Today's content
- Introduction to NFS
- Implement NFS file synchronization
- NFS configuration details
- Unified user
- Building web Services
- NFS for file sharing
Detailed content
1. Introduction to NFS
1.1 INTRODUCTION
Realize multiple web The server can share data resources, just put each web The data storage of the server is independent and stored in a NFS In the server, web Access when the server needs resources NFS Just get it
NFS yes Network File System Abbreviation and network file system. NFS The main function is to share files or directories between different host systems through local area network. NFS System and Windows Network shares, network drives, and the like, Just windows For LAN, NFS Used in enterprise cluster architecture, If it is a large website, More complex distributed file systems will be used FastDFS,glusterfs,HDFS,ceph
1.2 NFS application
1.User access NFS The client converts the request into a function 2.NFS adopt TCP/IP Connect server 3.NFS When the server receives the request, it will call portmap Process port mapping 4.Rpc.nfsd Process used to determine NFS Whether the client can connect to the server; 5.Rpc.mount The process is used to determine the operation permission of the client to the server 6.If the permission verification is passed, the server can be operated, modified or read
2. Implement NFS file synchronization
2.1 server
Installing NFS utils and rpcbind
yum install nfs-utils rpcbind -y
Modify the configuration file and configure the mount point (/ etc/exports)
vim /etc/exports [Mount point] [Client network segments allowed to access]([jurisdiction]) /web/nfs1 172.16.1.0/20(rw,all_sqush,sync)
Create mount point
mkdir -p /web/nfs{1..9}
Authorize the mount point (modify master and group)
# Because the parameter all_ Square, no matter what account the NFS client uses to access, it is mapped to the anonymous user of the NFS server So use nfsnobody chown -R nfsnobody.nfsnobody /web
Turn off firewall
setenforce 0 systemctl disable --now firewolld
Start NFS and rpcbind services
systemctl start nfs-server systemctl start rpcbind
Test whether the server is normal
showmount -e [The address of the server. The default is the local address] [root@nfs web]# showmount -e Export list for nfs: /web/upload 172.16.1.0/20
Remember to format the mount point
mkfs.xfs /web/nfs1
2.2 client
Installing NFS utils
yum install nfs-utils -y be careful : Both client and server need to be installed nfs-utils
Create directory
mkdir /web/nfs
Mount NFS
