catalogue
Species difference (connotation):
Creation and acquisition of session
Syntax analysis of access and deletion of session value
Species difference (connotation):
EL syntax - value by variable name
Jump to a jsp through the servlet and get the collection of user data in the jsp
EL syntax - get object property values
EL syntax - get set element - List
EL syntax - get collection elements - Map
EL syntax - execute expression
EL syntax - execute expression empty operator
Species difference (connotation):
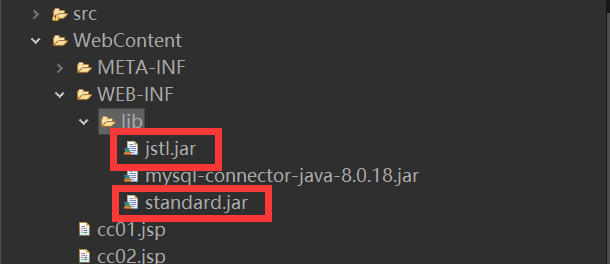
1. Guide the package and paste it directly into the lib of the project as shown in the figure
2. Paste the following fixed instructions on the JSP page
The if tag (conditional judgment) does not have else, but it can be used in another form:
Start stop and step of cycle label:
1, session Technology
definition:
Session is an object stored on the server side and used to save session data during the whole session.
Species difference (connotation):
1. The information is saved on the server side
2. Information is stored as objects
Creation and acquisition of session
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
Gets the HttpSession object in the request.
If the return value is null, create a session.
HttpSession session = request.getSession(boolean b);
The parameter is true, which is the same as the method without parameters.
The parameter is false. If the return value is null, it will return null and will not create a session.
Syntax analysis of access and deletion of session value
Save data in the form of key value pairs:
session.setAttribute(String name,Object obj);
Get data through key value:
session.getAttribute(String name);
Delete data by key value:
session.removeAttribute(String name);
Case:
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Set character encoding
request.setCharacterEncoding( "utf-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//Set generated properties
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
//Create Session object
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
//Save data to session
session.setAttribute("username","Zhang San");
//Delete data from session
session.removeAttribute("username");
//Get the data from the session and print the data to the web page
pw.print(session.getAttribute("username"));
pw.flush();
pw.close();
}2, EL
Why use EL?
Ask questions:
Is a large amount of Java code embedded in general JSP pages? When accessing data with complex structure, the code is cumbersome. Does it often need forced type conversion?
<%
Employee employee =(Employee) request.getAttribute("employee");
Computer comp = employee.getComputer();
String brand= comp.getBrand();
%>
How to solve it?
EL obtains data from domain objects and automatically performs type conversion, which makes the development of JSP easier
${requestScope.employee.computer.brand}
definition:
EL is an expression language embedded in JSP pages to obtain data from fields or built-in objects and operate
Species difference (connotation):
1. Embedded in JSP pages
2. Obtain data from the domain or built-in object 3. You can operate on the obtained data
EL syntax:
${EL expression }
Value by variable name
Gets the property value of the object
Get collection elements
Execute expression
EL syntax - value by variable name
${variable name} for example: ${username}
//Save data in Servlet or JSP
request.setAttribute("username", "LiYang");
//Accessing data in JSP
