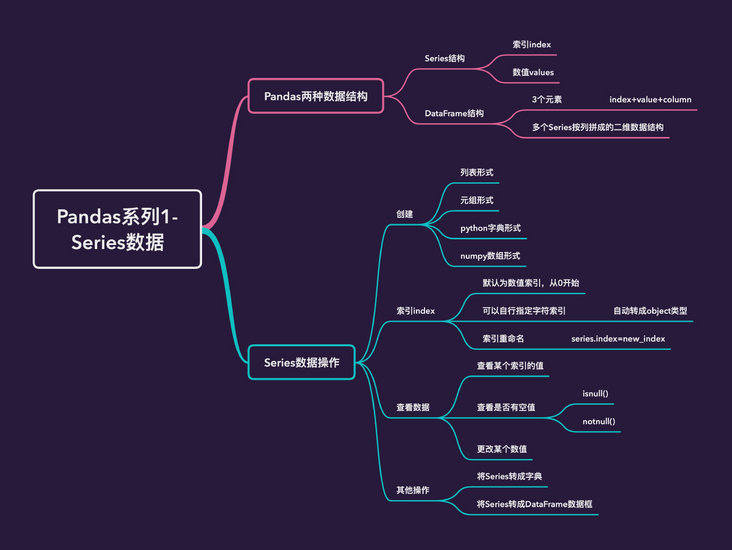
Series type data of Pandas series
This article begins to write a series of articles on Pandas, starting with: how to create data in Pandas. There are two types of data created in Pandas:
- Series type
- DataFrame type

<!--MORE-->
Content map
Series type
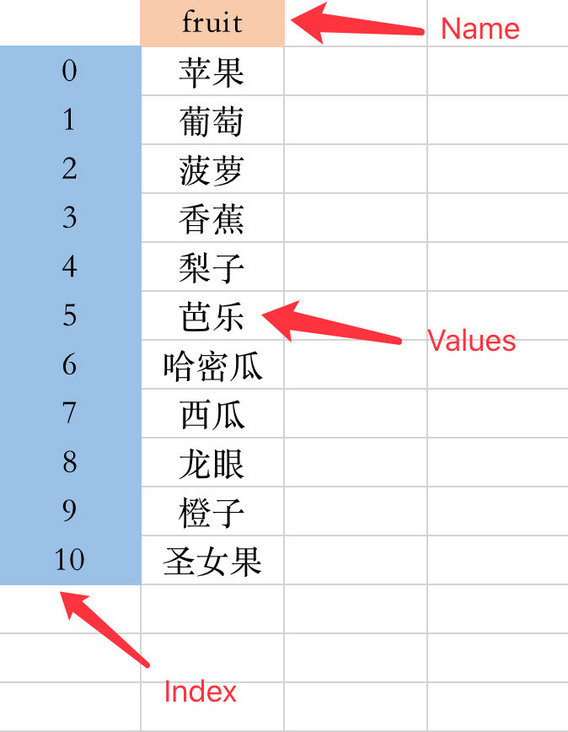
Series is a one-dimensional array structure, which is only composed of index and value.
Series indexes are unique. Indexes can be either numbers or characters. The system will automatically convert them into an object type (character type in pandas).
DataFrame type
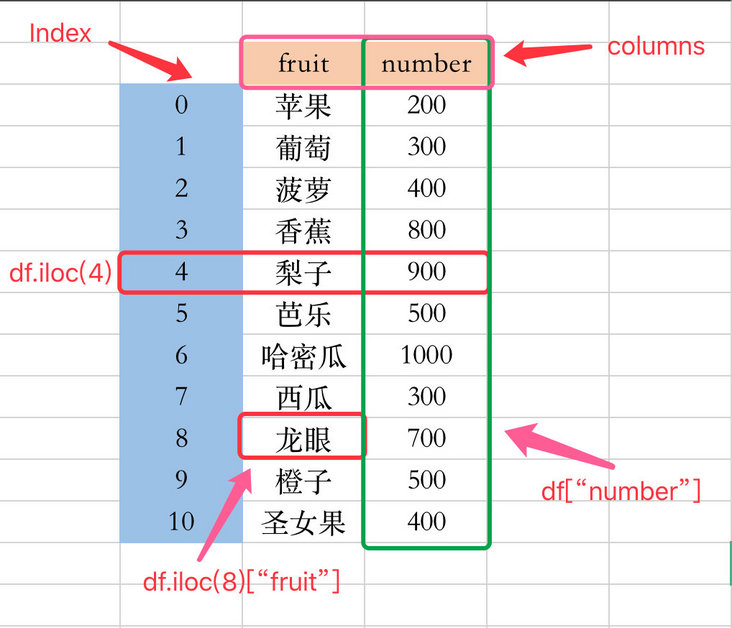
DataFrame is a two-dimensional data structure that combines several Series by column. Each column is taken out separately as a Series; Besides index and value, there is also column. In the following figure:
- Index: 0, 1, 2, 3
- Field attribute: fruit, number
- value: apple, grape, etc; 200, 300, etc
Import library
Import two libraries first:
import pandas as pd import numpy as np
Series type creation and operation
- Generated by iteratable type list and tuple
- Generated by python dictionary
- Generated by numpy array
List generation
Generate Series data by list
s1 = pd.Series([7,8,9,10]) s1 # result 0 7 1 8 2 9 3 10 dtype: int64
s2 = pd.Series(list(range(1,8))) s2 # result 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 dtype: int64
Tuple generation
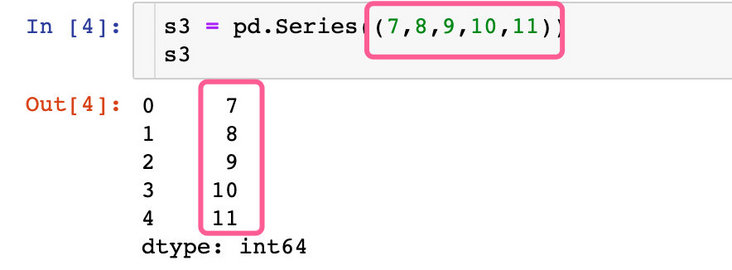
The following method is to generate Series data through tuples
s3 = pd.Series((7,8,9,10,11)) s3 # result 0 7 1 8 2 9 3 10 4 11 dtype: int64
s4 = pd.Series(tuple(range(1,8))) # From 1 to 8, excluding 8 s4 # result 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 dtype: int64
Create using dictionary
The key of the dictionary is the index, and the value is the value corresponding to the Series structure
