6. Integrate SpringBoot project practice
6.0 integration ideas
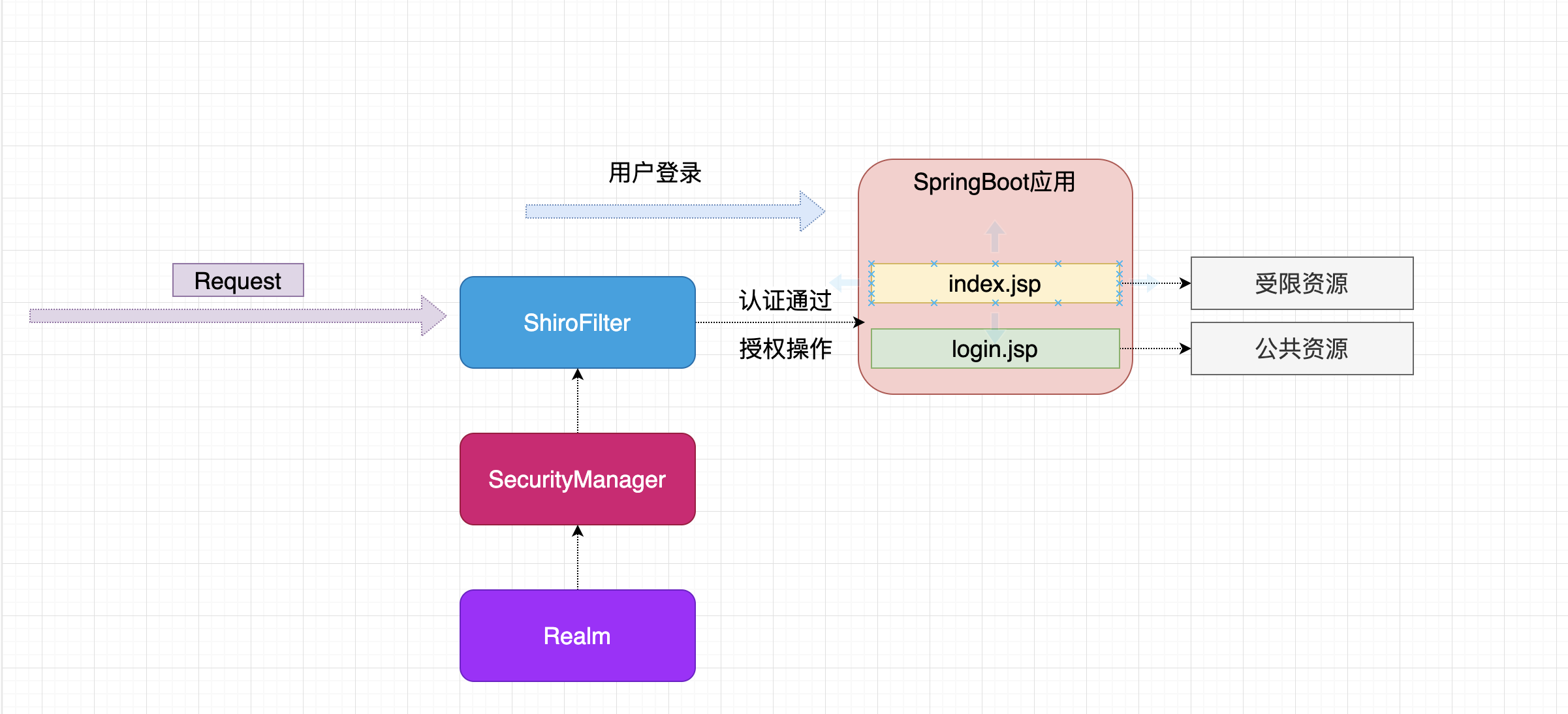
6.1 creating a springboot project

6.2 introducing shiro dependency
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.5.3</version> </dependency>
6.3 configuring shiro environment
0. Create configuration class

1. Configure shiroFilterFactoryBean
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(SecurityManager securityManager){
//Create shiro's filter
ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//Injection Security Manager
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
return shiroFilterFactoryBean;
}
2. Configure WebSecurityManager
@Bean
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getSecurityManager(Realm realm){
DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
defaultWebSecurityManager.setRealm(realm);
return defaultWebSecurityManager;
}
3. Create a custom realm

public class CustomerRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//Processing authorization
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
return null;
}
//Process authentication
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws
AuthenticationException {
return null;
}
}
4. Configure custom realm
//Create custom realm
@Bean
public Realm getRealm(){
return new CustomerRealm();
}
5. Write the controller and jump to index html
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("index")
public String index(){
System.out.println("Jump to home page");
return "index";
}
}


6. Start the springboot application to access the index
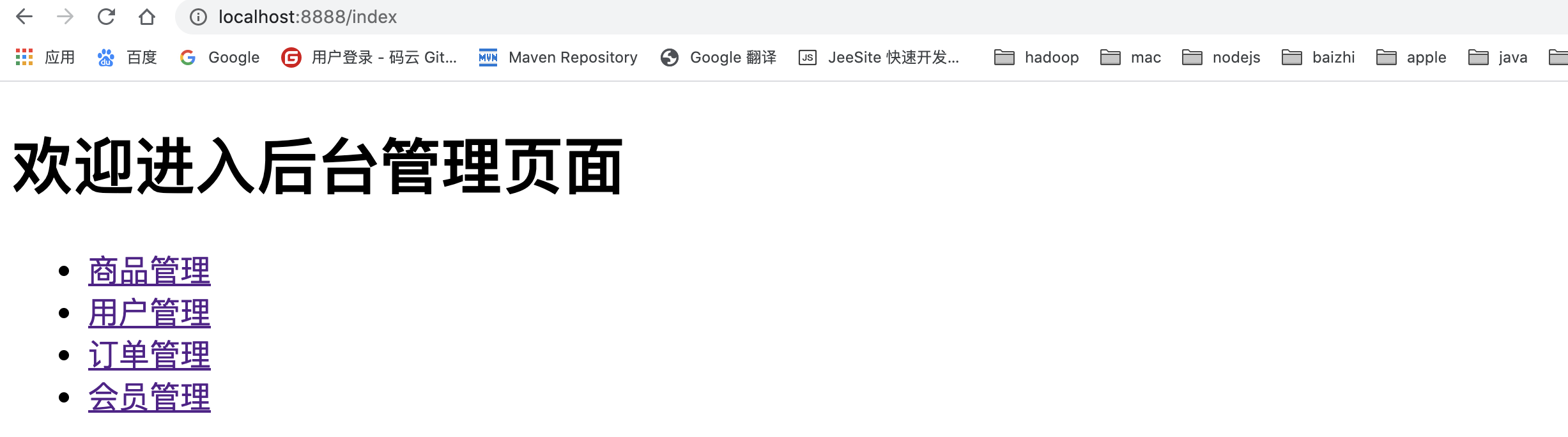
- be careful:
- By default, after the shiro environment is configured, there is no permission control for any resources in the project in the default environment. All resources in the project can be accessed through paths
7. Add permission control
-
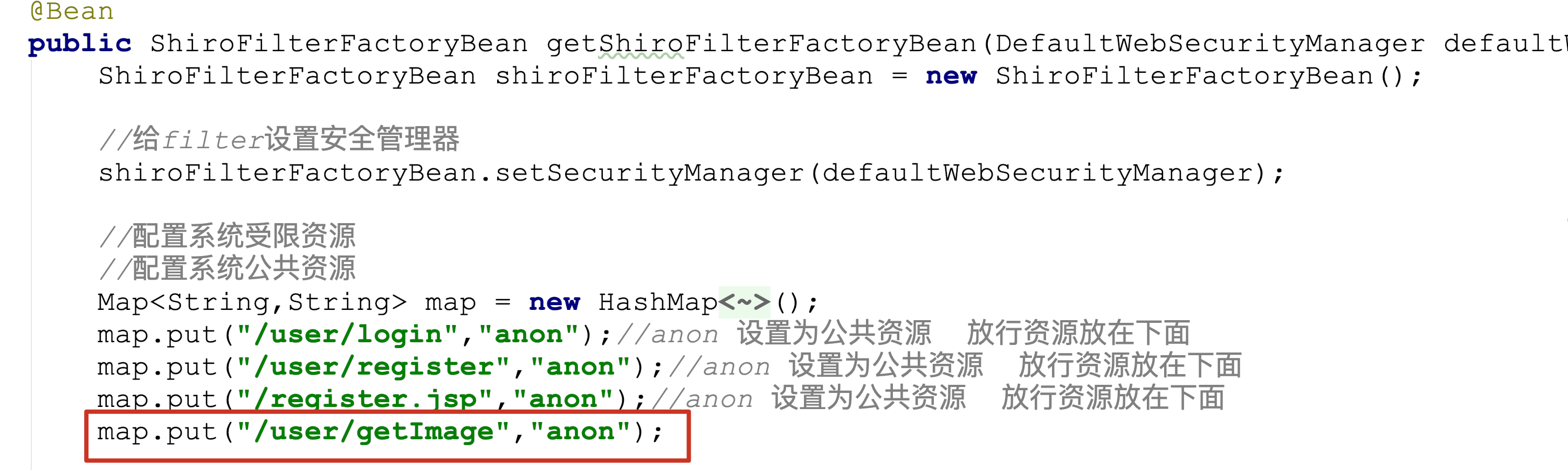
Modify ShiroFilterFactoryBean configuration
//Injection Security Manager shiroFilterFactoryBean.setSecurityManager(securityManager); Map<String,String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); map.put("/**","authc"); //Configure authentication and authorization rules shiroFilterFactoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map);[the external chain picture transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-932Hxa4K-1625454917389)(Shiro practical tutorial. assets/image-20200523102303320.png)]
- /**authc represents the alias of a filter in shiro. See the shiro filter list in the document for details
8. Restart project access view
6.4 common filters
- Note: shiro provides and multiple default filters. We can use these filters to configure the permission to control the specified url:
| Configuration abbreviation | Corresponding filter | function |
|---|---|---|
| anon | AnonymousFilter | Specifies that the url can be accessed anonymously |
| authc | FormAuthenticationFilter | The specified url requires form login. By default, the user name, password,rememberMe and other parameters will be obtained from the request and try to log in. If the login fails, it will jump to the path configured by loginUrl. We can also use this filter as the default login logic, but we usually write the login logic in the controller ourselves. If we write it ourselves, the error returned information can be customized. |
