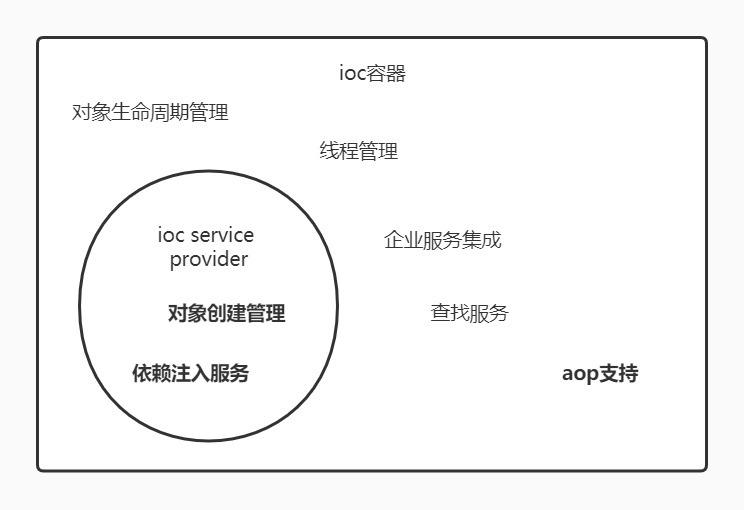
1 Overview
There is a certain intersection between the spring ioc container and the services provided by the ioc service provider.
spring provides two types of containers: BeanFactory and ApplicationContext
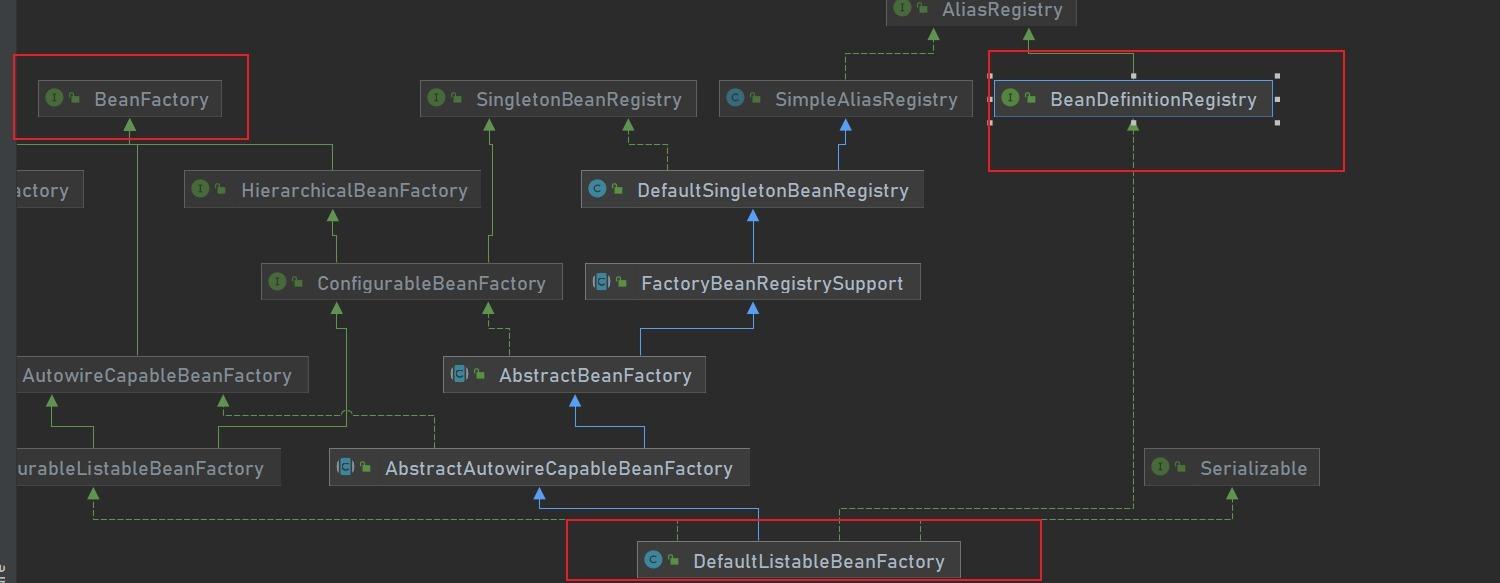
1.1 BeanFactory
beanfactory base type ioc container, which provides complete ioc services. Delayed initialization is adopted by default. Initialization and dependency injection are only performed when the client object needs to access an object in the container.
