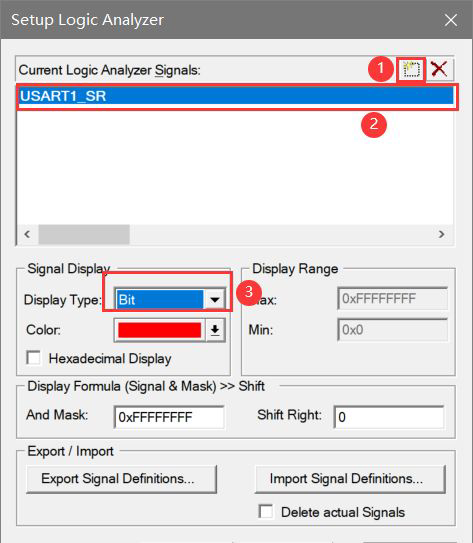
function
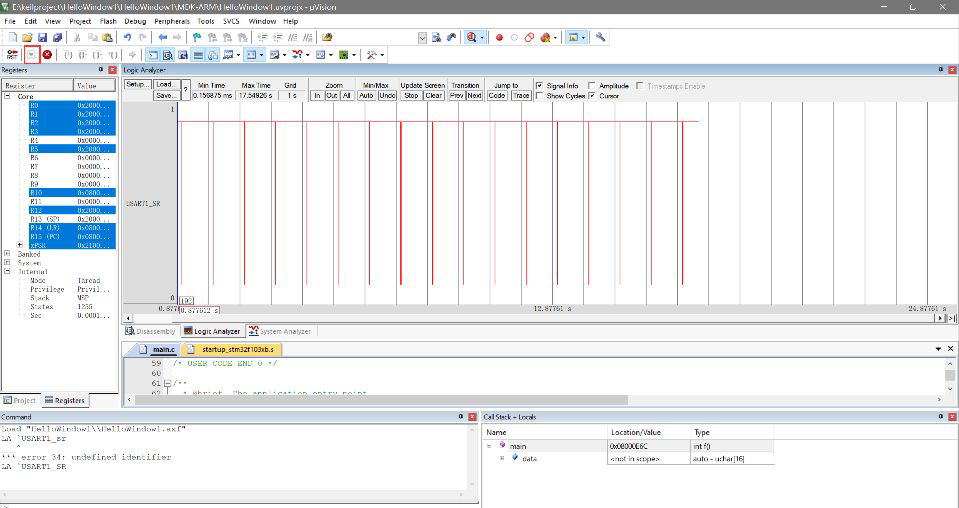
4, Summary
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46129506/article/details/120895633
https://blog.csdn.net/junseven164/article/details/120808687