| authcBasic | BasicHttpAuthenticationFilter | The specified url requires basic login |
| logout | LogoutFilter | Log out of the filter and configure the specified url to realize the exit function, which is very convenient |
| noSessionCreation | NoSessionCreationFilter | Disable session creation |
| perms | PermissionsAuthorizationFilter | You need to specify permissions to access |
| port | PortFilter | You need to specify a port to access |
| rest | HttpMethodPermissionFilter | Convert the http request method into the corresponding verb to construct a permission string. This doesn't make much sense. I'm interested in reading the comments of the source code |
| roles | RolesAuthorizationFilter | You need to specify a role to access |
| ssl | SslFilter | An https request is required to access |
| user | UserFilter | Users who are logged in or remember me are required to access |
6.5 certification realization
1. In login Developing authentication interface in JSP

<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/login" method="post">
user name:<input type="text" name="username" > <br/>
password : <input type="text" name="password"> <br>
<input type="submit" value="Sign in">
</form>
2. Develop controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
/**
* Used to handle identity authentication
* @param username
* @param password
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("login")
public String login(String username,String password){
//Get principal object
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
try {
subject.login(new UsernamePasswordToken(username,password));
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("User name error!");
}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Password error!");
}
return "redirect:/login.jsp";
}
}
- Use subject in the authentication process Login for authentication
3. Static data returned in the development realm (database not connected)
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("==========================");
String principal = (String) token.getPrincipal();
if("xiaochen".equals(principal)){
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal,"123",this.getName());
}
return null;
}
}
4. Start the project to authenticate the static data defined in realm

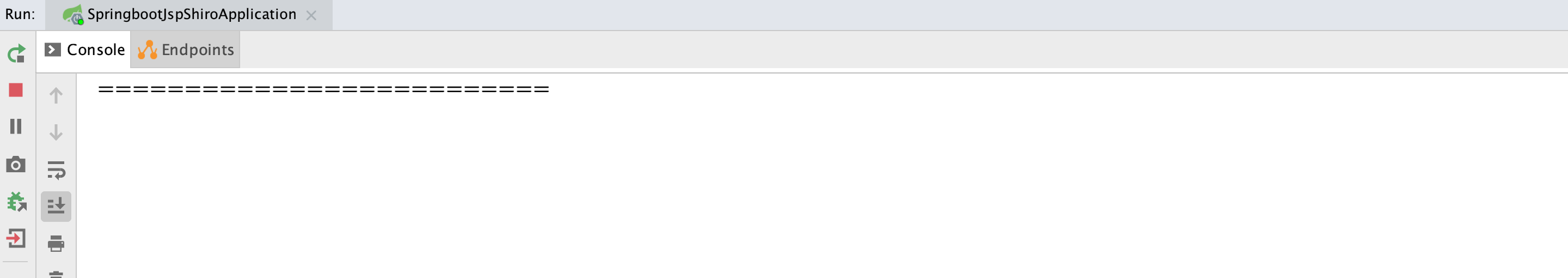

- The authentication function is realized without md5 and random salt authentication
6.6 withdrawal from certification
1. Exit the connection from the development page

2. Develop controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
/**
* Log out
*
*/
@RequestMapping("logout")
public String logout(){
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
subject.logout();//Exit user
return "redirect:/login.jsp";
}
}
3. Modify exit connection access exit path

4. After exiting, access restricted resources and return to the authentication interface immediately
6.7 MD5 and Salt authentication implementation
1. Development database registration
0. Develop registration interface
<h1>User registration</h1>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/register" method="post">
user name:<input type="text" name="username" > <br/>
password : <input type="text" name="password"> <br>
<input type="submit" value="Register now">
</form>
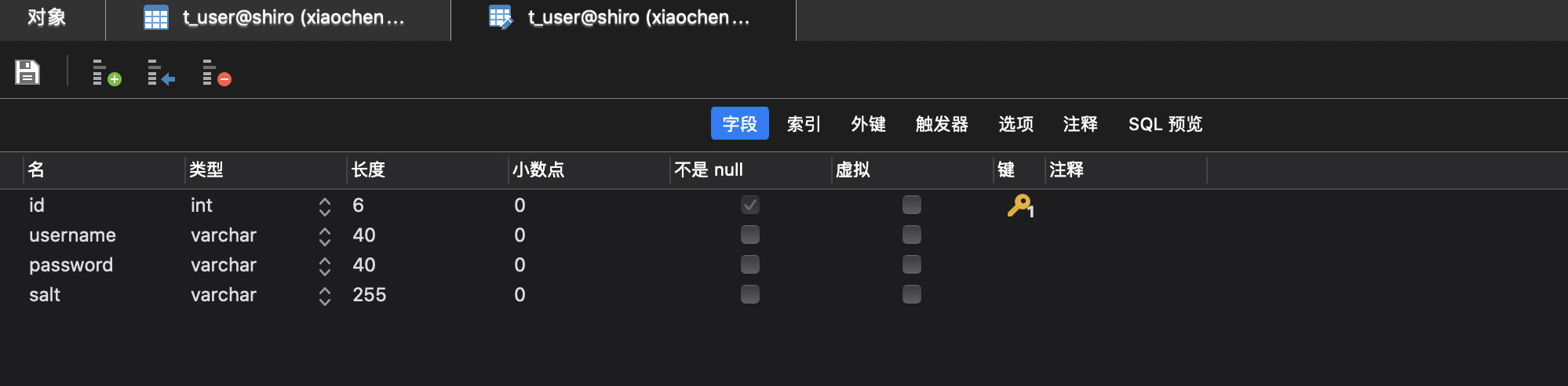
1. Create data table structure
