I DDL – operating databases and tables
1. Query
SHOW DATABASES;
2. Create
Create database
CREATE DATABASE Database name;
Create database (judge, create if it does not exist)
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS Database name;
3. Delete
Delete database
DROP DATABASE Database name;
Delete the database (judge, delete if it exists)
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS Database name;
4. Use database
View the database currently in use
SELECT DATABASE();
Use database
USE Database name;
5. Query table
Query all table names under the current database
SHOW TABLES;
Query table structure
DESC Table name;
6. Create table
CREATE TABLE Table name ( Field name 1 data type 1, Field name 2 data type 2, ... Field name n data type n, );
7. Delete table
Delete table
DROP TABLE Table name;
Judge whether the table exists when deleting the table
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Table name;
8. Modification table
Modify table name
ALTER TABLE Table name RENAME TO New table name;
Add a column
ALTER TABLE Table name ADD Column name data type;
Modify data type
ALTER TABLE Table name MODIFY Column name new data type;
Modify column names and data types
ALTER TABLE Table name CHANGE Column name new column name new data type;
Delete column
ALTER TABLE Table name DROP Listing;
II DML -- operation data
1. Delete data
DELETE FROM Table name [WHERE condition];
2. Add data
Adds data to the specified column
INSERT INTO Table name(Column name 1,Column name 2,...) VALUES(Value 1,Value 2,...);
Add data to all columns
INSERT INTO Table name VALUES(Value 1,Value 2,...);
Batch add data
INSERT INTO Table name(Column name 1,Column name 2,...) VALUES(Value 1,Value 2,...),(Value 1,Value 2,...),(Value 1,Value 2,...)...;
INSERT INTO Table name VALUES(Value 1,Value 2,...),(Value 1,Value 2,...),(Value 1,Value 2,...)...;
3. Modify data
Modify table data
UPDATE Table name SET Column name 1=Value 1,Column name 2=Value 2,... [WHERE condition];
III DQL
1. Basic query
Query multiple fields
SELECT Field list FROM Table name; SELECT * FROM Table name;--Query all data
Remove duplicate records
SELECT DISTINCT Field list FROM Table name;
Alias
AS: AS It can also be omitted
2. Query criteria (WHERE)
Syntax:
SELECT Field list FROM Table name WHERE Condition list;
Conditions:
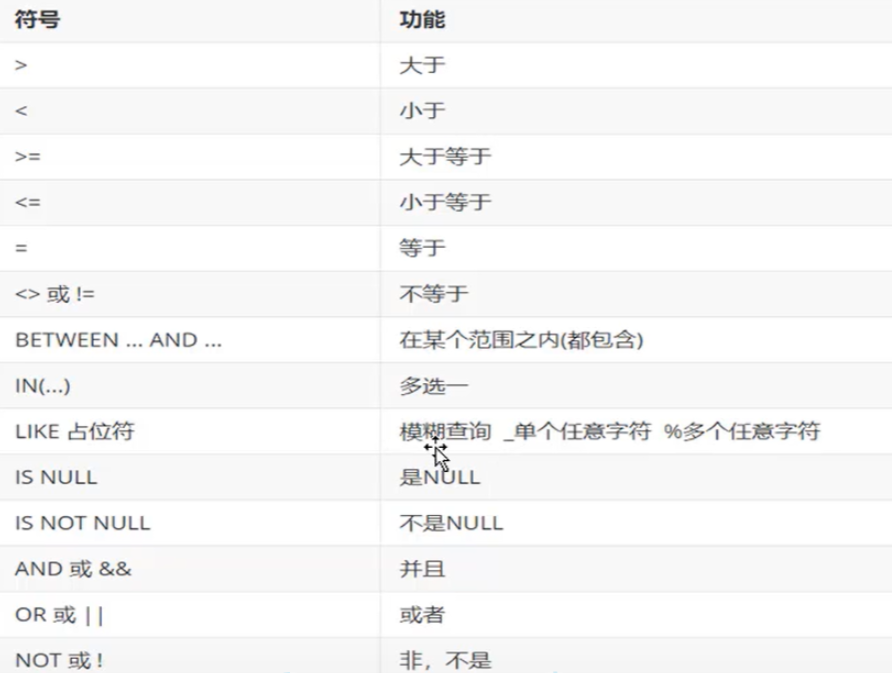
3. Sort query (ORDER BY)
SELECT Field list FROM Table name ORDER BY Sort field name 1 [Sort by 1],Sort field name 2 [Sort by 2] ...;
Sort by:
ASC: ascending sort (default)
DESC: descending order
Note: if there are multiple sorting conditions and the condition values of the current edge are the same, the sorting will be carried out according to the second condition
4. Group by
SELECT Field list FROM Table name [WHERE Conditions before grouping] GROUP BY Group field name [HAVING Conditional filtering after grouping];
Note: after grouping, the fields queried are aggregate functions and grouping fields. Querying other fields has no meaning
The difference between where and having:
The execution timing is different: where means to limit before grouping. If the where condition is not met, it will not participate in grouping, while having means to filter the results after grouping
The conditions for judging are different: where cannot judge the aggregate function, and having can.