mount -t nfs 172.16.1.31:/web/nfs1 /web/nfs -t : Specify mount nfs type be careful : Format before mounting nfs Mount point for
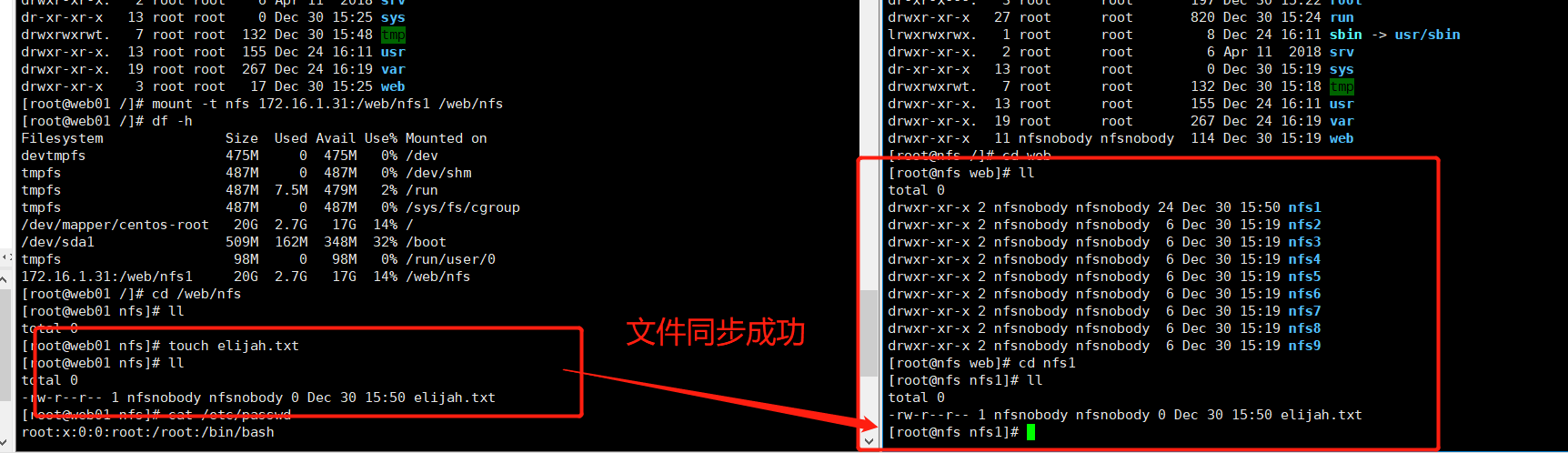
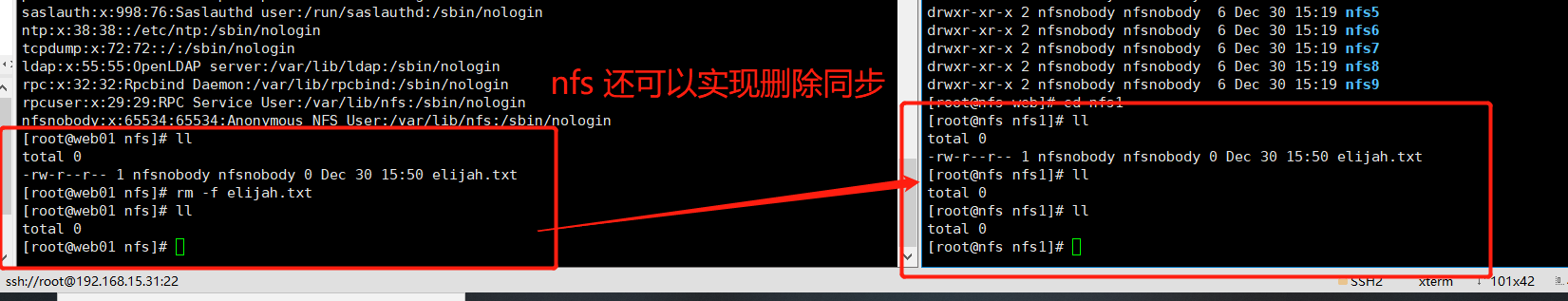
Test NFS synchronization
stay web01 Mount directory in /web/nfs Create file in see nfs Is the data synchronized in the mount point
3. NFS configuration details
| nfs shared parameters | Parameter action |
|---|---|
| rw | Read and write permissions (common) |
| ro | Read only permission (not commonly used) |
| root_squash | When NFS clients are accessed as root administrators, they are mapped to anonymous users of NFS servers (not commonly used) |
| no_root_squash | When an NFS client is accessed as a root administrator, it is mapped to the root administrator of the NFS server (not commonly used) |
| all_squash | No matter what account the NFS client uses to access, it is mapped to an anonymous user of the NFS server (commonly used) |
| no_all_squash | No matter what account NFS clients use to access, compression is not performed (not commonly used) |
| sync | Write data into memory and hard disk at the same time to ensure no data loss (common) |
| async | First save the data to the memory, and then write it to the hard disk; This is more efficient, but data may be lost (not commonly used) |
| anonuid | Configure all_squash is used to specify the user UID of NFS, which must exist in the system (common) |
| anongid | Configure all_squash is used to specify the GID of NFS user, and the system must exist (common) |
3.1. Control reading and writing
rw,ro
3.2. Control file permissions
root_squash
no_root_squash
all_squash
no_all_squash
3.3. Control write mode
sync async
3.4. Control users
anonuid
anongid
4. Unified user
explain
In order to make nfs The files in the server are easy to read by all client machines Obviously, it is very inconvenient that the group and owner of the file are different You can change all mount point files in the server to unified users and user groups www,Each client needs to use to create and access data files www Users, which facilitates the access of each client to public data
4.1 create www system user in nfs server
groupadd www -g 666 useradd www -u 666 -g 666 -M -r -s /sbin/nologin
4.2 authorized mount point (modify group and owner)
chown -R www.www /web
4.3 modifying the mount point configuration file
vim /etc/exports /web/nfs1 172.16.1.0/20(rw,all_squash,sync,anonuid=666,anongid=666)
4.4 restart NFS server and rpcbind
systemctl restart nfs-server systemctl restart rpcbind