SET NAMES utf8mb4; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for t_user -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_user`; CREATE TABLE `t_user` ( `id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `username` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL, `password` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL, `salt` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
2. Project introduction dependency
<!--mybatis Correlation dependency--> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.1.2</version> </dependency> <!--mysql--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.38</version> </dependency> <!--druid--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.19</version> </dependency>
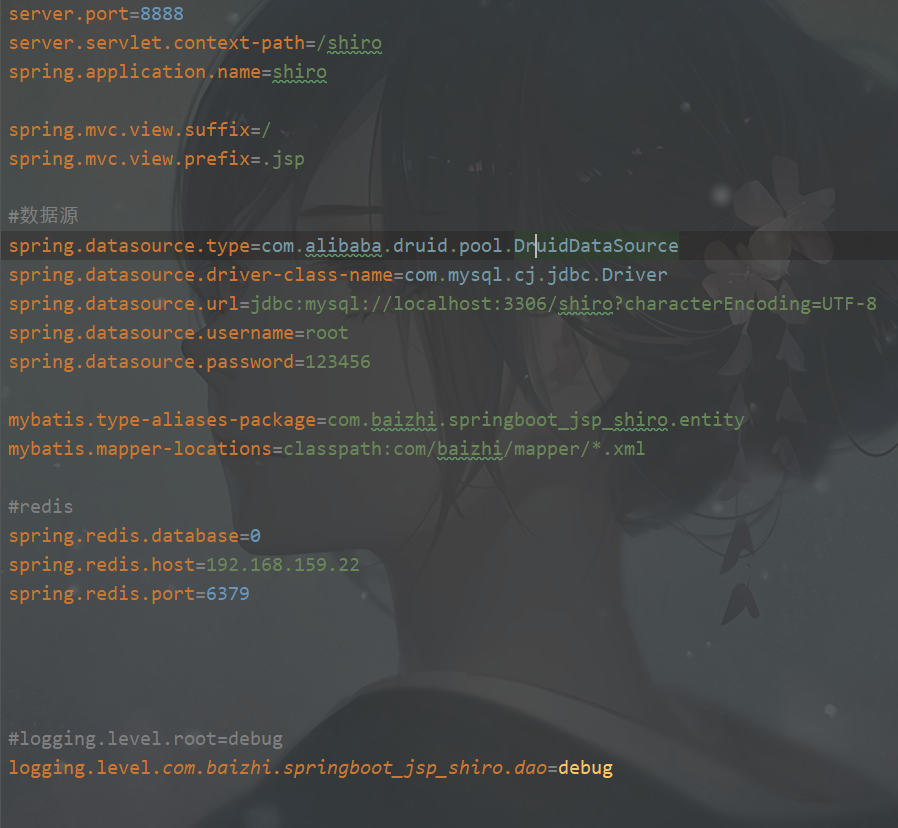
3. Configure application Properties configuration file
server.port=8888 server.servlet.context-path=/shiro spring.application.name=shiro spring.mvc.view.suffix=/ spring.mvc.view.prefix=.jsp #data source spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shiro?characterEncoding=UTF-8 spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.baizhi.springboot_jsp_shiro.entity mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:com/baizhi/mapper/*.xml #redis spring.redis.database=0 spring.redis.host=192.168.159.22 spring.redis.port=6379 #logging.level.root=debug logging.level.com.baizhi.springboot_jsp_shiro.dao=debug
4. Create entity
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private String id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String salt;
}
5. Create DAO interface
@Mapper
public interface UserDAO {
void save(User user);
}
6. Develop mapper configuration file
<insert id="save" parameterType="User" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into t_user values(#{id},#{username},#{password},#{salt})
</insert>
7. Develop service interface
public interface UserService {
//Registered user method
void register(User user);
}
8. Create salt tool class
public class SaltUtils {
/**
* Static method for generating salt
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static String getSalt(int n){
char[] chars = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz01234567890!@#$%^&*()".toCharArray();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char aChar = chars[new Random().nextInt(chars.length)];
sb.append(aChar);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
9. Develop service implementation class
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDAO userDAO;
@Override
public void register(User user) {
//Processing business calls dao
//1. Generate random salt
String salt = SaltUtils.getSalt(8);
//2. Save the random salt to the data
user.setSalt(salt);
//3. md5 + salt + hash for plaintext password
Md5Hash md5Hash = new Md5Hash(user.getPassword(),salt,1024);
user.setPassword(md5Hash.toHex());
userDAO.save(user);
}
}
10. Develop Controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* User registration
*/
@RequestMapping("register")
public String register(User user) {
try {
userService.register(user);
return "redirect:/login.jsp";
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return "redirect:/register.jsp";
}
}
}
11. Start the project for registration
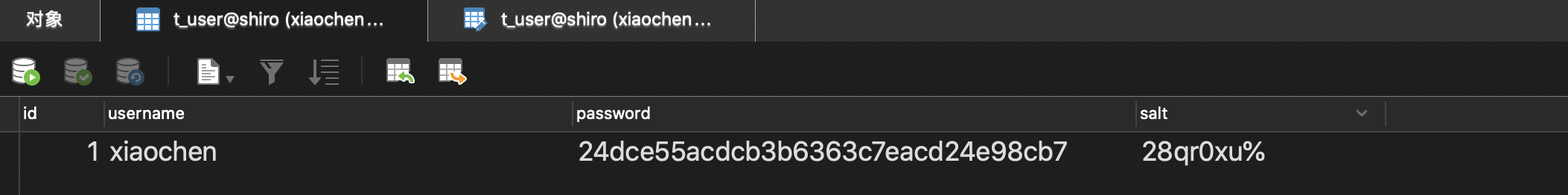
2. Develop database certification
0. Develop DAO
@Mapper
public interface UserDAO {