Name: ${username}
Specify scope:
| Scope name | Name in EL |
| page | pageScope |
| request | requestScope |
| session | sessionScope |
| application | applicationScope |
Case:
Jump to a jsp through the servlet and get the collection of user data in the jsp
In two ways:
1. No need el
TestELServlet.java in
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Set character encoding
request.setCharacterEncoding( "utf-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//Set generated properties
response.setContentType("text/html");
List<User> users=new ArrayList<User>();
User u1=new User(1,"Zhang San","123");
User u2=new User(2,"Li Si","123");
User u3=new User(3,"Wang Wu","123");
User u4=new User(4,"Zhao Liu","123");
users.add(u1);
users.add(u2);
users.add(u3);
users.add(u4);
request.setAttribute("users",users);
request.getRequestDispatcher("TestEL.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
TestEL.jsp in
<body>
<%
List<User> users=(List<User>)request.getAttribute("users");
User u=users.get(2);
out.print(u.toString());
%>
</body>2. Use el
TestELServlet.java in
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Set character encoding
request.setCharacterEncoding( "utf-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//Set generated properties
response.setContentType("text/html");
List<User> users=new ArrayList<User>();
User u1=new User(1,"Zhang San","123");
User u2=new User(2,"Li Si","123");
User u3=new User(3,"Wang Wu","123");
User u4=new User(4,"Zhao Liu","123");
users.add(u1);
users.add(u2);
users.add(u3);
users.add(u4);
request.setAttribute("users",users);
request.getRequestDispatcher("TestEL.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
TestEL.jsp in
<body>
${users[2]}
</body>EL syntax - get object property values
<%=( (User)request.getAttribute("user") ) .getName()%>
Equivalent to the following:
Point operator:
${user.name}
[] operator
${user["name"]}
EL syntax - get set element - List
//Save data in Servlet or JSP
List names = new ArrayList();names.add(0, "LiYang");
names.add(1,"WangHua");
request.setAttribute("names",names);
//Accessing data in JSP
Name: $names [0]} < br / >
Name: ${names [1]} < br / >
//Specify element subscript with []
EL syntax - get collection elements - Map
Save data in Servlet or JSP
Map names = new HashMap();
names.put("one","LiYang");
names.put("two", "WangHua");
request.setAttribute("names", names);
//Accessing data in JSP
Name: ${names. One} < br / >
Name: ${names ["two"]} < br / >
//According to the key in the key value pair
EL syntax - execute expression
It's OK to understand. The condition judgment in EL is generally not used. Now JSTL is used
| Arithmetic operator | explain | Example | result |
| + | plus | ${15+2} | 17 |
| - | reduce | ${15-2} | 13 |
| * | ride | ${15*2} | 30 |
| /Or div | except | ${15 / 2} or ${15 div 2} | 7 |
| %Or mod | Seeking remainder | ${15% 2} or ${15 mod 2} | 1 |
| Relational operator | explain | Example | result |
| ==(or eq) | be equal to | ${23 = = 5} or ${23 eq 5} ${"a" =="a"} or ${"a" eq "a"} | false true |
| ! = (or ne) | Not equal to | ${23! = 5} or ${23 ne 5} | true |
| < (or lt) | less than | ${23 < 5} or ${23 lt 5} | false |
| >(or gt) | greater than | ${23 > 5} or ${23 gt 5} | true |
| < = (or le) | Less than or equal to | ${23 < = 5} or ${23 le 5} | false |
| >=(or ge) | Greater than or equal to | ${23 > = 5} or ${23 ge 5} | true |
| Logical operator | explain | Example | result |