4.5 re mount in the client web01
[root@web01 ~]# umount /web/nfs [root@web01 ~]# mount -t nfs 172.16.1.31:/web/nfs1 /web/nfs
4.6 testing

5. Build web service (on client Web)
5.1 installing web software
yum -y httpd php php-devel
5.2 upload the code to the root directory of the website
# After downloading the web software, the website root directory / var/www will be automatically generated cd /var/www/html Unzip the code file unzip xxx
Upload web page code
# Create an upload folder under the html directory to receive uploaded files
5.3 authorize the root directory (modify the group owner)
chown -R www.www /var/www/html
5.4 turn off selinux and firewall
setenforce 0
systemctl disable --now firewalld
5.5 users who modify web software
vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf User www Group www # If this step is missing, an error will occur when synchronizing data because the original user does not have access rights
5.6 start web software
systemctl start httpd
5.7 testing
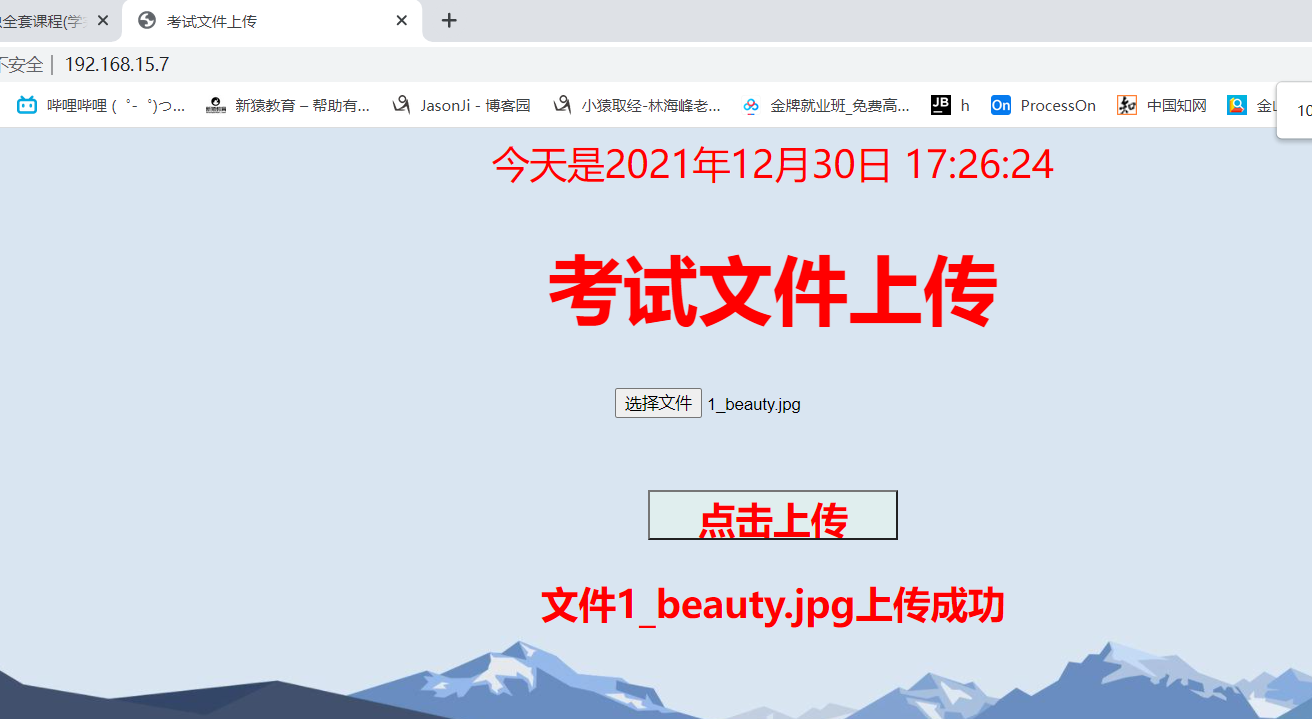
With what IP operation web Yes, with what IP Login, I use the public network IP
visit
http://192.168.15.7/upload/1_linux.jpg
# Note: add the folder upload folder in the root directory / var/www/html, and the uploaded file should be named 1_xxx
6. web service construction and file sharing with NFS
Server
6.1 modifying configuration files
vim /etc/exports /web/upload 172.16.1.0/20(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=666,anongid=666) To create a new mount point to store web Uploaded files
6.2 new mount point
mkdir /web/upload chown www.www /web/upload
6.3 restart nfs software
systemctl restart nfs-server rpcbind
client
6.4 installing and starting httpd and modifying its configuration
# All client machines shall install web service software, change their user name to WWW, and create www system users [root@web03 conf]# groupadd www -g 666 [root@web03 conf]# useradd www -u 666 -g 666 -M -r -s /sbin/nologin [root@web02 html]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf User www Group www [root@web02 html]# systemctl start httpd
6.5 install NFS software on all clients
# Note: if it cannot be mounted, the client should not download NFS software yum -y install nfs-utils
6.6 mounting
mount -t nfs 172.16.1.31:/web/upload /var/www/html/upload
6.7 testing
The pictures uploaded in different servers (clients) can be shared and found by each different client, realizing the synchronous sharing of resources
You can also play games