void save(User user);
//Method of authentication according to identity information
User findByUserName(String username);
}
1. Develop mapper configuration file
<select id="findByUserName" parameterType="String" resultType="User">
select id,username,password,salt from t_user
where username = #{username}
</select>
2. Develop Service interface
public interface UserService {
//Registered user method
void register(User user);
//Method of querying business according to user name
User findByUserName(String username);
}
3. Develop Service implementation class
@Service("userService")
@Transactional
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDAO userDAO;
@Override
public User findByUserName(String username) {
return userDAO.findByUserName(username);
}
}
4. Develop the tool class to obtain the bean object in the factory
@Component
public class ApplicationContextUtils implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext context;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.context = applicationContext;
}
//Get the specified bean object in the factory according to the bean name
public static Object getBean(String beanName){
return context.getBean(beanName);
}
}
5. Modify custom realm
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("==========================");
//According to identity information
String principal = (String) token.getPrincipal();
//Get the service object in the factory
UserService userService = (UserService) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("userService");
//Query according to identity information
User user = userService.findByUserName(principal);
if(!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(user)){
//Return database information
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user.getUsername(),user.getPassword(),
ByteSource.Util.bytes(user.getSalt()),this.getName());
}
return null;
}
6. Modify the voucher matcher and hash hash used by realm in ShiroConfig
@Bean
public Realm getRealm(){
CustomerRealm customerRealm = new CustomerRealm();
//Set hashed credential matcher
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
//Set md5 encryption
credentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("md5");
//Sets the number of hashes
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
customerRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher);
return customerRealm;
}
6.8 authorization realization
0. Page resource authorization
<%@taglib prefix="shiro" uri="http://shiro.apache.org/tags" %>
<shiro:hasAnyRoles name="user,admin">
<li><a href="">user management </a>
<ul>
<shiro:hasPermission name="user:add:*">
<li><a href="">add to</a></li>
</shiro:hasPermission>
<shiro:hasPermission name="user:delete:*">
<li><a href="">delete</a></li>
</shiro:hasPermission>
<shiro:hasPermission name="user:update:*">
<li><a href="">modify</a></li>
</shiro:hasPermission>
<shiro:hasPermission name="user:find:*">
<li><a href="">query</a></li>
</shiro:hasPermission>
</ul>
</li>
</shiro:hasAnyRoles>
<shiro:hasRole name="admin">
<li><a href="">Commodity management</a></li>
<li><a href="">Order management</a></li>
<li><a href="">physical distribution management</a></li>
</shiro:hasRole>
1. Code authorization
@RequestMapping("save")
public String save(){
System.out.println("Entry method");
//Get principal object