dic_data = {"0":"Apple", "1":"Banana", "2":"Hami melon","3":"orange"}
s5 = pd.Series(dic_data)
s5
# result
0 Apple
1 Banana
2 Hami melon
3 orange
dtype: object
Using numpy arrays
s6 = pd.Series(np.arange(3,9)) s6 # result 0 3 1 4 2 5 3 6 4 7 5 8 dtype: int64
Specify index (list)
The default indexes are numeric values starting from 0. You can specify each index when creating
# default s1 = pd.Series([7,8,9,10]) s1 # result 0 7 1 8 2 9 3 10 dtype: int64
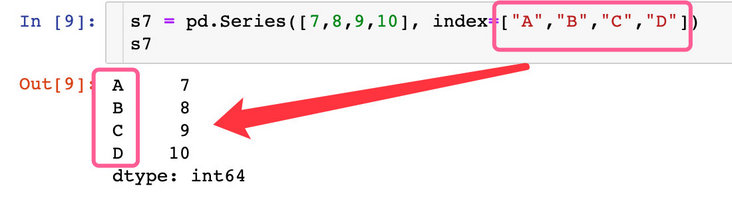
s7 = pd.Series([7,8,9,10], index=["A","B","C","D"]) # Specify index value s7 # result A 7 B 8 C 9 D 10 dtype: int64
Specify index (dictionary form)
Dictionary key as index value
dic_data = {"Fruit 1":"Apple",
"Fruit 2":"Banana",
"Fruit 3":"Hami melon",
"Fruit 4":"orange"
}
s8 = pd.Series(dic_data)
s8
# result
Fruit 1 Apple
Fruit 2 Banana
Fruit 3 Hami melon
Fruit 4 orange
dtype: object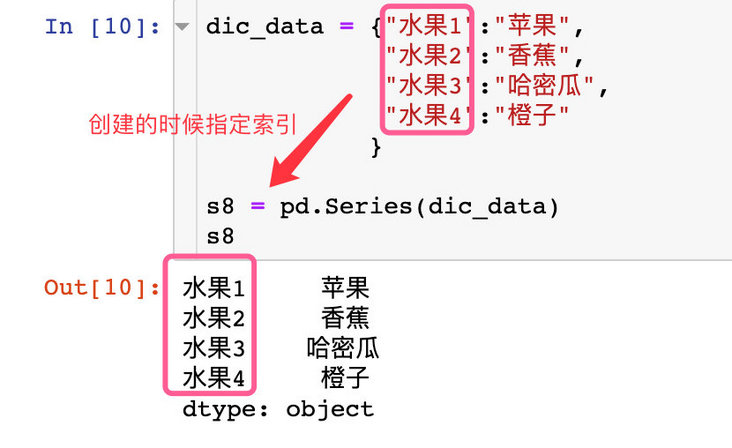
View index values
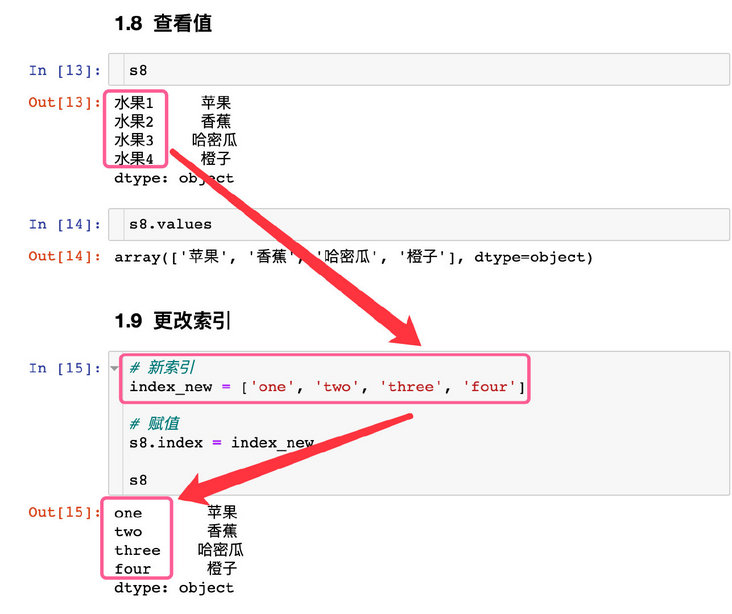
s8 # result Fruit 1 Apple Fruit 2 Banana Fruit 3 Hami melon Fruit 4 orange dtype: object
s8.index # View index values # result Index(['Fruit 1', 'Fruit 2', 'Fruit 3', 'Fruit 4'], dtype='object')
View values
s8 # result Fruit 1 Apple Fruit 2 Banana Fruit 3 Hami melon Fruit 4 orange dtype: object
s8.values # result array(['Apple', 'Banana', 'Hami melon', 'orange'], dtype=object)
Change index
# 1. New index index_new = ['one', 'two', 'three', 'four'] # 2. Assignment s8.index = index_new s8 # result one Apple two Banana three Hami melon four orange dtype: object
Check for null values
s7 # result A 7 B 8 C 9 D 10 dtype: int64
s7.isnull() # No null value # result A False B False C False D False dtype: bool
s7.notnull() # result A True B True C True D True dtype: bool
View the value of an index
s7 A 7 B 8 C 9 D 10 dtype: int64
There are two ways to view:
- View by custom index
- View through the corresponding numerical index