Execution order: where > aggregate function > having
5. Paging query (LIMIT)
SELECT Field list FROM Table name LIMIT Start index , Number of query entries;
Start index: from 0
Calculation formula: starting index = (current page number - 1) * number of entries displayed per page
tips:
Paging query limit is the dialect of MySQL database
Oracle paging queries use rownumber
SQL Server paging query uses top
6. Aggregate function
SELECT Aggregate function name(Listing) FROM surface; --null Value does not participate in all aggregate function operations
count,max,min,sum,avg
IV data type
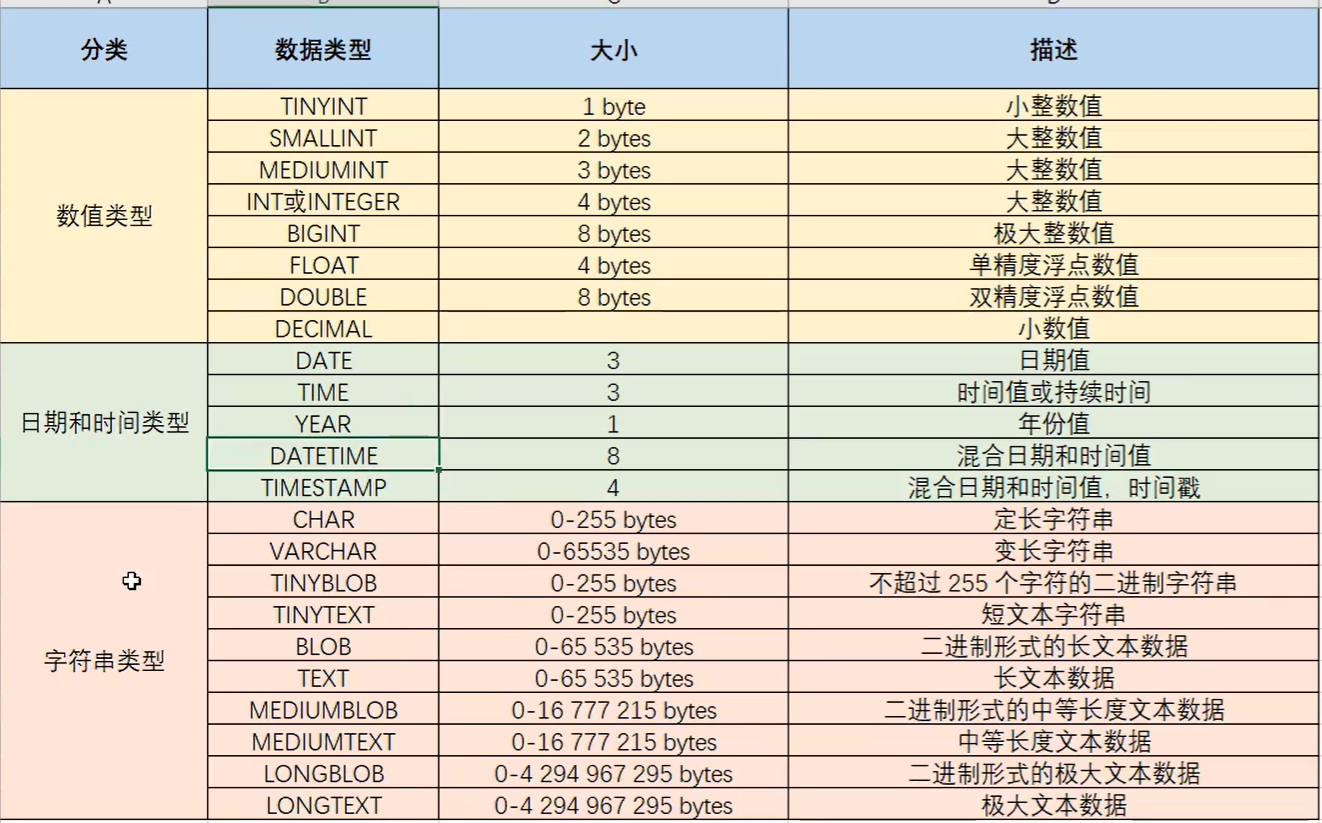
V constraint
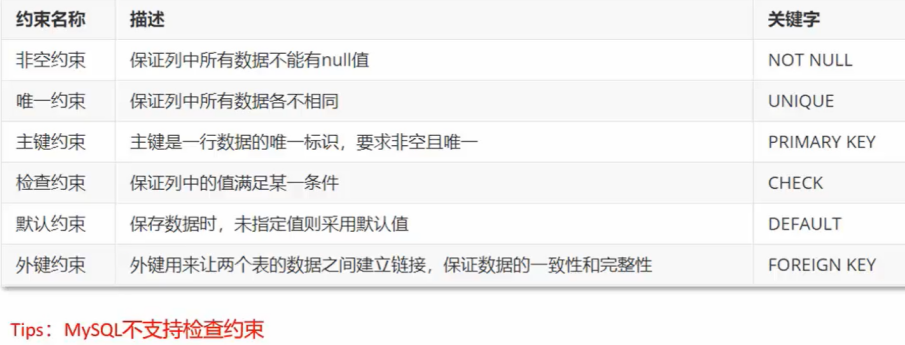
Foreign key constraint
Add constraint
-- Add foreign key constraints when creating tables CREATE TABLE Table name( Column name data type, ... [CONSTRAINT] [Foreign key name] FOREIGN KEY(Foreign key column name) REFERENCES Main table(Main table column name) );
-- Add foreign key constraints after creating the table ALTER TABLE Table name ADD CONSTRAINT Foreign key name FOREIGN KEY (Foreign key field name) REFERENCES Main table name(Main table column name);
Delete constraint
ALTER TABLE Table name DROP FOREIGN KEY Foreign key name
Vi multi-table query
Inner connection
--Implicit inner connection SELECT Field list FROM Table 1,Table 2... WHERE condition; --Explicit inner join SELECT Field list FROM Table 1,Table 2 [INNER] JOIN Table 2 ON condition;
External connection
--Left outer connection SELECT Field list FROM Table 1 LEFT [OUTER] JOIN Table 2 ON condition; --Right outer connection SELECT Field list FROM Table 1 RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN Table 2 ON condition;
Subquery