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//Code mode
if (subject.hasRole("admin")) {
System.out.println("Save order!");
}else{
System.out.println("No access!");
}
//Based on permission string
//....
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}

2. Method call authorization
- @RequiresRoles are used to authorize based on roles
- @RequiresPermissions is used to authorize based on permissions
@RequiresRoles(value={"admin","user"})//Used to judge that the role also has admin user
@RequiresPermissions("user:update:01") //String used to determine permission
@RequestMapping("save")
public String save(){
System.out.println("Entry method");
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}

3. Authorization data persistence
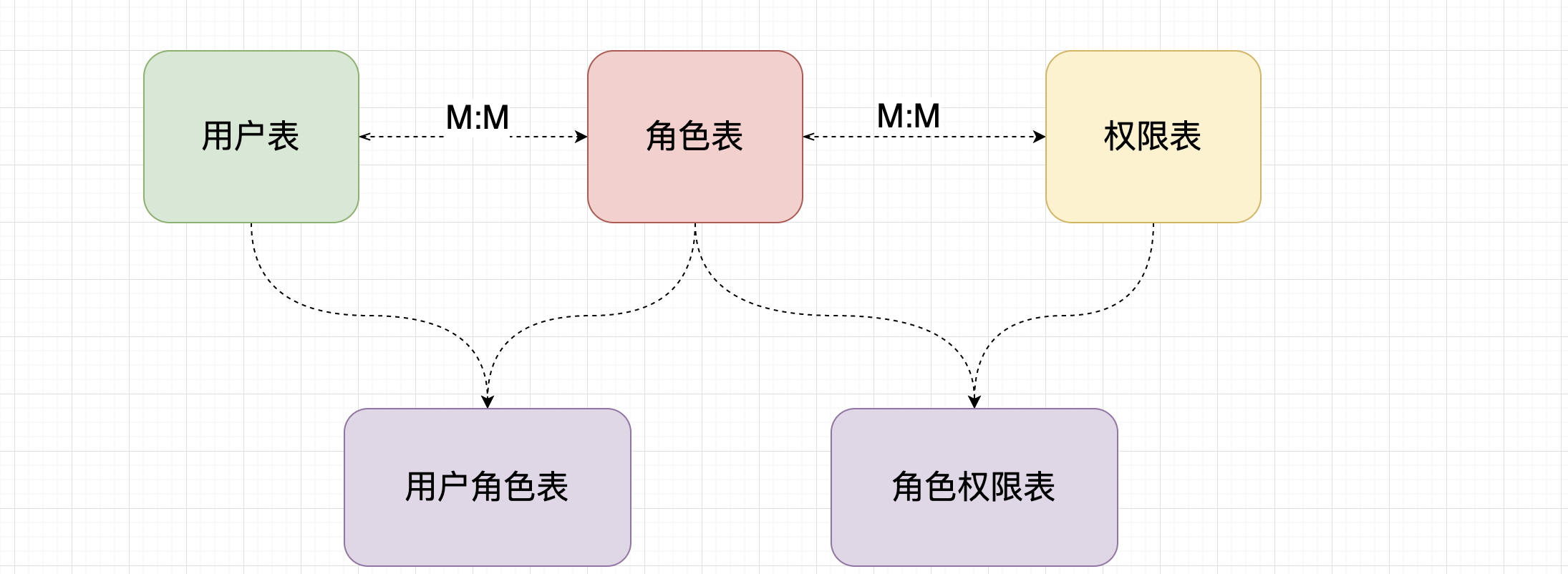
SET NAMES utf8mb4; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for t_pers -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_pers`; CREATE TABLE `t_pers` ( `id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL, `url` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for t_role -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_role`; CREATE TABLE `t_role` ( `id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for t_role_perms -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_role_perms`; CREATE TABLE `t_role_perms` ( `id` int(6) NOT NULL, `roleid` int(6) DEFAULT NULL, `permsid` int(6) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for t_user -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_user`; CREATE TABLE `t_user` ( `id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `username` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL, `password` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL, `salt` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for t_user_role -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_user_role`; CREATE TABLE `t_user_role` ( `id` int(6) NOT NULL, `userid` int(6) DEFAULT NULL, `roleid` int(6) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
4. Create dao method
//Query all roles by user name User findRolesByUserName(String username); //Query permission collection according to role id List<Perms> findPermsByRoleId(String id);
5.mapper implementation
<resultMap id="userMap" type="User">
<id column="uid" property="id"/>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<!--Role information-->
<collection property="roles" javaType="list" ofType="Role">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="rname" property="name"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findRolesByUserName" parameterType="String" resultMap="userMap">
SELECT u.id uid,u.username,r.id,r.NAME rname
FROM t_user u
LEFT JOIN t_user_role ur
ON u.id=ur.userid
LEFT JOIN t_role r
ON ur.roleid=r.id
WHERE u.username=#{username}
</select>
<select id="findPermsByRoleId" parameterType="String" resultType="Perms">
SELECT p.id,p.NAME,p.url,r.NAME
FROM t_role r
LEFT JOIN t_role_perms rp
ON r.id=rp.roleid
LEFT JOIN t_perms p ON rp.permsid=p.id
WHERE r.id=#{id}
</select>
6.Service interface
//Query all roles by user name User findRolesByUserName(String username); //Query permission collection according to role id List<Perms> findPermsByRoleId(String id);
7.Service implementation
@Override
public List<Perms> findPermsByRoleId(String id) {
return userDAO.findPermsByRoleId(id);
}
@Override