| &&(or and) | Logic and | If a is true and B is false, ${A & & B} (or ${A and B}) | false |
| ||(or) | Logical or | If A is true and B is false, ${A | B} (or ${A or B}) | true |
| ! (or not) | Logical non | If a is true, ${! A} (or ${not A}) | false |
EL syntax - execute expression empty operator
If it is empty or null, return true,
Otherwise, false is returned
Used to determine whether an object or variable is null or empty
${empty name}
EL implicit object
EL implicit objects are predefined objects that can be used directly in the expression language
Fetch object: param
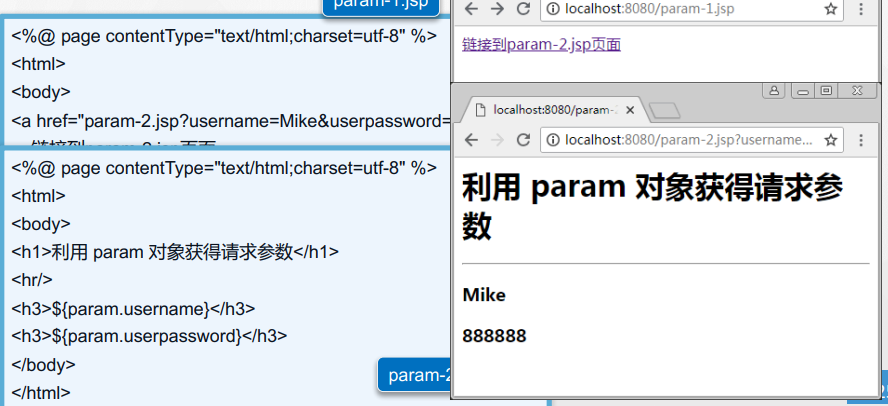
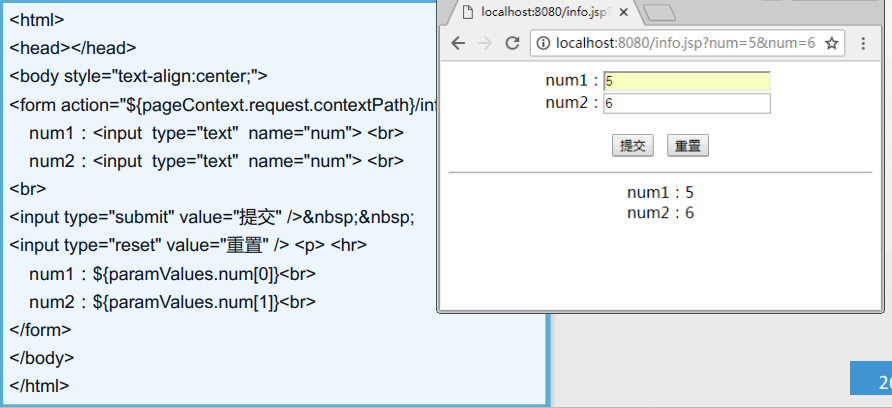
Check box object: paramValues
3, JSTL overview
Condition judgment in EL is generally not used. Now JSTL is used
Solve most <%% >
definition:
JSTL is a JSP standard tag library used to write various common core functions in Web applications
Species difference (connotation):
1. Use in web Applications
2. Used to write various common core functions
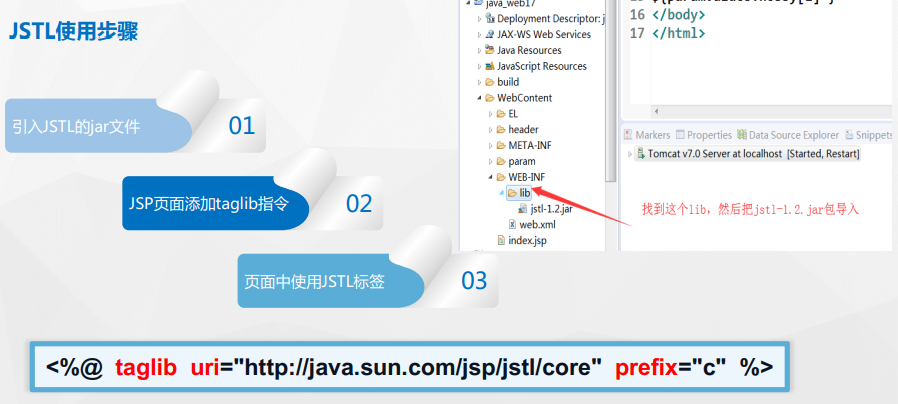
JSTL usage steps:
1. Guide the package and paste it directly into the lib of the project as shown in the figure
2. Paste the following fixed instructions on the JSP page
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
c in prefix means that all labels start with c, and if m is written in it, start with m
Position as shown in the figure:
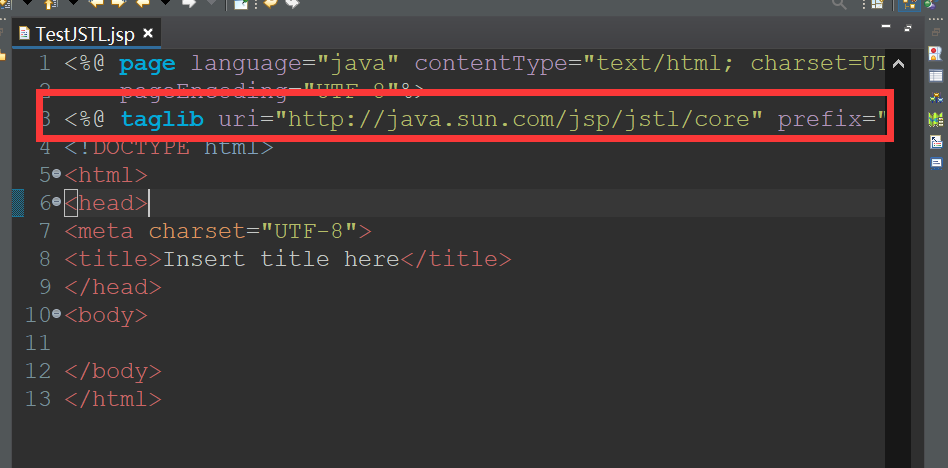
3. Write < C: each label prompt will appear
For example: (all in the body)
set tag:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- set Add data to the field and save data -->
<!-- scope=""Fill in the data wherever it is written -->
<!-- value=""What do you want to fill in -->
<!-- var=""What name do you want to fill in -->
<!-- Save data -->
<c:set scope="session" var="username" value="Chun Chun"></c:set>
<!-- amount to
HttpSession session = request.getSession( );
session.setAttribute("usernamel","Chun Chun"); -->
<!-- Fetch data -->
${username}
</body>
</html>out label:
<!-- print data -->
<c:out value="Chun Chun"></c:out>
<!-- amount to out.print("Chun Chun") -->The if tag (conditional judgment) does not have else, but it can be used in another form:
<!-- If it is judged that Chunchun exists, the output is working hard -->
<c:if test="${username=='Chun Chun'}">
<c:out value="In efforts"></c:out>
</c:if>
<!-- amount to else if -->
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${username=='Zhang San'}">
<c:out value="I'm learning"></c:out>
</c:when>
<c:when test="${username=='Li Si'}">
<c:out value="at school"></c:out>
</c:when>
<!-- amount to else -->
<c:otherwise>
<c:out value="Come on"></c:out>
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
Cycle label:
<c:set scope="session" var="cities" value="'Beijing','Shanghai','Hangzhou'"></c:set>
<!-- loop -->
<!-- items Property refers to what set you want to traverse -->
<!-- var Property refers to what is generated by each traversal -->
<c:forEach items="${cities}" var="city">
<c:out value="${city}"></c:out>
</c:forEach>Traverse the collection:
<c:forEach items="${users }" var="user">
<c:out value="${user }"></c:out>
</c:forEach>
Corresponding Servlet
request.setAttribute("users",users);
//request.getRequestDispatcher("TestEL.jsp").forward(request, response);
request.getRequestDispatcher("TestJSTL.jsp").forward(request, response);
Start stop and step of cycle label:

<c:forEach items="${cities }" var="city" begin="1" end="2" step="1">
<c:out value="${city }"></c:out>
</c:forEach>