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
public interface BeanFactory {
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException;
boolean containsBean(String name);
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
@Nullable
Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
String[] getAliases(String name);
}
The above interfaces are all query related methods to determine whether the object exists in the container and obtain the state or type of a bean.
1.2 ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext is built on the basis of beanfactory. In addition to all beanfactory support, it also provides advanced features of event publishing and international informatization. ApplicationContext is initialized and bound by default at startup, but it requires more system resources.
1.3 Beanfactory process
beanfactory will register and manage the dependencies between various business objects through xml files.
<bean id ="peo" class = "org.example.Person">
<property name="dog" ref="dog"/>
</bean>
<bean id = "dog" class="org.example.Dog">
</bean>
Load the configuration file and get the bean
//Load spring configuration file
ApplicationContext container =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//Get the corresponding content through getBean
Person person = (Person) container.getBean("per");
1.4 object registration and dependency binding of beanfactory
1.4.1 direct coding method
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
BeanFactory container = (BeanFactory) bindViaCode(beanFactory);
Person person = (Person) container.getBean("per");
person.sayDogName();
}
public static BeanFactory bindViaCode(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry){
AbstractBeanDefinition person=
new RootBeanDefinition(Person.class);
AbstractBeanDefinition dog=
new RootBeanDefinition(Dog.class);
//Register the bean definition into the container
registry.registerBeanDefinition("per",person);
registry.registerBeanDefinition("dog",dog);
//Specify dependencies
//1. Construction mode
//2. Construction mode
MutablePropertyValues propertyValues = new MutablePropertyValues();
propertyValues.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue("dog",dog));
person.setPropertyValues(propertyValues);
//3. Binding completed
return (BeanFactory) registry;
}
The beanfactory interface only defines how to access the methods of managing beans in the container. The specific implementation classes of each beanfactory are responsible for the registration and management of specific beans.
Bean definition registry defines Abstract bean registration logic.
In each managed object, there is an instance of BeanDefinition in each container. The instance of BeanDefinition is responsible for saving all necessary information of the object, including the class type of its corresponding object, whether it is an abstract class, etc.
Therefore, in this method, we construct the corresponding Beandefinition of the corresponding business object and register it in the registry.
1.4.2 xml configuration file mode
<bean id ="per" class = "org.example.Person">
<property name="dog" ref="dog"/>
</bean>
<bean id = "dog" class="org.example.Dog">
</bean>
Load profile
public static void main( String[] args )
{
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanRegistry = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
BeanFactory container = bindViaXmlFile(beanRegistry);
Person person =(Person)container.getBean("per");
person.sayDogName();
}
public static BeanFactory bindViaXmlFile(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry){
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(registry);
reader.loadBeanDefinitions("applicationContext.xml");
return (BeanFactory) registry;
//Simplified version
// return new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"));
}
xmlBeanDefinitionReader is responsible for reading and parsing the xml configuration in the format specified by spring, mapping the file to the corresponding BeanDefinition after parsing, and loading it into the corresponding BeanDefinitionRegistry.
1.4.3 annotation method
@Component
public class Person {
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
....
}
@Component
public class Dog {
.....
}
@AutoWired tells the container that it needs to inject those dependent objects into the current object@ Component is used in conjunction with classpath scanning
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="org.example"/>
</beans>
implement
< context: component scan / > the class marked @ component will be scanned under the specified package. If it is found, it will be added to the container for management, and the qualified objects will be injected according to @ Autowaired.
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person person = (Person) ctx.getBean("person");
person.sayDogName();
}