public User findRolesByUserName(String username) {
return userDAO.findRolesByUserName(username);
}
8. Modify custom realm
public class CustomerRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
//Get identity information
String primaryPrincipal = (String) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();
System.out.println("Invoke authorization validation: "+primaryPrincipal);
//Obtain role and permission information according to master identity information
UserService userService = (UserService) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("userService");
User user = userService.findRolesByUserName(primaryPrincipal);
//Authorization role information
if(!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(user.getRoles())){
SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
user.getRoles().forEach(role->{
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addRole(role.getName());
//permissions information
List<Perms> perms = userService.findPermsByRoleId(role.getId());
if(!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(perms)){
perms.forEach(perm->{
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermission(perm.getName());
});
}
});
return simpleAuthorizationInfo;
}
return null;
}
}
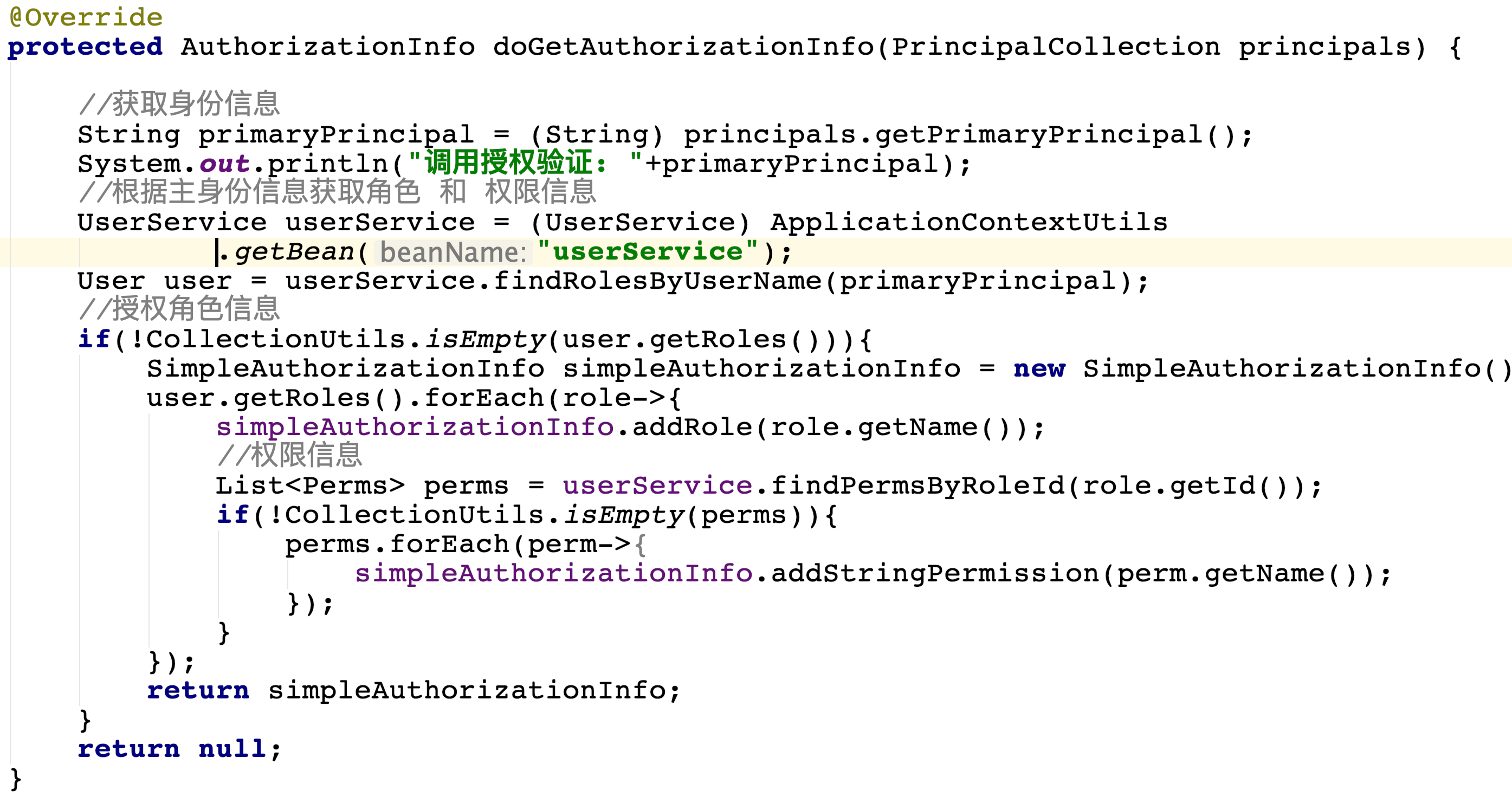
9. Start up test
6.9 using CacheManager
1.Cache function
- Cache: a piece of data in computer memory
- Function: it is used to reduce the access pressure of DB, so as to improve the query efficiency of the system
- technological process:
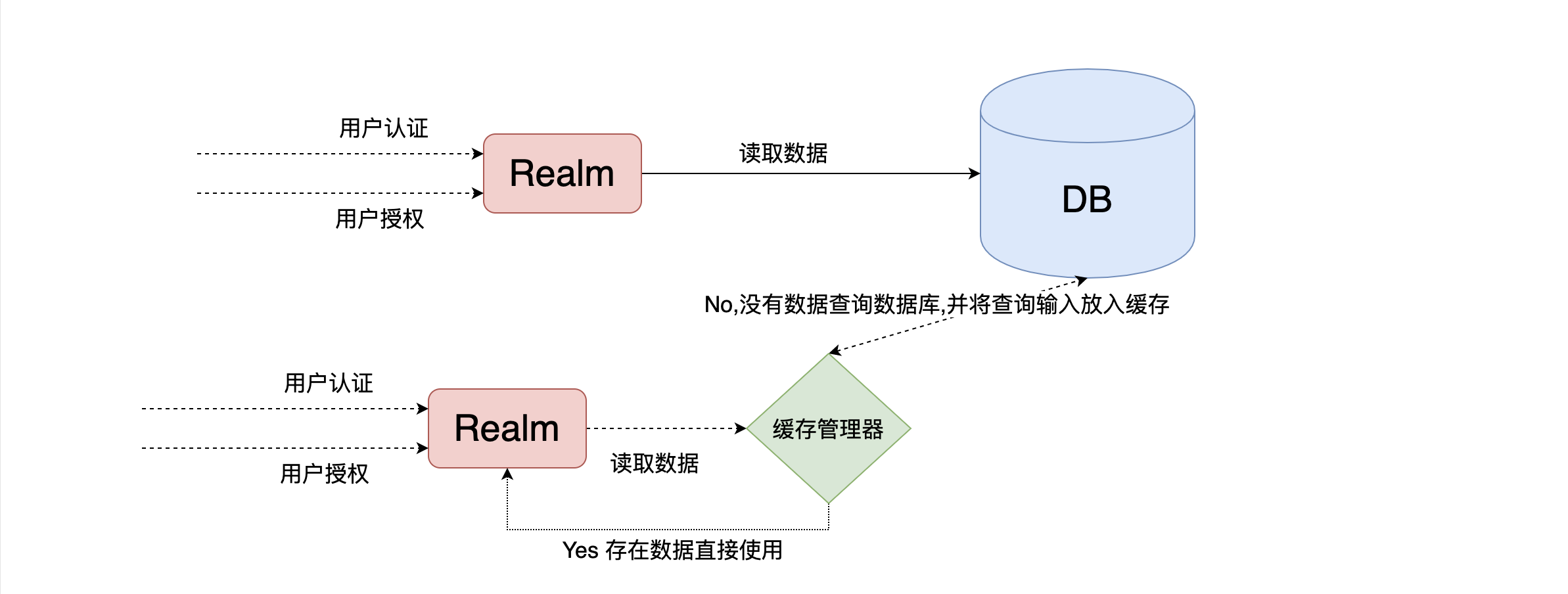
2. Use the default EhCache in shiro to implement caching
1. Introduce dependency
<!--introduce shiro and ehcache--> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-ehcache</artifactId> <version>1.5.3</version> </dependency>
2. Enable cache
//3. Create a custom realm
@Bean
public Realm getRealm(){
CustomerRealm customerRealm = new CustomerRealm();
//Modify voucher verification matcher
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
//Set the encryption algorithm to md5
credentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("MD5");
//Sets the number of hashes
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
customerRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher);
//Open cache manager
customerRealm.setCachingEnabled(true);
customerRealm.setAuthorizationCachingEnabled(true);
customerRealm.setAuthorizationCachingEnabled(true);
customerRealm.setCacheManager(new EhCacheManager());
return customerRealm;
}
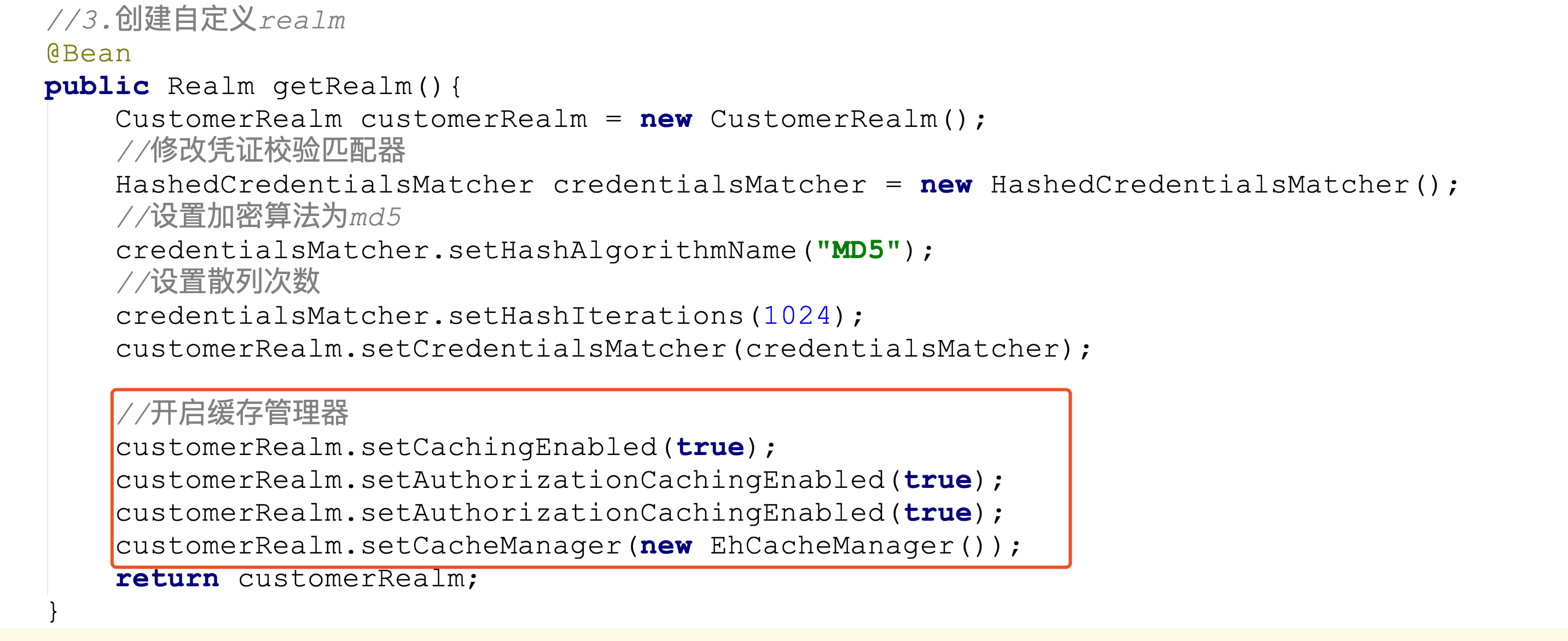
3. Start the refresh page to test
- Note: if there is no sql presentation on the console, the cache has been enabled
3. Redis is used as cache implementation in Shiro
1. Introduce redis dependency
<!--redis integration springboot--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency>
2. Configure redis connection
Here I use redis on the virtual machine
#redis spring.redis.database=0 spring.redis.host=192.168.159.22 spring.redis.port=6379
3. Start redis service
➜ bin ls dump.rdb redis-check-aof redis-cli redis-server redis.conf redis-benchmark redis-check-rdb redis-sentinel redis-trib.rb ➜ bin ./redis-server redis.conf
4. Develop RedisCacheManager
public class RedisCacheManager implements CacheManager {
@Override
public <K, V> Cache<K, V> getCache(String cacheName) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("Cache name: "+cacheName);