s7["A"] # Custom index value 7
s7[0] # Default numeric index 7
s7["D"] 10
s7[3] 10
Convert Series to dictionary
s_dic = s7.to_dict() # Convert to dictionary form
s_dic
# result
{'A': 7, 'B': 8, 'C': 9, 'D': 10}type(s_dic) # The result is displayed as a dictionary type # result dict
Name the Series index
s8 # result one Apple two Banana three Hami melon four orange dtype: object
s8.index # Original index Index(['one', 'two', 'three', 'four'], dtype='object')
s8.index.name = "Fruits" # Index naming s8
The results are displayed as:
Fruits one Apple two Banana three Hami melon four orange dtype: object
s8.index # Index after change
Index(['one', 'two', 'three', 'four'], dtype='object', name='Fruits')
Modify Series values
s8 # The result is Fruits one Apple two Banana three Hami melon four orange dtype: object
s8["three"] = "watermelon" # Equivalent to s8[2] = "watermelon" s8
The changed value is:
Fruits one Apple two Banana three watermelon four orange dtype: object
Convert Series structure to DataFrame structure
s8 Fruits one Apple two Banana three watermelon four orange dtype: object
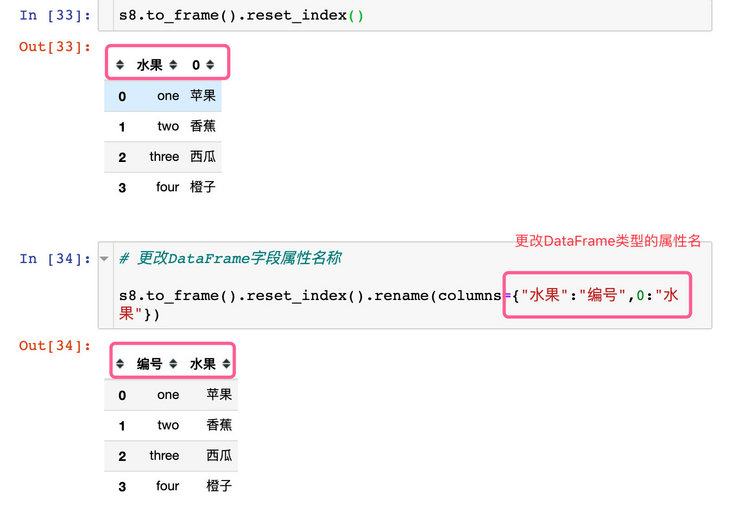
Three functions are involved in the process of converting s8 to DataFrame:
- to_frame: convert to DataFrame
- reset_index: index reset of DataFrame type
- rename: reset the field properties of the DataFrame
Please look forward to the detailed explanation of DataFrame in the next section!
Extended reading
Many knowledge points of pandas are used in the previously written travel strategy articles for learning:
- sea town: Xiamen is really more than Gulangyu
- Entertainment Capital: Does the stinky tofu with 31 yuan in Changsha smell good?
- Gourmet capital: Chengdu hot pot should be very hot!
- Ancient capital of the 13th Dynasty: Xi'an - when Qin Shihuang met biangbiang
- Northern Pearl: Northern Pearl Dalian is waiting for you