return new RedisCache<K,V>(cacheName);
}
}
5. RedisCache implementation
public class RedisCache<K,V> implements Cache<K,V> {
private String cacheName;
public RedisCache() {
}
public RedisCache(String cacheName) {
this.cacheName = cacheName;
}
@Override
public V get(K k) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("Get cache:"+ k);
return (V) getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().get(this.cacheName,k.toString());
}
@Override
public V put(K k, V v) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("Set cache key: "+k+" value:"+v);
getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().put(this.cacheName,k.toString(),v);
return null;
}
@Override
public V remove(K k) throws CacheException {
return (V) getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().delete(this.cacheName,k.toString());
}
@Override
public v remove(k k) throws CacheException {
return (v) getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().delete(this.cacheName,k.toString());
}
@Override
public void clear() throws CacheException {
getRedisTemplate().delete(this.cacheName);
}
@Override
public int size() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().size(this.cacheName).intValue();
}
@Override
public Set<k> keys() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().keys(this.cacheName);
}
@Override
public Collection<v> values() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().values(this.cacheName);
}
private RedisTemplate getRedisTemplate(){
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("redisTemplate");
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
return redisTemplate;
}
//Encapsulate and obtain redisTemplate
private RedisTemplate getRedisTemplate(){
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("redisTemplate");
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
return redisTemplate;
}
}
6. Start the project test and report an error

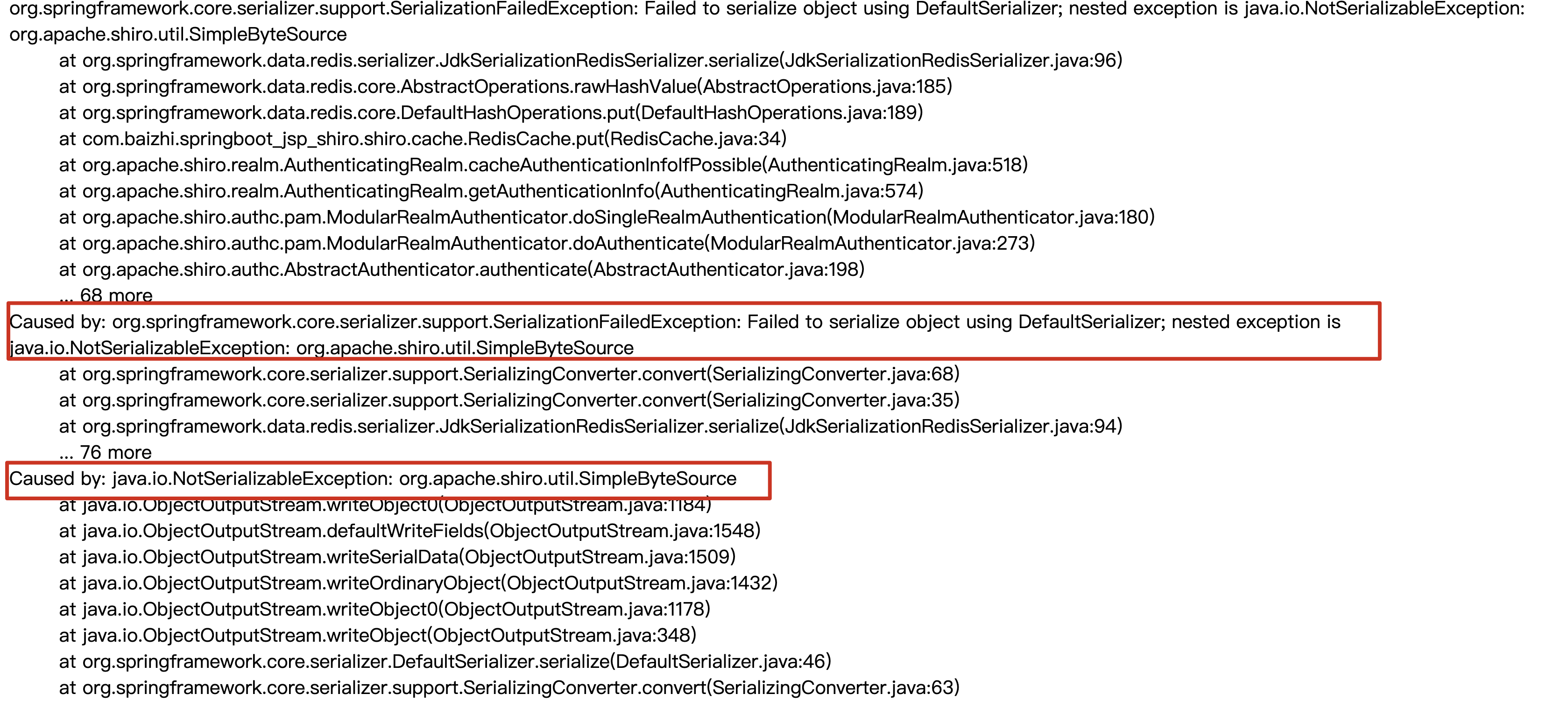
-
Error explanation: because the simpleByteSource implementation provided in shiro does not realize serialization, all error messages appear during authentication
-
Solution: automatic salt serialization is required
-
Custom salt implementation serialization
//Custom salt serialization interface public class MyByteSource extends SimpleByteSource implements Serializable { public MyByteSource(String string) { super(string); } } -
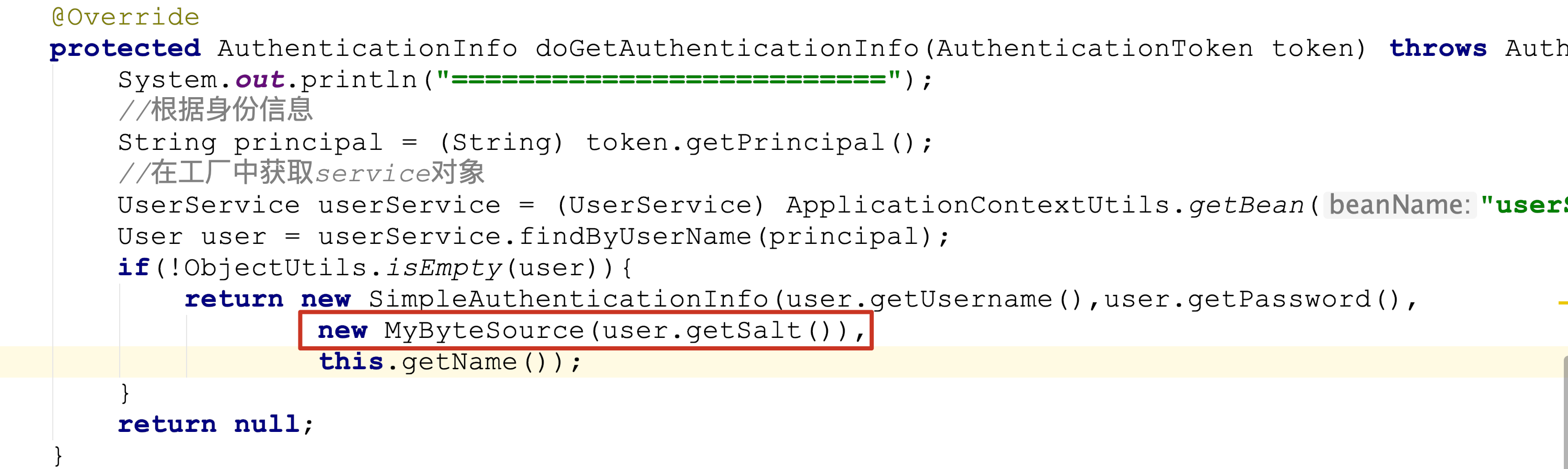
Using custom salt in realm
@Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("=========================="); //According to identity information String principal = (String) token.getPrincipal(); //Get the service object in the factory UserService userService = (UserService) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("userService"); User user = userService.findByUserName(principal); if(!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(user)){ return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user.getUsername(),user.getPassword(), new MyByteSource(user.getSalt()),this.getName()); } return null; }
-
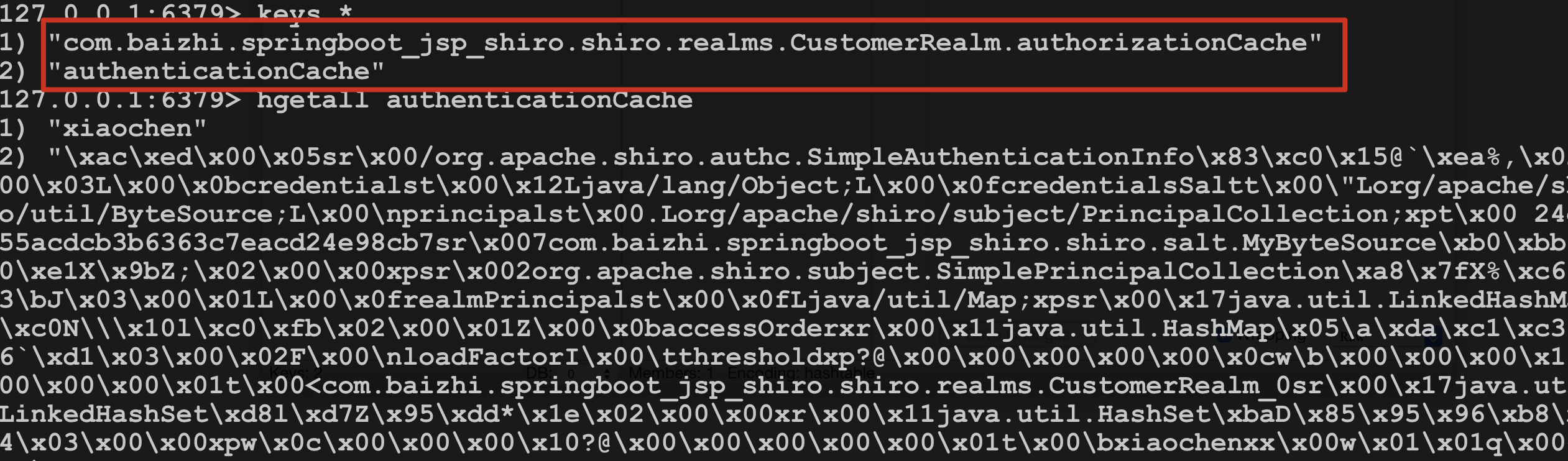
7. Start the test again and find that it can be successfully put into the redis cache
4. Add verification code
0. Add verification code to the development page
-
Development controller
@RequestMapping("getImage") public void getImage(HttpSession session, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException { //Generate verification code String code = VerifyCodeUtils.generateVerifyCode(4); //Put the verification code into the session session.setAttribute("code",code); //Verification code stored in picture ServletOutputStream os = response.getOutputStream(); response.setContentType("image/png"); VerifyCodeUtils.outputImage(220,60,os,code); } -
Release verification code
- Development page

-
Modify the certification process
@RequestMapping("login") public String login(String username, String password,String code,HttpSession session) { //Comparison verification code String codes = (String) session.getAttribute("code"); try { if (codes.equalsIgnoreCase(code)){ //Get principal object Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); subject.login(new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password)); return "redirect:/index.jsp"; }else{ throw new RuntimeException("Verification code error!"); } } catch (UnknownAccountException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("User name error!"); } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("Password error!"); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } return "redirect:/login.jsp"; } -
Modify the problem that salt cannot be serialized
//Custom salt serialization interface public class MyByteSource implements ByteSource,Serializable { private byte[] bytes; private String cachedHex; private String cachedBase64; //Adding parameterless construction method to realize serialization and deserialization public MyByteSource(){ } public MyByteSource(byte[] bytes) { this.bytes = bytes; } public MyByteSource(char[] chars) { this.bytes = CodecSupport.toBytes(chars); } public MyByteSource(String string) { this.bytes = CodecSupport.toBytes(string); } public MyByteSource(ByteSource source) { this.bytes = source.getBytes(); } public MyByteSource(File file) { this.bytes = (new MyByteSource.BytesHelper()).getBytes(file); } public MyByteSource(InputStream stream) { this.bytes = (new MyByteSource.BytesHelper()).getBytes(stream); } public static boolean isCompatible(Object o) { return o instanceof byte[] || o instanceof char[] || o instanceof String || o instanceof ByteSource || o instanceof File || o instanceof InputStream; } public byte[] getBytes() { return this.bytes; } public boolean isEmpty() { return this.bytes == null || this.bytes.length == 0; } public String toHex() { if (this.cachedHex == null) { this.cachedHex = Hex.encodeToString(this.getBytes()); } return this.cachedHex; } public String toBase64() { if (this.cachedBase64 == null) { this.cachedBase64 = Base64.encodeToString(this.getBytes()); } return this.cachedBase64; } public String toString() { return this.toBase64(); } public int hashCode() { return this.bytes != null && this.bytes.length != 0 ? Arrays.hashCode(this.bytes) : 0; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } else if (o instanceof ByteSource) { ByteSource bs = (ByteSource)o; return Arrays.equals(this.getBytes(), bs.getBytes()); } else { return false; } } private static final class BytesHelper extends CodecSupport { private BytesHelper() { } public byte[] getBytes(File file) { return this.toBytes(file); } public byte[] getBytes(InputStream stream) { return this.toBytes(stream); } } }